MEDS2003 MCQ
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
What are the differences between glucokinase and hexokinase?
- Hexokinase is inhibited by a build up of G6P
- Hexokinase works at Vmax when glucose is 5mM
- Glucokinase never works at Vmax in real life
Can Glucokinase catalyse the hydrolysis of G6P?
No
What is the G in this picture of glycogen?
- Glycogenin (a protein core of the glycogen).
- This is where the very first glucose of the branched glycogen chain will form/be added.
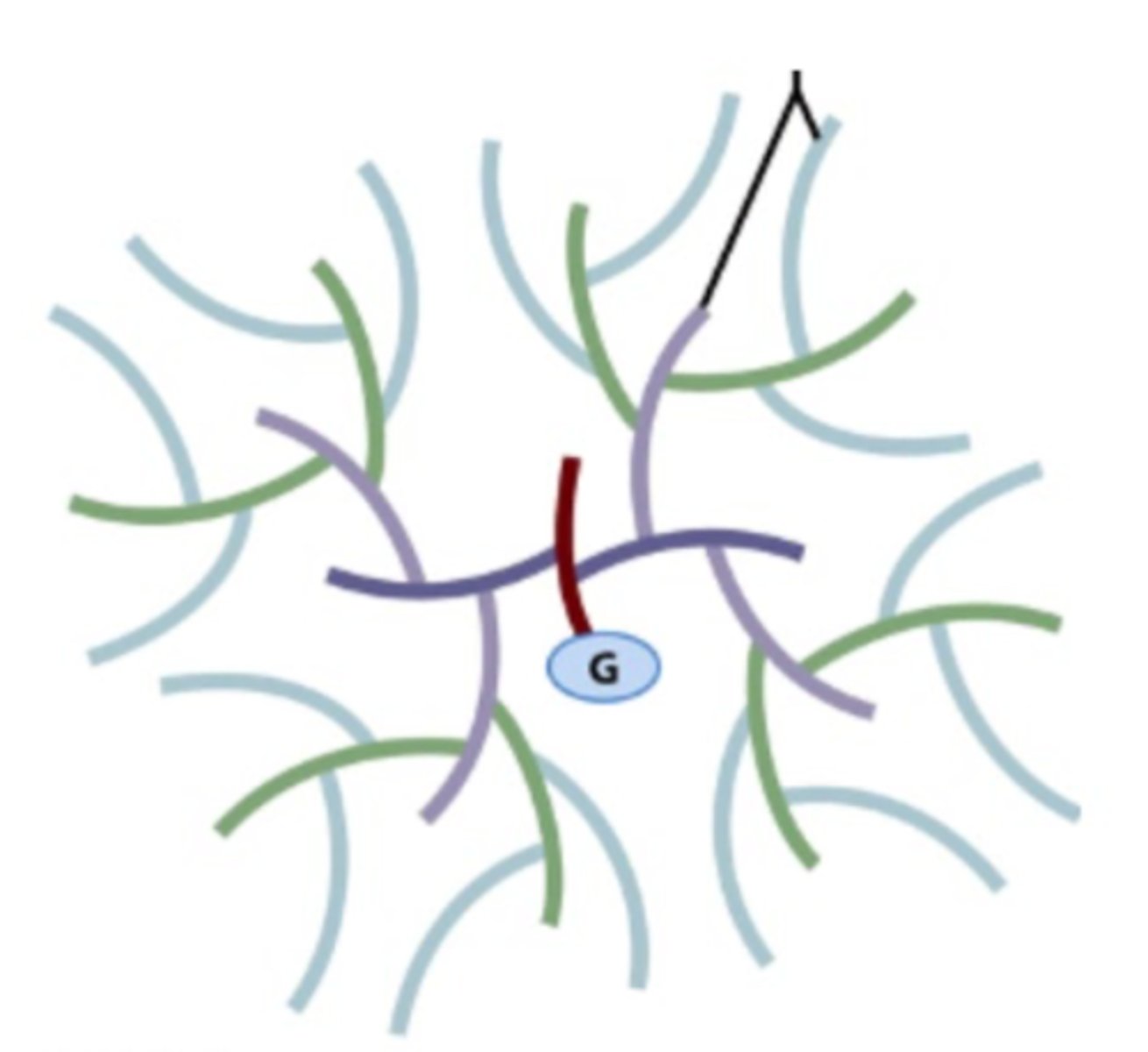
Role of Glycogen synthase
- An enzyme that builds glycogen by adding glucose to growing chains.
