CIV250 - Hydraulics and Hydrology | Weeks 1-3
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Hydrology
Study of water in its different forms
Hydraulics
Study of liquid movement
Hydrologic systen
A set of interacting parts that take in water and other inputs, processes them internally, and then produces outputs.
Water Cycle
Evaporation, Evapotranspiration, Sublimation, Condensation, Precipitation, Infiltration, Runoff
Watershed
Area of land that drains to the same lowest hydrographic feature, separated from other watersheds by a watershed divide or surface divide
Open Watershed
Flow exits through an outlet
Closed Watershed
Flow within boundaries of a watershed
Watershed Characteristics
Area, slope, shape, soil type, land use
Lumped
Averaged as a single spatial unit where flow is a function of time.
Distributed
Various points in space where flow is a function of space and time.
Unsteady
Changes with time
Steady
No change with time
Event Based
Single event
Continuous
Multiple events
Deterministic
Same input always results in a consistent output
Stochastic
Model includes some random component
Frontal Air Mass
Warm air is lifted over cooler air by frontal passage
Orographic Air Mass
Air mass rises to pass over a mountain range
Convective
Air is drawn upwards by surface heating
Conditions for Precipitation
i) satruated atmosphere
ii) small particles for condensation/sublimation
iii) water coalesce enough to fall
Drizzle
Diameter < 0.5 mm, intensity < 1 mm/hr
Rain
Diameter > 0.5 mm
Sleet
Small frozen raindrops
Snow
Ice crystals formed by sublimation
Hail
Ice particles, from thunderstorms with strong upward wind
Atmospheric Circulation
Process where the atmosphere functions as a vast heat engine, transferring energy from the equator toward the poles
Circulation Cells
Hadley Cell, Ferrel Cell, Polar Cell
Areal Measurement
The process of quantifying the area of a specific region, often used in hydrology to assess watershed characteristics
Microwave Sensors
Detect microwave radiation reflected by precipitation particles
Infrared Sensors
Detect the temperature of cloud tops
Visible and Near-Infrared Sensors
Observe cloud cover, identify cloud types, and estimate cloud motion
Precipitation Intensity
depth/time
Precipitation Hyetograph
depth/intensity over time
Precipitation Mass Curve
Cumulative precipitation hyetograph
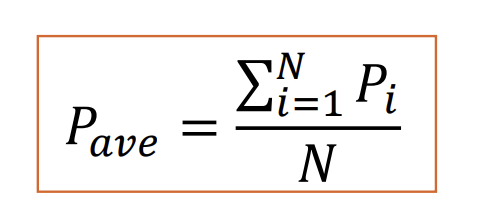
Arithmetic Mean
Method that takes the average of the precipitation gages
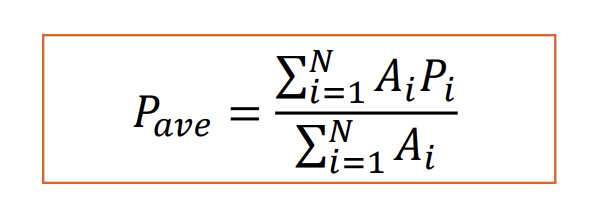
Thiessen Polygons
Method that takes the average of the precipitation gages weighted by area
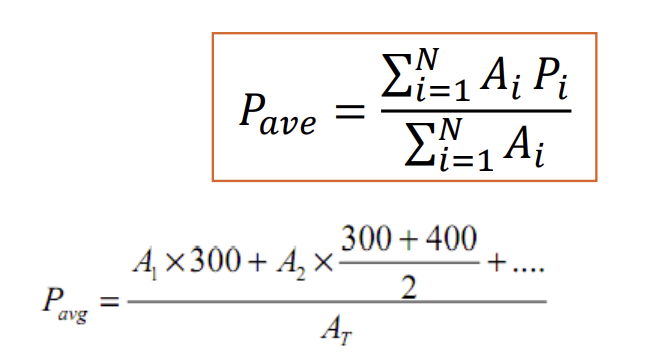
Isohyetal Method
Method that takes the average of the precipitation gages weighted by contour lines
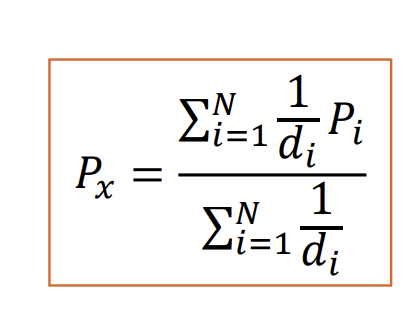
Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW) Interpolation
Interpolate values at locations with no precipitation gages
Evapotranspiration
i) evaporation from the soil
ii) evaporation of the intercepted water
iii) evaporation from the depression storage
iv) transpiration of water by plants and trees
Transpiration
evaporation of water absorbed by plants
Factors Affecting Transpiration
humidity, temperature, wind speed, solar radiation
Potential Evapotranspiration (PET)
Max amount of water to evapotranspire
Actual Evapotranspiration (AET)
Actual amount of water to evapotranspire
Reference Crop Evapotranspiration (ETo)
PET of an idealized crop of a uniform height, completely covering the ground, growing actively
Crop Evapotranspiration (ETc)
is determined from ETo by applying a crop coefficient (Kc) that simulates the condition of the specific crop