North Carolina Life Insurance Exam
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
143 Terms
Adverse Selection
the insuring of risks that are more prone to losses than the average risk
Agent/Producer
a legal representative of an insurance company; the classification of producer usually includes agents and brokers; agents are the agents of the insurer
Applicant or proposed insured
a person applying for insurance
Attained Age
the insured’s age at the time the policy is issued or renewed
Beneficiary
a person who receives the benefits of an insurance policy
Cash Value
a policy’s savings element or living benefit
Death Benefit
the amount paid upon the death of the insured in a life insurance policy
Lump-Sum distribution to beneficiary and Principal are TAX FREE
Interest is taxable if paid in installments (not lump-sum)
Deferred
withheld or postponed until a specified time or event in the future
Endow
to have cash value of a whole life policy reach the contractual face amount (ex. whole life insurance endows at age 100, so the cash value of all premium payments will sum to equal the face amount at that age)
Face Amount
the amount of benefit stated in the life insurance policy
Insured
person covered by the insurance policy; may or may not be the policyowner
Insurer(Principal)
the company that issues an insurance policy
Lapse
Policy termination due to nonpayment of premium
Level Premium
the premium that does not change through the life of a policy
Nonforfeiture Values
benefits in a life insurance policy that the policyowner cannot lose even if the policy is surrendered or lapses
Policyowner
the person entitled to exercise the rights and privileges in the policy
Policy Maturity
in life policies, the time when the face value is paid out
Premium
the money paid to the insurance company for the insurance policy
NOT TAX DEDUCTIBLE
Securities
financial instruments that may trade for value (ex. stocks, bonds)
Permanent Life Insurance
refers to various forms of life insurance policies that build cash value and remain in effect for the entire life of the insured (or until age 100) as long as the premium is paid.
Whole Life Insurance
Key Characteristics:
Level Premium based on issue age
Death Benefit is guaranteed & remains level
Cash value (AKA nonforfeiture value) = face value at 100 y/o, and are credited to the policy regularly with guaranteed interest rate. Does not usually accumulate until the third policy year and grows tax deferred
Living Benefits allow policy owner to borrow against the cash value (aka nonforfeiture value) while policy is in effect or can receive cash value if policy is surrendered
3 Main types: Straight, limited pay, single premium
provides lifetime protection, and includes a savings element (or cash value). Endow at age 100. Policy premium calculated assuming that the policy owner will be paying until age 100 and are usually higher than term insurance.
Straight (Ordinary/Continuous Premium) Whole Life Insurance
The basic whole life policy. Policyowner pays premium from the time the policy is issued until the insured’s death or age 100. Has the lowest annual premium of the whole life policies. Cash Value increases overtime, premium stays constant
Limited-Pay Whole life
Designed so that premiums are all paid before age 100. Short premium-paying period, so higher annual premium than straight life. Cash Value builds up faster than straight life. Ideal for individuals who do not want to pay premiums after a certain point in time
Types: 20-pay life (all premiums paid within 20 years), life paid-up at 65(all premiums paid by age 65)
Single Premium Whole Life
provide a level death benefit to insured’s age 100 with a one-time, lump-sum premium payment. Cash Value is immediately generated and grows over time
Indexed (AKA Equity Index) Whole Life
Cash Value dependent on performance of an equity index (ex. S&P 500). Guaranteed minimum interest rate. Face amount increases annually to adjust for inflation w/o requiring evidence of insurability.
If policyowner assumes the risk, premium increase with increasing face amount. If Insurer assumes the risk, premium stays constant.
Modified Whole Life
Charges a lower premium (similar to term rates) in the first few years, then premium increases for remainder of insured’s life. Higher premium usually higher than straight life for equal age and coverage. Intend to help people with limited finances short-term
Graded-Premium Whole Life
Premiums start low then increase to a level point in the future. Starts with premium 50% lower than that of straight life. Then, premium gradually increases each year for ~5-10 years, then levels off.
Indeterminate Premium Whole Life
premium varies yearly, two rates; guaranteed level premium (maximum premium) or nonguaranteed lower premium. Premiums paid for set period and then new rates are established based on expected company mortality, expenses, and investments. Can never exceed the maximum
Interest-sensitive (Current Assumption) Whole Life
Guaranteed death benefit to age 100. Premium based on current assumptions abt risk, interest, and expense. If actual values are different, company will change premium. Credit Cash value with the current interest rate that can be higher than guaranteed levels. Guaranteed minimum interest rate.
