Cell Anatomy & Transport
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://quizlet.com/170251548/ap-biology-chapter-11-multiple-choice-cell-communication-flash-cards/
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
micrometer to millimeter conversion
1,000 um = 1 mm
a cell that is 1-10 um is probably…
bacteria/prokaryote
a cell that is 10-100 um is probably…
eukaryote
cell size is determined by…
surface area to volume ratio
You MUST have a larger surface area than volume to survive as a cell
plasma membrane must be large enough relative to cell volume to regulate passage of materials
volume inc faster than surface area so cell must DIVIDE
cell size & shape is related to its function
prokaryotes & eukaryotes both have…
plasma membrane
cytosol that contains organelles
chromosomes which have genes in form of DNA
ribosomes
where is DNA located in a prokaryote vs eukaryote?
E:
LINEAR chromosomes contained in membrane-enclosed organelle (nucleus)
P:
DNA concentrated in nucleoid region w/o membrane separating it from rest of cell (all jumbled up chromatin)
free ribosomes
STAY IN THE CELL
synthesize proteins that function within the cytosol
bound ribosomes
Proteins attached to the rough ER will either go into the membrane (and stay there) or be exported out of the cell
smooth ER
rich in enzymes & plays role in metabolic processes
enzymes of smooth ER synthesize lipids (e.g. oils, phospholipids, steroids, sex hormones, etc.)
also catalyzes key step in mobilization of glucose from stored glycogen (carbohydrate) in liver
other enzymes in smooth ER of liver detoxify drugs, poisons, alc, etc
frequent exposure leads to proliferation of smooth ER, inc tolerance to target & other drugs
rough ER
esp abundant in cells that secrete proteins
as polypeptide is synthesized by ribosome, it’s threaded into cisternal space thru pore in ER membrane
these secretory proteins are packaged in transport vesicles that carry them to their next stage
also a membrane factory
membrane-bound proteins are synthesized directly into membrane
enzymes in rough ER also synthesize phospholipids
as ER membrane expands, parts can be transferred as transport vesicles to other components of endomembrane system
Golgi apparatus
many transport vesicles from ER travel to golgi for modification of their contents
golgi = center of manufacturing, warehousing, storing, & shipping (thru transport vesicles)
esp extensive in cells specialized for secretion (bound ribosomes)
cis side receives material; trans side buds off vesicles that travel to other sites (products modified in btwn)
golgi can also manufacture its own macromolecules, including pectin & other non-cellulose polysaccharides
lysosomes
animal cells ONLY
lysosomal enzymes can hydrolyze proteins, fats, polysaccharides, & nucleic acids (e.g. digest food)
enzymes work best at pH 5
proteins in lysosomal membrane pump hydrogen ions from cytosol to lumen of lysosomes
while rupturing one or a few lysosomes has little impact on cell, but massive leakage from lysosomes can destroy cell by autodigestion
used to destroy old cells (cell death)
lysosomal enzymes & membrane synthesized by rough ER then transferred to Golgi
phagocytosis
process wherein a cell binds to the item it wants to engulf on the cell surface
draws the item inward while engulfing around it
often happens when the cell is trying to destroy something (e.g. virus/infected cell)
often used by immune system cells (e.g. white blood cells)
mitochondria
sites of cellular respiration & generating ATP
chloroplasts
found ONLY in plants & eukaryotic algae
sites of photosynthesis
convert solar energy to chem energy for food
endosymbiotic theory (name at least 3 justifications)
