PAPER 2 combined
1/308
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
309 Terms
gamete
a sex cell that contains half the normal chromosome number
chromosome
a long dna molecule containing many genes
gene
a small section of dna on a chromosome that codes for a partiular sequence of amino acids to make a specific protein
allele
different versions of the same gene
dominant allele
this allele is always expressed even if only one copy is present. represented by a capital letter
recessive allele
an allele that is only expressed if two/both copies are present. represented by a lower case letter
homozygous
if two alleles present are the same, individuals are said to be homozygous for that trait
heterozygous
if two alleles present are different, individuals are said to be heterozygous for that trait
genotype
describes the alleles present or genetic makeup of an individual regarding a particular characteristic
phenotype
the physical appearance of an individual regarding a particular characteristic
how many parents in sexual reproduction
2, opposite sex
how many parents in asexual
1
sexual reproduction
genetic information
offspring
genetic information is mixed
variety in offspring as reproductive cells in meiosis
asexual reproduction
genetic information
offspring
no mixing of genetic information
genetically identical offspring (clones)
only mitosis involved
where do cells divide by meiosis
reproductive organs to produce gametes
3 stages of MEIOSIS
copies of genetic information are made
cell divides TWICE to form FOUR gametes with single set of chromosomes (haploid cells)
all gametes are genetically different from each other (creates variation)
what happens when gametes join
ferilisation
normal number chromosomes restored
cells divide by mitosis
cells differentiate in embryo
sexual reproduction speed and energy cost
MORE energy and time needed to reproduce (find mate+ spread gametes)
asexual reproduction speed and energy cost
LESS energy and time needed to reproduce (more efficient)
variation with sexual reproduction (why is this good)
genetic variation in offspring
if environment changes = survival advantage
some will survive and reproduce
variation with asexual (pros and cons)
no genetic variation
many identical offspring can be produced if conditions are favourable
vulnerable if conditions change
if 1 individual can’t survive, none can
is artificial selection possible with sexual reproduction?
yes
speeds up natural selection
used by humans in selective breeding
is artificial selection possible with asexual reproduction?
NO
organisms that reproduce w sexual + asexual
fungi (asexual by spores, sexual for variation)
malaria (asexual in human, sexual in mosquito)
plants (asexual = runners, strawberry plants + daffodil bulbs. sexual = seeds)
dna is a ____ made up of _______
polymer
two strands forming a double helix
DNA monomers
nucleotide
phosphate group + sugar backbone
base (at, cg)
genome
the entire genetic material of an organism
studying genome allows us to
search for genes linked to different types of diseases
understand and treat inherited disorders
trace human migration patterns of the past
sequence of bases form a….
code
how many bases in a codon
3
what does a codon code for
amino acid in a protein
order of bases controls order of amino acid
joined to make specific protein
what carries code for sequence of amino acid
template molecule
coded for by genes in nucleus
goes to ribosome
amino acids assembled by
carrier molecules (bring specific amino acids to protein chain)
what happens when chain is complete
protein folds into specific shape for job (enzyme, hormorne, structural components, antibodies)
mutation
change in the DNA base sequence
occur continuously, particularly when dna replicated
few mutations code for
altered protein with different shape, affects the shape + functionality of the protein
Non coding parts of dna…..
switch genes on and off, variations will impact whether protein is made
female chromosomes
XX
male chromosomes
XY
chance of male/female
50%
polydactyly- dominant or recessive?
dominant
what is polydactyly?
having extra fingers/toes
what genotype to not have polydacyly?
homozygous recessive
cystic fibrosis- dominant or recessive?
recessive
to have CF, what genotype?
homozygous recessive
to be carrier of CF, what genotype?
