Lecture 1: Nucleus
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Progeria
A genetic disease in which patients age so rapidly they die in their second decade of life from advanced atherosclerosis, which is typically a disease of the elderly
Nuclear transport (import vs export)
Role of nuclear lamins in membrane assembly/disassembly
2 important functions of nucleus:
aging and cardiovascular disease (structure/function of nucleus)
by studying Progeria, we could expect to learn more about:
tiny things (nutrients, vitamins, hormones, steroid hormones, small peptide hormones)
what are some things that can pass through the nuclear ring via diffusion?
nuclear lamins (type of IF)
what connects chromatin to the nuclear membrane?
dephosphorylated
during interphase, nuclear lamins are _______
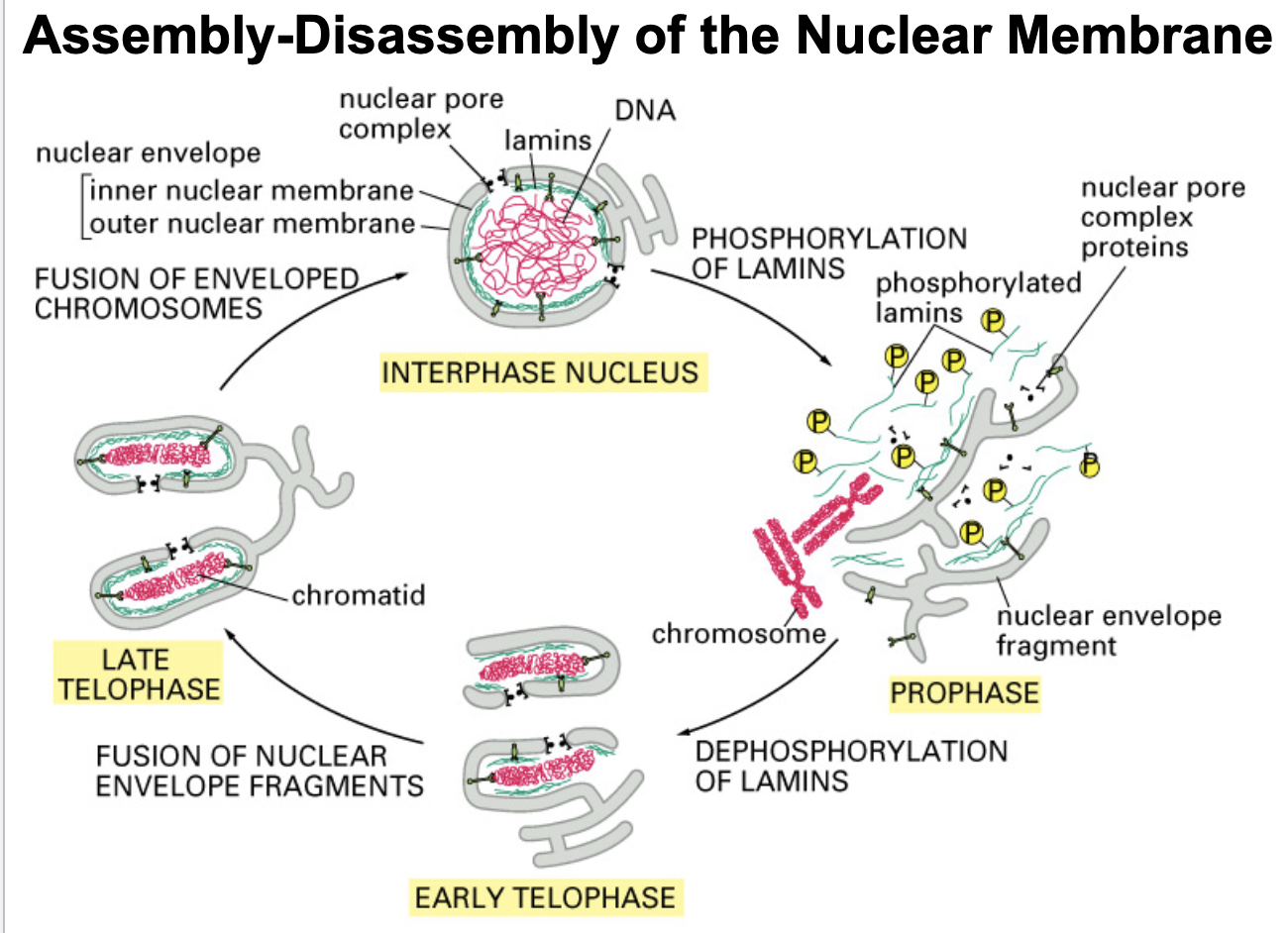
lamin phosphorylation (done by kinase)
what initiates the beginning of mitosis?