mitochondria & chloroplasts evolved from prokaryotes
justifications:
both have small quantities of DNA that direct synthesis of polypeptides produced by internal ribosomes
both can grow & reproduce as semi-autonomous organelles
both organelles around size of prokaryotic cell
have 2 layers for plasma membrane, similar to prokaryotes
peroxisomes
contain enzymes that transfer H from various substrates to O2
an intermediate product of this process is hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), but the peroxisome has another enzyme that converts H2O2 to water
sometimes breakdown fatty acids to smaller molecules that are transported to mitochondria for fuel
some detoxify alc & other harmful compounds
NOT formed by endomembrane system, but by incorporation of proteins & lipids from cytosol
cytoskeleton functions
maintains shape of cell
fibers act like a geodesic dome to stabilize balance btwn opposing forces
provides anchorage for many organelles & cytosolic enzymes
dynamic, dismantling one part & reassembling in another to change shape of cell
cell mobility (location o cell & limited mvmts of parts of cell)
interacts w/ motor proteins
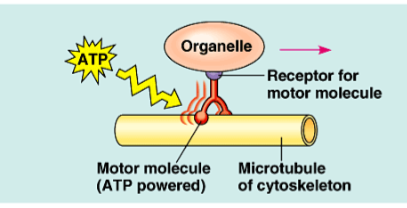
motor protein
carry vesicles or organelles to various destinations along “monorails” provided by cytoskeleton
interactions of motor proteins & cytoskeleton circulate materials within cell via streaming
recently, evidence is accumulating that cytoskeleton may transmit mechanical signals that rearrange nucleoli and other structures
requires ATP
3 main types of fibers in cytoskeleton
microtubules
microfilaments
intermediate filaments
microtubules
thickest fibers
hollow rods abt 25 microns in diameter
move chromosomes during cell division
acts as tracks that guide motor proteins carrying organelles to destination
grow out from centrosome near nucleus
resist compression to the cell
central structural supports in cilia & flagella
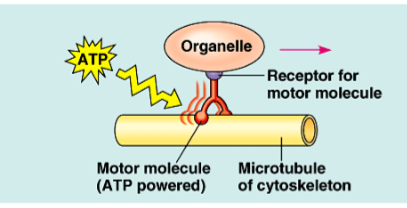
centrioles
in ANIMAL cells, centrosome has pair of centrioles
found inside centrosome
each w/ 9 triplets of microtubules arranged in ring
during cell division, centrioles replicate
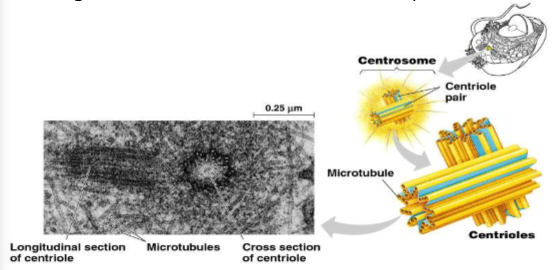
cilia vs flagella
cilia usually occur in large numbers on cell surface
abt 2-20 microns long
usually just one or few flagella per cell
10-200 microns long
e.g. sperm cell
hwvr, both have same ultrastructure
core microtubules sheathed by plasma membrane
can move unicellular/small multicellular organisms by propelling water past organism
microfilaments
thinnest class of cytoskeletal fibers
solid rods
provide rigidity and shape to the cell and facilitate cellular movements
w/ other proteins, they form 3D network inside plasma membrane
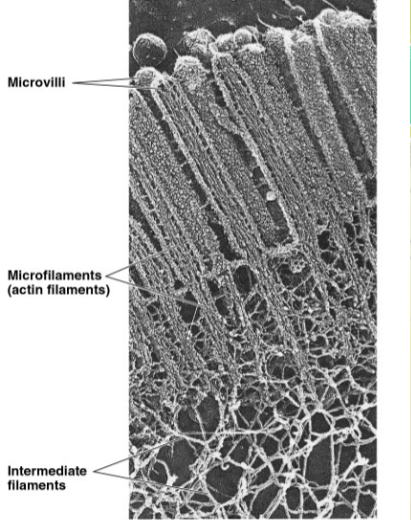
intermediate filaments
intermediate size of all cytoskeletal fibers
bear tension and anchor the nucleus and other organelles in place
more permanent fixtures of cytoskeleton than are the other two classes
cell wall
found in prokaryotes, fungi, some protists, & plant cells
in plants:
protects cell
maintains its shape
prevents excessive uptake of water
supports plan against force of gravity
consists of microfibrils of cellulose embedded in matrix of proteins & other polysaccharides
mature cell wall → primary cell wall, middle lamella w/ sticky polysaccharides that hold cell together, & layers of secondary cell wall
extracellular matrix (ECM)
lacking cell walls, animal cells do have elaborate ECM
contains primarily glycoproteins, esp collagen fibers, embedded in network of proteoglycans
fibronectins in ECM connect to integrins (intrinsic membrane proteins)
integrins connect ECM to cytoskeleton
in what ways can the ECM regulate cell behavior?
