BIO 2010 Micro- Lab: 5&12 "Eight-Minute Surgical Scrub Activity" and "Control of Microbial Growth"
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What organism is named as the most common colonizer of human skin?
Staphylococcus epidermidis.
What is the difference between resident flora and transient flora?
Resident flora are microbes that live in the deeper pores and is harder to remove. Transient flora are microbes that come from contact with other people or objects and lives on the surface of the skin (can be washed off).
Resident flora are less firmly adherent to the skin surface than transient flora.
False (Resident flora are firmly adherent; transient flora are less firmly adherent.)
Who demonstrated that handwashing could prevent infection?
Ignaz Semmelweis.
What are the two most important things that you can do to protect yourself and others from disease?
proper handwashing and proper sneeze/cough hygiene
What's an example of proper handwashing technique?
Proper hand washing requires application of soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
What's an example of proper sneeze/cough hygiene?
Proper sneeze/cough hygiene requires shielding of the mouth and nose with the inside of your elbow or your shoulder not your hand.
Name two environments or sources that hands can transmit organisms
Examples: other people, the nose (organisms from the nose), skin, feces, toilet tissue contamination (dysentery-causing microbe).
What types of infections are mentioned as being easily spread in hospitals by unclean hands?
Nosocomial or iatrogenic infections.
According to the surgical scrub protocol, how many total minutes of scrubbing with soap are performed (not counting the initial no-soap scrub)?
8 minutes. (Four soap scrubs, every 2 minutes = 8 minutes in total.)
Put these surgical scrub steps in the order they occur
(A) Pour sterile water into Basin 1.
(B) Scrub each hand under the water for 30 seconds.
(C) Provide a sterile brush to the scrubber.
(D) Supervisor opens basin package and sets aside top four basins.
D → A → C → B
what is the purpose of performing a 30-second scrub in a basin with sterile water after the timed soap scrub?
To count microorganisms remaining on the hands after the timed soap scrub
What is a pipette?
A pipette is a sterile tool used to accurately measure and transfer small volumes of liquid.