Same benefits as other traditional whole life policies with added benefit of current interest rates, which can increase cash value accumulation or decrease premium-paying period
Endowment Whole Life
Same features of regular whole life policies just with earlier maturity date. Permanent, level death protection if insured dies prematurely, accumulates cash values, premiums can be paid up to endowment date or in lump-sum. Intended to be used while the insurer is alive. Premiums considerably higher than straight life. the shorter the premium period, the higher the premium
Flexible Premium Policies
Allows policyowner to pay more or less than the planned premium
Adjustable (Term/Whole) Life
Intended to combine term and permanent coverage. Insured determines how much coverage is needed and affordable premium. Insurer determines appropriate type of insurance. As insured’s needs change, policyowner can make adjustments (increase/decrease premium, increase/decrease premium-paying period, increase/decrease face amount, or change period of protection) to the policy.
Can be converted from term to whole life or vice versa. Increasing death benefit or decreasing premium usually requires proof of insurability. Cash value only develops when premiums paid > cost of the policy
Universal Life (Flexible Premium Adjustable Life)
policyowner can increase premium, later decrease, or skip premium. Cash value must cover monthly cost of insurance to skip premium payments, otherwise policy will lapse.
Policyowner may have minimum and target premiums. Minimum keeps policy in force for current year and behaves like an annually renewable term product. Target is recommended to cover cost of insurance protection and keep policy in force throughout its lifetime
interest-sensitive, guaranteed contract interest rate or nonguaranteed current market interest rate (whichever is higher)
Two components: Annually renewable term insurance and cash account.
Partial withdrawal(Surrender) of cash value is allowed. There may be associated withdrawal limits, charges, and frequency. Interest earned on the withdrawn cash value may be subject to taxation. Death benefit reduces by the withdrawn amount. NOT A POLICY LOAN
Universal Life Option A
Level death benefit
Cash Value gradually increases, lowering pure insurance in later years
Required corridor between cash value and death benefit to be considered life insurance
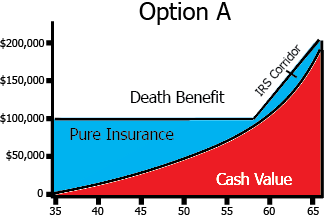
Universal Life Option B
Increasing Death Benefit
Cash Value increases annually and is included in the death benefit, meaning the death benefit increases annually. Total death benefit always = face amount + current amount of cash value
Pure insurance remains level for life, expenses are much higher than the other option.
Cash value lowers in the older years (all else equal)
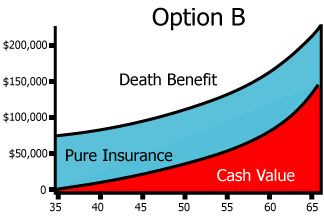
Fixed Life Insurance or Annuities
contracts that offer guaranteed minimum or fixed benefits that are stated in the contract
Variable Life Insurance or Annuities
Contacts where cash values accumulate based on a portfolio of stocks WITHOUT guarantees of performance.
Keep pace with inflation and are determined by securities backing it
Variable Whole Life Insurance
investment-based
level, fixed premium with guaranteed minimum death benefit.
Cash value is NOT guaranteed & fluctuates with portfolio
Premiums are invested by the INSURER
Policyowner specifies where cash value should be invested and bears investment risk
Assets in a separate account (NOT in insurance general account) that acts as a mutual fund(unit trust)
Variable Universal Whole Life
Flexible premium
increasing/decreasing amount of insurance
Cash withdrawals & Policy Loans
Return not guaranteed compared to Universal Life
Regulation of Variable Products
SEC, FINRA, State & Federal Governments
Agents must be registered with FINRA; be licensed by the state to sell life insurance; and have received a securities license
Family Protection Policy
Combination of Whole Life and Term insurance to cover family members in one policy
Breadwinner covered under whole life
Spouse and dependents under convertible term insurance which can be converted to permanent coverage between 21 and max dependent age or before 65 years old for the spouse WITHOUT evidence of insurability
Family Income Policy
Combination of decreasing term insurance and whole life insurance on family breadwinner
Income period funded with decreasing term; term covers surviving family with income payments for the remaining period should breadwinner die during income period.