interconnections from ECM to cytoskeleton via fibronectin-integrin link permit interaction of changes inside & outside cell
embryonic cells can migrate along specific pathways by matching orientation of microfilaments to “grain” of fibers in extracellular matric
extracellular matric can influence activity of genes in nucleus via combo of chemical & mechanical signaling pathways
this may coordinate all cells within a tissue
plasmodesmata
plant cells have this
channels that allow cytosol to pass btwn cells
allows neighboring cells to communicate thru direct physical contact
animal cells’ 3 main types of intercellular links
tight junctions
desmosomes
gap junctions
tight junctions
membranes of adjacent cells are fused, forming continuous belts around cells
prevents leakage of extracellular fluid
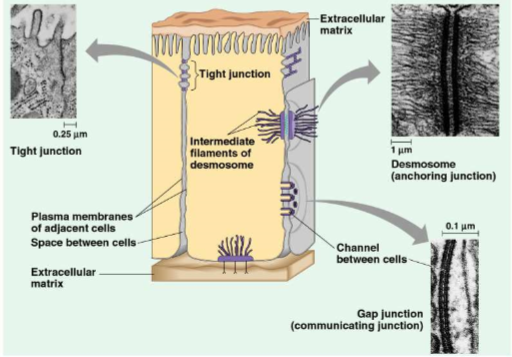
desmosomes
also called anchoring junction
fastens cells together into strong sheets, like rivets
intermediate filaments of keratin reinforce desmosomes
gap junctions
also called communicating junctions
provide cytoplasmic channels btwn adjacent cells
special membrane proteins surrounding these pores
salt ions, sugar, amino acids, & other small molecules can pass
phospholipids
most abundant lipid in plasma membrane
amphipathic
hydrophilic head
2 hydrophobic tails
fluid mosaic model
membrane is fluid structure w/ “mosaic” of various proteins embedded in it when view from top
phospholipids can more laterally (left/right)
membrane proteins also move side to side or laterally, making membrane fluid
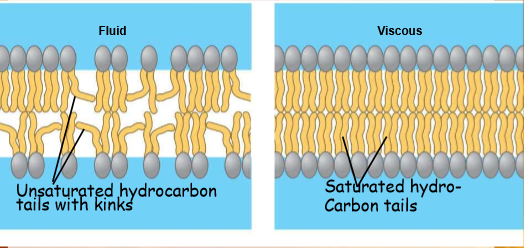
how do different types of hydrocarbon tails affect the fluidity of the plasma membrane?
unsaturated hydrocarbon tails w/ kinks → more fluid
saturated hydrocarbon tails w/ no kinks → less fluid
cell should have good mix of both
integral proteins
penetrate hydrophobic core of lipid bilayer
often transmembrane proteins, completely spanning membrane
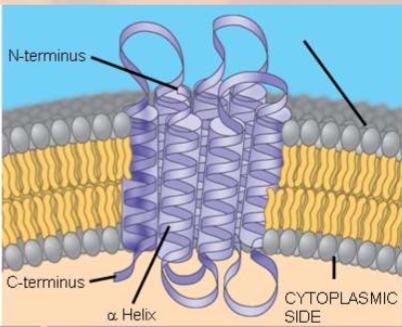
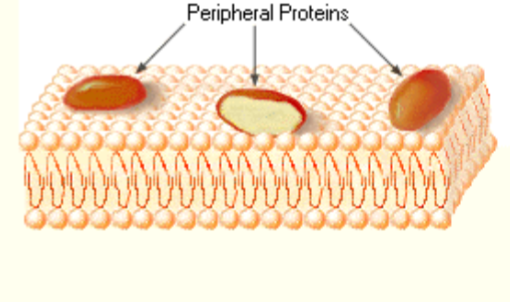
peripheral proteins
appendages loosely bound to surface of membrane
six major functions of membrane proteins
transport to substances in and out of cell
enzymatic activity
protein built into membrane may be enzyme
signal transduction
protein may have binding site w/ specific shape that fits shape of chemical messenger, such as hormone
cell-to-cell recognition
intercellular joining
membrane proteins of adjacent cells may hook together
attachment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matric
elements of cytoskeleton may be bonded to membrane proteins
helps maintain cell shape & stabilizes location of certain membrane proteins
what is the role of membrane carbohydrates in cell-to-cell recognition?
