Colon Polyps and Hernia
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Polyps
A discrete mass or lesion that extends into the intestinal lumen and can either be sporadic or familial
Mucosal adenomatous (tubular, tubulovillous, villous), Muscosal serrated (hyperplastic, sessile, traditional serrated adenoma), Mucosal non-neoplastic (juvenile, hamartoma inflammatory), submucosal (lipomas, lymphoid aggregates, carcinoids, pneumatosis cystoids intestinalis)
Pathological groups of polyps
70%, adenomatous; 30%, serrated
_____ of polyps removed during colonoscopy are _____________, of the remaining _____ most are _________.
Present in adults over 50 (30% of em), 95% convert to adenocarcinoma (dysplastic transition)
Tell me about non-familial adenomatous and serrated polyps
inactivation of APC gene (chromosomal instability)
What causes the dysplastic transition in adenomatous polyps?
Kras mutations or BRAF oncogene activation (inactivation of tumor suppression, mismatch of repair)
What causes the dysplastic transition in serrated polyps - greater risk of cancer progression since they arise from hyperplastic polyps?
Proximal to the splenic flexure (1 cm+ (under 1 cm is low risk)); rectosigmoid region under 5 mm - don’t care
Dysplastic transition is more common in what area
1 cm+ (10 mm), villous features, high grade dysplasia
Signs of advanced adenoma - higher risk for advancing to carcinoma
FOBT, FIT, CBC (anemia), Colonoscopy (#1 draft pick), CT colonography (sensitivity is fine for big polyps but not small ones, okay for screening)
67 y/o male Patient presents to the clinic for fatigue. He notes that the last few weeks he has noticed blood on the toilet paper when going to the bathroom. On physical exam you note pallor and gross blood on DRE. What diagnostics do you want?
colonoscopy
All patients with + FOBT, FIT, DNA testing, or unexplained anemia are getting a, say it with me….
Colonoscopic polypectomy (risk of perf 0.2%, risk of significant bleeding 1%) follow up with repeat colonoscopy in 3 months
67 y/o male Patient presents to the clinic for fatigue. He notes that the last few weeks he has noticed blood on the toilet paper when going to the bathroom. On physical exam you note pallor and gross blood on DRE. Labs are as follows Hgb low, HCT low, RBC low. FOBT +. Colonoscopy reveals polyps. What is your treatment plan?

it is completely excised and submitted for histology, clean margins, NO vascular or lymphatic involvement
Polyps are only consisted completely removed IF (if these aren’t met bowel section is required)
10 years
If we find NO polyps when are we repeating a colonoscopy?
5-10 years
If we find 1-2 small tubular adenomas without villous features or dysplasia when are we repeating a colonoscopy?
3 years
If we find 3-10 adenomas, adenoma bigger than 1 cm, or villous features or high grade dysplasia when are we repeating a colonoscopy?
1-2 years + a r/o for familial polyposis syndrome (genetic testing)
If we find 10+ adenomas when are we repeating a colonoscopy?
5 years
If we find small serrated polyps without dysplasia when are we repeating a colonoscopy?
3 years
If we find large serrated polyps and those with cytologic dysplasia when are we repeating a colonoscopy?
nothing until 50
If we find small, typical hyperplastic polyps in the rectum and distal colon without dysplasia when are we repeating a colonoscopy?
Hereditary Polyposis
A germline mutation with a high risk of cancer (4% of colorectal cancers) - family hx is important
more that 1+ family member with polyposis, personal or fam hx of colorectal cancer <50, personal/fam hx of 20+ polyps