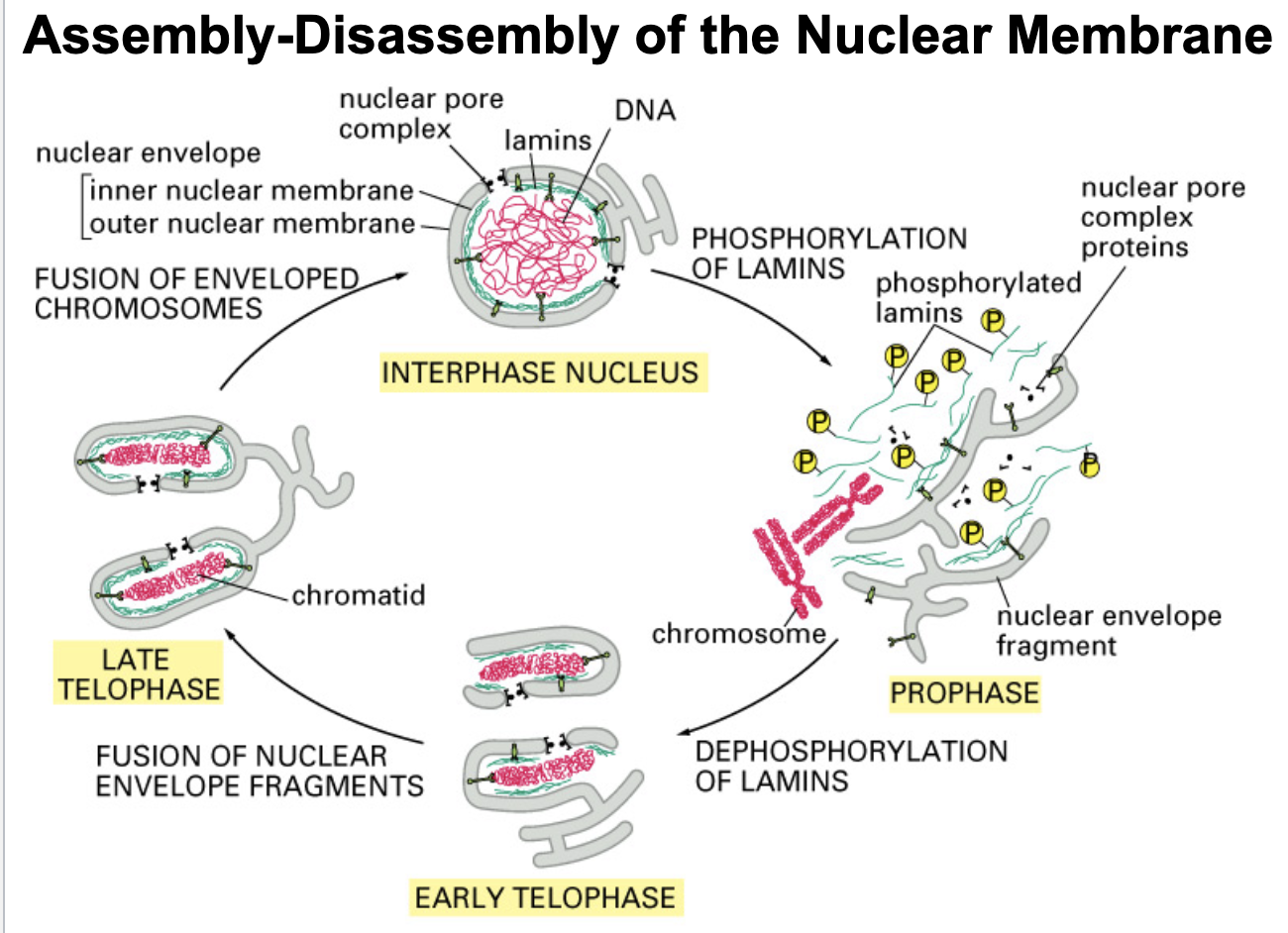
lamin phosphorylation
what allows/ initiates the condensation of chromosomes in preparation to replicate?
