Periodic Trends, Orbital Diagrams, and Ionic Configurations in Chemistry
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What does Coulomb's Law describe?
The force experienced by electrons in an atom based on charge and distance.
What happens to the magnitude of force (F) as the charge (q) increases?
The magnitude of F increases, resulting in more attraction or repulsion.
What happens to the magnitude of force (F) as the distance (d) increases?
The magnitude of F decreases, resulting in less attraction or repulsion.
How does effective nuclear charge (Zeff) change as you move left to right on the periodic table?
Zeff increases, leading to a decrease in atomic size.
What is the formula for calculating effective nuclear charge (Zeff)?
Zeff = Z - S, where Z is the atomic number and S is the shielding constant.
What is the effect of increasing Zeff on atomic radius?
As Zeff increases, the atomic radius decreases due to increased attraction.
What happens to Zeff as you move down a column on the periodic table?
Zeff remains constant, but atomic size increases due to shielding and larger orbitals.
What is Hund's Rule?
When filling orbitals of the same type, electrons are allocated singly first with parallel spins.
What is the Aufbau Principle?
Electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first.
What is the favored charge for Na+ and why?
Na+ has a charge of +1 because it loses one electron to achieve a fully filled n=2 orbital.
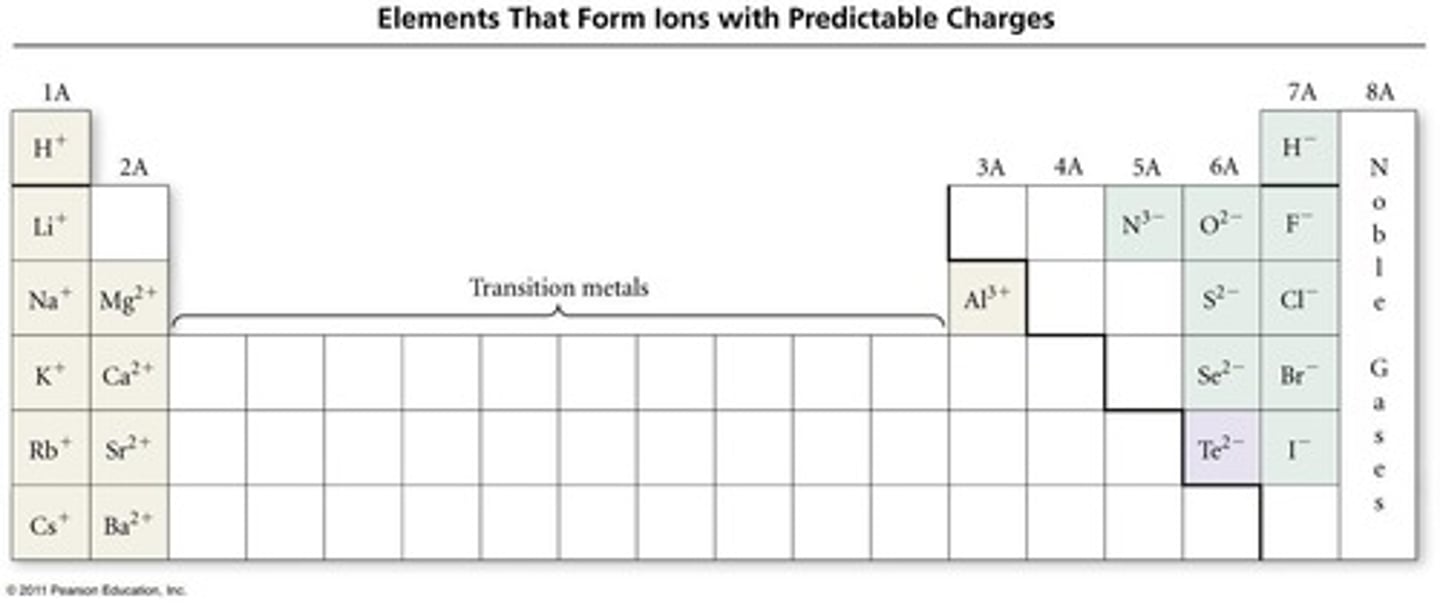
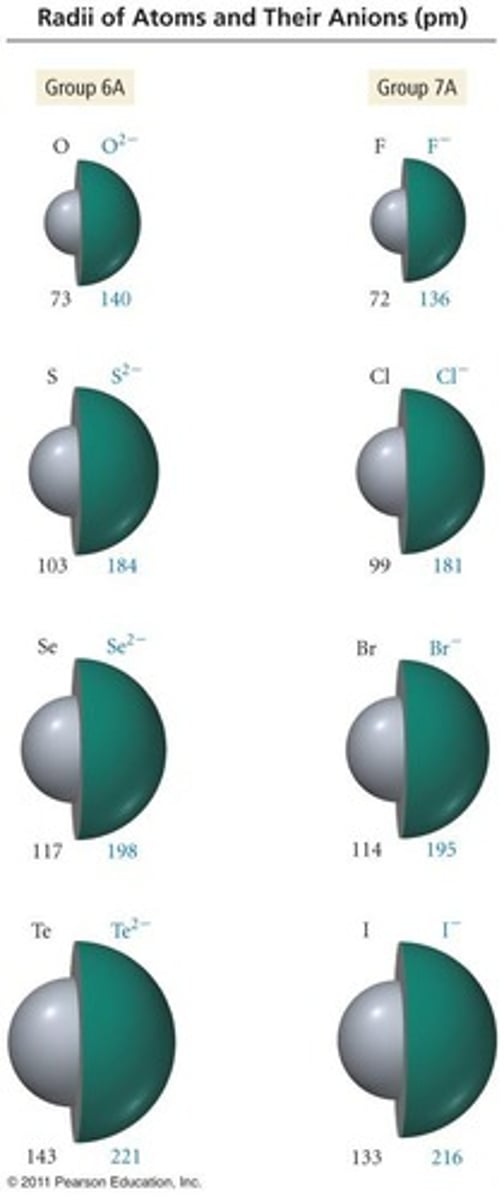
What is the favored charge for Cl- and why?