heterozygous
gene therapy
replacing faulty genes
positives of embryo screening
reduces no. of people with disease (if aborted)
reduces healthcare costs (if aborted)
expensive to have babies with disease
informed choice about abortion
prepare financially + emotionally
negatives of embryo screening
possible damage/risk to embryo
possible harm/risk to mother
screening expensive
right to life
ethical/moral/religious desicions about abortion
motor neurone
cns → effector
synapse
physical gap between 2 neurones
electronic impulse converted to chemical neurotransmitter
diffuses across and binds to next neurone
slows down
stimulus
a change in environment
receptor
detects stimulus and converts info to impulse
effector
muscle/gland = contract/secrete hormone
response
response to stimulus
reflex arc
REACTION = AUTOMATIC/INVOLUNTARY
protects person from damage
doesn’t go to brain
stimulus → receptor →sensory neurone → relay neurone → motor neurone → effector → response
order of nervous system
stimulus → receptor →sensory neurone → CNS→ motor neurone → effector → response
relay neurones in brain
neurone differentiation
fatty myelin sheath - insulation
long - dendrons/dendrites
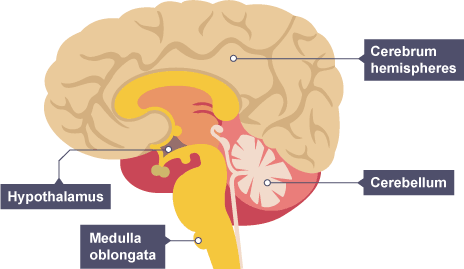
cerebellum
muscle movement/coordination
cerebral cortex
consciousness, intelligence, memory and language
medulla
unconcious activity - breathing + heartbeat
hypothalmus
temperature regulation
location of cerebral cortex, medulla and cerebellum
3 ways to study brain
mri scans (magnetic resonance imaging) - detailed picture
electrically stimulating brain - sees what part of brain controls what
studying patients with brain damage
why is studying brain risky
brain is complex and delicate
can lead to damage
eye in dim light
pupil dilates
circular muscles relax
radial muscles contract
more light enters eye
what is the eye
a sense organ containing receptors sensitive to light intensity + colour
what is accomodation
changing the shape of the lens to focus on near or distant objects
optic nerve
sensory neurones that send impulses to brain
transmits visual information from eye to brain as electrical impulses
retina
contains light sensitive cells that send neural impulses to the brain when stimulated by light.
thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye
focusing on distant objects
ciliary muscles relax = larger diameter
suspensory ligaments pulled tight
lens pulled thinner = slightly refracts/less convergent
Light focused on retina
focusing on near objects
ciliary muscles contract = smaller diameter
suspensory ligament loosen
lens = thick, strongly refracts/more convergent
light focused on retina
blind spot
unaware of this - brain fills gap
point where the optic nerve leaves the eye - no retina
eye in bright light
pupil constrics
circular muscles contract
radial muscles relax
less light enters eye
pupil
hole through which light enters the eye
controls the amount of light that enters the eye
ciliary muscles
controls the shape of the lens
contract and relax to change the shape of the lens
allows accomodation
sclera
white outer layer
tough + strong so the eyeball is not easily damaged
myopia
short sightedness
close = clear
distant = blurred
light focused in front of retina = blurry
concave lens
hyperopia
long sightedness
distant = clear
close = blurry
light focused behind retina = blurry
convex lens
cornea
transparent part of sclera at from of eyeball
lets into eye
curved surface refracts light rays, focused on retina
iris
circular + radial muscles that contract and relax to change the size of the pupil
controls size of puil
controls amount of light reaching retina
suspensory ligament
holds lens in place
attach the lens to ciliary muscles (helps accomodation)
corrective technology
spectacles/contact lenses
laser eye surgery (aters shape of cornea)
replacement lens
lens
clear disc held in place by suspensory ligament + ciliary muscles
fine tunes the focusing of light rays, changing their direction to produce a clear image on retina
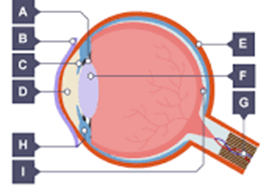
a - suspensory ligament
b - cornea
c - iris
d - pupil
e - sclera
f - lens
g - optic nerve
h - ciliary muscle
i - retina
3 reasons for differences
genetics causes
environmental causes
combination of both causes
what is variation due to
mutation
how do mutations effect phenotype
most have no effect
some influence
very few change
evolution is
the change in inherited characteristics of a populaiton over time.
this is through natural selection, which can eventually form new species
when did simpler life forms first develop
more than three billion years ago
a species is
a group of organisms with similar characteristics which can reproduce to produce fertile offspring
which 2 scientists proposed theory of evolution by natural selection
charles darwin, alfred russel wallace
charles darwin famous for work on
finches in galapogos islands
wallace famous for research on
warning colouration and speciation
4 steps of natural selection
genetic variation in a characteristic in a species due to a random mutation
those with characteristic best suited to the environment are more likely to survive and reproduce
pass on beneficial alleles for that characteristic to their offspring
the frequency of the beneficial allele increases in the population over time.
3 reasons why natural selection was not accepted initially
strong religious beliefs
insufficient evidence (no microscopes)
mechanism of inheritence not known till 50 yrs later
lamarck’s theory
inheritance of acquired characteristics over a life time,
if an individual needs to adapt it will, and pass on to offspring
4 main steps for speciation
isolation
mutation
natural selection
speciation
isolation is…
geographical/physical barrier that seperated population