At the end of income period, face amount of the whole life coverage has been paid to the beneficiary
If insured dies after income period, only whole life portion will be paid to the beneficiary
Joint Whole Life
Insures two or more lives; can be spouses or business partners
can be in the form of term or permanent insurance
premium for joint life is less than separate premiums for each person
premium is based on joint average age
death benefit paid upon first death only
Survivorship Whole Life (Second to Die)
Insures two or more lives
premium based on average age
pays on the last death
lower premium than Joint Whole Life
Often used to offset the liability of estate tax
Jumping Juvenile Life
life insurance written on the life of a minor
Face amount increases at a predetermined age (often 21)
Face amount “jumps” premium remains constant
Double or Triple (Multiple) Protection
Combine permanent and level term insurance
pay double or triple the face amount if insured dies during specified period
If insured dies after the period, policy only pays face amount
Term Riders
allow for an additional amount of temporary insurance without needing to issue another policy
Typically attached to whole life to provide more protection at reduced cost
Limited Benefit
cover certain expenses from specifically namd illnesses, injuries, or circumstances
IRS
Internal Revenue Service: a US government agency responsible for collecting taxes and enforcing Internal Revenue Code
Life Contingency
dependent upon whether or not the insured is alive
Liquidation of an estate
converting a person’s net worth into a cash flow
Natural Person
a human being
Qualified Plan
a retirement plan that meets the IRS guidelines for receiving favorable tax treatment
Suitability
a requirement to determine if an insurance product or an investment is appropriate for a particular customer
Annuity
contract that provides income for a specified period of years, or for life
protects individuals against outliving their money main use is for retirement income or education expenses
NOT life insurance
Vehicle for the accumulation of money and liquidation of an estate
Do not pay face amount upon death of annuitant; payments stop upon death
Uses mortality tables with longer life expectancy than life insurance
Mortality Table
inddicates the number of individuals within a specified group starting at a certain age, who are expected to be alive at a succeeding age (e.g. males, females, smokers, nonsmokers, etc)
Annuity Owner
purchaser of the annuity contract but not necessarily the one who receives the benefits
has all of the rights to name beneficiary and to surrender the annuity
May be a corporation, trust, or other legal entity
Annuitant
the NATURAL PERSON who receives benefits from an annuity
life expectancy taken into consideration
annuity is written for this person
Beneficiary
the person who receives annuity assets (amount paid in or cash value; whichever is greater) if the annuitant dies during the accumulation period
Accumulation Period AKA Pay-in period
period of time over which the owner makes payments (premiums) into an annuity. Payments earn interest on a tax-deferred basis
Annuity Period AKA Annuitization Period, Liquidation Period, or Pay-Out Period
time when the accumulated sum is converted into income payments to the annuitant. Can last for the lifetime of the annuitant or for a specified period
Annuity Income
based on cash value accumulated, frequency of payment, interest rate, and annuitants age & gender
shorter life expectancy = higher benefit
longer life expectancy = lower benefit
Beneficiary receives cash value or total premiums paid (whichever is greater) if annuitant dies during accumulation period
Premium Payment Annuity Options
Single Premium: one, lump-sum payment
Periodic Premium: premium paid in installments over a period of time
Can be level premium or flexible premium
Immediate vs Deferred Annuities
Immediate: purchased with single, lump-sum payment and provides income payments within one year from purchase date. Can be as early as one month
Deferred: income payments begin after one year, can be lump-sum or periodic payments.
The longer it is deferred, more flexible payment premiums
Nonforfeiture
Deferred Annuity must have a guaranteed surrender value that is available. 10% penalty applied to withdrawals before 59.5 y/o
Surrender Charges
Compensates company for loss of investment value due to early surrender; typically decreases over time
Fixed Annuity
-Guaranteed minimum rate of interest or the current interest rate (whichever is higher)
-Income payments that do not vary from one payment to the next (Level benefit payment amount)
-Guaranteed specified dollar amount for each payment and length of period of payments
-Do not adjust for inflation
-Premiums are placed in company’s general account
-Insurer bears the investment risk
(Equity) Indexed Annuities
Fixed annuity that is tied to an index like the S&P 500
Company keeps some of interest earned but excess interest is credited to account
Less risky than variable annuity or mutual fund and typically higher interest rate than fixed annuity
Variable Annuity
Considered a security; regulated by SEC and State Insurance Regulations
No guaranteed minimum interest rate
payments are invested into insurer’s separate account NOT general account
Agent/Company must be registered with FINRA and have securities license
Pure Life (Life-only or Straight Life) Annuity
Payment stops at annuitants death
highest monthly benefits
no guarantee that entire principal will be paid out
Life with Guaranteed Minimum (Refund Life) Settlement
Principal will be refunded to beneficiary if annuitant dies before principal amount has been paid out. Guarantees entire principal will be paid out. Benefits subject to taxation when paid to beneficiary
Cash Refund: lump-sum payment of principal-benefit payments made to annuitant. Does not guarantee interest
Installment Refund: beneficiary receives guaranteed installments until principal has been paid
Life with period (term) certain
Annuity payments guaranteed for lifetime of annuitant and for a specified period for beneficiary.