cell-cell recognition → cell’s ability to distinguish one type of neighboring cell from another
interact w/ surface molecules of other cells, helping facilitate cell-to-cell recognition
how would you expect the saturation levels of membrane fatty acids to differ in plants adapted to cold environments and plant adapted to hot environments?
cold → more unsaturated → more fluidity
hot → more saturated → less fluidity
carbs are attached to proteins and lipids in ER & Golgi; the new membrane them forms transport vesicles that travel to cell surface and will merge w/ cell membrane. on which side of the vesicle membrane are the carbs?
inside
polar vs nonpolar molecules passing thru plasma membrane
nonpolar = hydrophobic; lipid soluble and can pass thru membrane rapidly
polar molecules do NOT cross membrane rapidly
transport proteins
allow passage of hydrophilic substances across membrane
passive transport
diffusion of substance across membrane w/o energy (including osmosis)
e.g. CO2, H2O, O2
osmosis
diffusion of water
affected by concentration gradient of dissolved substances called solution’s tonicity
aquaporin proteins move polar water molecules past phobic tails (high to low concentration)
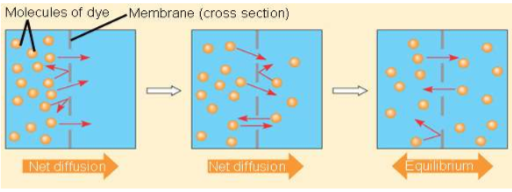
diffusion
tendency for molecules to spread evenly into available space
move from HIGH to LOW concentration
DOWN concentration gradient
NO ENERGY NEEDED
tonicity
ability of solution to cause cell to gain or lose water
has great impact on cells w/o walls
3 states of tonicity:
hypertonic
isotonic
hypotonic
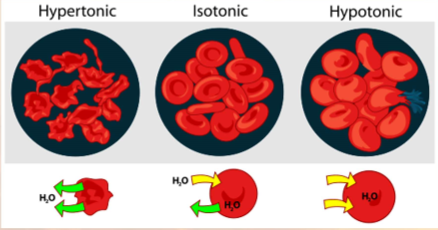
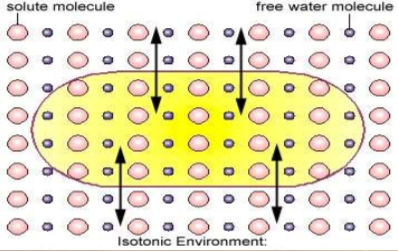
isotonic
concentration of solutes inside cell is same as outside
no net mvmt of water
hypertonic
concentration of solutes outside is greater than inside
cell will lose water (plasmolysis)
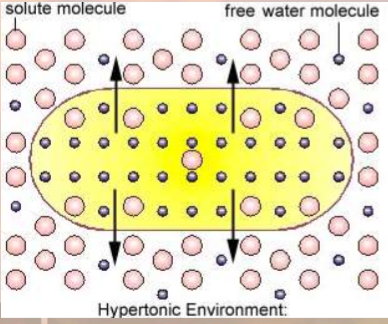
hypotonic
concentration of solutes is less outside than inside the cell
cell will gain water
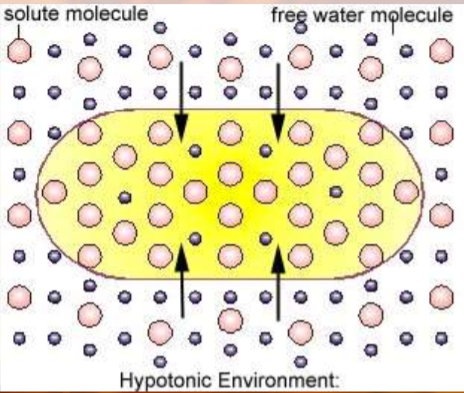
turgor pressure
pressure of water inside plant cell pushing outward against cell membrane
if a plant cell is turgid, it’s in a ____ environment
hypotonic
firm, healthy state in most plants
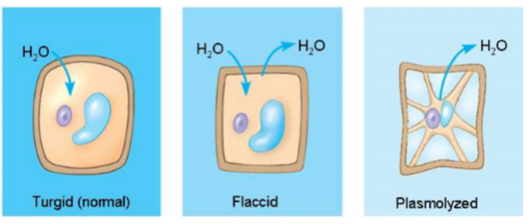
if a plant cell is flaccid, it’s in a ____ environment
isotonic or hypertonic
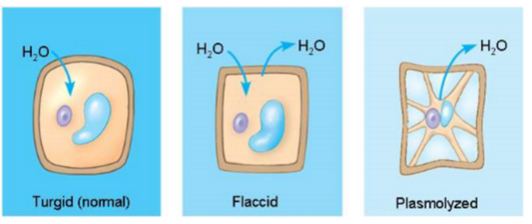
animal cells survive best in which tonicity?