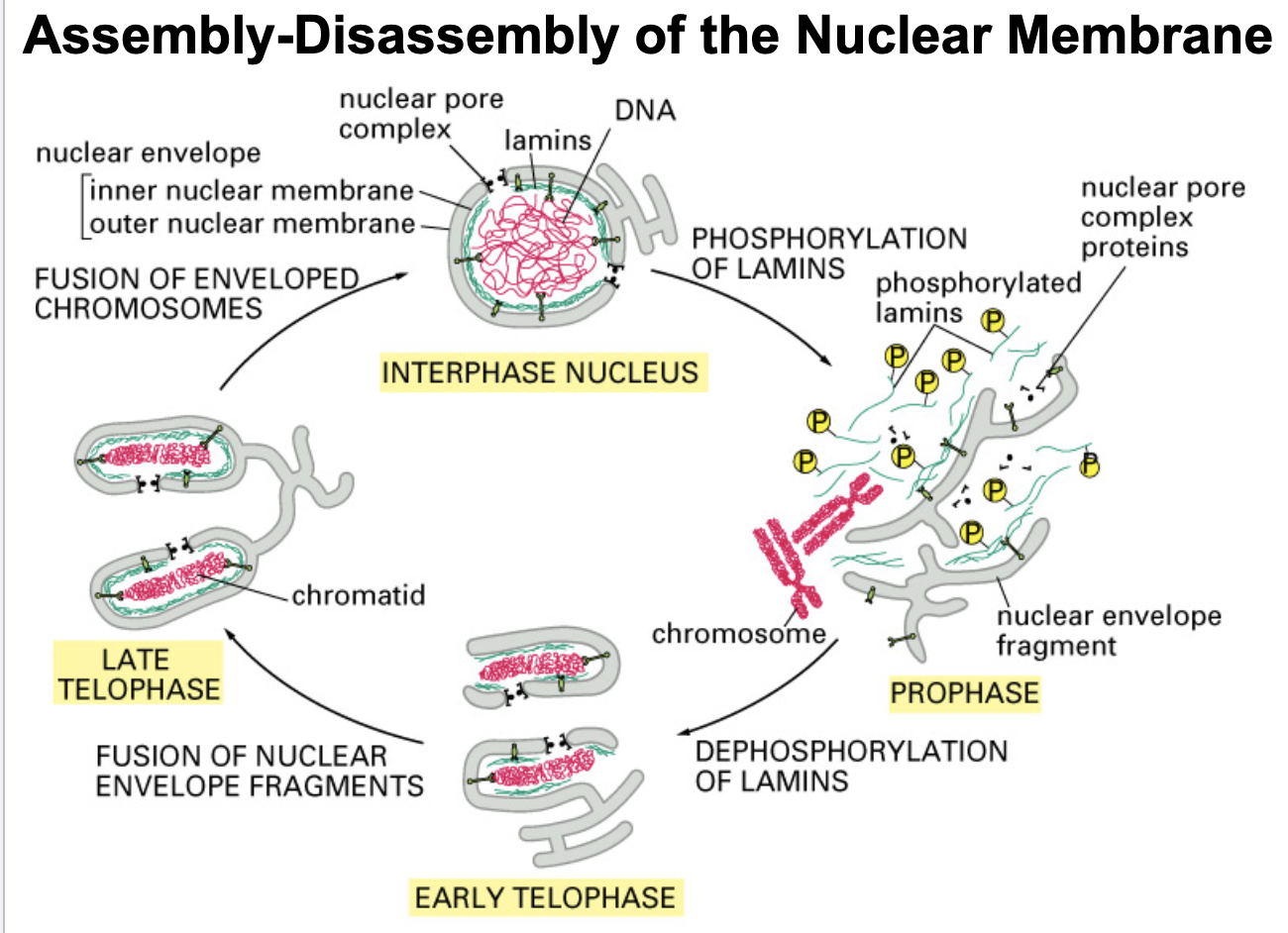
dephosphorylated
During interphase, when the nuclear envelope is intact, lamins are in the _________ state
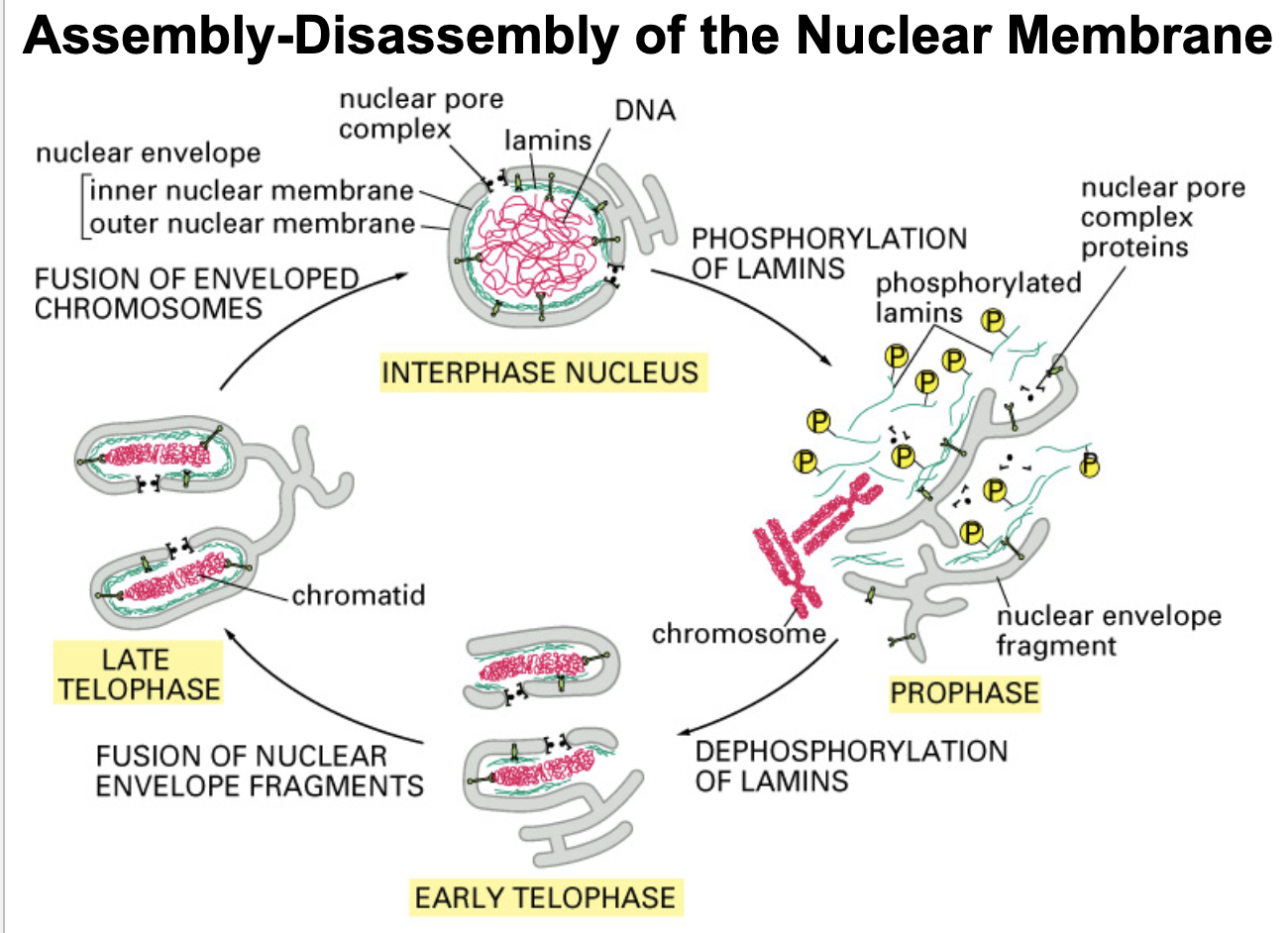
phosphorylated
Early in mitosis, lamins are ________ causing the chromatin-nuclear membrane connection to break, thus beginning the process of nuclear membrane disassembly
5-10
