MedChem
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
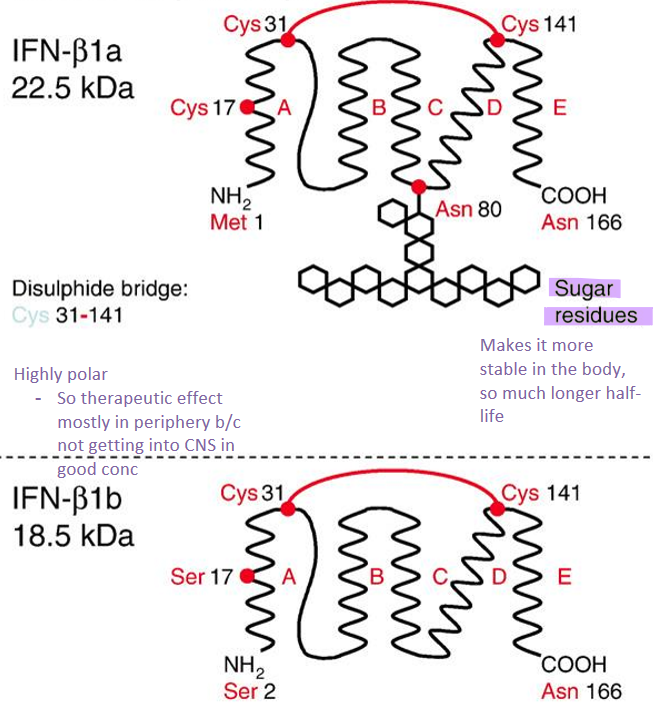
What are the differences between IFN-1a and IFN 1b?
IFN-1a
glycosylated at Asn 80→ more stable in body and longer half-life
166 amino acids
IFN-1b
nonglycosylated
165 amino acids
similarities
disulphide bridge Cys 31-141
highly polar, so mostly in periphery
What is glatiramer acetate?
synthetic polypeptide
Alanine, glutamate, lysine and tyrosine
acts in periphery
cannot give orally → amide bonds undergo degradation in the gut
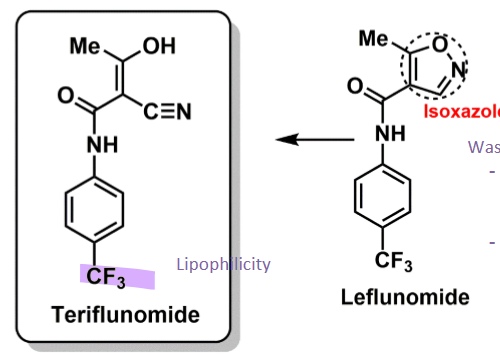
Teriflunomide
How does teriflunomide work?
is active metabolite of leflunomide (prodrug) used in RA
had isoxazole ring that undergoes degradation by 1A2
in MS use just the active metabolite
triflouro increases lipophilicity → act in CNS and periphery
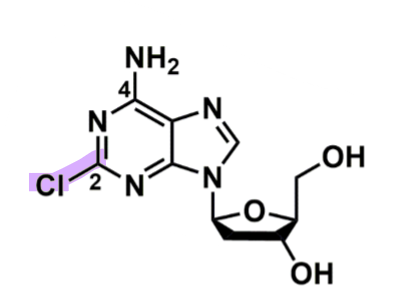
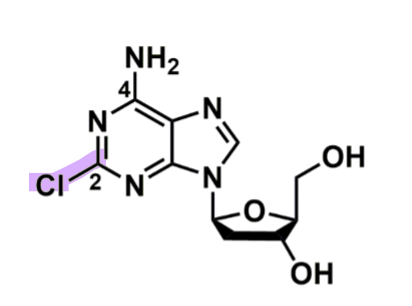
Cladribine
How does cladribine work?
pharmacophore: Purine + pentose (5 member sugar)
Cl @C2 → stable for oral route
w/o or change to amine or alkyl group lose that
could change to Br
prodrug → cladribine triphosphate
via deoxycytidine kinase adds 3 phosphate groups (in periphery or CNS)
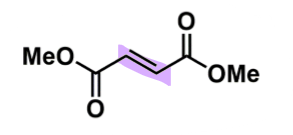
Dimethyl fumarate
How does dimethyl fumarate work?
consider prodrug (parent some activity) → monomethyl fumarate
when only 1 ester undergoes hydrolysis
needs to be an unsaturated ester with trans geometry
double bond = light sensitive
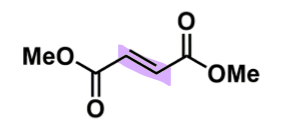
Why can dimethyl fumarate not be combined with alcohol?