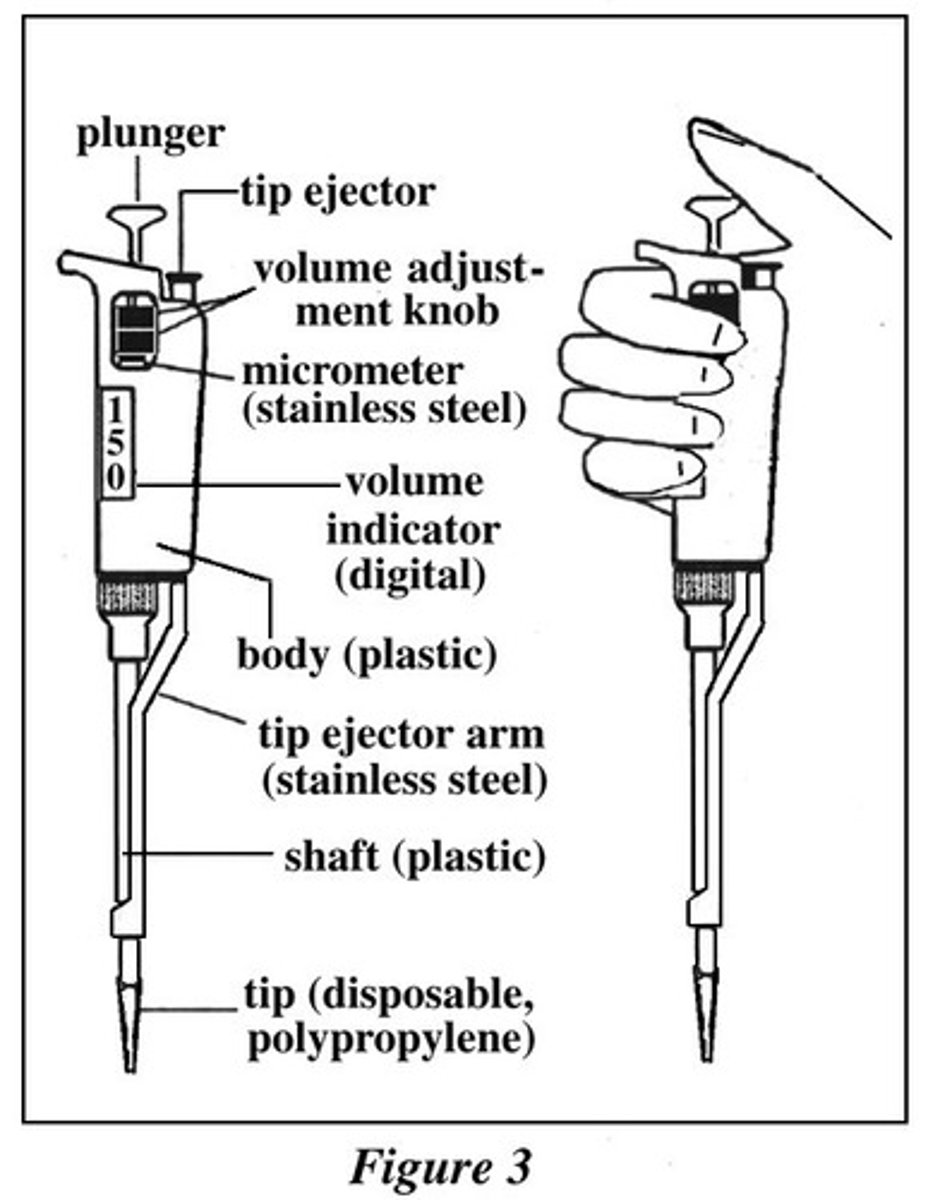
How was pipettes used in this basin sample experiment?
In this experiment it is used to stir the basin water to evenly distribute the microbes and then
transfer specific sample volumes (0.1 ml, 0.2 ml, and 0.4 ml) of the basin water onto the petri dishes for plating and colony counting.
What are the most common units used to describe bacterial cell concentration in a liquid?
CFU/ml and CFU/L
What does CFU stand for?
colony forming unit
What is the formula for calculating colony forming units (CFU) per milliliter?
CFU/ml= Average number of CFU per plate x Dilution Factor/Sample size (ml) per plate
What is the formula for calculating colony forming unit (CFU) per liter?
CFU/L=CFU/ml×1000
If two duplicate plates inoculated with 0.1 ml of basin water show colony counts of 188 and 172, what is the CFU/ml and CFU/L?
(188 + 172) / 2 = 180.
Sample size = 0.1 ml → CFU/ml = 180 / 0.1 = 1800 CFU/ml.
CFU/L = 1800 × 1000 = 1,800,000 CFU/L (1.8 × 10^6).
what three sample volumes are plated for each basin?
0.1 ml, 0.2 ml, 0.4 ml
Why are the sample sizes used in three different volumes (0.1, 0.2, 0.4 ml)?
to increase the chance of getting plates with a countable range of colonies (30-300 CFU).
What is TNTC and TFTC?
Too numerous to count
too few to count
What is considered TNTC (Too numerous to count)?
> 300 CFU/plate is considered 'Too Numerous To Count' (TNTC)
What is considered TFTC (too few to count)?
<30 CFU/plate is considered 'Too Few To Count'
What are two aseptic cautions given for pouring molten TSA onto samples?
1) Do not collect all agar tubes at once because they will solidfy and
2) Cool agar slightly before pouring and use aseptic techniques to avoid contamination.
What is the difference between microbicidal and microbiostatic action?
Microbicidal = kills microorganisms.
Microbiostatic = inhibits microbial growth but does not kill them.
Which of the following is NOT a major microbial target of control methods?
A) Cell envelope
B) Proteins
C) Nucleic acids
D) Ribosomes
D) Ribosomes
What are the mechanisms of killing microbes? (you may not need to know this)
-Denaturing enzymes (proteins)
-Disrupt DNA (nucleic acids)
-Altering permeability of membranes (lipids)
What are the two broad categories of microbial control killing?
Physical and Chemical
What are the 3 methods of control?
