A&P 1-1.3 The Cell (copy)
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
cell
smallest unit that can carry out all activities we associate with life.
basic unit of life
When provided with essential nutrients & an appropriate environment, some ____ can be kept alive & growing for many years.
No isolated part of a ___ is capable of sustained survival.
bacteria & protists
unicellular organisms
humans, plants, animals
multicellular organisms
cell theory
the idea that cells are the basic unit of life & that all cells come from other cells.
Cells are the basic living units of organization & function in all organisms.
All cells come from other cells.
Discovered by German scientists Schleidan, Schwann, & Virchow.
cells; basic living units; organization; function
cells; other cells
cell theory:
____ are the ____ of _____ & ____ in all organisms.
All ____ come from ____.
Schwann, Schleidan, Virchow
discovered the cell theory
most cells…
are small enough that they can’t be seen with the eye alone.
Require magnification with a light microscope: a device that passes light through a thin sample of the cell medium & then through a magnifying lens to be seen by the human eye.
few cells…
are as big as 1 millimeter (mm) in diameter (1/25th of an inch) & are large enough to be seen by the human eye.
Ex: frog egg.
small; can’t
magnification; light microscope
most cells: are ___ enough that they can’t be seen with the eye alone.
Require ____ with a ______: a device that passes light through a thin sample of the cell medium & then through a magnifying lens to be seen by the human eye.
light microscope
a device that passes light through a thin sample of the cell medium & then through a magnifying lens to be seen by the human eye.
light; thin; magnifying lens
light microscope: a device that passes ____ through a ____ sample of the cell medium & then through a ______ to be seen by the human eye.
1 millimeter (mm); large; frog
few cells: are as big as ______ in diameter (1/25th of an inch) & are ____ enough to be seen by the human eye.
Ex: ____ egg.
organelles
parts within a cell
_____ need to be functioning for the cell to survive, just like we need our organ systems functioning to continue life.
can be used for energy conversion & for synthesis of needed compounds.
biomacromolecules
(proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, & nucleic acids) that make up organelles
organelles; organ
____ are to a cell what an ____ is to a human.
energy conversion; synthesis
organelles can be used for ______ & for the _____ of needed compounds.
Cytosol
fluid portion that surrounds the organelles.
Enables all the organelles to be held in place.
fluid; surrounds
held in place
cytosol: ____ portion that _____ the organelles.
Enables all the organelles to be _____.
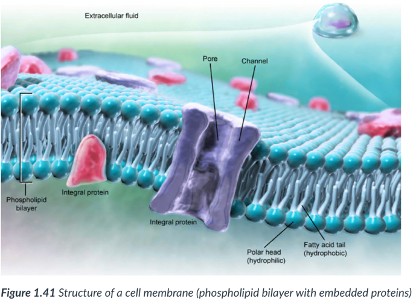
Plasma membrane
Everything that enters or leaves a cell must pass through its _____
surrounds all cells & contains specialized “pumps” & “gates” that regulate the passage of materials in & out of the cell.
Substances either go through protein channels or move directly through the ________.
NOT a free-flowing structure: there’s a containment method.
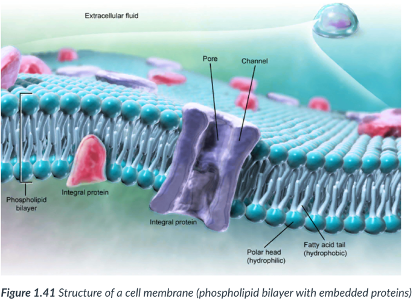
surrounds; “pumps” & “gates”; regulate; materials in & out
protein channels; directly through
containment
Plasma membrane: ______ all cells & contains specialized _____ that ______ the passage of _____ of the cell.
Substances either go through _____ or move _____ the membrane.
NOT a free-flowing structure: there’s a _____ method.
cell size must be kept small
As a cell grows, the surface area-to-volume ratio changes.
Cells need to remain relatively small bc as a cell expands, the amount of surface area relative to the volume of the cell decreases.
The smaller cell is more active bc relative to its volume, its surface area is larger than a bigger cell.
Important that the cell stays small bc the ratio of SA to volume needs to be large bc the cell needs to have a lot of SA to be able to take in the nutrients it needs & excrete wastes.
W/ a larger surface area (relative to volume) this allows the metabolic processes to occur faster.
Metabolic processes such as diffusion (transportation of particles across the membrane), can all occur faster.

grows; changes
expands; decreases
smaller; larger
As a cell ____, the surface area-to-volume ratio ____.
Cells need to remain relatively small bc as a cell ___, the amount of surface area relative to the volume of the cell _____.
The _____ cell is more active bc relative to its volume, its surface area is ____ than a bigger cell.

small; large
nutrients; wastes
larger; metabolic processes; faster
Important that the cell stays ____ bc the ratio of SA to volume needs to be ____ bc the cell needs to have a lot of SA to be able to take in the ____ it needs & excrete ____.
W/ a ____ surface area (relative to volume) this allows the ___ to occur ____.

diffusion
transportation of particles across the membrane
cells; organelles
numerous folds; small; increase
____ (those of the intestinal wall) & _____ (mitochondria) that are actively carrying out biochemical processes have adaptations (______) in addition to their ____ size, that greatly ____ their surface area.