Cargo smaller than ____ kDa can enter nucleus via diffusion through nuclear pores
actively
Cargo smaller than 5-10 kDa can enter nucleus via diffusion through nuclear pores, but larger cargo must be _______ transported through nuclear pores
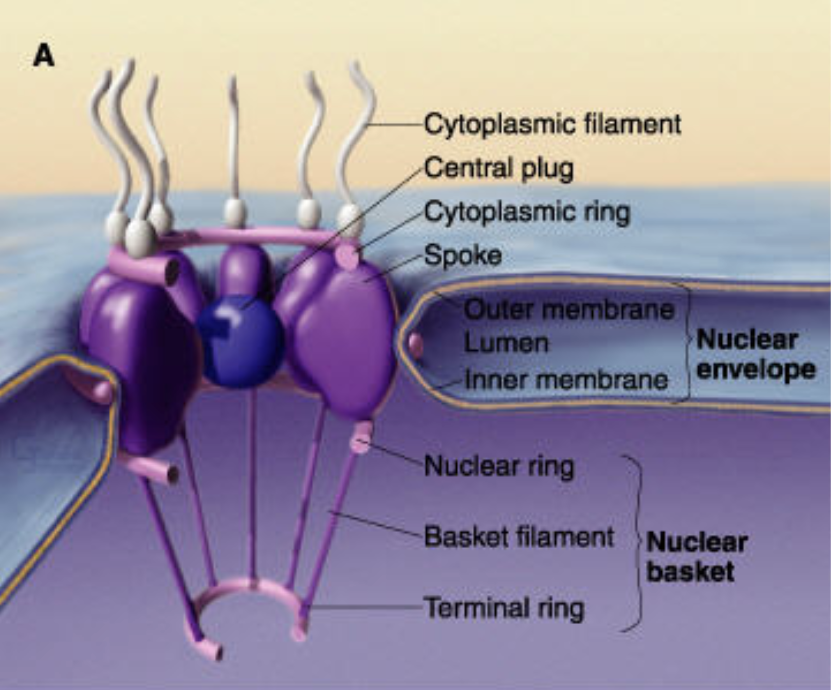
nuclear ring
which part of the nuclear pore opens/closes but can’t keep really small things out?