ester can under degradation and become ethylester (Me → Et)
activity decreases
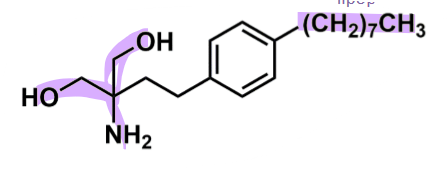
Fingolimod
How does fingolimod work?
amino alcohol derivative
amphiphilic molecule → good into CNS
long lipophilic tail
propene dialcohol polar head
very potent > affinity vs natural substrate
prodrug → fingolimod-phosphate
attaches monophosphate by sphingosine kinase
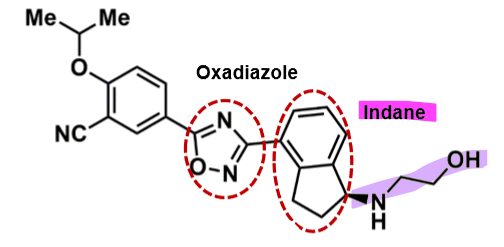
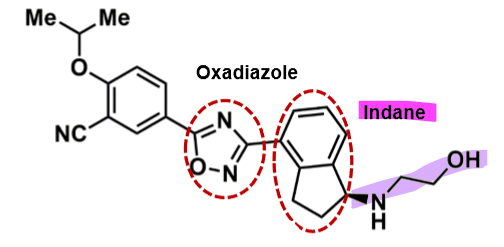
Ozanimod
How does ozanimod work?
pharmacophore: indane +oxadiazole
amphiphilic molecule → good into CNS
aminoethanol polar group
ethoepxy phenol lipophilic group
more potent than fingolimod
less cytotoxic profile b/c more selective to receptor
active metabolites + active parent
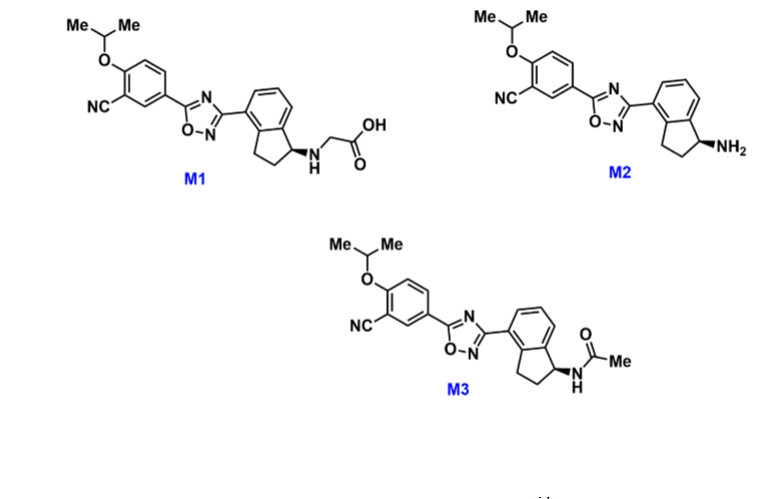
What are the ozanimod metabolites?
*metabolites from rapid first pass effect by 3A4 and other alcohol related enzymes
M1 → alcohol convert to acid
M2 → alcohol degraded to primary amine
M3 → alcohol converted to methyl ketone
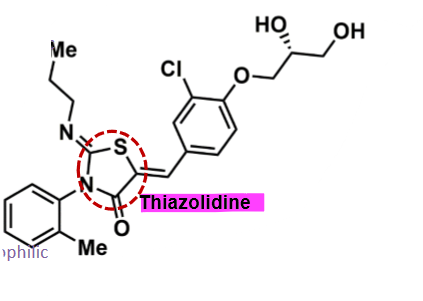
Ponesimod
How does ponesimod work?
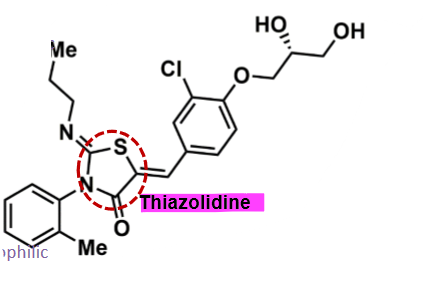
pharmacophore: thiazolidine
amphiphilic molecule → good into CNS
polar alcohol functional groups
2 lipophilic groups - aminopropyl and methylbenzene
more potent than fingolimod, and less potent than ozanimod