2 basic types of cells
prokaryotic & eukaryotic
prokaryotic & eukaryotic
2 basic types of cells
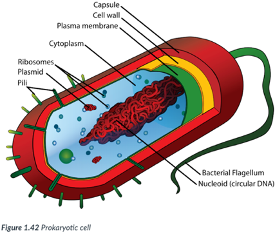
prokaryotic cells
simple cells. ex-bacteria
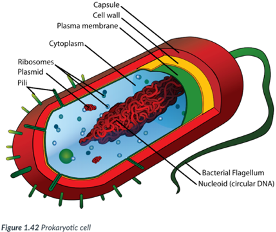
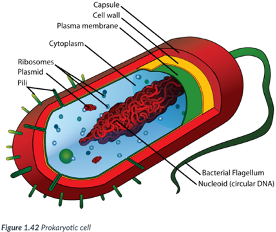
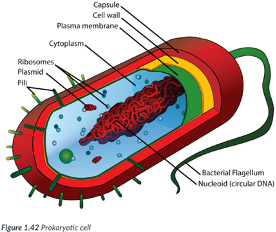
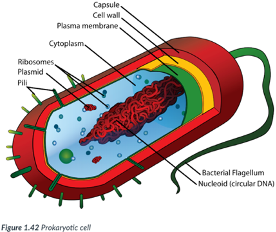
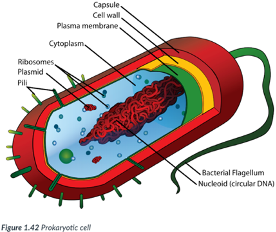
Prokaryotic cells
simple cells for 3 reasons: Ex: Bacteria.
1) Typically, smaller than eukaryotic cells.
Most are between 1-10 μm (micrometers) in size (~ 1/30,000 of an inch); just visible with the light microscope.
2) DNA is NOT enclosed in a nuclear membrane (prokaryotic = “before the nucleus”).
DNA is circular & free-floating.
3) Do NOT contain many of the internal membrane-bound organelles of eukaryotic cells.
Like eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells contain a plasma membrane & ribosomes.
Ribosomes are composed of ribonucleic acid (RNA) & synthesize proteins for use by the cell; they are NOT surrounded by a membrane.
Membranes provide a location for metabolic processes to occur.
Bc prokaryotes lack organelles w/ membranes, the plasma membrane of a prokaryotic cell is often folded inward to create numerous folds where metabolic processes take place.
Prokaryotic cells: simple cells for 3 reasons:
1) Typically, smaller than eukaryotic cells.
Most are between 1-10 μm (micrometers) in size (~ 1/30,000 of an inch); just visible with the light microscope.
2) DNA is NOT enclosed in a nuclear membrane (prokaryotic = “before the nucleus”).
DNA is circular & free-floating.
3) Do NOT contain many of the internal membrane-bound organelles of eukaryotic cells.
simple; bacteria
smaller; 1-10 μm; light
NOT enclosed; before
circular
Do NOT contain
Prokaryotic cells: ____ cells for 3 reasons: Ex: ____.
1) Typically, ____ than eukaryotic cells.
Most are between _____ (micrometers) in size (~ 1/30,000 of an inch); just visible with the ____ microscope.
2) DNA is _____ in a nuclear membrane (prokaryotic = “___ the nucleus”).
DNA is ____ & free-floating.
3) _____ many of the internal membrane-bound organelles of eukaryotic cells.
plasma membran; ribosomes
Ribosomes; ribonucleic acid (RNA); proteins
Membranes
lack; folded inward; numerous folds
Like eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells contain a ______ & ______.
_____ are composed of _____ & synthesize ____ for use by the cell; they are NOT surrounded by a membrane.
_____ provide a location for metabolic processes to occur.
Bc prokaryotes ____ organelles w/ membranes, the plasma membrane of a prokaryotic cell is often ____ to create ____ where metabolic processes take place.
membranes
provide a location for metabolic processes to occur.
inward; numerous folds; metabolic processes
prokaryotic plasma membranes are folded ____ to create ____ where ____ take place
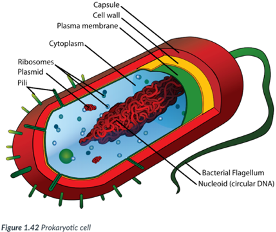
bacteria
Most people think of ____ as causing diseases.
Ex: botulism: type of food poisoning that can lead to paralysis & sometimes death.
The bacterium, Clostridium botulinum, can form a dormant, extremely durable cell called an endospore, which is released by the bacterium under adverse conditions.
During the canning process, food must be heated to boiling for 3-4 minutes to kill any highly heat-resistant endospores that might be present.
botulism
type of food poisoning that can lead to paralysis & sometimes death.
The bacterium, Clostridium botulinum, can form a dormant, extremely durable cell called an endospore, which is released by the bacterium under adverse conditions.
During the canning process, food must be heated to boiling for 3-4 minutes to kill any highly heat-resistant endospores that might be present.
Clostridium botulinum
bacteria that causes botulism by releasing endospores
food poisoning; paralysis; death
Clostridium botulinum; endospore; adverse
canning
botulism: type of ____ that can lead to ____ & sometimes ____.
The bacterium, ____, can form a dormant, extremely durable cell called an ____, which is released by the bacterium under ____ conditions.
During the ____ process, food must be heated to boiling for 3-4 minutes to kill any highly heat-resistant endospores that might be present.
endospore
a dormant, extremely durable cell released by the Clostridium botulinum bacterium under adverse conditions.