isotonic
how will water move across semi-permeable membrane?
solution A: 100 molecules of glucose/mL
solution B: 100 molecules of NaCl/mL
each molecules of NaCl will dissociate to form Na+ ion & Cl- ion
→ final concentration of solutes is 200 molecules/mL
therefore, there will be net mvmt of water from solution A to solution B until both solutions have equal concentrations of solute
facilitate diffusion
type of PASSIVE transport aided by proteins
transport proteins speed mvmt of molecules across plasma membrane
channel & carrier proteins
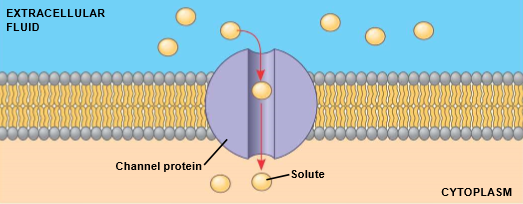
channel proteins
facilitated diffusion
provide corridors that allow specific molecule or ion to cross membrane
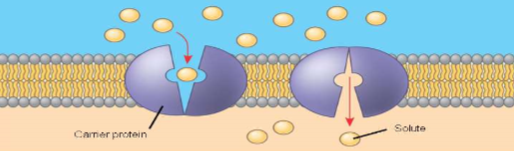
carrier proteins
undergo subtle change in shape that translocates solute-binding site across membrane
protein can transport solute in either direction (in or out of cell) w/ net mvmt being DOWN concentration gradient of solute
active transport
uses energy to move solutes against concentration gradient
requires energy, usually ATP
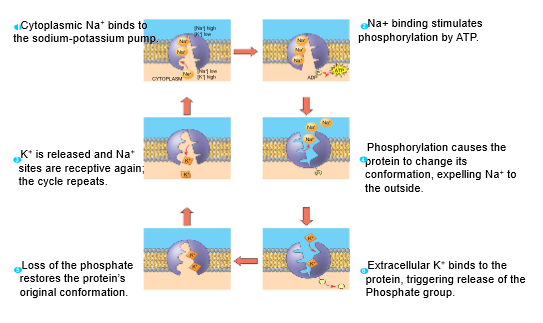
e.g. sodium-potassium pump
sometimes move against concentration gradient
sodium-potassium pump
active transport
membrane potential
voltage difference across membrane
electrochemical gradient
caused by concentration electrical gradient of ions across membrane
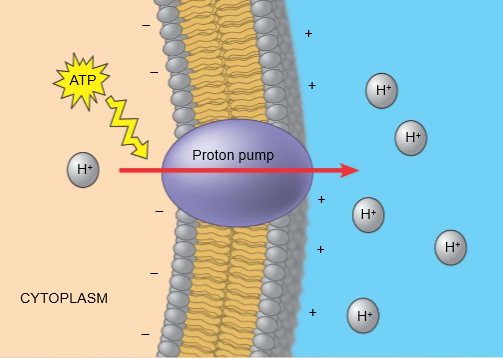
electrogenic pump
transport protein that generates voltage across membrane
proton pump
cotransport
occurs when active transport of specific solute indirectly drives active transport of another solute
involved transport by membrane protein
driven by concentration gradient
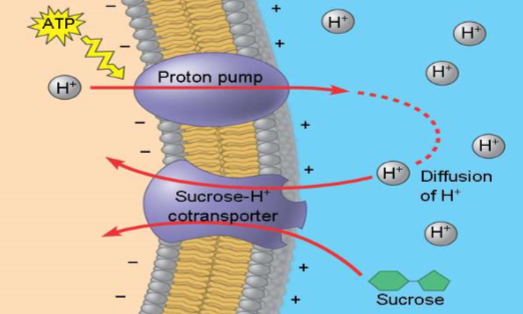
bulk transport