High temperature, UV radiation and toxic Chemcials (ex. disinfectants)
Denaturation
Is a permanent change in the three-dimensional shape of a protein, caused by factors like heat, chemicals, or pH changes.
What effect does elevated temperature have on cell membranes?
temperature mainly denatures enzymes (that's the primary lethal effect), but it can also disrupt and damage cell membranes, making them more permeable and less able to protect the cell.
Is it possible for an organism to still live even after the proteins are denatured?
No. If proteins are denatured, metabolism will stop and the organism will die.
thermoduric
able to survive exposure to high temperatures without being killed.
Which organism tends to be more thermoduric (heat resistant) Gram-positive or Gram-negative?
Gram positive organisms tend to be more thermoduric than Gram negative organisms due to the large amount of peptidoglycan in their walls
What other type of organism could be considered thermoduric?
Bacterial endospores (their
spore coat offers additional protection)
What is Thermal Death Point (TDP)?
Is defined as the lowest temperature to kill a culture of organisms in 10 minutes at a pH of 7.
Which organism would you expect to be more heat resistant: E. coli or Bacillus subtilis? Why?
Bacillus subtilis, because it forms resistant endospores.
How do antimicrobial chemicals typically inhibit microbial growth?
It inhibits microbial growth by altering the permeability of the plasma membrane or damaging the cell wall, which makes the cell leaky and disrupts transport. They may also intefere with metabolism and reproduction.
What is an disinfectant?
Harsh chemicals that can only be used on inanimate objects
What is an antiseptic?