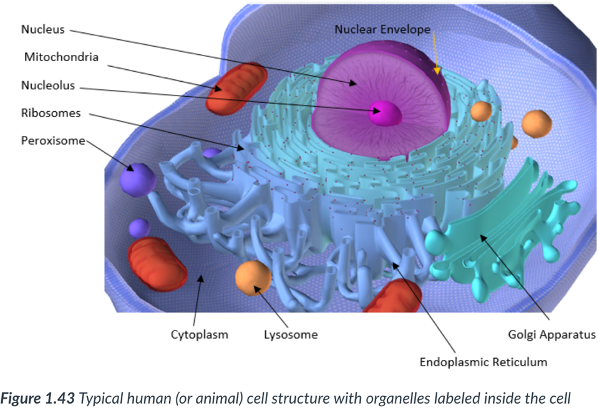
Eukaryotic cells
complex cells. Ex: Plants, animals, & humans.
10-100 times larger than prokaryotic cells
Possess a nuclear membrane (eukaryotic = “true nucleus”) that houses the DNA.
DNA is linear.
Contain many membrane-bound organelles.
Membranes are important to a complex cell bc they:
Form compartments within organelles where reactants are more likely to come into contact.
Keep certain compounds away from one another.
Form a work surface where many enzymes can congregate to complete a complex reaction.
eukaryotic cells are complex cells for 3 reasons. Ex: humans, plants, animals
10-100 times larger than prokaryotic cells
Possess a nuclear membrane (eukaryotic = “true nucleus”) that houses the DNA.
DNA is linear.
Contain many membrane-bound organelles.
Membranes are important to a complex cell bc they:
Form compartments within organelles where reactants are more likely to come into contact.
Keep certain compounds away from one another.
Form a work surface where many enzymes can congregate to complete a complex reaction.
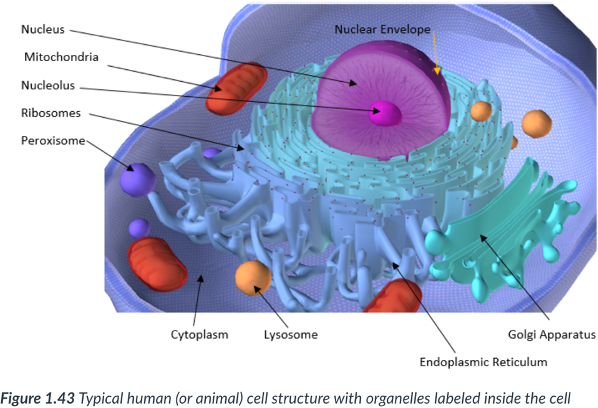
complex; Plants, animals, & humans.
larger
Possess; true; houses
linear
contain
eukaryotic cells are _____ cells. Ex: _____
10-100 times ___ than prokaryotic cells
_____ a nuclear membrane (eukaryotic = “____ nucleus”) that ____ the DNA.
DNA is ____.
_____ many membrane-bound organelles.
Membranes are important to a complex cell bc they:
Form compartments within organelles where reactants are more likely to come into contact.
Keep certain compounds away from one another.
Form a work surface where many enzymes can congregate to complete a complex reaction.
membranes
compartments; reactants; come into contact
away
work surface; congregate
_____ are important to a complex cell bc they:
Form ______ within organelles where ____ are more likely to ______.
Keep certain compounds ____ from one another.
Form a ____ where many enzymes can ____ to complete a complex reaction.
organelles
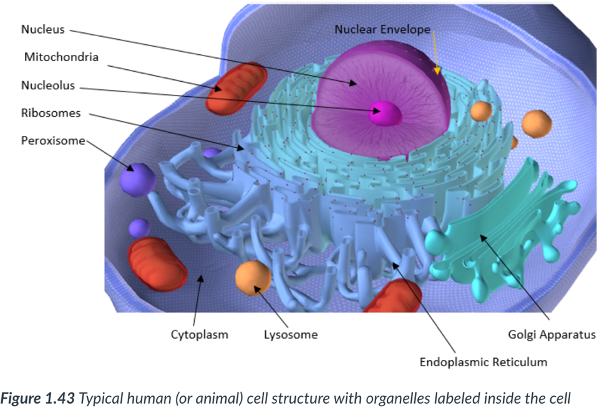
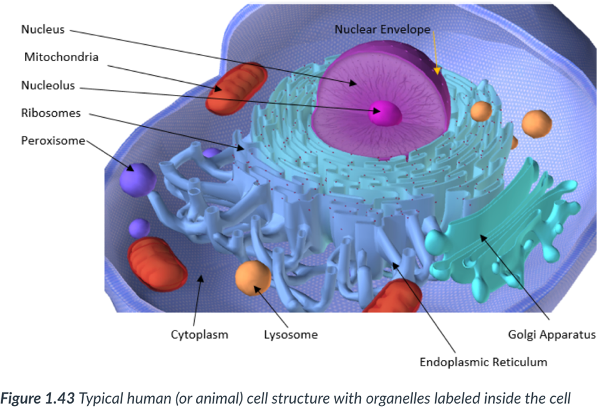
Eukaryotic cells have ______ inside each cell.
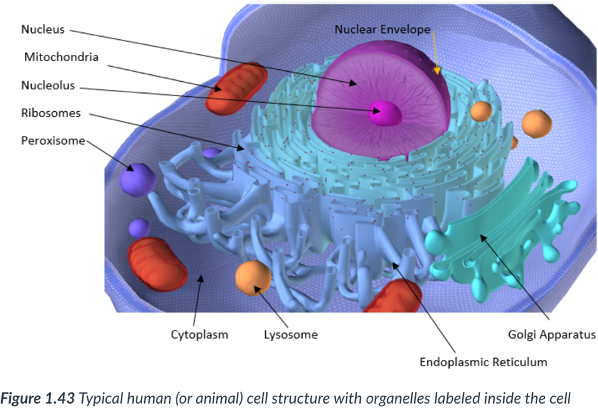
nucleus
surrounded by a nuclear membrane (envelope).