chaperone proteins that escort newly synthesized proteins with an NLS to the nuclear pore
what are importins?
nuclear localization signals (NLS)
Chaperone proteins bind to _______ on cargo and escort cargo into nuclear pore
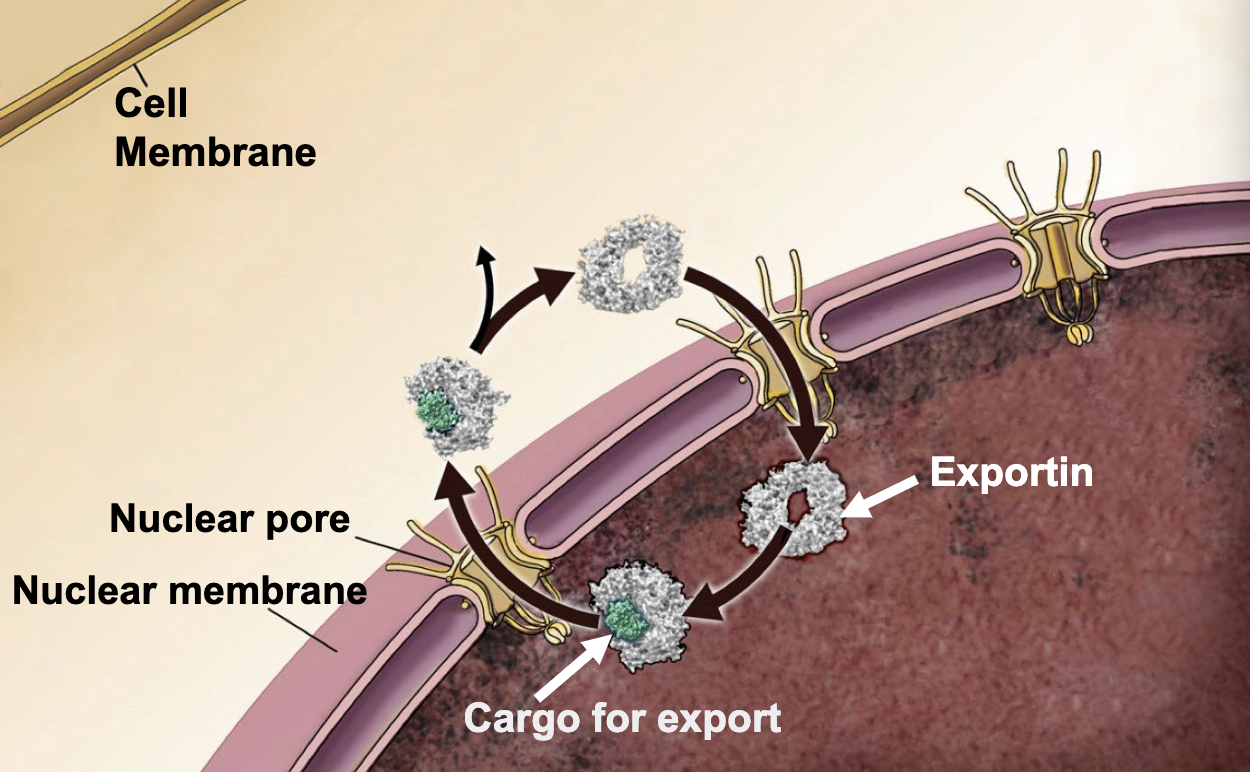
exportins
proteins and ribonucleo-protein complexes destined for export have Nuclear Export Signals that are recognized by _______
nuclear export signals (NES)
proteins and ribonucleo-protein complexes destined for export have __________ that are recognized by exportins
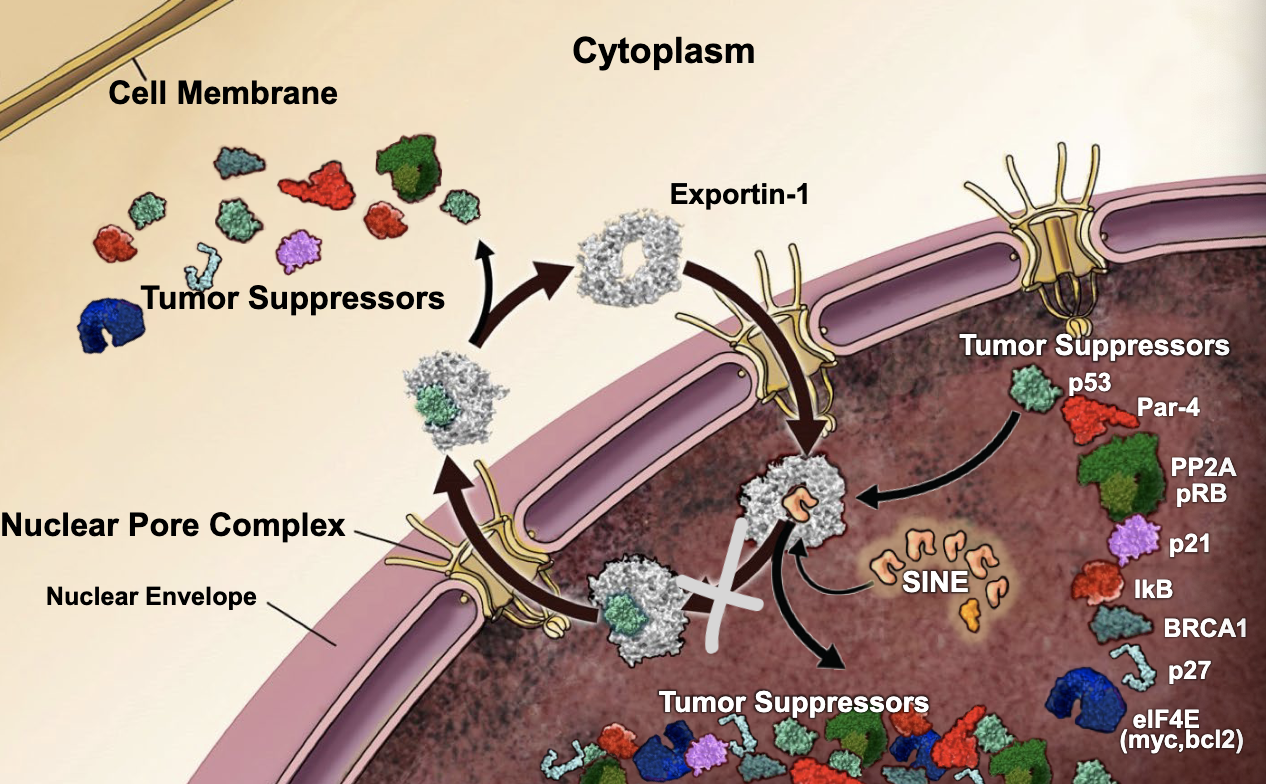
exportin-1