Red flags for genetic testing
Familial adenomatous polyps (FAP), hamartomatous polyposis syndrome, lynch syndrome
Types of Hereditary Polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyps (FAP)
A genetic disorder characterized by the development of 100-1000s of colonic adenomatous polyps PLUS soft tissue tumors, osteomas, hypertrophy of retinal pigment
autosomal dominant mutation of APC gene (90%) or MUTYH
Mutation in FAP
Prophylactic colectomy to prevent colon cancer, complete proctocolectomy with ileoanal anastomosis/colectomy with ileorectal anastomosis before 20, EGD every 1-3 years for screening, Sulindac (NSAID), Celebrex (Cox 2), offer genetic testing
Treatment of FAP
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome, familial juvenile polyposis, PTEN multiple hamartoma syndrome (Cowden’s)
Types of hamartomatous polyposis syndromes
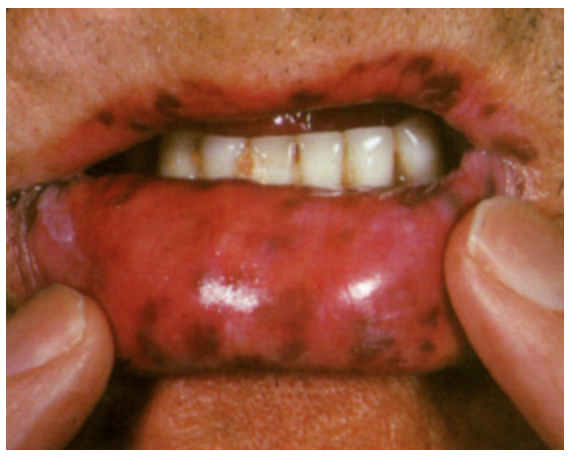
Peutz-jeghers syndrome
An autosomal dominant disorder of the serine threanonine kinase 11 gene that is characterized by polyps throughout the intestines (usually small), pigmented macules on lips, GI cancers (60% of patients), breast cancer (50% of patients)
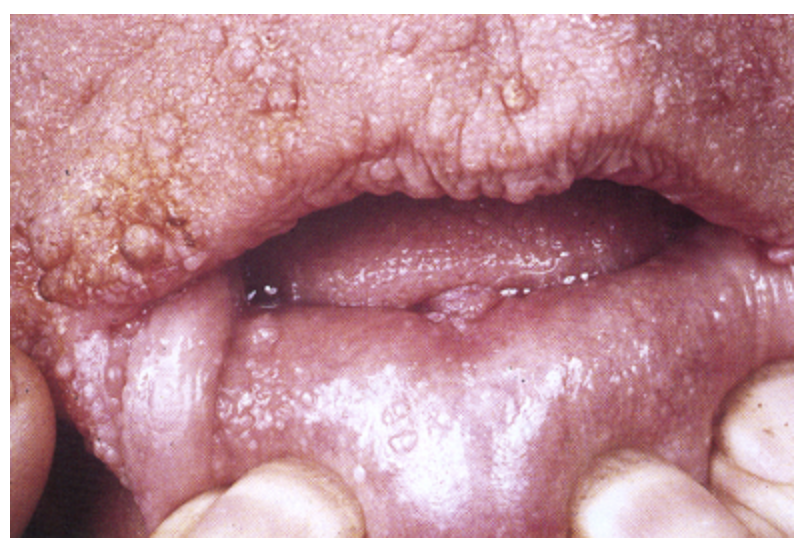
familial juvenile polyposis
An autosomal disorder of the 18q and 10q gene that is characterized by 10+ polyps (m/c colon), adenomatous polyps, and adenocarcinoma (risk is 50%)
PTEN multiple hamartoma syndrome (Cowden’s)
A mutation of the PTEN gene that results in polyps and lipomas throughout the GI tract, trichilemmomas, cerebellar lesions, and an increased risk of cancer in the thyroid, breast, and GU tract
Lynch Syndrome (Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colon Cancer (HNPCC))
An autosomal dominant disorder in the MLH1, MSH2, MHS6, or PMS2 that are vital for DNA base-pair matching and starts with a few, flat adenomas with villous features or high grade dysplasia that have a RAPIDO transition (1-2 years) to cancerous lesions (3% of all colorectal cancer)
early onset of colorectal cancer, FHx of colorectal cancer or other cancers at a young age or in multiple members
You gotta r/o lynch syndrome if you see…
Colorectal (22-75%), endometrial (30-60%), ovarian, renal, hepatobiliary, gastric, SI
Lynch syndrome peeps have a higher risk of which cancers at a younger age
colorectal cancer before 50, multiple/recurring colorectal or HNPCC associated tumors, colorectal cancer in 1 or more 1st degree relative before 50, colorectal cancer in 2 or more 1st degree relative, tumors with infiltrating lymphocytes, mucinous signet ring differentiation, or medullary growth patterns in patients younger than 50
Bethesda criteria for Lynch syndrome (finds about 70% of em)
Hernia
A protrusion, bulge, or projection of an organ/part of an organ through weak spots on the abdominal or pelvic wall - second most common cause of bowel obstruction
obesity, pregnancy, straining, trauma/surg, smoking, ascites, aging, FHx of hernia, connective tissue disease (marfan, Ehlers-Danlos, Loeys-Dietz)
Risk factors for hernia

Reducible
45 y/o male presents to the clinic for a “bulge” in his abdomen - he reports a dull pain (3/10) and that is comes and goes. On physical exam you no a palpable mass that returns to the abdomen with light manual pressure. How would you classify this?
Incarcerated or irreducible - can become a surgical emergencies
45 y/o male presents to the ER for abdominal pain and N/V. On physical exam you note localized tenderness around a palpable mass. This does NOT return the abdomen with light pressure, how would you classify this?