“Brain” of the cell.
Most prominent organelle in the cell.
Contains DNA.
Serves as the control center of the cell: directs all cellular activities.
nuclear membrane
brain
Most prominent
DNA
control center
Nucleus: surrounded by a _____ (envelope).
“_____” of the cell.
____ organelle in the cell.
Contains ____.
Serves as the _____ of the cell: directs all cellular activities.
nuclear membrane (envelope)
surrounds the nucleus
DNA
composed of sequences of nucleotides.
nucleotides
DNA is composed of sequences of ____.
chromosomes
the organized or “packaged” form of DNA inside a cell.
organized; DNA
chromosomes: the ______ or “packaged” form of ____ inside a cell.
genes
sections of nucleotide sequences; portions of chromosomes.
Determine what proteins are synthesized in the ribosomes.
sections; portions
proteins
genes: _____ of nucleotide sequences; ____ of chromosomes.
Determine what ____ are synthesized in the ribosomes.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
DNA is copied in this form so it can leave the nucleus to make proteins; transfers information from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes.
Takes the coded amino acid sequence from the nucleus to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
DNA; leave; nucleus
proteins; ribosomes
coded amino acid sequence; protein synthesis.
Messenger RNA (mRNA): ____ is copied in this form so it can ____ the _____ to make _____; transfers information from the DNA in the nucleus to the ____.
Takes the ____ from the nucleus to the ribosome for _____
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
RNA found in the ribosomes.
Synthesized in a region of the nucleus called the nucleolus.
ribosomes
nucleolus
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): RNA found in the ____.
Synthesized in a region of the nucleus called the ____.
nucleolus
center of the nucleus; synthesizes rRNA.
center; rRNA
Nucleolus: ____ of the nucleus ; synthesizes ____.
ribosomes
tiny manufacturing plants that assemble proteins.
Translate that DNA message to get to a protein.
Visible as small granules.
Contain ribosomal RNA plus the enzymes necessary to form peptide bonds between amino acids.
assemble proteins
Translate
granules
ribosomal RNA; enzymes; peptide bonds
ribosomes: tiny manufacturing plants that ____.
______ that DNA message to get to a protein.
Visible as small ____.
Contain ____ plus the _____ necessary to form____ between amino acids.
proteins
Each type of cell produces a unique combination of _____.
DNA nucleotides; code; order
amino acids
The unique sequence of ____ in a cell serves as a ___ that specifies the ___ in which _____ are assembled.
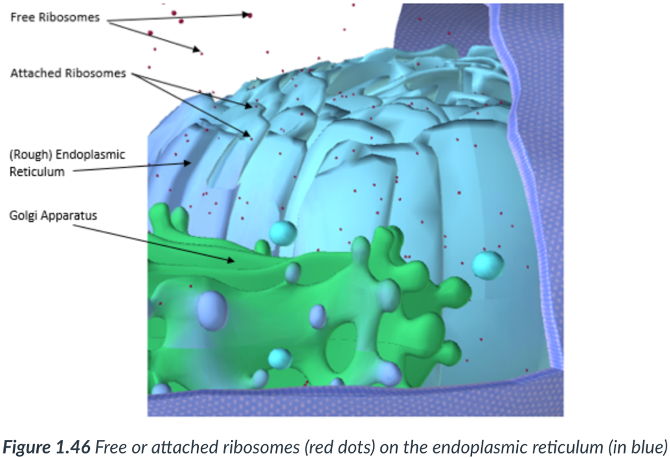
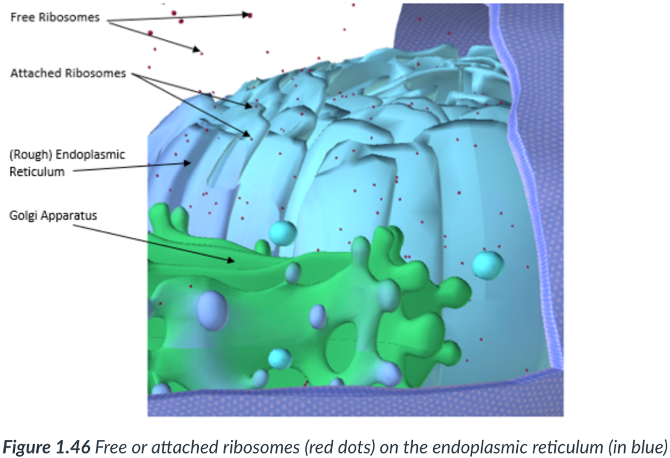
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
a maze of tightly packed & flattened, sac-like structures that form interconnected compartments within the cytoplasm.
An extension of the outer membrane of the nucleus.
Modifies & transports proteins that are derived from ribosomes found along its surface.
After proteins are assembled by the ribosomes, they’re modified & transported by the _____.
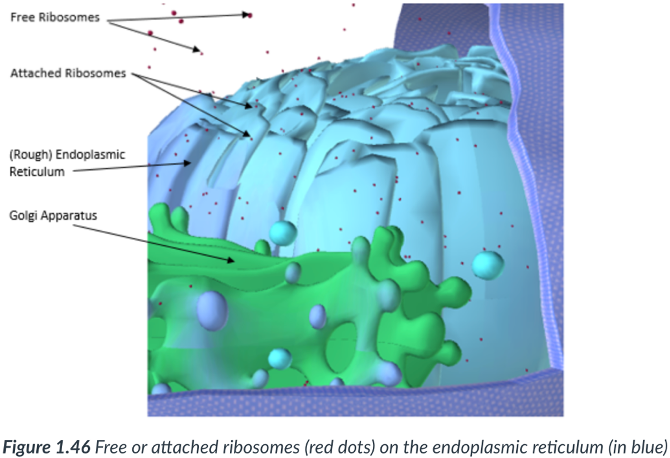
sac-like
interconnected; cytoplasm
membrane; nucleus
Modifies; transports; ribosomes
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): a maze of tightly packed & flattened, ____ structures that form _____ compartments within the ______.