Joint Life Annuity
two or more annuitants receive payments until the first death among the annuitants
Joint and Survivor
guarantees an income for two recipients that neither can outlive. Typically survivor receives reduced payment.
No guarantee that all proceeds will be paid out if both beneficiaries die
Lump-Sum Annuity
Paid at annuitization; all interest accumulated is taxable; 10% penalty for withdrawal before 59.5 y/o
Annuities Certain
Payment guaranteed for fixed period or until certain fixed amount paid. NO life option
Activities of Daily Living
a person’s essential activities that include bathing, dressing, eating, transferring, toileting, continence
Contingent Beneficiary
beneficiary who has second claim to the policy proceeds after the death of the insured (usually after the death of primary beneficiary)
Principal Amount
face value of the policy; original amount invested before earnings
Entire Contract
Policy + Copy of application + any riders or amendments
Insuring Clause (Insuring Agreement)
agreement between the insurer and the insured promising to pay the death benefit upon the insured’s death. Defines who the parties are, how long coverage lasts, and type of loss insured against
Free Look
policyowner has 10 days from receiving the policy from the agent to look over policy and return it for a full premium refund
Owners rights
Only policyowner has rights under the policy and are responsible for paying the premiums and must have an insurable interest in the insured. They can name/change the beneficiary, receive living benefits, select benefit payment options, and assign the policy
Absolute Assignment
transferring all rights of ownership to another person or entity. Permanent and total transfer of all the policy rights. New policyowner does not need to have an insurable interest in the insured
Collateral Assignment
transfer of partial rights to another person. Usually done in order to secure a loan or some other transaction. temporary assignment of some policy rights until debt is repaid
No named beneficiary
policy proceeds go to the insured’s estate
Revocable vs Irrevocable Beneficiaries
Revocable can be removed by policyowner at any time
Irrevocable can only be changed with the consent of the beneficiary. Owner cannot borrow against the policy’s cash value or assign policy to another person without beneficiary’s consent
Changing the Beneficiary: recording or filing method
policyowner completes a form with the change and submits it to the insurance company
Changing the Beneficiary: Endorsement Method
policy owner is required to send the request for change with the contract to the home office of the insurer. Home office will have to approve and make the change
Uniform Simultaneous Death Law
if policy owner and beneficiary die at the same time with no indication of who died first, the policy will be distributed as if the beneficiary died first and will go to the contingent beneficiary
Common Disaster Clause
Protects Contingent Beneficiary
If insured and primary beneficiary died in a common disaster, the policy will be distributed as if the beneficiary died first and will go to the contingent beneficiary or estate. Primary beneficiary must die within 14-30 days from the insured for this to be utilized
Net Premium
Mortality-Interest
Gross Premium
Net Premium (AKA Mortality-Interest) + Expense(AKA loading)
Grace Period
period of time after the premium due date that the policyowner has to pay the premium before the policy lapses (usually a month)
Misstatement of age or Gender on Application
results in adjustment of premiums or benefits
Reinstatement Provision
a lapsed policy can be put back in force if all premiums, interest, and outstanding loans and reinstated within a specified maximum time limit with evidence of insurability. Policy will be restored to original status and the insured’s issue age. Does not apply to surrendered policies
Incontestability Clause
If policy has been in force for at least 2 years, insurer cannot deny a claim based on misstatements on application. Does not apply to nonpayment, statements relating to age, sex, or identity
Conversion and Change of Plan
changing to a higher premium plan does NOT require proof of insurability
changing to a lower premium plan REQUIRES proof of insurability
Days of written notice required to tell policyowner that policy is going to lapse
30
Policy Loans
ONLY available in policies with cash value (whole life)