Anatomy year 1 semester 1
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Describe the anatomical position
Body erect; feet flat, facing forward; eyes facing forward; arms to the side, palms facing forward with thumbs pointing out.
body planes (5)
median
sagittal
coronal
transverse
oblique
main types of tissue (4)
connective
epithelial
muscle
nervous tissue
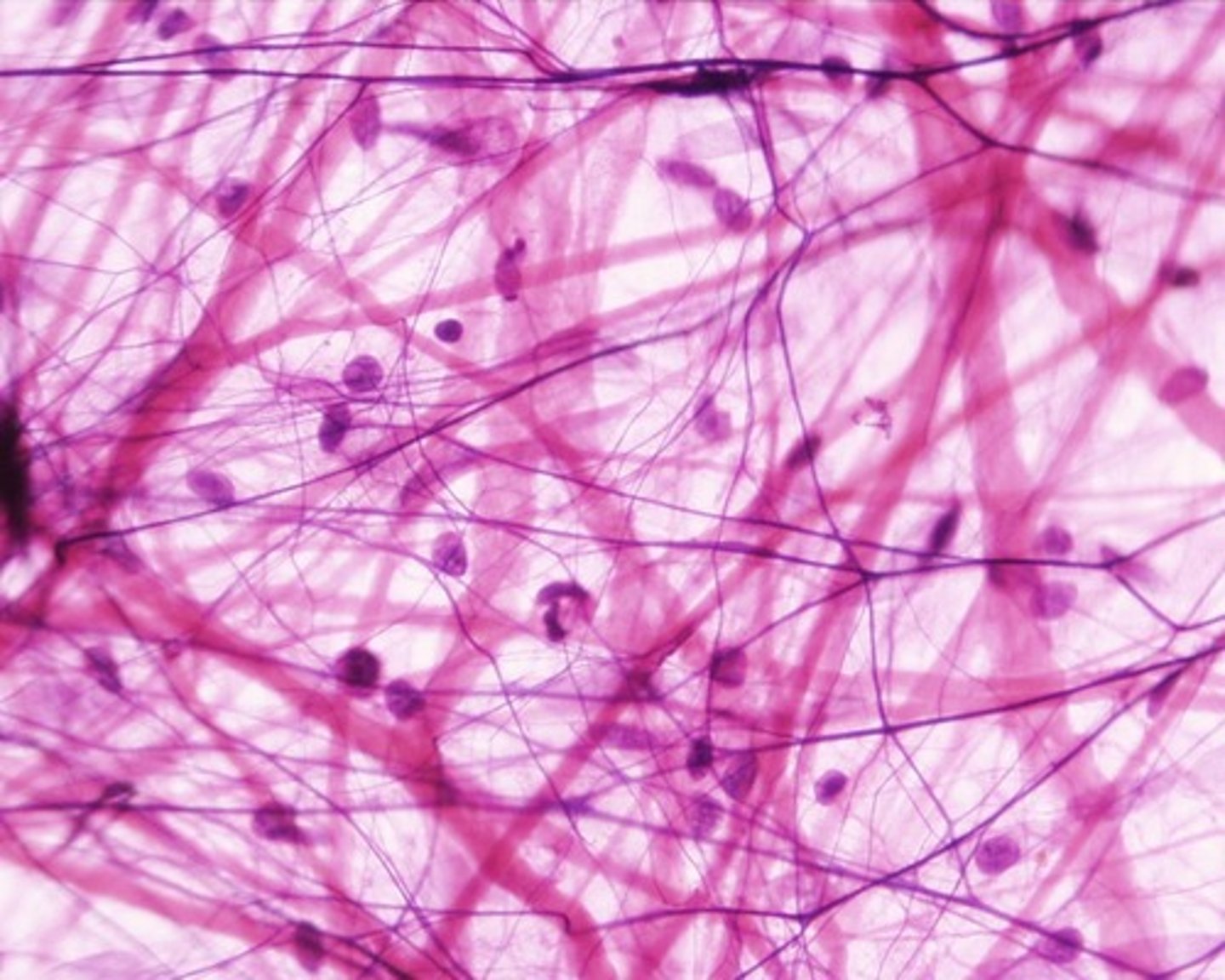
name and describe this tissue (general not type)
connective tissue
elastic fibres (purple defined lines)
collagen fibres
ground substance and tissue fluid
can be loose, dense regular or dense irregular
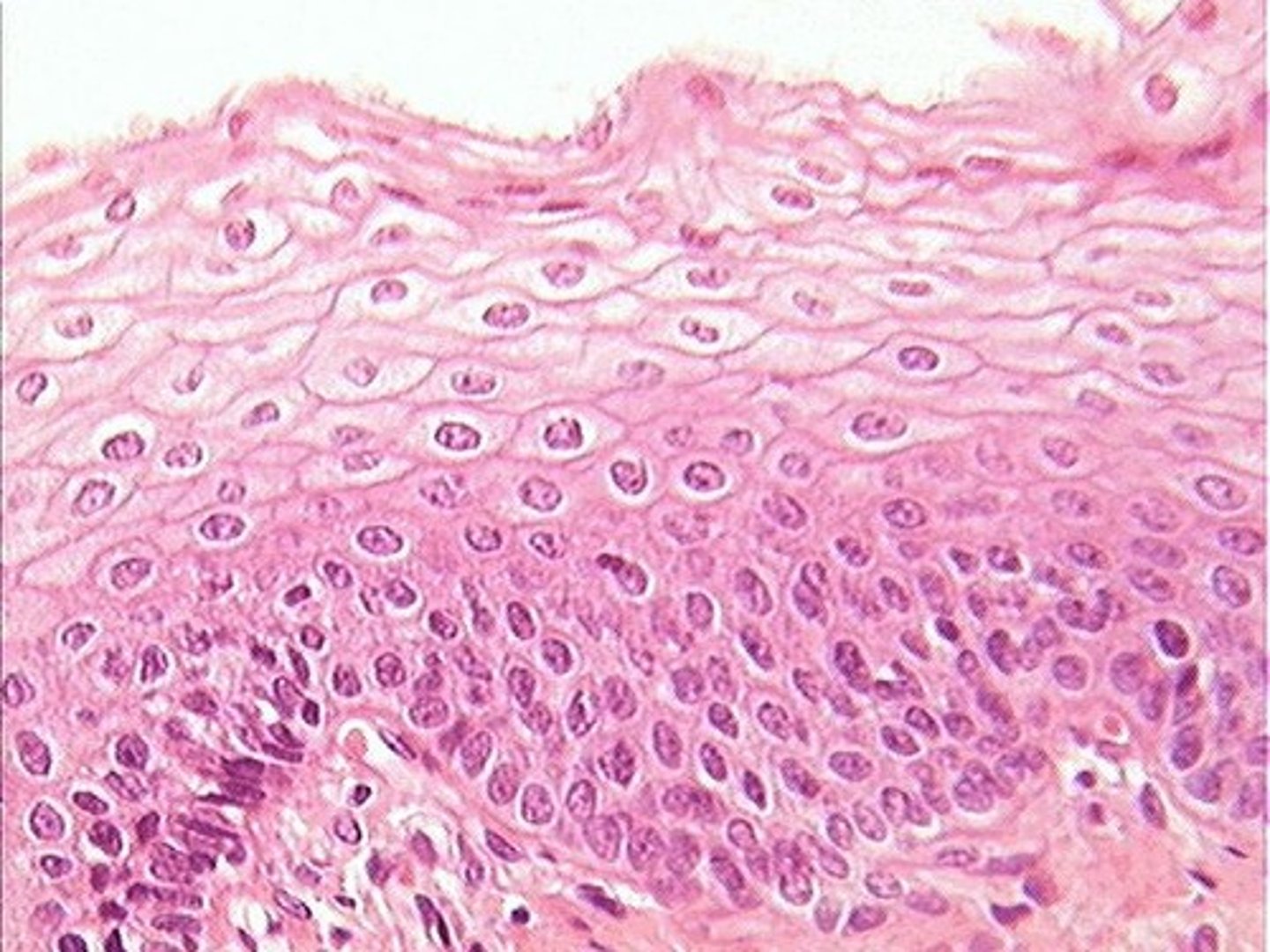
name and describe this tissue
epithelial
covers surfaces
simple, stratified or pseudostratified
cuboidal, squamous or columnar
name and describe this tissue (not specific type)
muscle
can be skeletal, smooth or cardiac
sometimes striated
contractile long thin cells
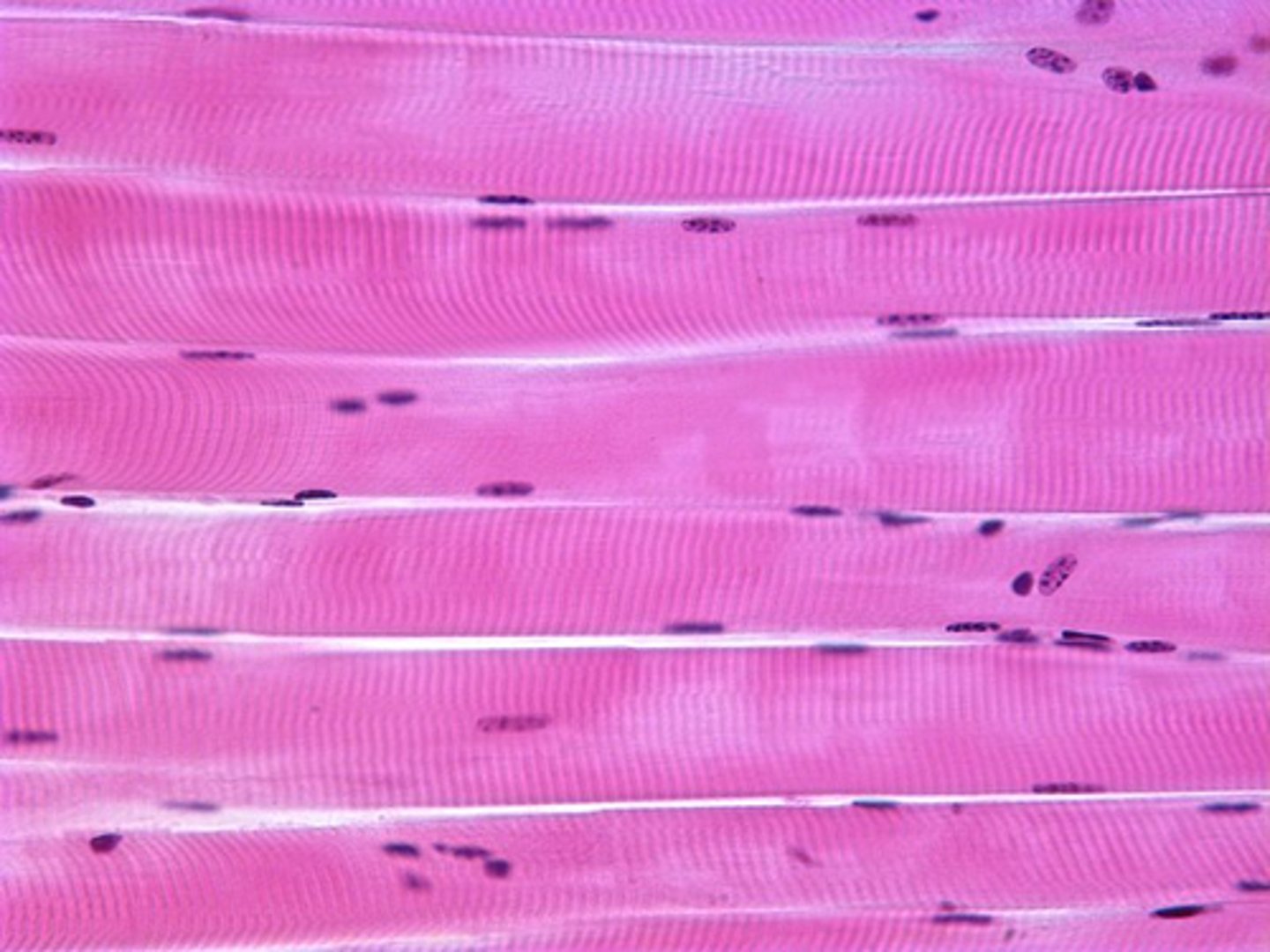
name and describe this tissue
skeletal muscle
long striated multinucleated and highly ordered
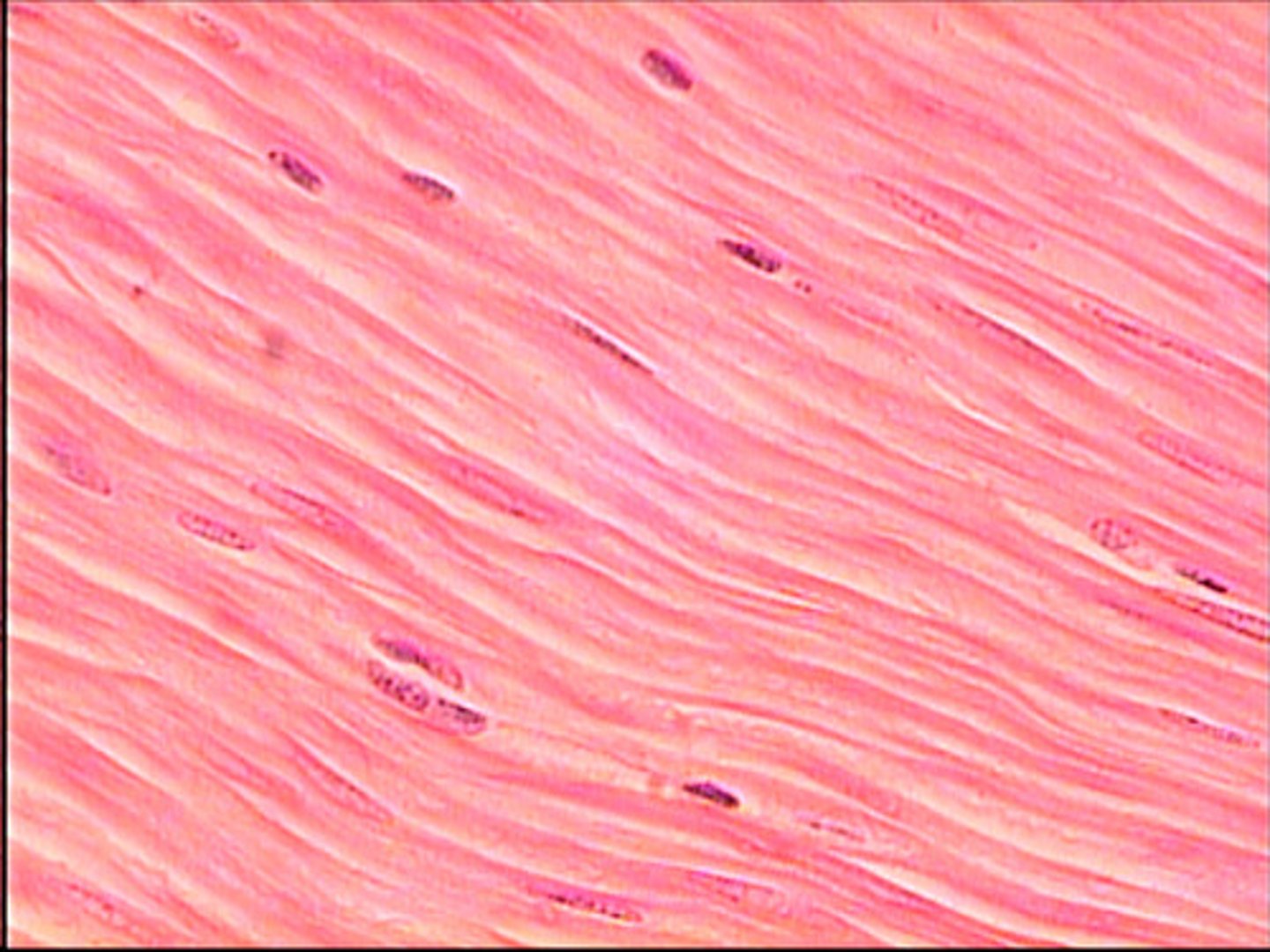
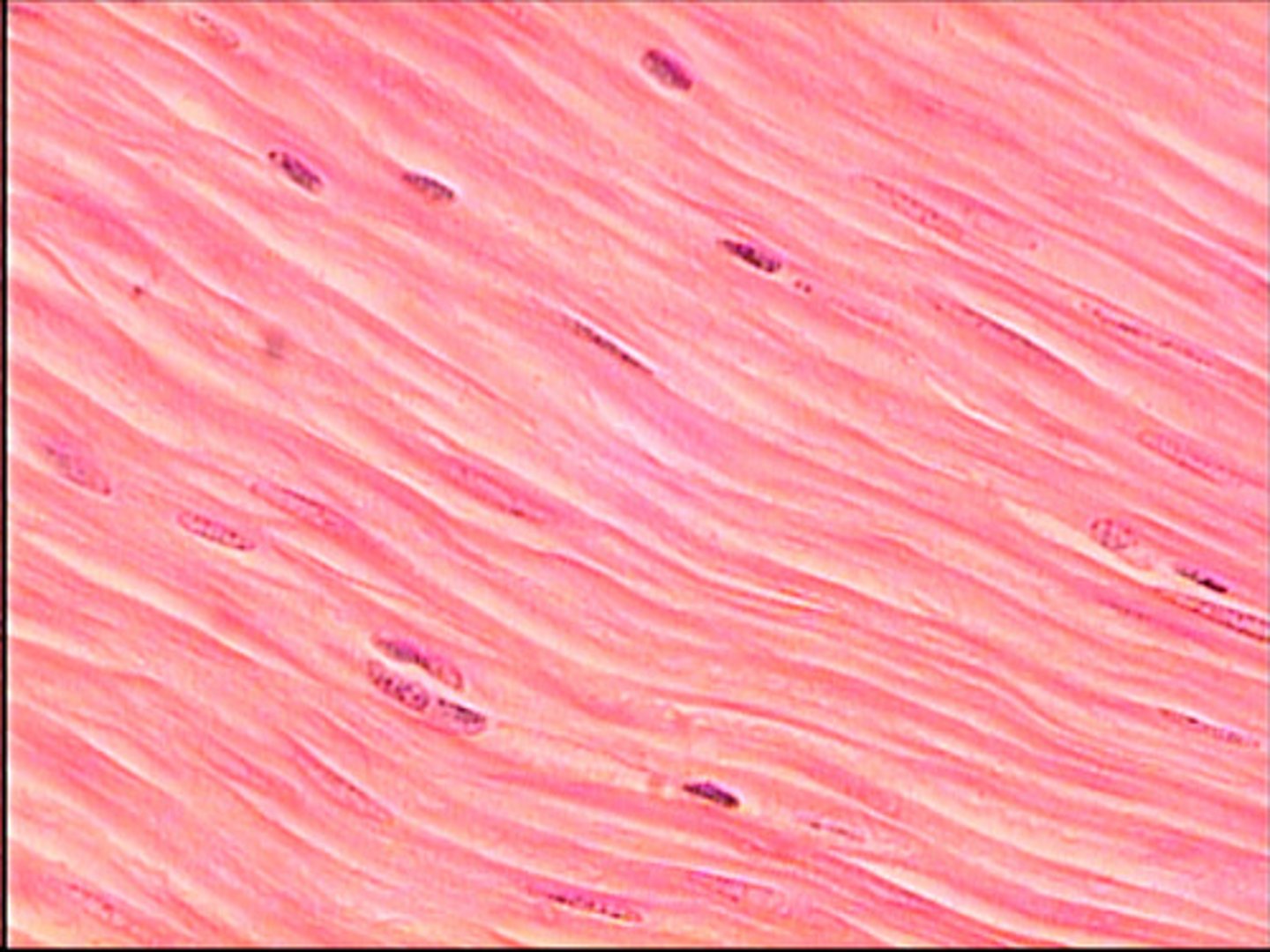
name and describe this tissue
smooth muscle
non striated randomly ordered
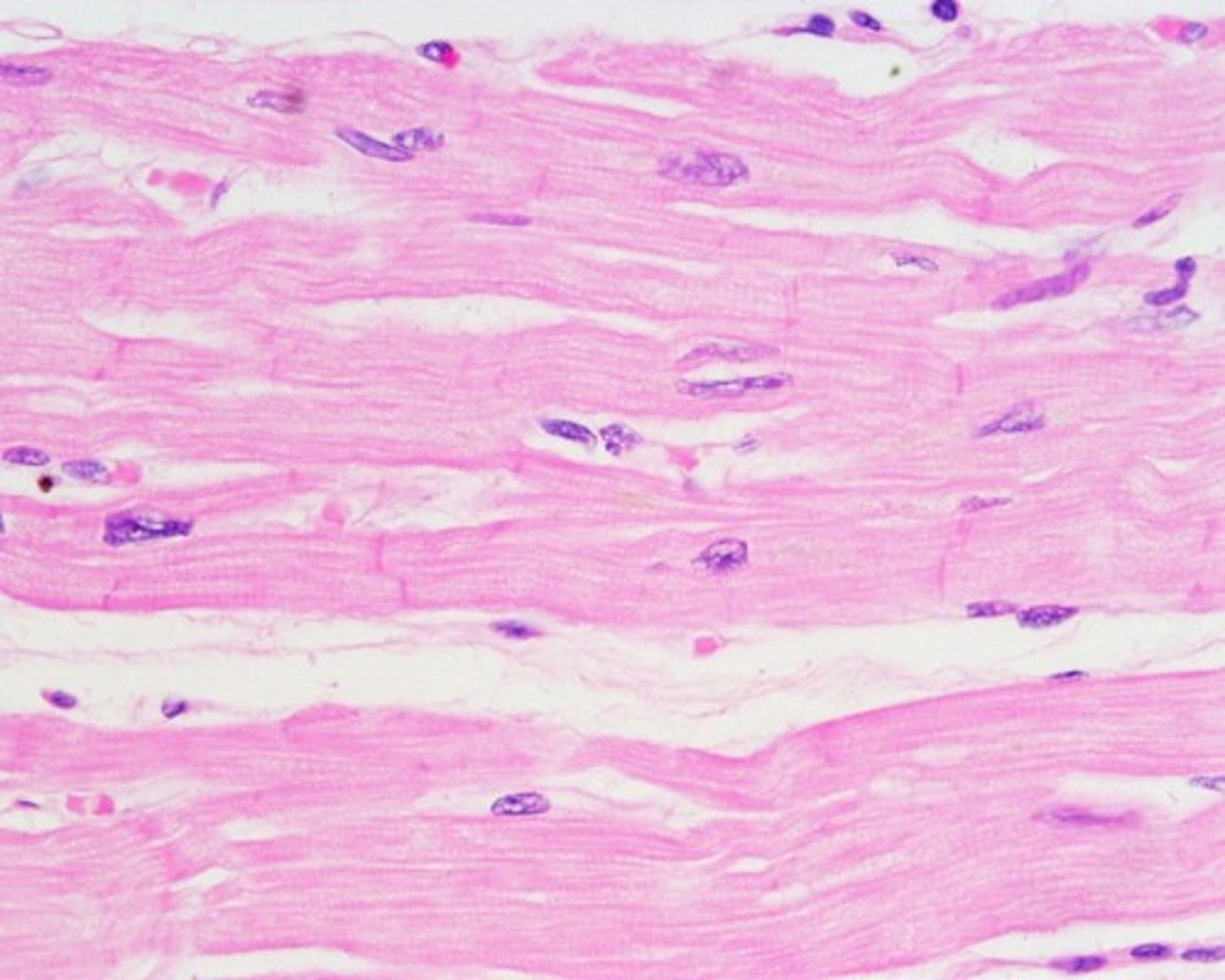