specializes in exporting tumor suppressors, apoptosis inducers, and anti-proliferative molecules that exert their normal biological activities via binding to DNA
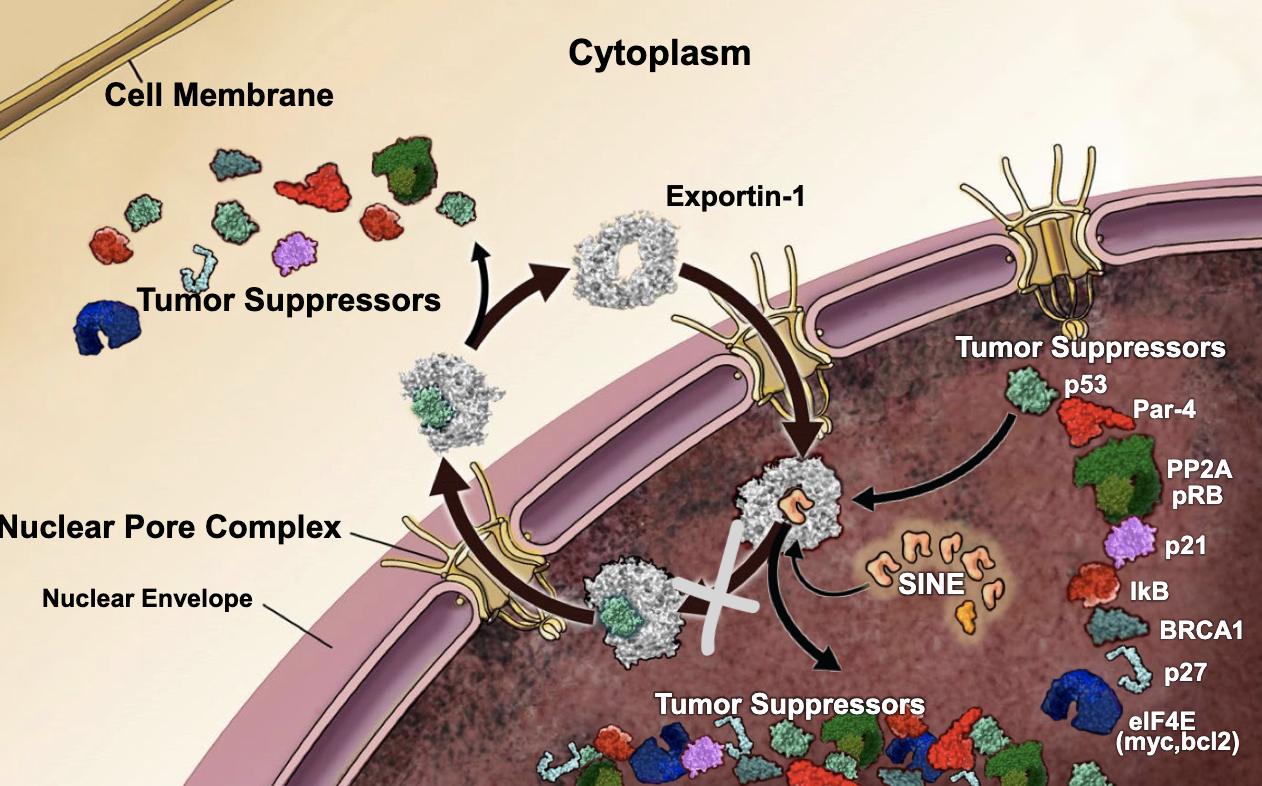
exportin-1
Cancer cells greatly over-express ________ resulting in a death of tumor suppressors, apoptosis inducers, and anti-proliferative molecules in the nucleus, which leads to excessive cell proliferation, ie, tumor growth
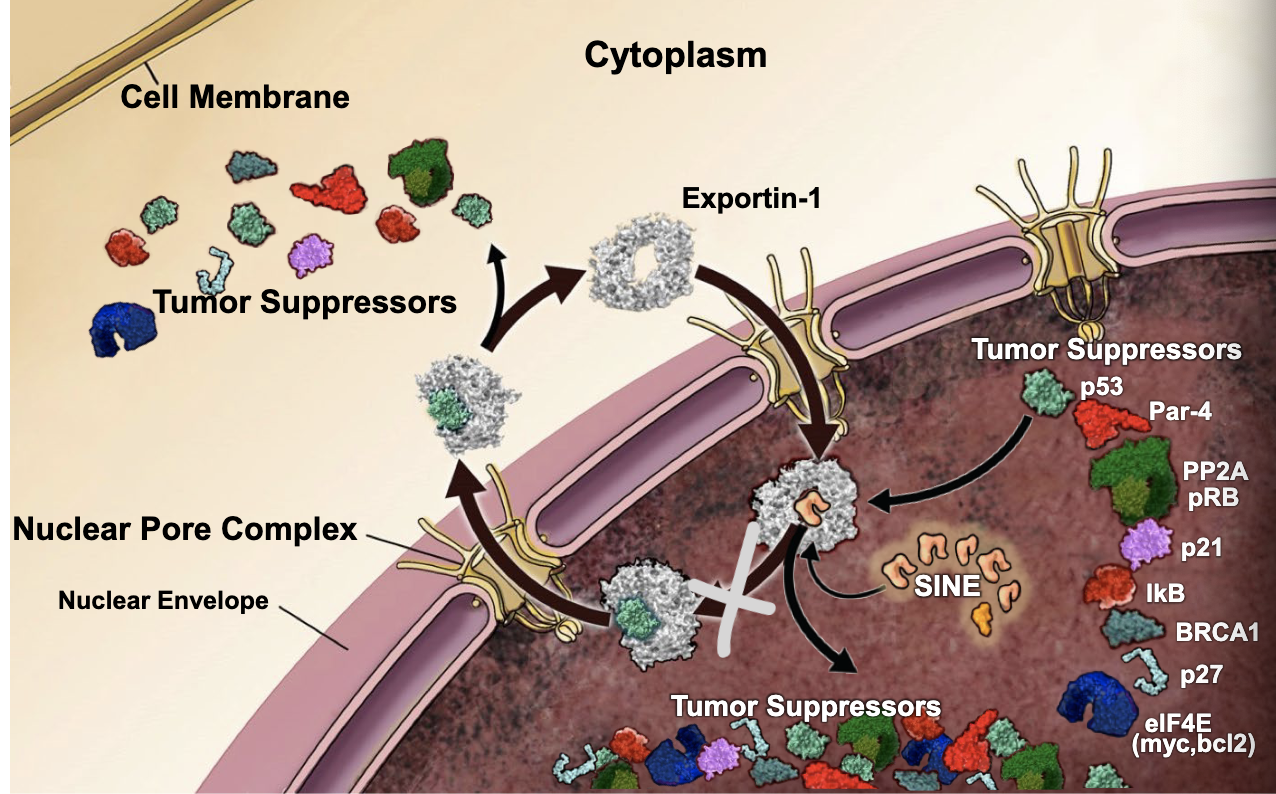
increase
by targeting the exportin-1 protein to decrease its presence in the nucleus, you should see an _________ in tumor suppressors within the nucleus