Cl- has a charge of -1 because it gains one electron to achieve a fully filled n=3 orbital.
What is the favored charge for Zn2+ and why?
Zn2+ has a charge of +2 because it loses two electrons to achieve a fully filled n=3 orbital.
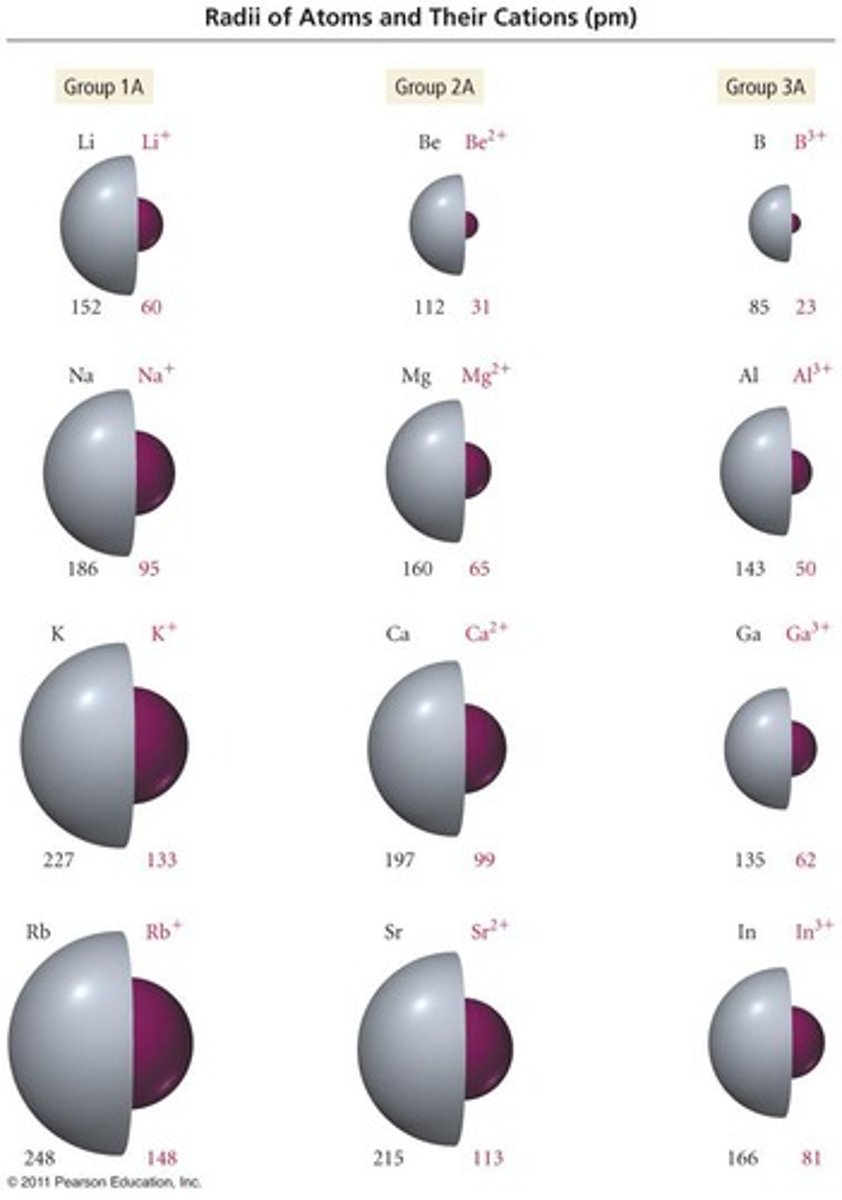
What is the favored charge for Al3+ and why?
Al3+ has a charge of +3 because it loses three electrons to achieve a fully filled n=2 orbital.
What is the electron configuration for Chlorine?
[Ne] 3s2 3p5
What is the electron configuration for Manganese (valence only)?
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d5
How do you rank the following ions from largest to smallest: O2-, F-, Na+, Mg2+?
O2- > F- > Na+ > Mg2+
What is the significance of fully filled subshells in terms of stability?
Fully filled subshells provide added stability and lower energy.
What is the impact of increasing orbital size (n) on atomic radius?
As n increases, the atomic size increases due to larger orbitals.
What is the relationship between effective nuclear charge and atomic radius when moving left to right?
Effective nuclear charge increases, leading to a decrease in atomic radius.
What is the relationship between effective nuclear charge and atomic radius when moving down a column?
Effective nuclear charge remains constant, but atomic radius increases due to shielding.