name and describe this tissue
cardiac muscle
striated and less ordered
intercalated discs
name and describe this tissue
nervous
has neurons and support cells involved in communication
What is an exocrine gland?
a gland that produces and secretes substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct e.g sweat
What are endocrine glands? (+ 5 example)
a gland that release into the blood stream
pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands
What is adipose tissue?
fat used for:
triglyceride storage
insulation
structural fill
shock absorbing padding
what abnormalities can occur in (ciliated) epithelia cells
Over-proliferation
Under-proliferation
Over-secretion
Under-secretion
Loose cilia
what abnormalities can occur in epithelial glands
growth hormone
in uterine tube mucous gland can become infected and block sperm/ egg causing infertility
what abnormalities can occur in connective tissue (4)
leukemia
abnormal fibres
cartilage tear
osteoporosis
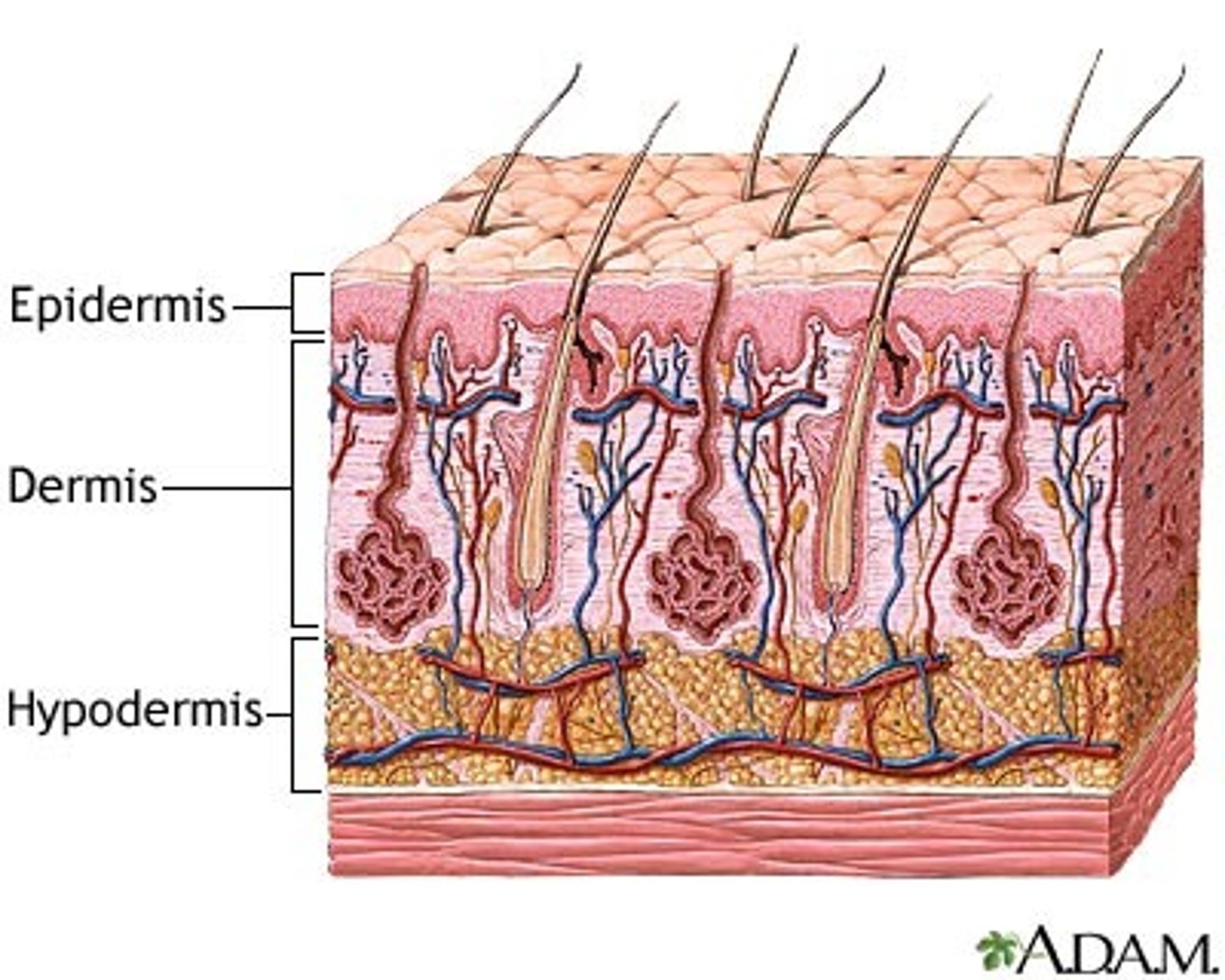
what is the structure of the skin
epidermis
-epithelium
-forms boundary between external and internal environment
dermis
- connective tissue
- gives structural strength
hypodermis
What are the layers of the epidermis?
stratum corneum,
stratum lucidum,