- Can't start from nothing - needs to add glucose onto glycogenin.
If all the glycogen molecules in a liver cell looked like this, what would be the most effective way of increasing glycogen stores in that cell?
- Cells need to have more glycogenin to start building glycogen.
- As each glycogen granule has a size limit (due to need to maintain high surface area-to-volume ratio for efficient enzyme access) the only way to store more glycogen is to create new granules - which requires making more glycogenin.
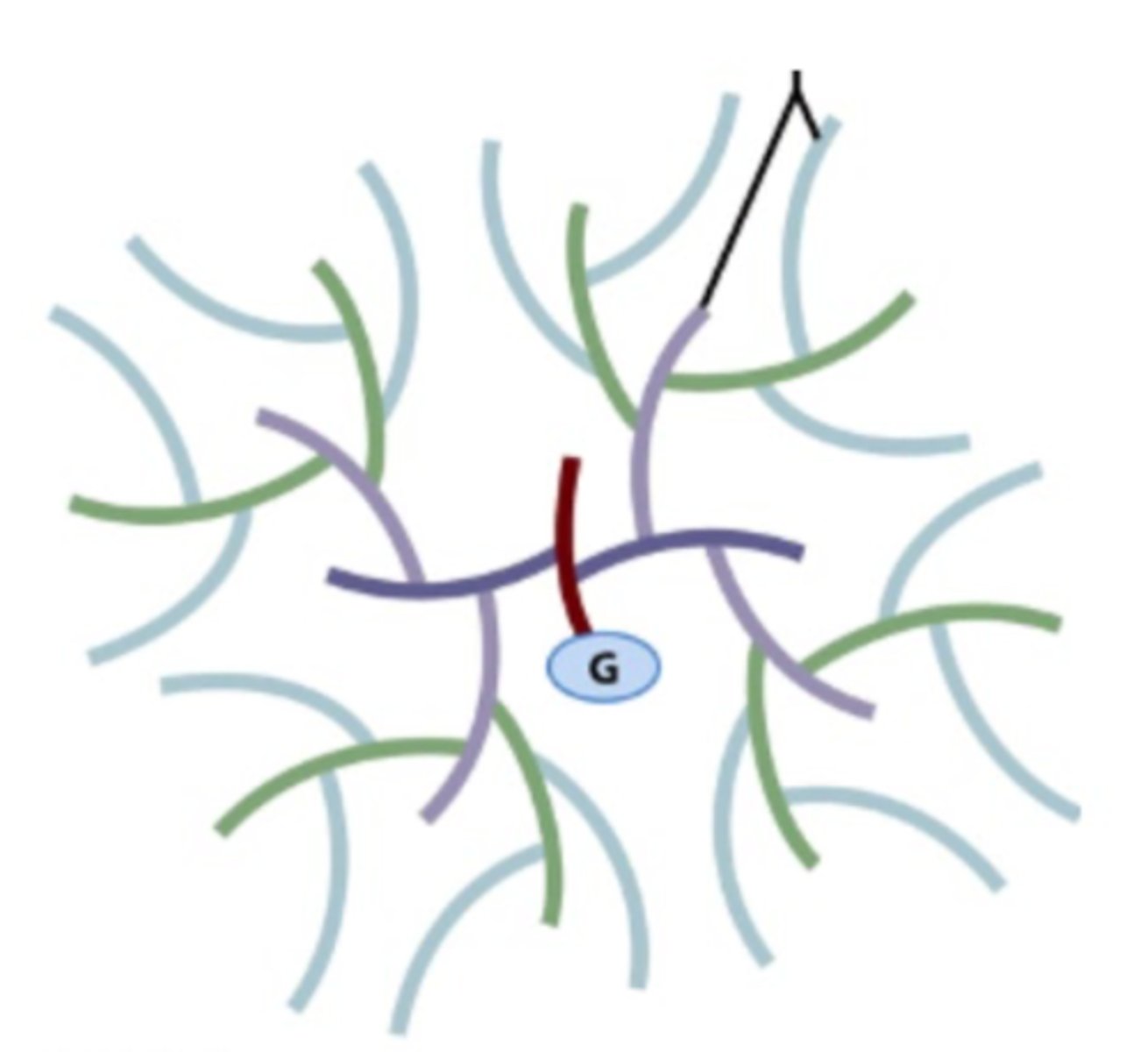
Why is it important to regulate glycogenin?