occurs by exocytosis & endocytosis
large proteins cross membrane by diff mechanisms
exocytosis
transport vesicles migrate to plasma membrane, fuse w/ it, & release their contents
endocytosis
cell takes in macromolecules by forming new vesicle from plasma membrane
cell theory
all living things are made of cells
cells = basic unit of structure & function of life
cells are derived from reproduction of existing cells
light microscope
visible light passes thru specimen; then thru glass lenses
can see nucleus/chromosomes in dividing cells/central vacuole/NOT other organelles
can observe LIVING cells
electron microscope
electromagnets focus beam of electrons
better resolution than light microscope
can only observe organelles in DEAD cells
transmission electron microscope
thin sections of specimen are stained w/ heavy metals for contrast
can see organelles (ultrastructure) of cells
scanning electron microscope
useful for studying surface structure
sample surface = covered w/ thin film of gold
image appears 3D
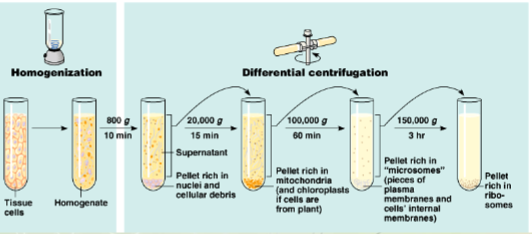
cell fractionation
uses machine (ultracentrifuge) to separate major organelles for study
separates by size/mass (bigger/heavier organelles sink to pellet'; lighter ones in supernatant)
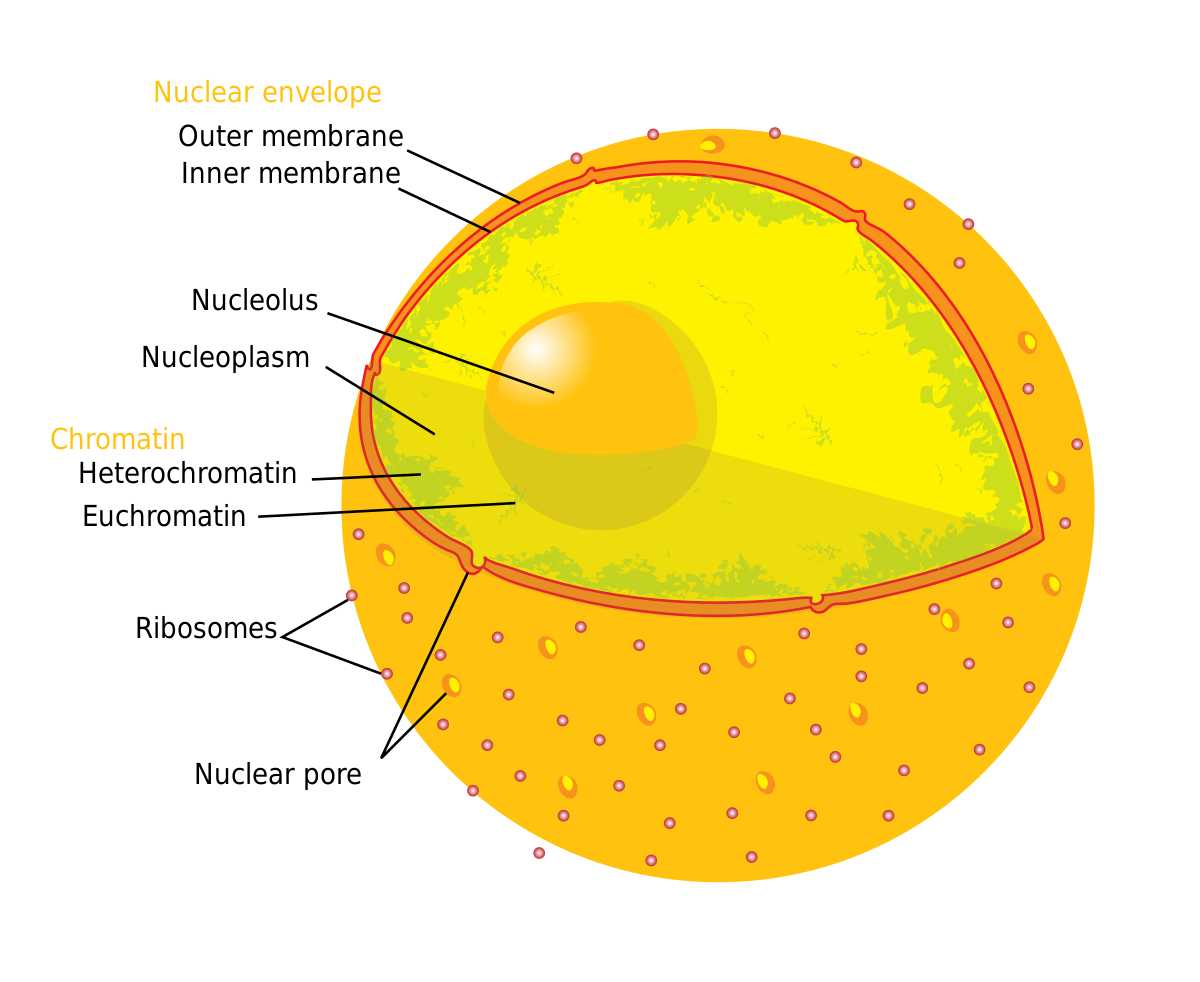
nuclear envelope
contains genes in eukaryotes (additional genes in mitochondria & chloroplasts)
surrounded by DOUBLE MEMBRANE separated by 20-40 nm space
nuclear pores lined by proteins (nuclear pore complex) → regulates passage of molecules in & out
nuclear side of envelope lined by network of protein filaments (nuclear lamina) → maintains shape
chromatin fibers - DNA + histone proteins
wraps into chromosomes (more tightly packed form) during cell division