An extension of the outer _____ of the ____.
____ & ____ proteins that are derived from _____ found along its surface.
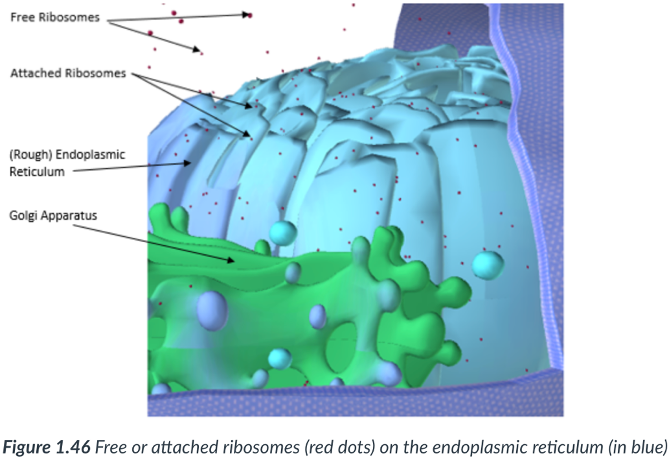
rough ER & smooth ER
There are 2 continuous sections to the ER
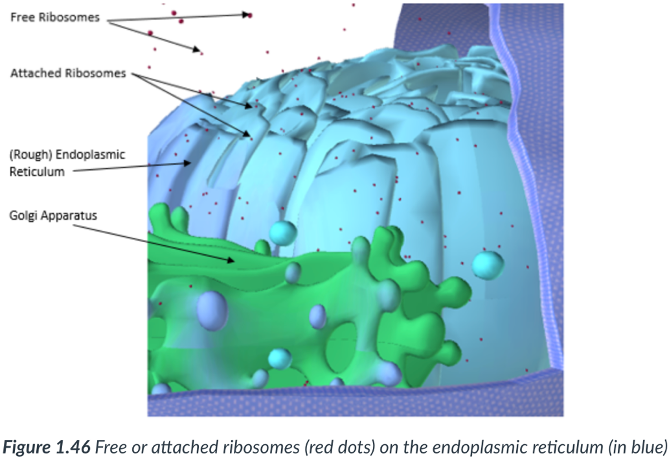
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Modifies & transports proteins that are derived from ribosomes found along its surface.
Sections that possess ribosomes appear “bumpy.”
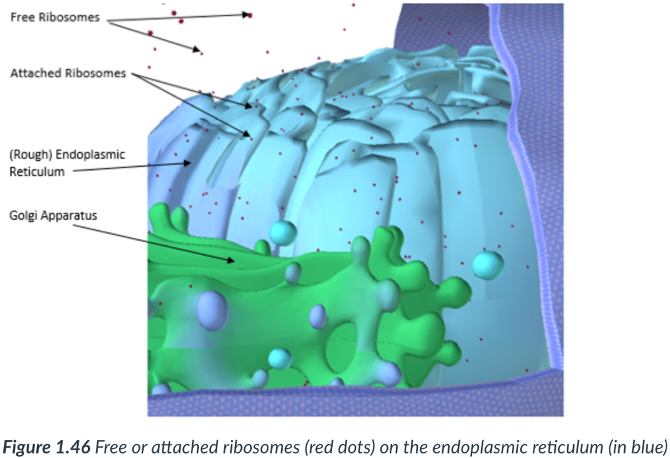
Ribosomes
Modifies; transports; proteins
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER): _____ are located on the ER.
____ & ____ _____ that are derived from ribosomes found along its surface.
Sections that possess ribosomes appear “bumpy.”
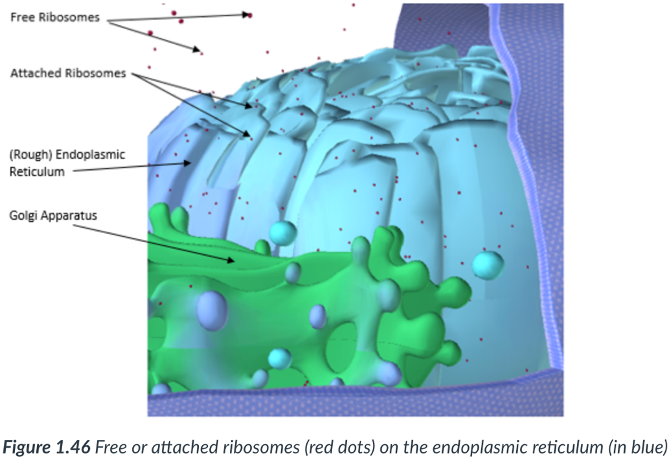
smooth ER
has NO attached ribosomes.
Responsible for the synthesis of lipids.
Human liver cells possess extensive amounts of ____.
This is where cholesterol, a major component of cell membranes, is formed.
NO attached
synthesis of lipids
liver
cholesterol
Smooth ER: has ______ ribosomes.
Responsible for the ______.
Human ____ cells possess extensive amounts of smooth ER.
This is where ____, a major component of cell membranes, is formed.
cytosol
the fluid portion of the cell & NOT INCLUDING all the organelles outside of the nucleus.