stratum granulosum,
stratum spinosum,
stratum Basale
what are the layers of the dermis
papillary layer
reticular layer
what is the sensory receptors of the Skin
Meissner's corpuscles - light touch (fingertips)
Pacinian corpuscle - vibration and pressure
pain and thermoreceptors
what is keratinisation
organic process where keratin is deposited in cells which then become hard such as dead skin cells and hair
what connective tissue is found in the dermis of the skin
papillary - loose connective
reticular - dense connective
what is the main type of connective tissue found in the hypodermis
loose connective tissue
Describe the arrector pili muscle
Smooth muscle attaching to base of hair follicle when contracting causes hair to stand up
what are the glands of the skin (3)
sebaceous (hair follicle)
apocrine sweat gland
eccrine sweat gland
what is the function of bones (4)
weight bearing
blood formation
mineral store
protection
what are the types of bone (6)
flat
sutural
short
long
sesamoid
irregular
Describe endochondral ossification
forms a cartilage model first
blood vessels then invade
cartilage then replaced with bone
Cartilage remains in epiphyseal plate
Describe intramembranous ossification (3)
no cartilage model
Mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into osteoprogenitor cells that mature into osteoblasts that start depositing bone
Residual mesenchymal cells develop into blood vessels and bone marrow
what is the composition of bone (5)
osteoblasts
osteoclasts
osteocytes
minerals (give strengthen and stiffness)
collagen (gives some flexibility)
what cells are responsible for bone remodelling
osteoclasts (bone reabsorbing cells)
osteoblasts (bones forming cells)
what are the 2 types of bone growth
appositional
interstitial
what are the 3 types of joints
fibrous (cranial structures)
cartilaginous (intervertebral discs)
synovial (knee joint)
what are the main features of a fibrous joint
dense fibrous connective tissue with little movement in adults
what are the main features of cartilaginous joints
Synchondronses (primary)
hyaline
endochondral ossification
temporary/permanent
Symphyses (secondary)
midline of body
hyaline and firbrous
what are the main features of a synovial joint
provide the greases movement
fluid filled capsule
may also have articular discs and ligaments
what created joint stability
shape of articulating surfaces
fibrous capsule and ligaments
muscles
describe blood and nerve supply of joints
have a rich blood and nerve supply