milder, safer chemicals that can touch human skin and tissue
Sterilants
destroy all microorganisms
Bacteriocidal
kills bacteria
Bacteriostatic
inhibits bacterial growth
Bacteriocidal can kill any bacteria except....?
bacterial endospores, protozoal cysts, or viruses
What laboratory method is commonly used to test chemical effectiveness against microbes?
disk diffusion method (Kirby-Bauer method)
What makes gram-negative organisms more resistant to to chemical control than gram-positive?
The lipid outer membrane of the cell wall of the Gram negative organisms will make them quite resistant to chemical control, while the Gram positive organisms will be very susceptible
What type of radiation is ultraviolet (UV) light?
non-ionizing radiation
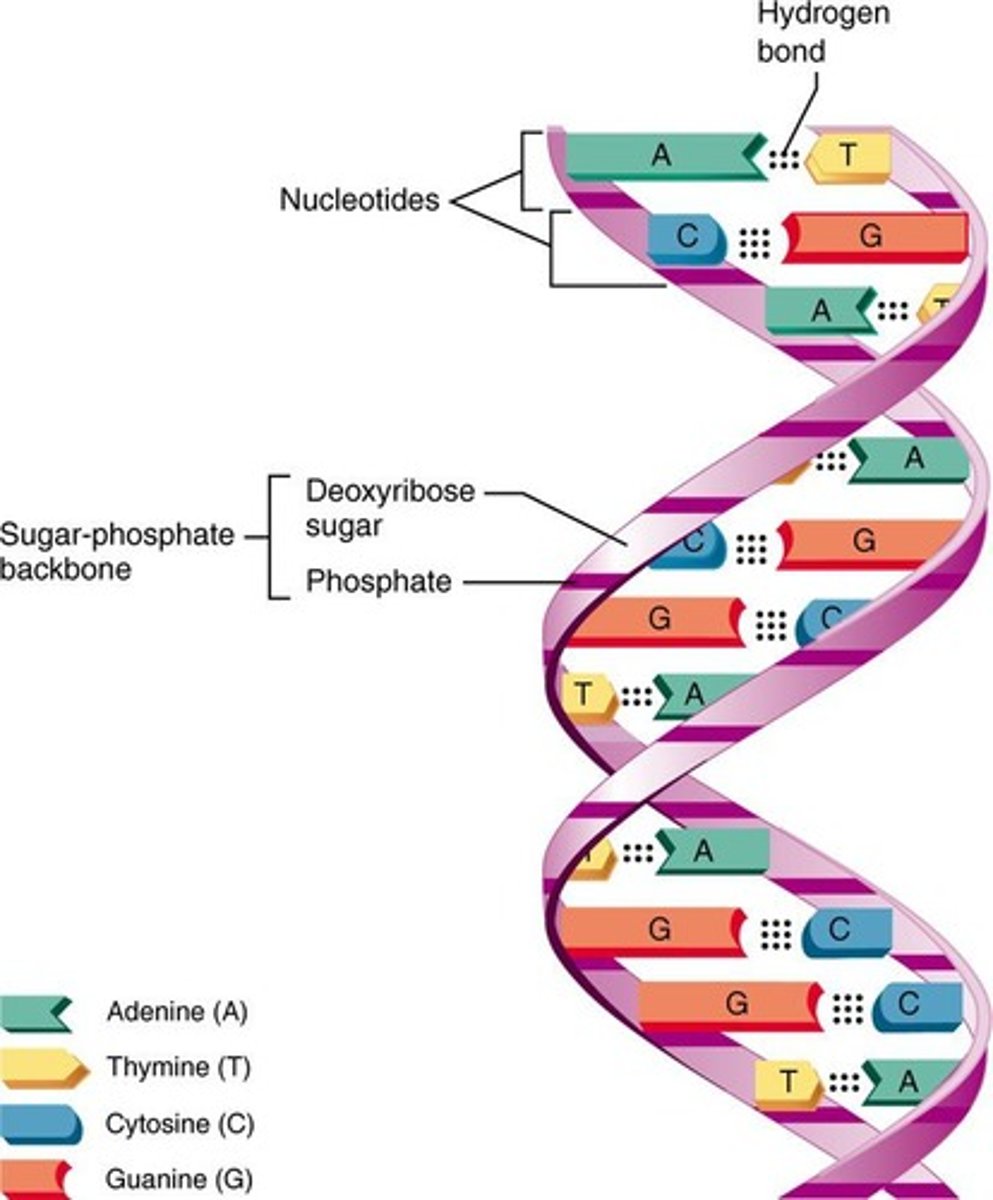
What is DNA composed of?
DNA is a double helix made of two nucleotide strands with alternating sugar and phosphate backbones.
How does UV light damage microbial DNA?
UV light damages microbial DNA by causing abnormal bonding between adjacent pyrimidine bases, creating thymine or cytosine dimers, which disrupt replication.
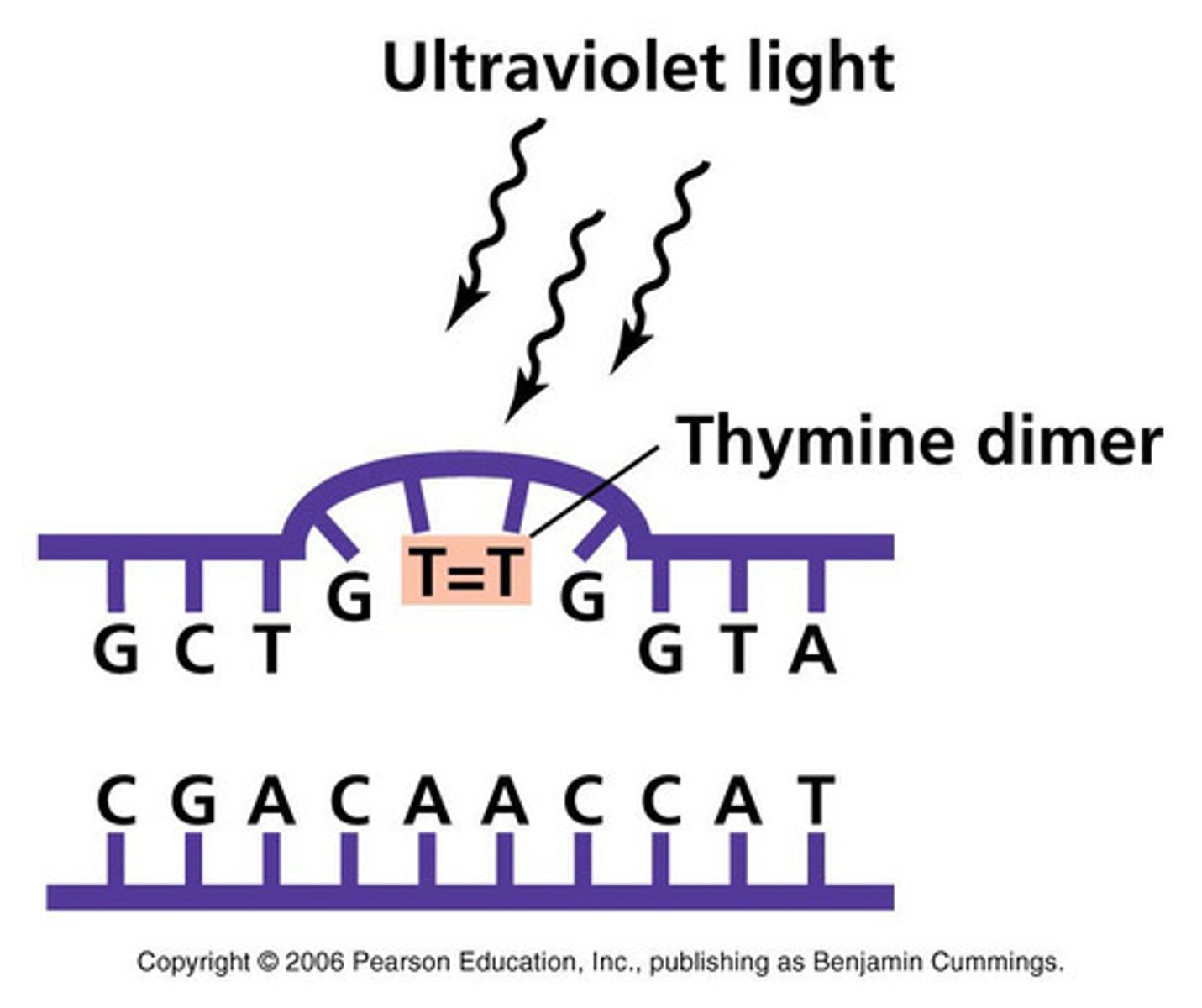
thymine dimers
an abnormal bond formed between two adjacent thymine bases in DNA when exposed to UV light, which can block replication and harm the cell.
cytosine dimer
an abnormal bond formed between two adjacent cytosine bases on the same DNA strand when exposed to UV light, which can disrupt replication and harm the cell.
What are thymine and cytosine classified as?
They are pyrimidine bases.
Why are pyrimidine dimers harmful?
They prevent hydrogen bonding with complementary bases during cell division, leading to mutations that may be lethal.