Cytoplasm
the fluid portion of the cell INLCUDING all the organelles outside of the nucleus
fluid; NOT INCLUDING
cytosol: the ___ portion of the cell & _____ all the organelles outside of the nucleus.
fluid; INCLUDING
cytoplasm: the ____ portion of the cell ____ all the organelles outside of the nucleus
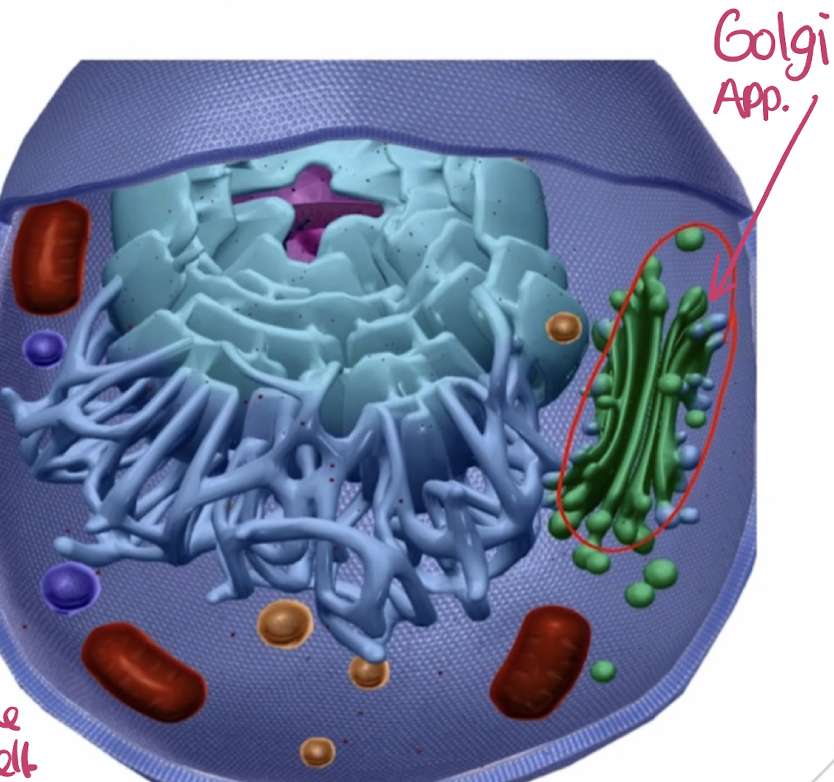
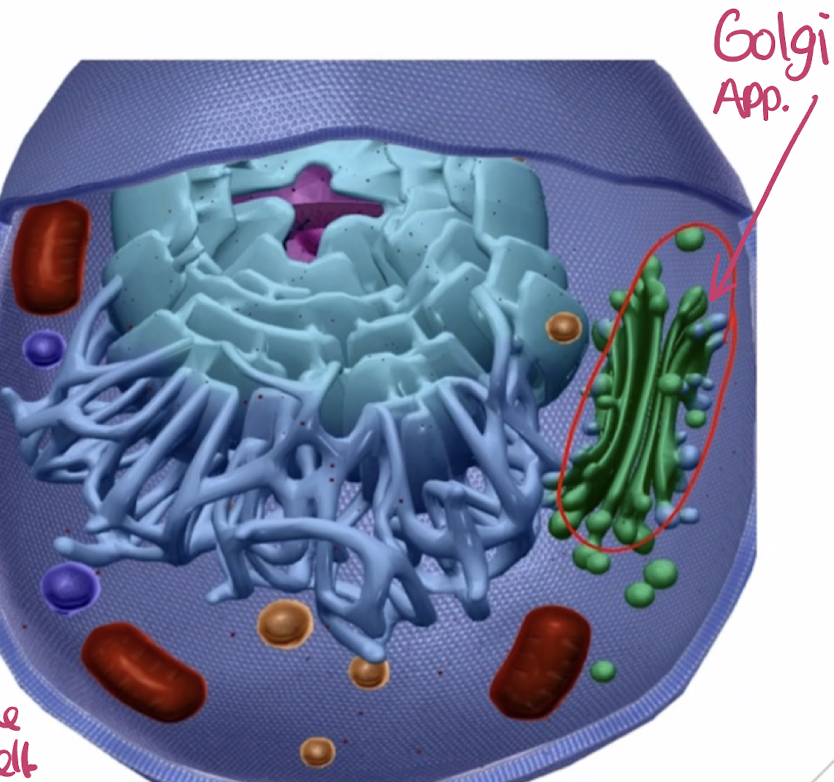
Golgi complex (apparatus)
an organelle made up of a stack of many flattened sacs (cisternae).
Named after the scientist who discovered it.
Parts of the ___ are connected, however, most form separate compartments.
Responsible for receiving lipids & proteins synthesized by the ER, altering their structures, & shipping them to other parts of the cell.
The ____ receives its products from the ER & they go through the series of flattened sacs (cisternae) & modifies them to get them ready to be sent out in the cell or sent outside of the cell.
As portions pinch off from the _____ membrane forming enclosed sacs called vesicles, they & their contents can be transported to other organelles within the cell or exported out of the cell through the cell membrane.
Accomplished through fusion of the vesicles with the plasma membrane of the cell or other membrane-bound organelles.
Fusion can occur because all membranes within the cell are structured similarly.
cisternae
connected; separate compartments
lipids & proteins; ER; altering; shipping
vesicles
fusion
Golgi complex (apparatus): an organelle made up of a stack of many flattened sacs (____).
Named after the scientist who discovered it.
Parts of the Golgi complex are _____, however, most form _____.
Responsible for receiving ______ synthesized by the ____, _____ their structures, & _____ them to other parts of the cell.