the nerve supplying a muscle crossing a joint also supplies the joint
what are tendons (4)
dense connective tissue
bone to muscle
does not shorten
can alter force direction
What is aponeurosis?
flat sheet of dense fibrous connective tissue, like tendon
wide area of attachement
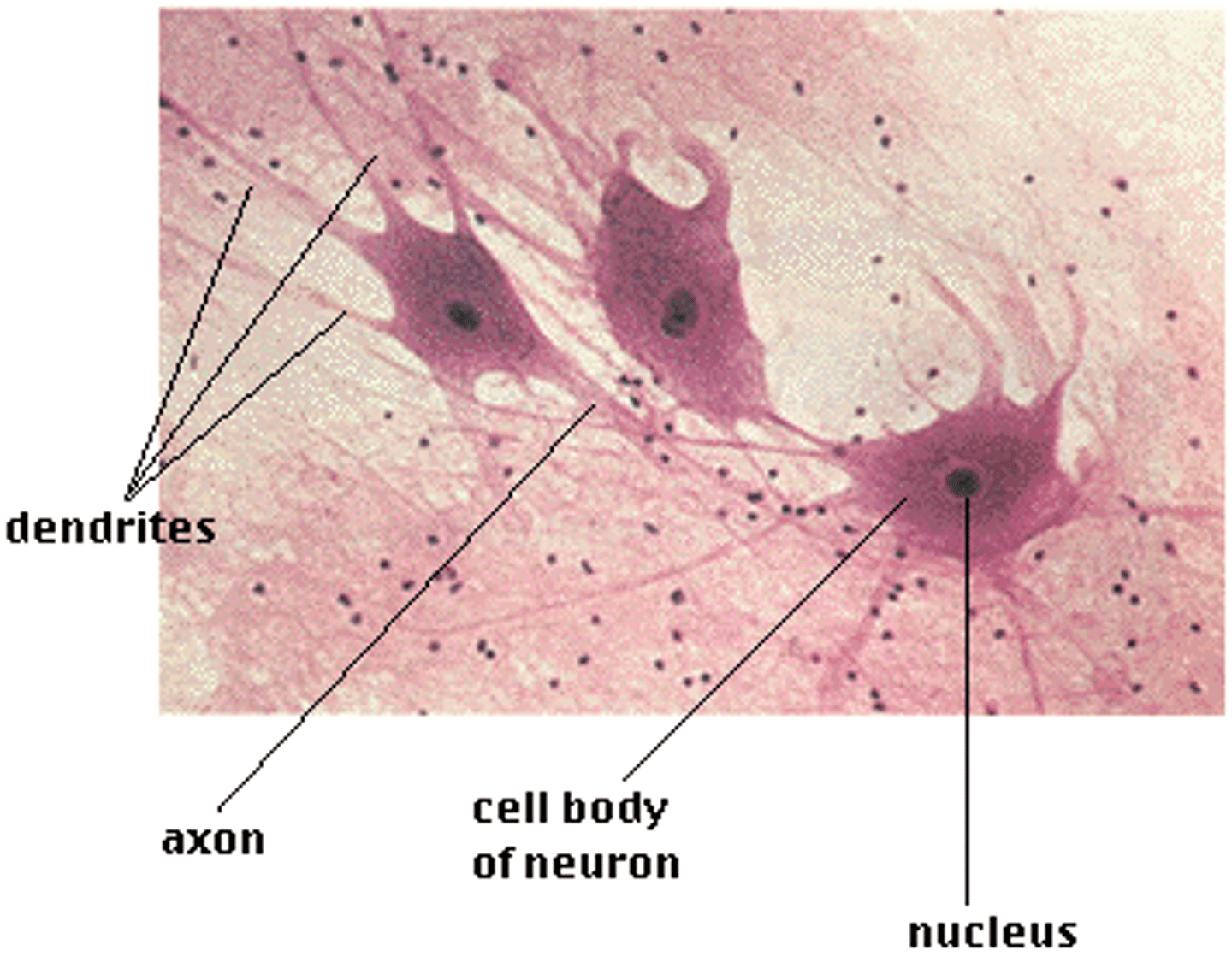
what is the structure of a neuron
cell body
dendrites
axon
terminales
describe spinal nerves (3 parts)
roots
- sensory or motor
Spinal Nerves
- sensory and motor
- exits through intervertebral foramen
rami
- sensory and motor
what are the main bones of the vertebral column
cervical
thoracic
lumbar
sacral
what joins two vertebrae together
intervertebral joint which is secondary cartilaginous
what joins the articular facets on the vertebral bodies and what type of joint is it
facet joints
synovial plane
what joint and type of joints join the ribs to the spine
costovertebral joints
synovial plane
what type of joint joins skull and atlas
Synovial ellipsoid
what type of joint joins atlas and axis
synovial pivot
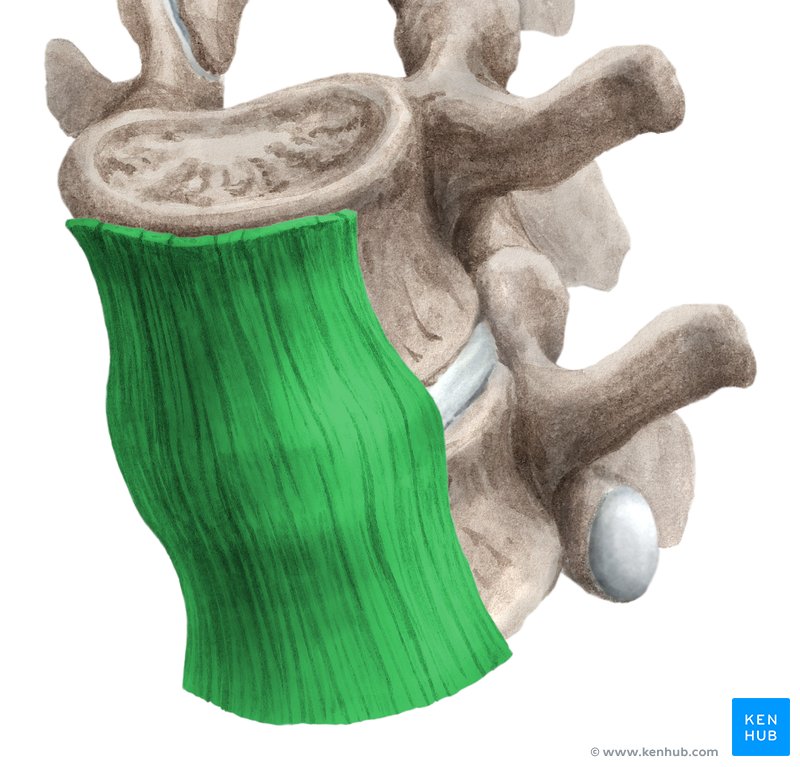
what ligament is this
anterior longitudinal ligament
what ligament prevents over flexion
posterior longitudinal ligament
what ligament if found at back of vertebral arch and in-between lamina