Strangulation → surgical emergency
If hernia contents become trapped and the blood supply becomes compromised → ischemia → necrosis what is this known as
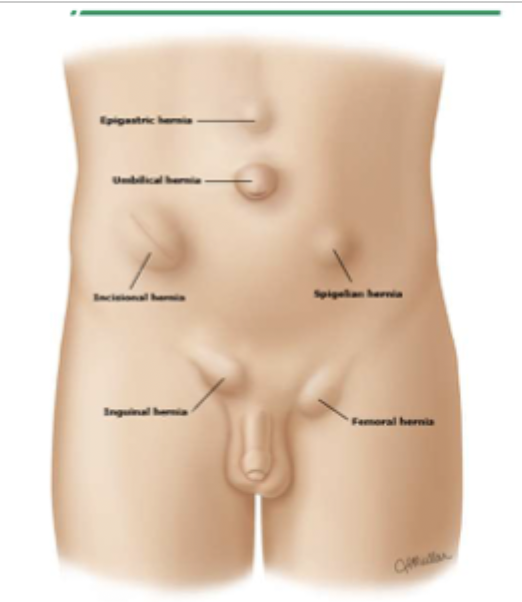
incisional, umbilical, epigastric, spigelian
What are the types of hernias through the abdominal wall (Ventral)
incisional
A protrusion through an incision site <1 year post-surg (defect in fascial closure)
umbilical
A protrusion through the umbilicus
epigastric
A protrusion in the epigastric region
Spigelian
A protrusion through the lateral wall
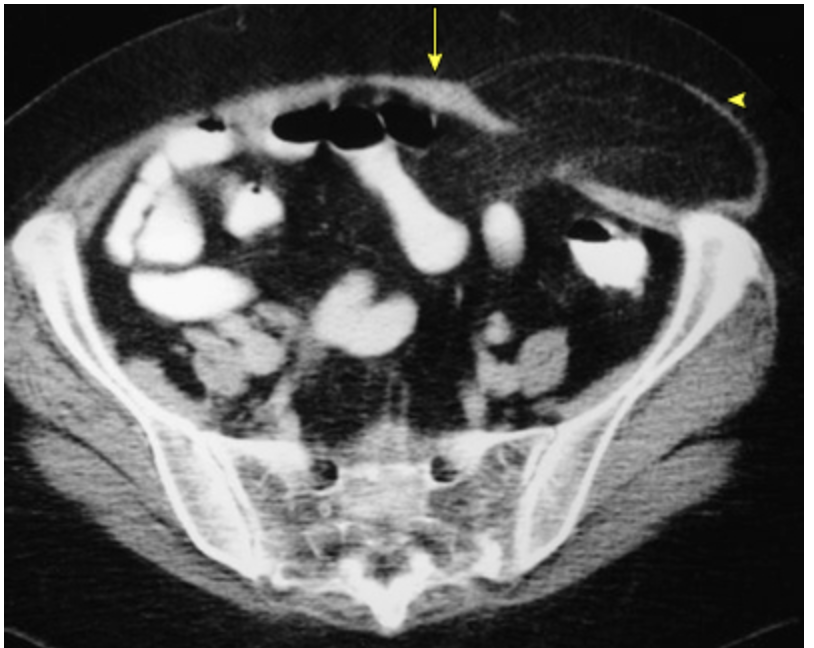
Congenital (kids), ascites, pregnancy, obesity, cysts, malignancy
Risk factors for umbilical hernias
Heal spontaneously in kids under 2, surgical repair with a suture or mesh (adults, 11% recurrence)
Treatment plan for umbilical hernias
Inguinal (groin)
What is the most common site of all hernias
Indirect (males and females; right side), direct, femoral (more commonly incarcerated)
Types of inguinal hernias
indirect inguinal hernia
A protrusion at the internal inguinal ring, which is the site where the spermatic cord in males and the round ligament in females exits the abd cavity - usually mesenteric fat, intestines, ovary, fallopian tubes, or uterus
More often found in the scrotum, often congenital, high strangulation risk, bimodal distribution (0-1; 10-30), 5-10% recurrence rate after surgery
Indirect inguinal hernia fun facts
Direct inguinal hernia
The herniated sac protrudes directly through the inguinal wall medial to the inferior epigastric vessels within Hesselbach’s triangle - less likely to end up in the scrotum
Femoral inguinal hernia
Which hernia is located inferior to the inguinal ligament and protrudes through the femoral ring (medial to the femoral vein, lateral to the lacunar ligament)
more common in females, Right side more common than left, initially asymptomatic, high risk for strangulation and and incarceration, 5-10% recurrence rate
Femoral inguinal hernia FUN FACTS
direct
37 y/o male presents to the ED for sharp pain radiating into the groin that started after he was deadlifting at the gym. On physical exam you note a palpable mass superior to the pubic tubercle and localized swelling. You also note a mass touching the side of your finger. What type of hernia?
Indirect
37 y/o male presents to the ED for sharp pain radiating into the groin that started after he was deadlifting at the gym. On physical exam you note a scrotal enlargement that does NOT transilluminate and localized swelling. You also note a mass touching the tip of the finger. What type of hernia
U/S (differentiating scrotal masses), Abd x-ray series, CT with contrast
What imaging do you want for inguinal hernias?
Daytime truss, avoid straining, manual reduction using supine positioning, Herniorrhaphy/hernioplasty (return to normal activity 3-6 weeks)
Inguinal hernia treatment plan
hemorrhage, severed vas deferens, resection/entrapment of nerve, ischemic orchitis, testicular atrophy, bladder or bowel injury, infection, failure, recurrence
Complications of inguinal hernia surgical repair
Kidney stone, testicular mass (tumor, hydrocele), varicocele (left sided hernia), direct trauma, ischemia bowel disease, appendicitis, ovarian torsion, testicular torsion
DDx for inguinal hernia