Helps a cell/organ/tissue to regulate the amount of glycogen that is being stored in muscles.
How does insulin stimulate the rate of glycogen synthase (GS) in muscle?
It stimulates protein phosphatases.
How do we stimulate the rate of glycogen synthase (GS) activity in the liver?
Stimulated by high glucose and insulin levels (increasing glucose uptake?), which:
- Increases glucose-6-phosphate (an activator of GS).
- Causes dephosphorylation of glycogen synthase, activating it.
What is the role of glycogen synthase?
- Builds glycogen from glucose.
- Active in both liver and muscle.
Which statement about 'push' and 'pull' models of glycogen synthesis (GS) is true?
Insulin stimulates glycogen synthase to 'pull' GS.
Imagine the situation 24 hours into starvation. How much glucose is the brain using at this stage?
At this stage, the brain is using about 5 glucose per hour (120g per day).
What is happening in the brain during the first 24 hours into starvation?
- Brain is mainly relying on stores of glycogen, supplied by liver glycogen and gluconeogenesis.
- Lactate from muscles and red blood cells are recycled into glucose via the Cori cycle to help support this.
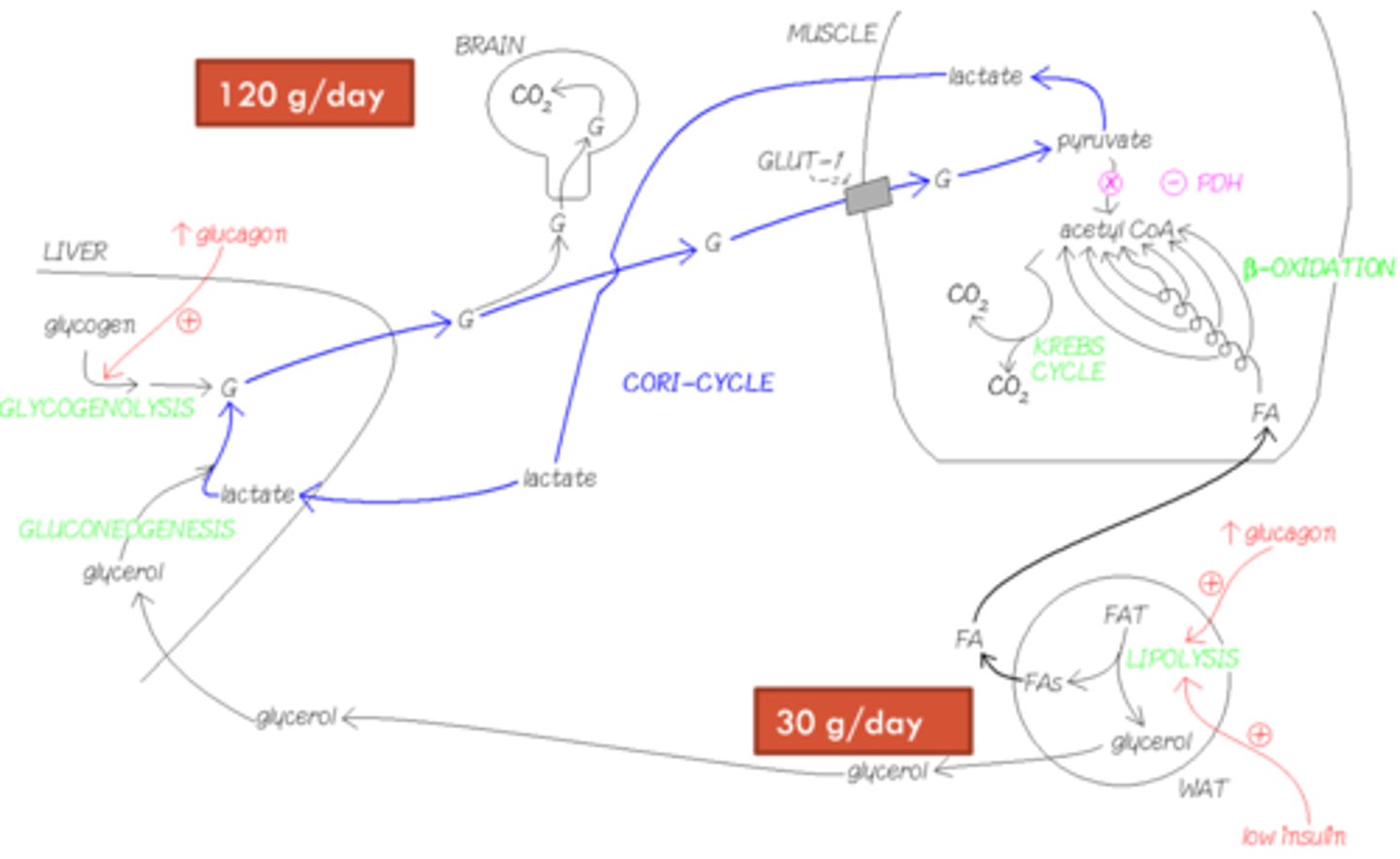
How much glucose does the brain use per day, and how is it metabolised?
- 120g/day (5g/hour)
- It burns glucose completely to CO2, as it has limited fuel options.
What happens to glucose in muscle cells during fasting?
Glucose is converted to pyruvate, then to lactate, which is sent to the liver and recycled into glucose via the Cori cycle.