ligamentum flavum (pl flava)
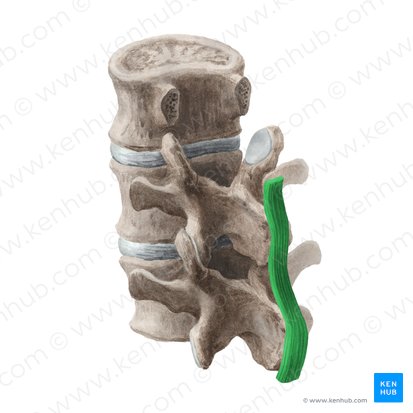
what ligament is this
supraspinous ligament
what ligament is found between the spines
interspinous ligament
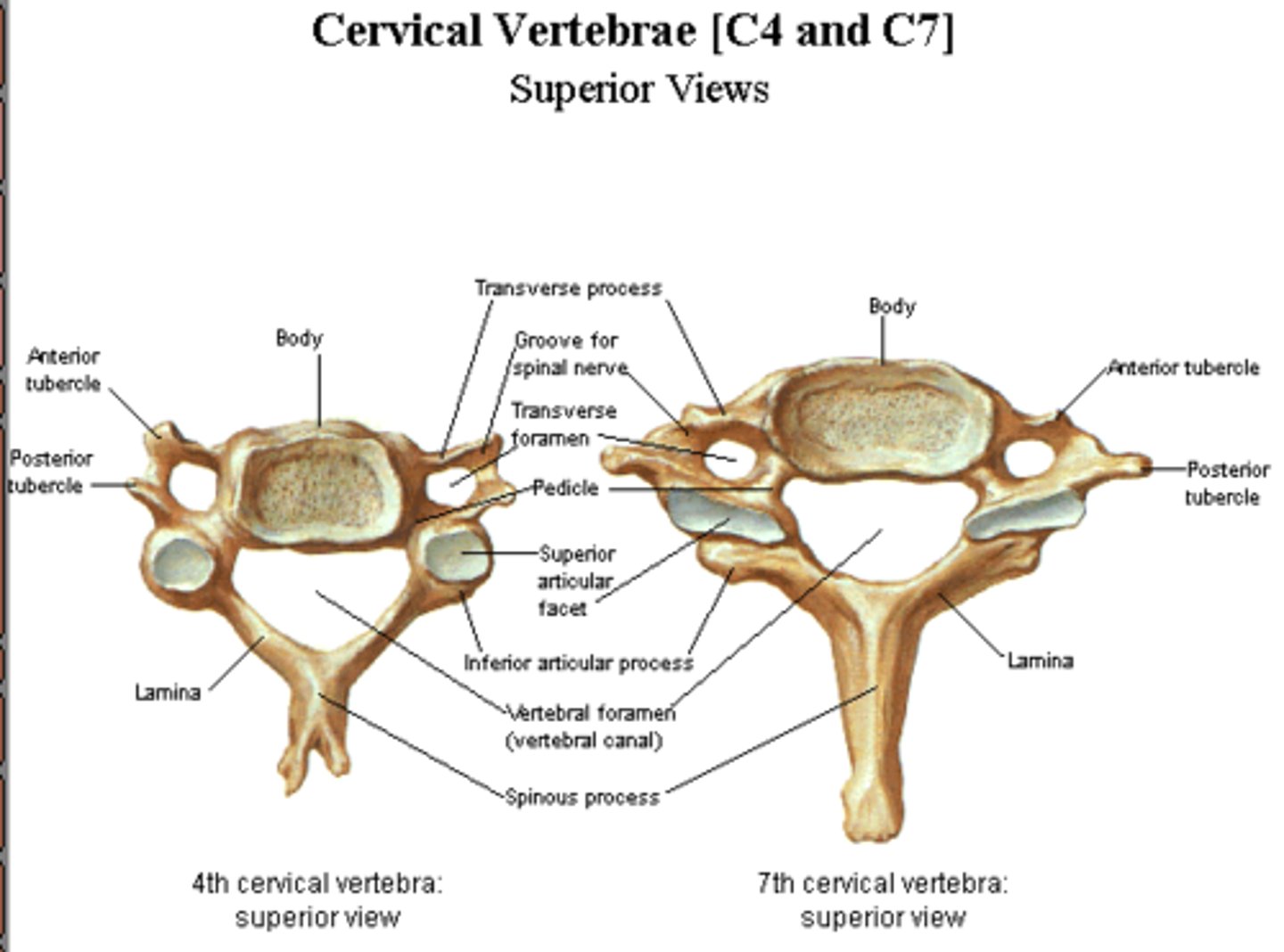
Describe the cervical vertebrae (4)
large triangular vertebral foramen
short bifid spinous process
small body
foramen transverseium
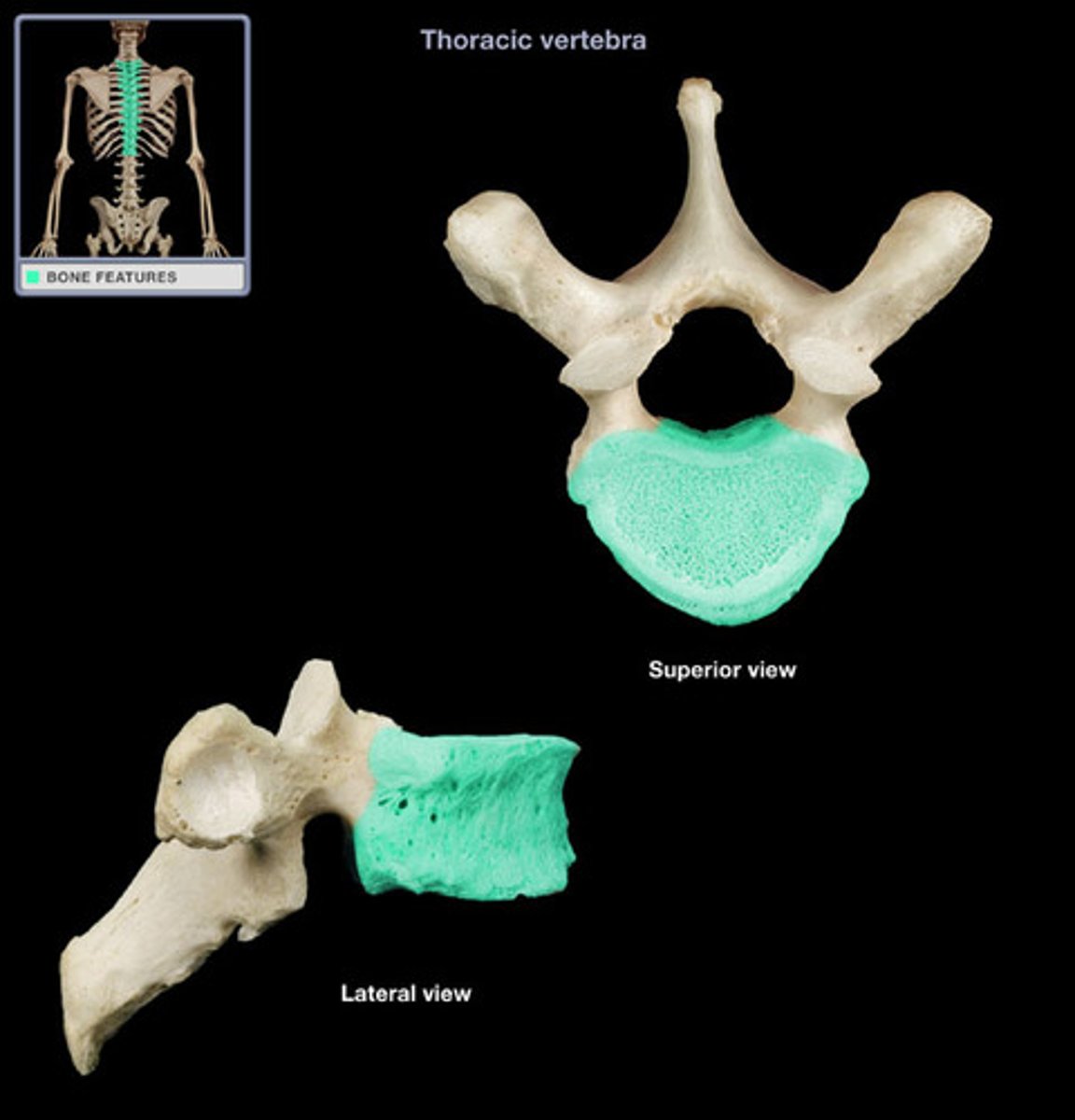
Describe the thoracic vertebrae (4)
has costal facets
small circular vertebral foramen
long spinous process that slopes posteriorly
heart shaped body
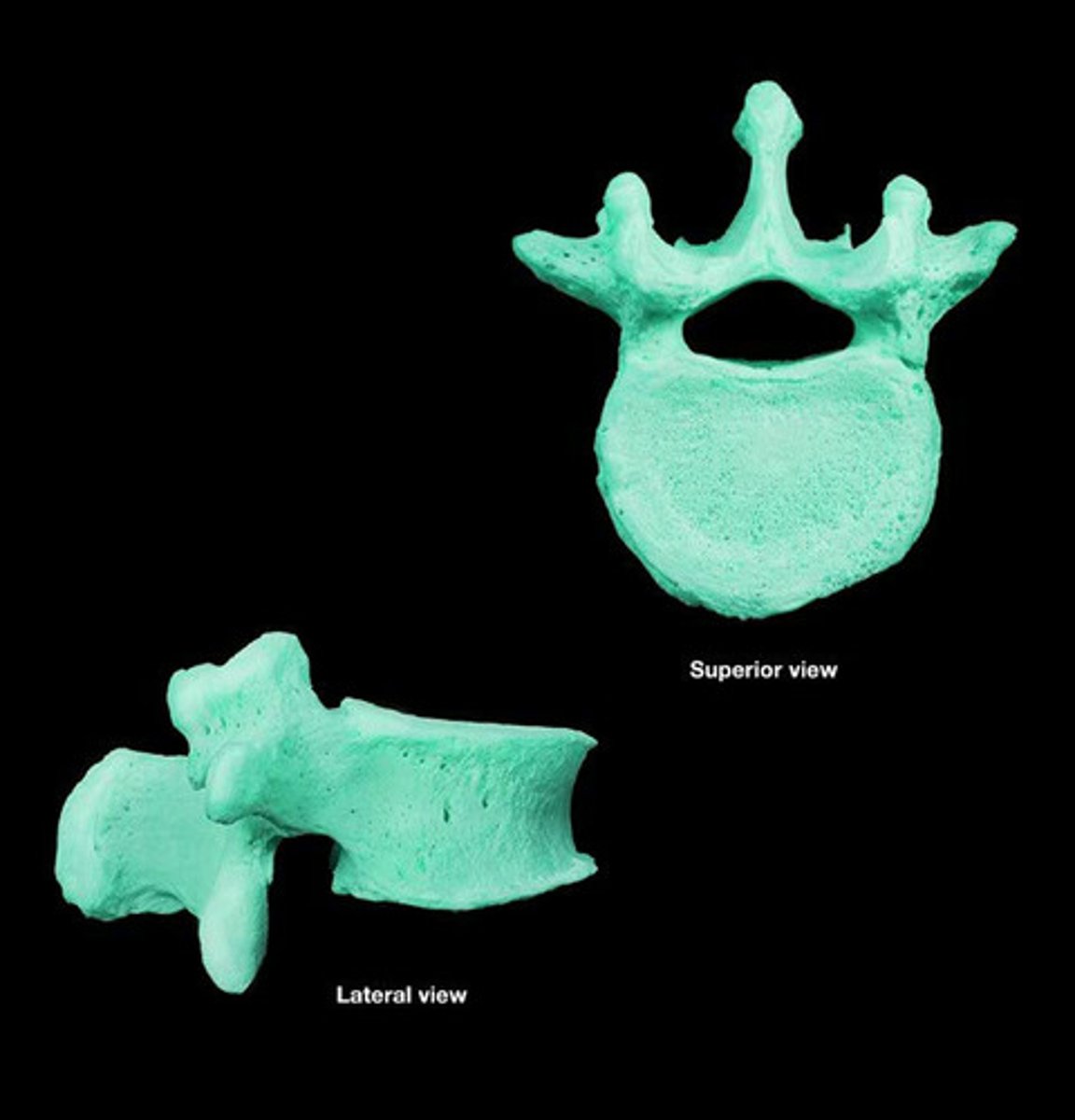
Describe the lumbar vertebrae
mamillary and accessory process
small triangular vertebral foramen
short sturdy rectangular spinous process
large kidney shaped body
what makes up intervertebral discs
nucleus pulposus
- central core with high water content
annulus fibrosus
-layers of cartilage surrounding the core
what are the two main back muscle groups
extrinsic and intrinsic
which two muscles are responsible for bilateral flexion of the back
rectus abdominus and psaos major
what is responsible for bilateral extension of the back
erector spinae
what muscles are responsible for rotation of back
internal and external oblique
erector spinae