The Golgi apparatus receives its products from the ER & they go through the series of flattened sacs (cisternae) & modifies them to get them ready to be sent out in the cell or sent outside of the cell.
As portions pinch off from the Golgi membrane forming enclosed sacs called _____, they & their contents can be transported to other organelles within the cell or exported out of the cell through the cell membrane.
Accomplished through _____ of the vesicles with the plasma membrane of the cell or other membrane-bound organelles.
Fusion can occur because all membranes within the cell are structured similarly
lysosomes
The Golgi complex also produces small sacs of digestive enzymes called lysosomes ("lysis" = to disintegrate).
Lysosomes: contain digestive enzymes to break down waste products & harmful materials.
break down biomacromolecules (proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, & nucleic acids) that originate inside or outside of the cell.
Once broken into their building block monomers, these molecules can later be recycled into new biomacromolecules.
Lysosomes can also fuse with other vesicles containing harmful bacteria.
The bacteria can then be degraded into its components.
Golgi complex; lysosomes
The _____ also produces small sacs of digestive enzymes called _____
("lysis" = to disintegrate).
lysosomes
contain digestive enzymes to break down waste products & harmful materials.
break down biomacromolecules (proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, & nucleic acids) that originate inside or outside of the cell.
Once broken into their building block monomers, these molecules can later be recycled into new biomacromolecules.
________ can also fuse with other vesicles containing harmful bacteria.
The bacteria can then be degraded into its components.
digestive enzymes
biomacromolecules
recycled; biomacromolecules
vesicles
degraded;
Lysosomes: contain _____ to break down waste products & harmful materials.
break down _____ (proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, & nucleic acids) that originate inside or outside of the cell.
Once broken into their building block monomers, these molecules can later be ____ into new _____.
Lysosomes can also fuse with other ____ containing harmful bacteria.
The bacteria can then be ____ into its components.
Tay-Sachs
genetic disease
1 of the normally present digestive enzymes inside lysosomes is lacking. Thus, a toxic lipid in the brain cells cannot be broken down.
The resulting buildup of lipids in these cells can cause intellectual disability & death.
disease
digestive enzymes; lacking; toxic lipid
brain
intellectual disability & death
Tay-Sachs: genetic _____.
1 of the normally present _____ inside lysosomes is ____. Thus, a _____ in the ___ cells cannot be broken down.
The resulting buildup of lipids in these cells can cause ______
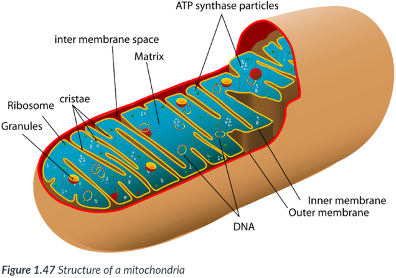
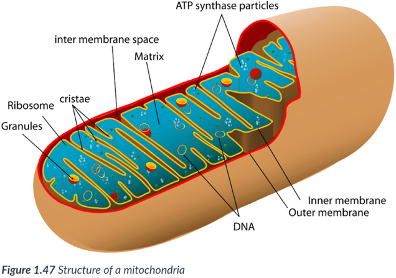
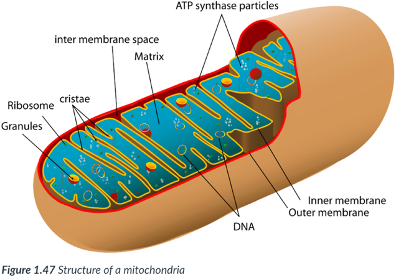
Mitochondria (singular, mitochondrion)
organelle responsible for converting the chemical energy found in food into ATP.
converting; chemical energy
ATP
Mitochondria (singular, mitochondrion): organelle responsible for _____ the ___ found in food into ___.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
a high-energy molecule that provides energy for the cell to carry out its activities.
high-energy; energy
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP): a ____ molecule that provides ___ for the cell to carry out its activities.
Aerobic cellular respiration
converting the chemical energy found in food into ATP using oxygen.
Carbon dioxide, water, & ATP are produced.
chemical energy; ATP
oxygen
Carbon dioxide, water, & ATP
Aerobic cellular respiration: converting the _____ found in food into ___ using ____.
_______ are produced.
Cellular respiration
oxygen is required to break down food (usually in the form of glucose).
Carbon dioxide, water, & ATP are produced.
**This is very much like respiration (breathing) in your lungs, but at the cellular level.
It is through the lungs that the necessary oxygen is obtained to be used by the cells for respiration.
oxygen; break down; glucose
Carbon dioxide, water, & ATP
lungs
Cellular respiration: ______ is required to ____ food (usually in the form of ___).
______ are produced.
**This is very much like respiration (breathing) in your lungs, but at the cellular level.
It is through the ____ that the necessary oxygen is obtained to be used by the cells for respiration.
2
Each mitochondrion is bound by a double membrane.
There are _____ membranes, one inside the other.
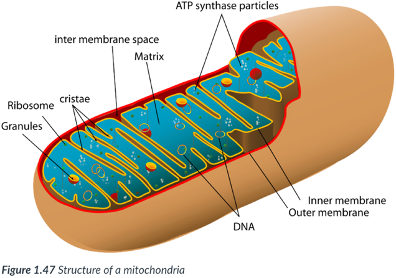
Intermembrane space
space between the inner & outer membranes of mitochondria.