How do fat cells respond to high glucagon levels?
Fat cells activate hormone-sensitive lipase and perilipin via cAMP and PKA, releasing fatty acids and glycerol into the bloodstream.
What is the fate of fatty acids during early starvation?
Fatty acids generate acetyl-CoA for the Krebs cycle. High acetyl-CoA inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase, limiting glucose oxidation to pyruvate.
What happens to glycerol released from fat breakdown?
Glycerol is taken up by the liver and used as a substrate for gluconeogenesis, providing about 30g of glucose per day.
Are fatty acids are bound to albumin before being released from the adipocyte into the bloodstream?
No - they are bound after being released.
What is lipolysis, and what triggers it?
- The hydrolysis of stored triaglycerol in adipose tissue, releasing 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol per triglyceride.
- Is trigger when Hormone Sensitive Lipase (HSL) is phosphorylated.
How do fatty acids help prevent the oxidation of glucose in insulin-sensitive cells?
The oxidation of fatty acids inhibits the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
The muscle is said to be 'selfish' with its glycogen. Which statement related to this idea is true?
Muscle has a very low glucose 6-phosphatase activity.
2-fluoro-2-deoxyribose (FdG) is commonly used to detect cancer in clinical diagnostics. Which of the following properties is exploited in these tests?
Phosphorylated FdG cannot be isomerised for the next step of glycolysis to continue.
