Halogenoalkanes
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is a primary halogenoalkane?
One carbon atom joined to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen.
What is a secondary halogenoalkane?
Two carbons attached to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen.
What is a tertiary halogenoalkane?
Three carbons attached to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen.
What is nucleophilic substitution?
When a nucleophile replaces a leaving group.
Leaving group is halogen and nucleophiles include :OH- :CN- and NH3.
What are nucleophiles?
Nucleus loving atom with a lone pair of electrons/ electron pair donator.
They attack the partially positive carbon atom and form a bond with them which leads to the C-X bond breaking and a halogen ion being produced.
Learn the order of the strength of the C-X bonds weakest to strongest
C-I
C-Br
C-Cl
C-F
This is due to the order of bond enthalpy rather than polarity which is less significant in determining reactivity.
Nucleophilic substitution with aqueous hydroxide ions
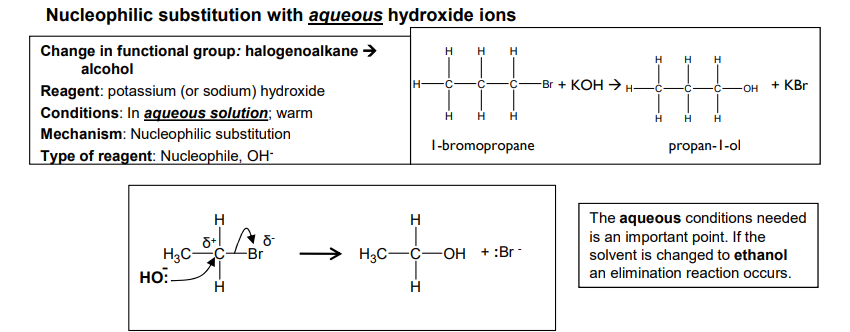
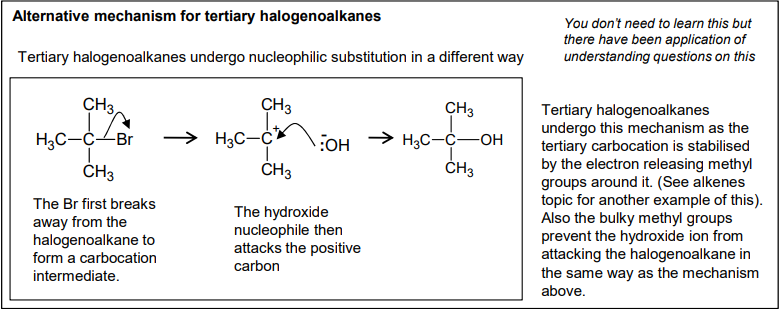
An intermediate in chemistry refers to a short-lived species that is formed during a reaction but is not the final product.

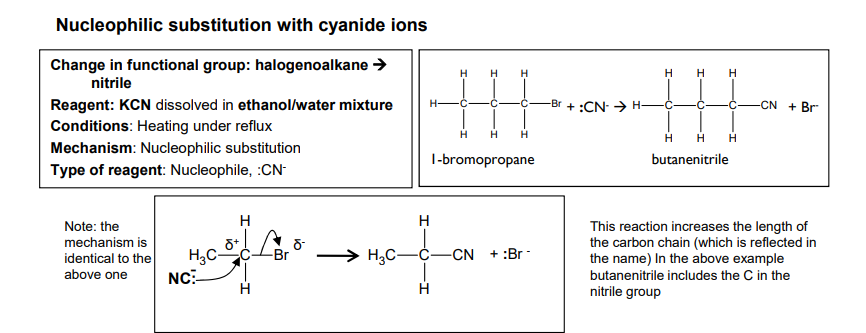
Nucleophilic substitution with cyanide ions

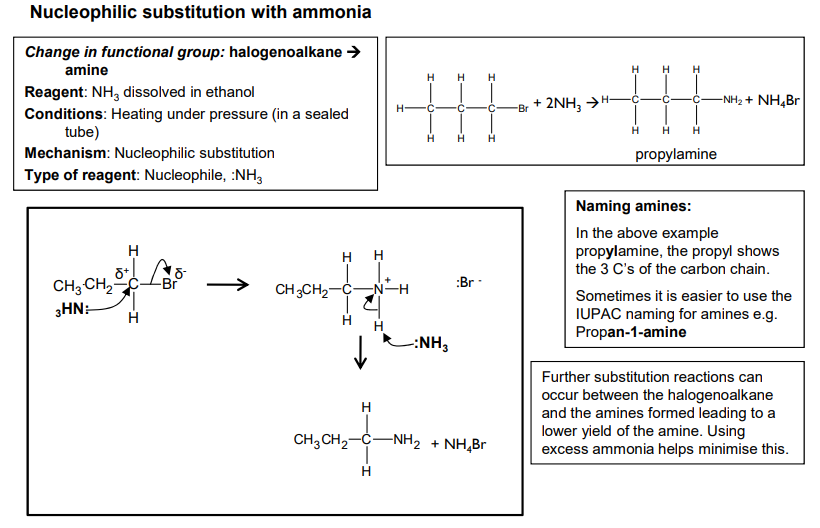
Nucleophilic substitution with ammonia

What is elimination?
Removal of small molecule (often water) from the organic molecule.
Elimination reaction of halogenoalkanes
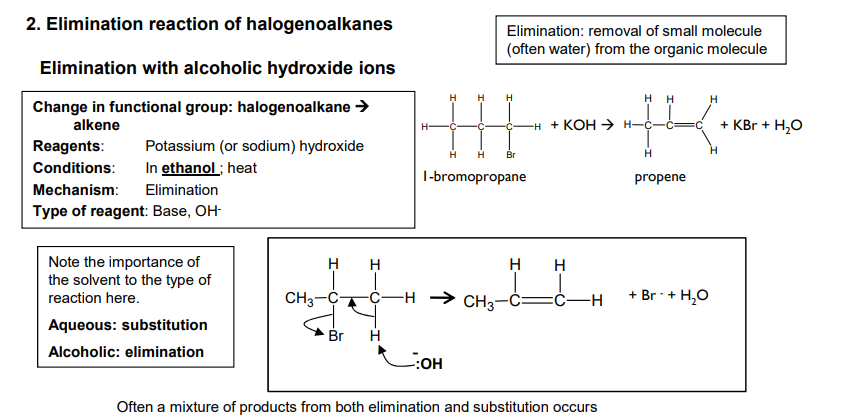
What can happen with unsymmetrical secondary and tertiary halogenoalkanes?
Two or three structural isomers can be formed.
What do primary halogenoalkanes tend towards?
Substitution
What do tertiary halogenoalkanes tend towards?
Elimination
What can chloroalkanes and chlorofluoroalkanes be used for?
Solvents
Halogenoalkanes have also been used as refrigerants, pesticides and aerosol propellants.
What is ozone?
The naturally occurring layer of O3 in the upper atmosphere which filters out much of the suns harmful UV radiation.
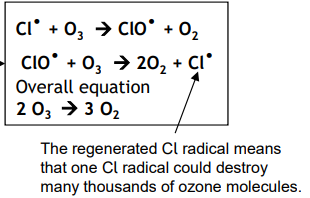
Ozone depletion
Chlorine radicals are formed (from CFCs) in the upper atmosphere as UV radiation causes C-Cl bonds to break.
The Cl radical catalyses the decomposition on ozone and these reactions contributed to the formation of the hole in the ozone layer.

What are HFCs used for and why is this safer?
Refrigerators and air conditioners.
Safer as they do not contain C-Cl bond.
C-F bond is strong and not affect by UV.