nucleolus → site of ribosome (rRNA) production
endomembrane system
directly continuous or connect via transfer of membrane sacs (vesicles)
includes nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, & plasma membrane
vesicles & vacuoles
vacuoles = larger vesicles
membrane-bound sacs w/ varied functions
contractile vacuoles in freshwater protists → pump excess water out/maintain water-salt balance
large CENTRAL vacuole in many mature plant cells
purpose of central vacuole
stockpile proteins or inorganic ions
dispose metabolic byproducts
hold pigments
store defensive compounds to defend plant against herbivores
large vacuole reduces area of cytosol, so surface area/volume ratio inc
water storage makes plants TURGID
facilitated diffusion w/ ion channels
transmembrane proteins form “tunnels” across membrane
moves from high to low concentration
moves charged ions (Na+, K+, Ca++, Cl-) past hydrophobic tails in center
can be “gated” or not
gates can open/close in response to electrical/chemical changes
water potential
solute potential (always neg) + pressure potential (always pos) = water potential
the greater the concentration of a solute, the lower the water potential (INVERSE relationship)
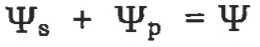
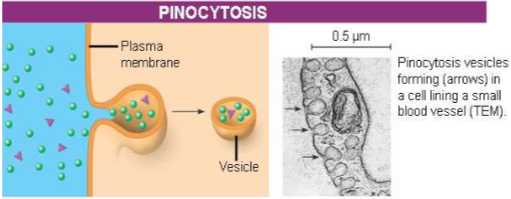
pinocytosis
cell “gulps” droplets of extracellular fluid into tiny vesicles
not the fluid itself that is needed by cell, but molecules inside droplet
b/c any & all included solutes are taken into the cell, pinocytosis is nonspecific in the substances it transports
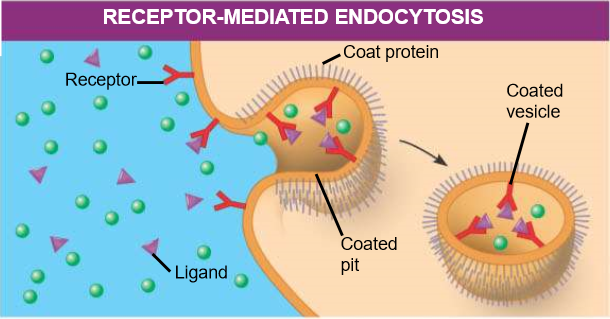
receptor-mediated endocytosis
enables cell to acquire bulk quantities of specific substances, even tho those substances may not be very concentrated in extracellular fluid