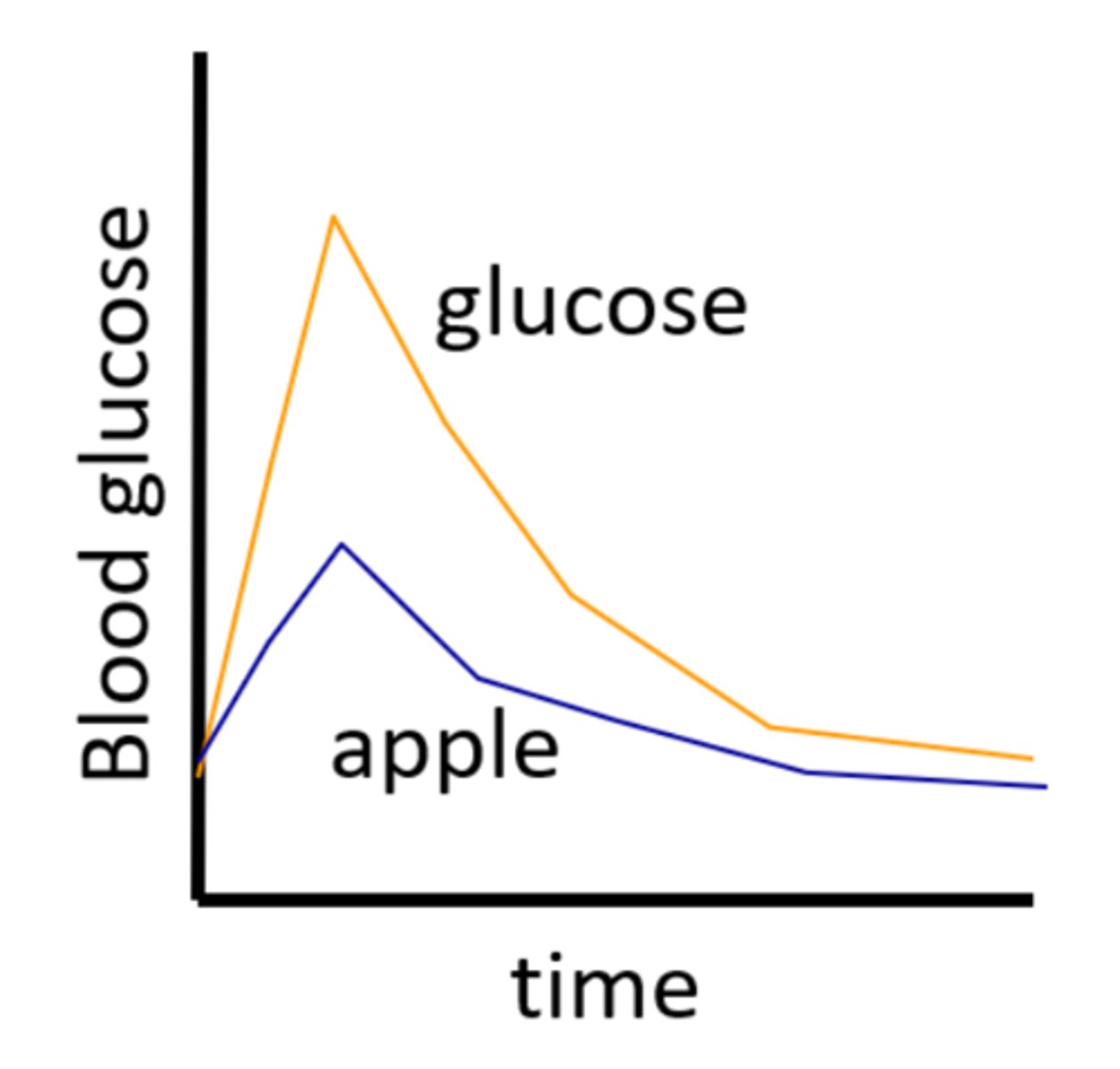
Day 1: subject consumes 50g of pure glucose, and their blood glucose response is recorded. Day 2: the same measurements are made after they consume a 50g apple. How do you then calculate the GI of the apple?
- Measurement not done properly.
-> The apple should contain 50g of available carbohydrate (has much less)
-> For valid GI testing: compare equal amounts of available carbohydrate from the reference food (glucose) and the test food (apple).
What is an example of amylose?
Fermentation in the lower bowel (fatulence).
Features of amylopectin
- A polymer of glucose with branch points
- Made of only glucose units
- Rapidly digested - branched structure allows enzymes (amylase) to work simultaneously, speeding up glucose release.
Following consumption of 50g of glucose, what [blood glucose] would indicate that a person was glucose intolerant?
>8 mM after 120 minutes
Which of the following DOES NOT stimulate acetyl CoA carboxylase?
A build up of the lipogenic product.
What are some factors that stimulate acetyl CoA?
- High [citrate] in the cytoplasm signalling a high energy change.
- Dephosphorylation by a protein phosphatase.
- The binding of insulin to receptors on the cell surface.
What is the primary purpose of acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACC)?
It activated acetyl CoA for lipogenesis.
- It activates acetyl-CoA for lipogenesis.
-> Converts acetyl-CoA into malonyl-CoA, activating it for lipogenesis (fatty acid synthesis) - Essential for building fatty acids.
-> The required reducing power (NADPH) comes from the pentose phosphate pathway.