What is photoreactivation, and which organism can perform it?
Photoreactivation is a light-dependent DNA repair process used by some bacteria, such as Serratia marcescens, to repair UV-induced pyrimidine dimers.
Can a UV be considered a disnifectant or a sterilizing method?
UV is considered a disinfectant because it only kills microbes on surfaces and cannot penetrate barriers or liquids, so it does not achieve full sterilization.
What are some factors that can determine how effective UV radiation can be?
-wavelength
-time of exposure
-intensity of exposure
What is the most lethal wavelength of UV radiation?
260 nanometers.
What wavelength do laboratory UV lamps typically generate?
254 nanometers.
How does exposure time affect UV lethality?
The longer the exposure, the more effective the killing action
Why is UV radiation not very penetrating?
It requires direct contact between the light source and the organisms in order to have an efficient
killing effect so anything that shields or shadows the specimen may prevent the radiation from killing
the organisms.
In what situations are UV lamps commonly used?
Ultraviolet radiation lamps are used in laboratory situations, hospitals, food processing
plants, and meat lockers to reduce numbers of organisms.
Which two organisms are tested in the TDP experiment?
Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis.
What happens in the Control sector for the TDP experiment?
It shows normal growth without heat exposure.
What are the four disinfectants used in the chemical experiment?
Alcohol (ethanol), Lysol, Bleach, Zephiran chloride.
What organism is used in the UV radiation experiment?
Serratia marcescens.
What pigment does Serratia marcescens produce at 25-30°C?
A red/pink pigment.