S2 T4 Physics EOT
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Scalar quantities
Quantities that only have magnitude
Temperature
Mass
Distance
Vector
Quantities with both magnitude and direction
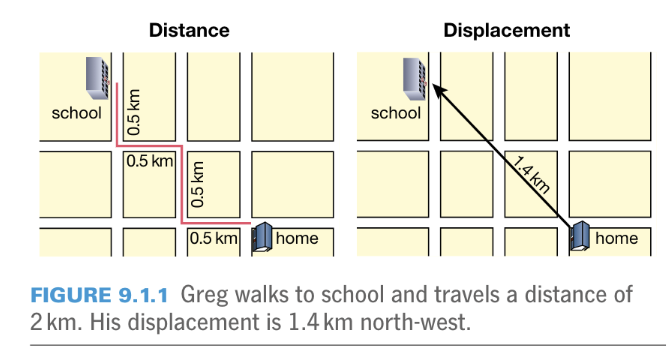
Displacement
Force
Velocity
Displacement
Straight line distance between finishing and starting points
Specifies direction of end point and starting point
Speed
Measure of how fast something moves
Average speed
A measure of how fast something moves overall.
→ Ignores stops and changes, assumes object was travelling at same speed the whole time.
Instantaneous speed
Speed at a particular instant
→ shown on speedometer
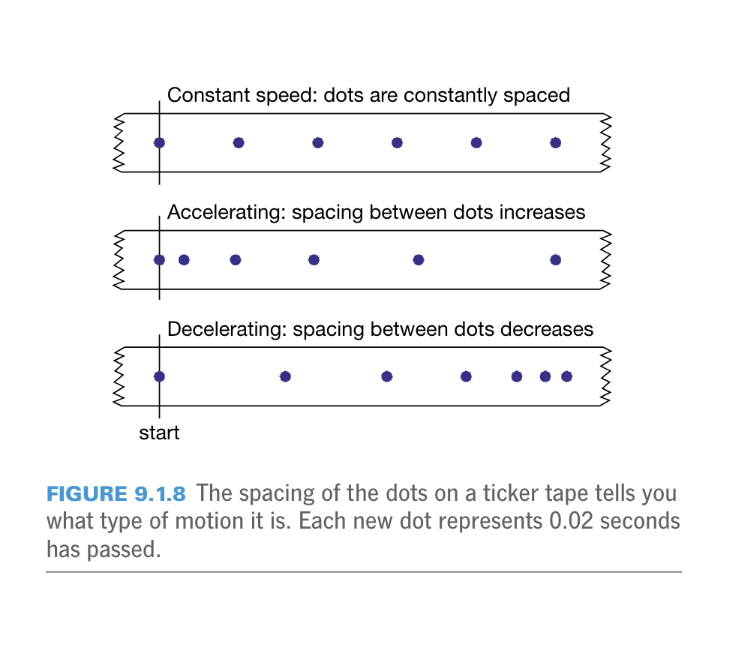
Ticker timer speeds
Speed conversions
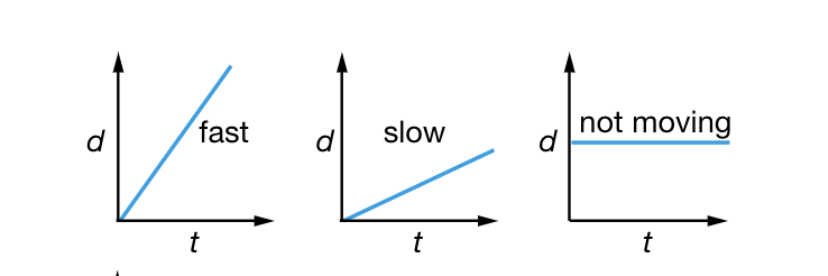
Distance-Time graphs
Show how far an object travels as time progresses
Flat line → Motion has stopped
Steep slope → covers greater distance
Gradient = objects average speed over a time interval
distance on vertical axis
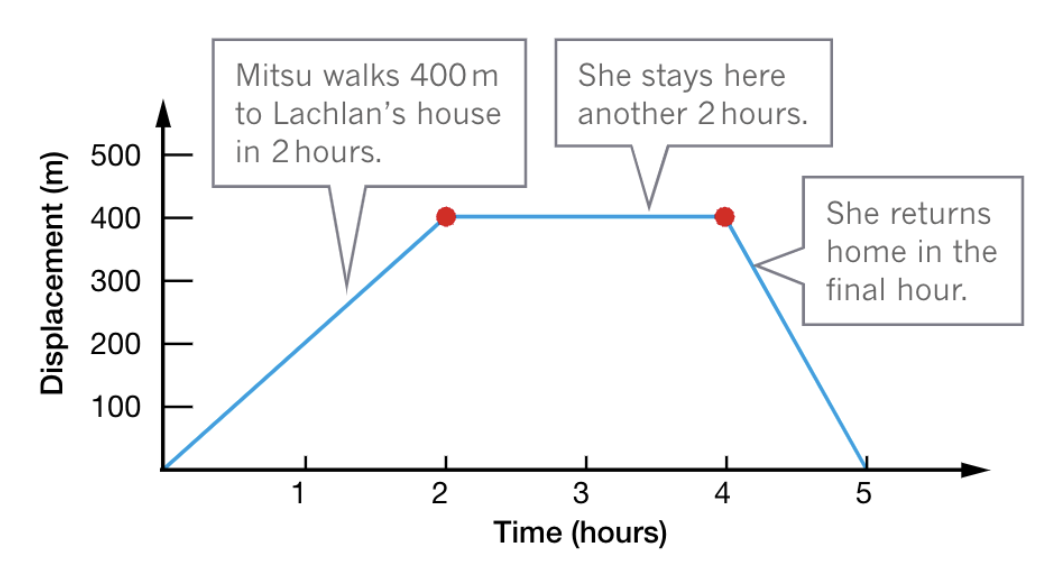
Displacement-time
Displacement is on vertical axis
Speed-time graphs
flat line = constant
increase = graph rising upwards
descrease = graph falling downwards
Acceleration
a measure of how quickly a change of speed occurs
a = v-u/t
gravitational acceleration
an object near the surface of the Earth falls with an acceleration of 9.8 m/s/s
linear acceleration
v = u+at.