Where does the oxidation of acetyl CoA to make ATP?
Inside mitochondria.
Esterification requires glycerol 3-phosphate which comes from?
Glucose going down glycolysis.
What is the final step of fat (triglyceride) synthesis?
The attachment of fatty acids to the glycerol backbone.
When does the Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP) make NADPH (reductant needed to build fatty acids)?
As G6P is made into 5-carbon sugar phosphates.
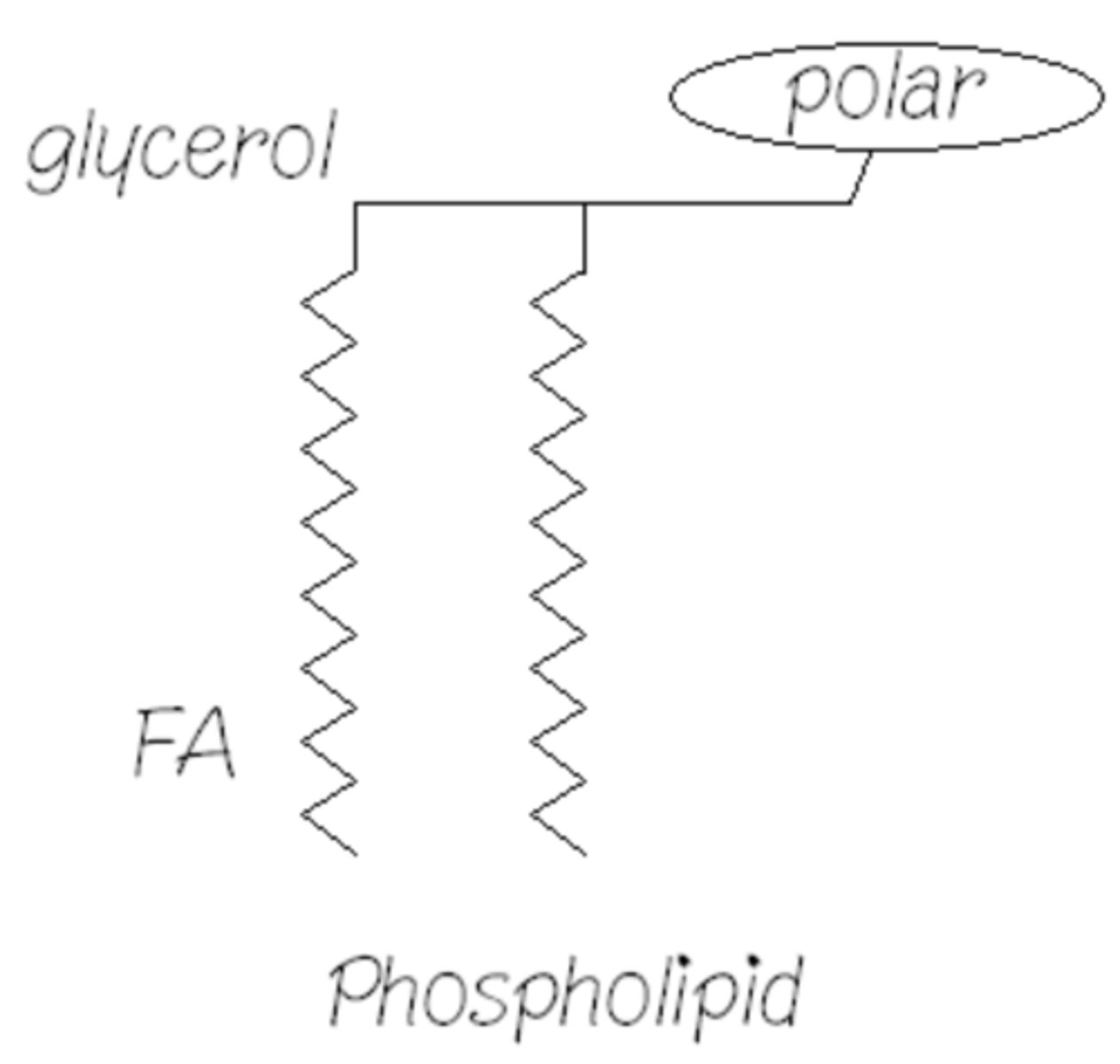
How do molecules like this help fat metabolism?