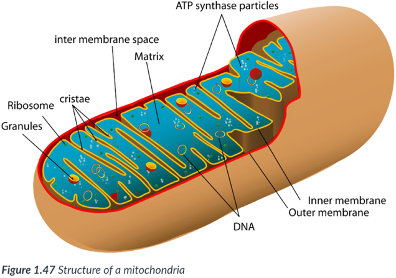
Matrix
forms the center of the mitochondrion, bound by just the inner membrane.
center; inner
matrix: forms the ___ of the mitochondrion, bound by just the ____ membrane.
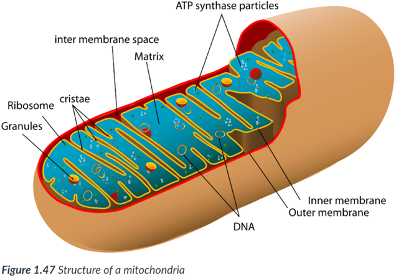
inner mitochondrial membrane
possesses numerous folds that increase the surface area.
Allows ample room for the chemical reactions & enzymes required to transfer the chemical energy in food into ATP.
More production of ATP can occur inside the mitochondria.
folds; increase
ample room; chemical reactions & enzymes
More; inside
inner mitochondrial membrane: possesses numerous ____ that ____ the surface area.
Allows ___ for the ____ required to transfer the chemical energy in food into ATP.
____ production of ATP can occur ____ the mitochondria.
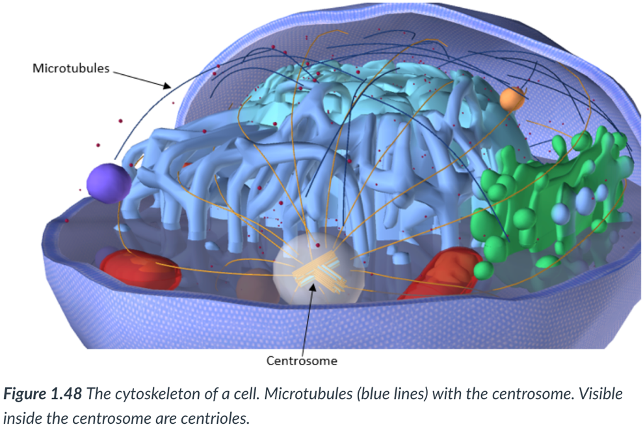
cytoskeleton
Eukaryotic cells also contain a ____: found outside of the cell; consists of a network of protein fibers that provide structural support & movement within the cell.
They’re like what our skeleton is for our body, but for the cell.
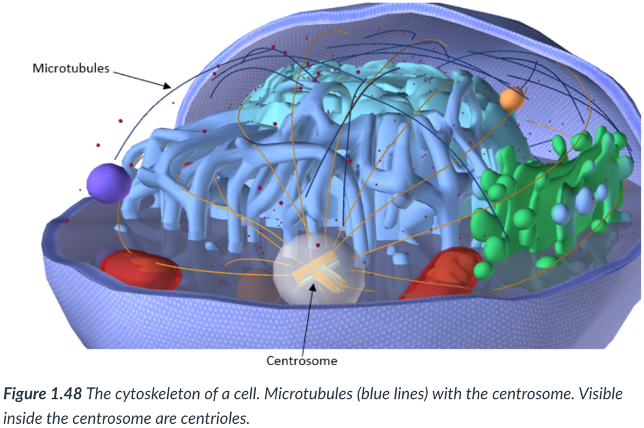
outside
protein fibers; structural support & movement
Eukaryotic cells also contain a cytoskeleton: found ____ of the cell; consists of a network of ____ that provide ____ & _____ within the cell.
They’re like what our skeleton is for our body, but for the cell.
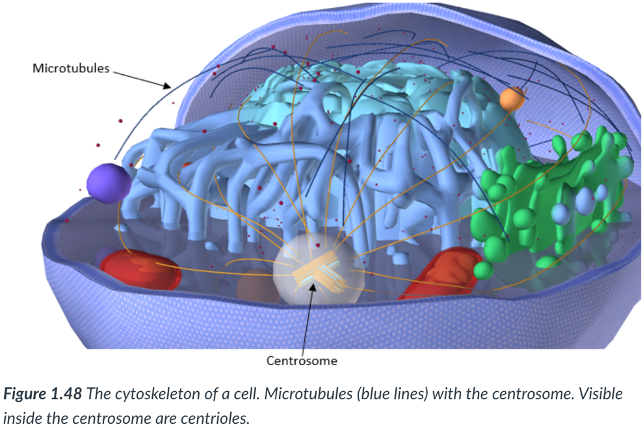
microtubules & microfilaments
2 types of protein fibers that compose the cytoskeleton, both of which can be rapidly assembled & disassembled
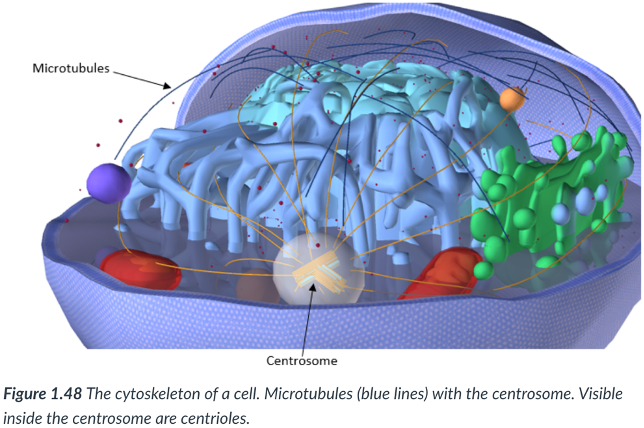
Microtubules
hollow cylinders (like a tube) that are involved in the movement of chromosomes during cell division & in the structure of cilia & flagella.