Lecture 6- Simple Diode Rectifier and Full Wave Rectifier
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What are a rectifier purpose?
(1) to convert the mains voltage AC source to a lower voltage DC output and (2) to regulate the DC voltage and protect the device from fluctuations in the AC grid voltage.
Rectifier
A power converter is called a rectifier when it converts AC voltage/current/power to DC. By contrast, a converter is called an inverter when it converts DC to AC.
controllable converter
A power converter that uses a controllable semi-conductor switch is a controllable converter;
uncontrollable converter
an uncontrollable converter is one that does not use a controllable switch (a passive device).
Diode
: An uncontrollable switch or device which turns on when a voltage is applied in a particular direction and turns off when the applied voltage is zero or negative.
Thyristor:
A semi-controllable switch or device which turns on when a control signal is applied but only turns off when the voltage applied to the device is zero or negative.
Transistor:
A controllable switch or device which is switched on and off by a control signal.
A simple diode rectifier
The diode is a unidirectional switch so only conducts when the device is positively biased, meaning it has a relatively positive voltage applied to its anode compared to the cathode. When positively biased, the ideal diode acts as a short circuit (with zero resistance) and applies the source voltage 𝑣𝑠 to the load and conducts current
Limitations of half-wave rectifier
The half-wave rectifier provides a simple means of converting AC to DC but it has its limitations
• By only rectifying half the source voltage, the output does not make maximum use of the source.
• The output voltage has a period of zero output and no load current. This leads to problems such as flicker in LED lighting. The light has on/off periods during the 50 Hz electrical cycle and the human eye can detect this.
• The converter is passive such that the source voltage determines the output. There is no output control.
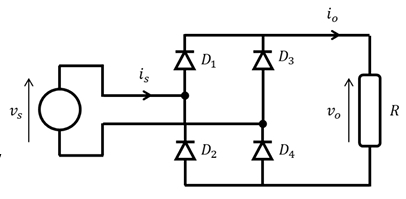
Diodes in full wave diode rectifier
Positive source: 𝐷1 and 𝐷4are positively biased.
Negative source: 𝐷2 and 𝐷3are positively biased.