Newton’s first law
An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by a force
An object that is moving will continue to move at the same speed + direction unless an unbalanced force acts upon it
types of forces
balanced: all of the forces acting are equal in size but opposite in direction, then balanced.
balanced → motion doesn’t change
rested → stationary
unbalanced → speeds up, slows down, change direction
force that is not balanced acts on an object then the motion of the object will change.
examples of first law
When a train begins to move, your feet move forwards with it. However, your body tends to remain stationary, making it appear as if you are ‘falling backwards
first law relation to car safety
travelling in car at 60km/h and stops, you will continue to travel forward at 60km/h. seatbelts restrainbody so that u will stop with the car
air bag reduces the force on a passenger in a collision and prevents their head hitting the stering wheel or side of the car
inertia
the tendency to resist any change in motion is called an objects inertia
increaseased msss → greater inertia, harder it is to change
Newton’s second law
acceleration directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass
examples of newtons second law
Pushing a car and a truck.
truck is heavier therefore requires more force. trcuk will accelerate less
to calculate net force
f = ma
f on top
m on bottom left
a on bottom right
Newton’s third law
For every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force
example of newtons third law
forces always occur in pairs
tennis ball hit by raquet.
force that racquet applies to tennis ball is aactionforce
the force that the ball applies to the racquet is called a reaction force
kinetic energy
energy of a moving object
depends of mass and speed.
mass doubles → energy doubles
speed doubles → energy increase by factor of 4
kinetic energy relation to car safety
in collision, energy is transferred to other objects or transformed into other forms of energy
heavier vehicle and greater the speed, more energy transferred and more damage
cars travelling at higher speed need longer distances to brake and stop.
potential energy
energy that an object has because of it's position or structure. oftenc called stored energy
gravitational potential energy
an object positioned above the ground has it.
higher above the ground = greater gravitational energy
greater mass = greater potential energy
energy efficiency
useful energy output/total energy input x 100
kinetic energy formula
½ mass * speed ²
Ek is measured in J, Mass is measured in kg and speed is measured in m/s
GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL ENERGY FORMULA
mass * acceleration due to gravity * height
gravity is 9.8 N/Kg
conservation of energy
energy may be transferred from one object to another, but is never created or destroyed.
acceleration
the rate of change of velocity
(v-u)/t
air resistance
the retarding force (drag) caused by collisions between air and moving objects (friction)
average speed
the ratio of distance travelled to time taken (scalar)
displacement
an objects change in position due to it starting position and final position. straight line connecting start and end points specified in terms of length and direction
distance
a measurement of how far an object travels during a parrticular mtion or journey
efficiency
the percentage of energy that is effectively transformed by a system. A measure of useful energy output of an energy transfer
elastic potential energy
energy stored in a stretched or compressed material such as a spring
free fall
motion where gravity is the only force acting on the body
gravitational potential
hte potential energy available to an object due to its position in a gravitational field
law of conservation of energy
the energy in a system before an interaction is exactly equal to the energy in a system after the interaction
magnitude
the size or extent of something, with no need for direction. A quantitative measure expressed as a number of a standard unit
mechanical energy
the energy that a body possesses due to its position or motion.
kinetic energy, gravitational energy and eleastic postential energy
velocity
the ratio of displacement to time taken (vector)
speed of an object tin a given direction
terminal velocity
the final velocity at which an object falls, with no further acceleration possible due to air resistance
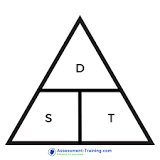
speed distance time triangle
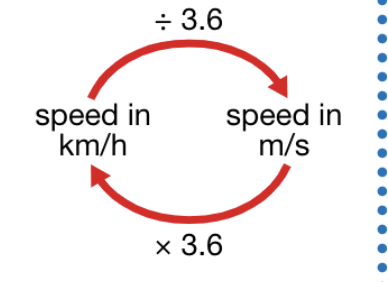
converting between km/h and m/s
divide by 3.6 to go from km/h to m/s
times by 3.6 to go from m/s to km/h