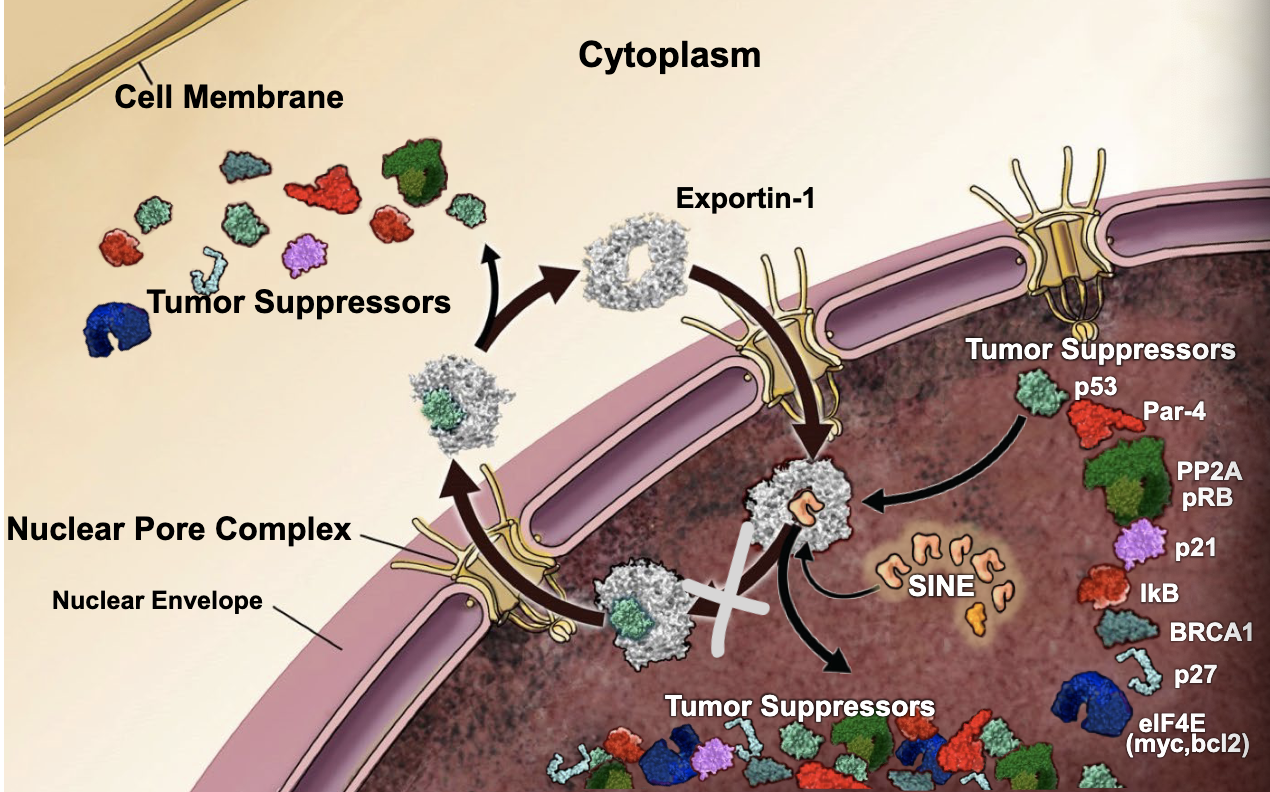
selective inhibitors of nuclear export (SINEs)
small molecules that block the pocket on exportin-1, thus keeping tumor suppressors in the nucleus:
laminopathy
what type of disease is Progeria?
nuclear import
Huntington's Disease is caused by what change in normal nuclear transport?
nuclear export
what nuclear function does SINEs (anti-cancer drugs) attack?
size
what feature of the Huntingin fragments allow them to bypass the nuclear import regulation?
- phosphorylation
- size
- sequence
Huntington's disease
this disease is caused by small fragments of miss-folded protein entering the nuclear pores due to their small size and negatively affecting the cells nucleus
glutamine
cytoplasmic protein Huntingtin is mutated via addition of multiple _________ residues
CAG
what AA sequence is found in mutated repeats in the Huntingtin gene?
Huntington's disease
during gene testing, a patient is found to have many trinucleotide CAG repeats in the HTT gene. This is a diagnostic characteristic of what disease?
nuclear lamina (flexible but strong)
forms a strong network beneath nuclear membrane and connects nuclear membrane to chromatin
3 proteins
the nuclear lamina is made up of