IB Physics - Kinematics & Work, Energy, and Power
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Distance
Total length of the path traveled by an object
Scalar
(m)
Displacement
Final position - initial position
Vector
(m)
Vector
Magnitude + Direction
Scalar
Magnitude
Speed
How fast the distance of an object is changing
Scalar
(m/s)
Velocity
How fast and in which direction the distance of an object in changing
Vector
(m/s)
Average Speed Formula
total distance / total time
Average Velocity Formula
total displacement / total time
Acceleration
How fast the velocity of an object is changing
Vector
(m/s²)
When the acceleration and velocity have the same sign (+ or -), the object is
Speeding up
When the acceleration and velocity have different signs (+ and -), the object is
Slowing down
Newton’s 1st Law / Law of Inertia
An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in the same motion, unless acted upon an unbalanced force
Newton’s 2nd Law
F=ma
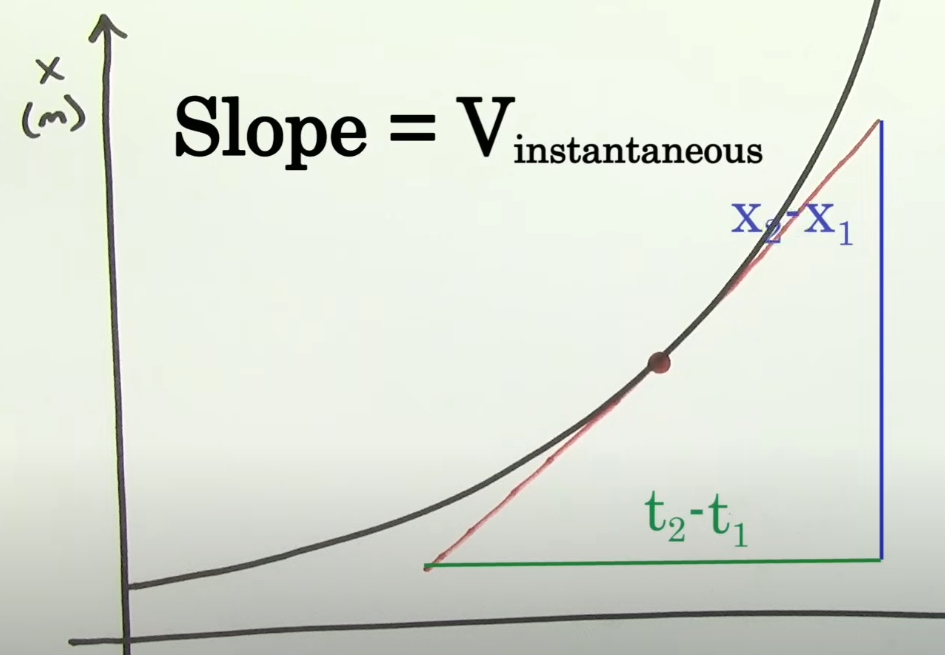
Instantaneous Speed/Velocity
The speed/velocity at a particular point in time
Instantaneous Velocity is equal to the
The slope of a point on a position v. time graph
Unit of Work
Joules (J) / kg⋅(m/s)²
Work is equal to the
change of kinetic energy
When the speed of an object is slowing down
Work is negative
When the speed of an object is speeding up
Work is positive
Mechanical Energy
Kinetic + Potential Energy
Power
Rate of which work is done
Rate of which energy is transferred
Work / Time
Units of Power
Joules / Seconds
Watts
Conservation of Potential and Kinematic Energy
Ke1 + Pe1 = Ke2 + Pe2
Internal Energy of a Real Gas
Sum of kinetic and potential energy of molecules