Bio 2 Seedless Plants
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Aquatic Plants
all terrestrial plants are descended from aquatic plants (mostly green algae)
aquatic plant have it easy
no treat of desiccation, no need for structural support, water protects from UV rays, gametes are transported through water
How did aquatic plants colonize terrestrial environments?
had to adapt to living outside of water, dry conditions, UV rays
Disadvantages of colonizing terrestrial environments
threat of desiccation (a threat to terrestrial plants that involves water loss)
UV rays
need structural support
plant reproduction is water- dependent
zygote is water- dependent
Advantages of colonizing terrestrial environments
sunlight is abundant
carbon dioxide is abundant
no competitors for resources
no predators
First terrestrial plant strategies
bryophytes or mosses
live near water and/ or colonize humid environments
develop tolerance to desiccation
stay small
develop mechanism to protect against UV rays
Time
Natural selection will act on genetic variation and select for beneficial traits
Adaptations to terrestrial life
Sporopollenin
protects spores/ pollen from desiccation
Alternation of generations life cycle
Two life stages in the same individual: Sporophyte stage that produces sores and a gametophyte stage that produces gametes
Apical meristem in roots and shoots
allows vertical growth
Waxy cuticle on leaves and stem
prevents desiccation
Lignin in vascular tissues (only present in vascular plants)
Structural support
Sporopollenin
Spores have thick cell walls made of sporopollenin
Sporopollenin is organic molecules that are similar to fatty acids, and carotenoids
Very resistant to desiccation and degradation
This is an adaptation to protect spores
Alternation of Generations
All sexually reproducing organisms have diploid and haploid stages
Plants’ diploid stage amnd haploid stage are both multicellular
Alternation of generations describes the life cycle of organism that have multicellular diploid and haploid
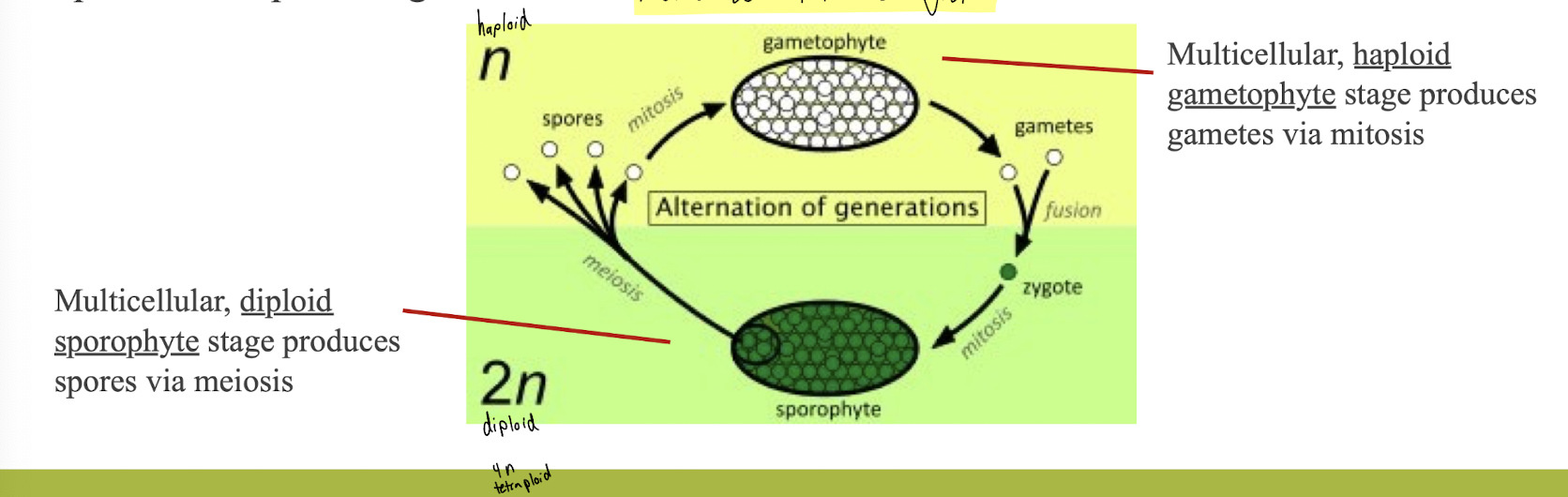
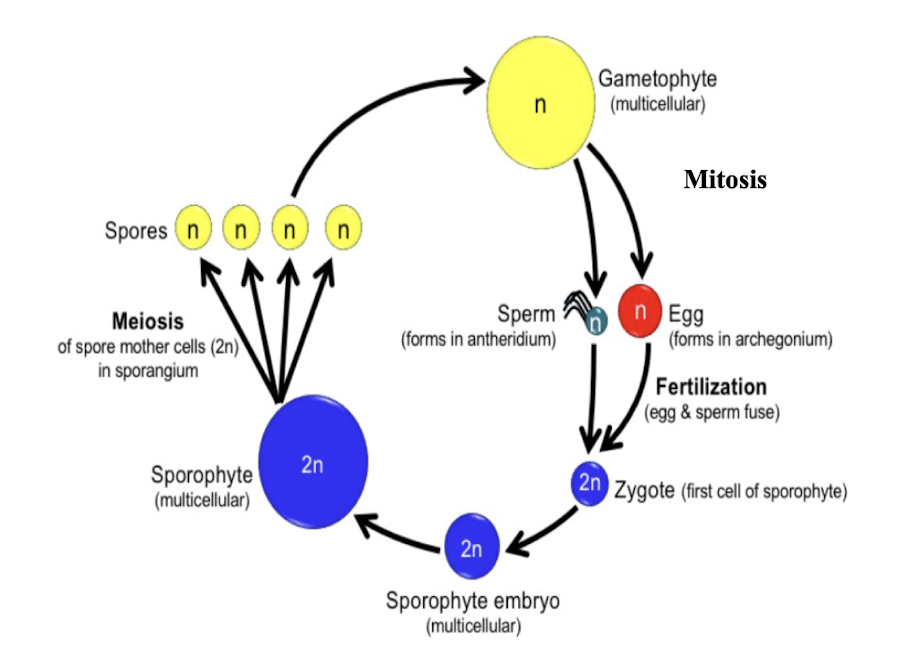
General life cycle of seedless plants
The haploid gametophyte stage produces haploid gametes through mitosis
The sperm of one plant fertilized the egg of a separate plant to create a new individual plant, the diploid sporophyte
The diploid sporophyte stage produces haploid spores through meiosis
Spores germinate into new gametophyte plants
Sporangia in Seedless Plants
In seedless plants, the sporophyte is the diploid (2n) stage (the sporophyte is the result of gamete fusion aka fertilization)
In nonvascular seedless plants, the sporophyte stage is dependent on gametophyte (n) stage
The sporophyte produces sporangia
the sporangium structure is made of cells called sporocytes
sporocyte cells produce haploid spores through meiosis
Spores are released from the sporangia, disperse, and then germinate into a new haploid gametophyte plants
What is the sporangium structure made of?
cells called sporocytes
sporocyte cells produce haploid spores through what?
meiosis
What are the two types of spores?
Homosporous and Heterosporous
Homosporous
Sporohytes that produce only one type of spore are called homosporous (“same spore”)
These pores typically germinate into a monoecious gametophyte
Monoecious: both male and female on same plant
Most, but not all, seedless plants are homosporous