what muscles are responsible for lateral flexion of back
internal, external oblique and erector spinae
same as lateral rotation
What is the conus medullaris?
conical inferior end of spinal cord
emerges into Cauda equina
What is the cauda equina?
bundle of spinal nerve roots in the lumbar cistern
What is the filum terminale?
longitudinal support to spinal cord
continuation of pia matter
what is the dural cistern
dilated dural sac
ends at S2
describe sympathetic outflow
thoracolumbar
T1-L2
cell bodies located at lateral horn of grey matter
describe parasympathetic outflow
craniosacral
cranial outflow from the brain
sacral outflow from pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2-S4)
describe a spinal cord injury
blunt trauma or penetrating injury
cord compression from disc prolapse bone metastases
complete or partial loss of motor and sensory function
what is spinal cord ischemia
deficiency of blood supply to spinal cord
leads to muscle weakness and paralysis
what type of nerves are found in different parts of spine
dorsal root=
ventral root=
spinal nerve=
Dorsal rami=
ventral rami=
lateral horn=
sensory
motor
mixed
mixed
mixed
autonomic
what is the propose of spinal meninges
protects CNS
what are the coverings of the spinal cord
Dura matter
Arachnoid matter
Pia matter
Where is cerebrospinal fluid found?
subarachnoid space
describe the Dural sac
terminates at S2
attached to tip of Coccyx by filum terminale
what are the curvatures of the spine and when are they developed
thoracic and sacral are primary, already present in fetus
cervical and lumbar are secondary, developed during infancy
what type of neurons does the lateral horn have
sympathetic neurons
describe part 1 of sympathetic chain
sympathetic fibres originate in the lateral horns between spinal levels T1-L2
describe part 2 of sympathetic chain
travels in the ventral root of the spinal nerve to the mixed spinal nerve
describe part 3 of sympathetic chain
leaves the mixed spinal nerve via white ramus communicans as preganglionic fibres to enter the sympathetic ganglion at same vertebral level
describe part 4 of sympathetic chain
After synapsing in the sympathetic chain ganglion, they re-enter the spinal nerve via GREY RAMUS COMMUNICANS as POST ganglionic fibres and are distributed in both dorsal and ventral rami of the spinal nerve
describe part 5 of sympathetic trunk
rami then go on to supply skin and body wall structures such as arrector pili muscles, blood vessels and glands at that dermatome with sympathetic input