They can form monolayer shells around lipid.
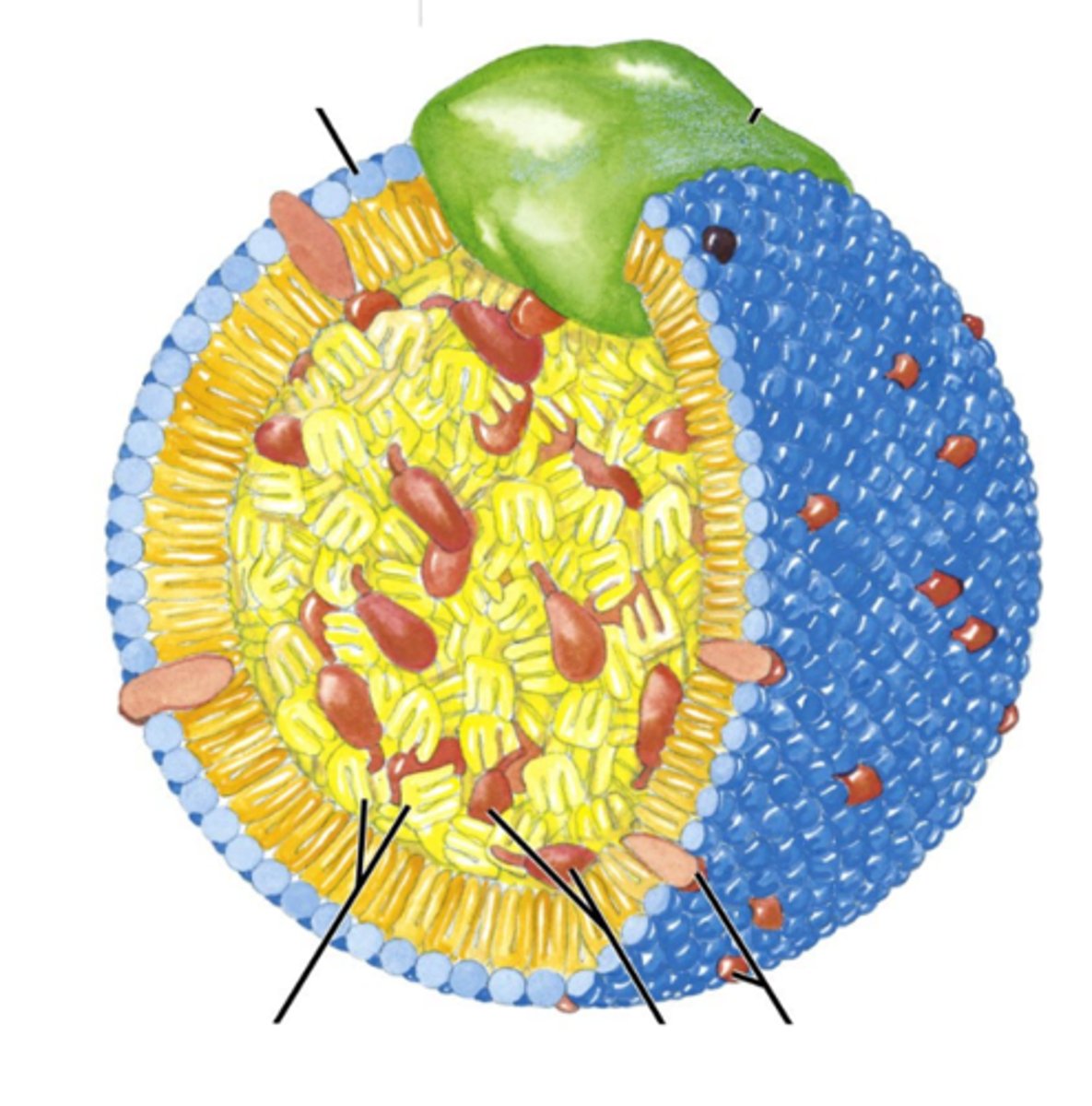
Which statements about this picture of a lipoprotein are correct?
The yellow inside is hydrophobic.
The type of lipoprotein is partially defined by the green blob.
The green blob is an apoprotein.
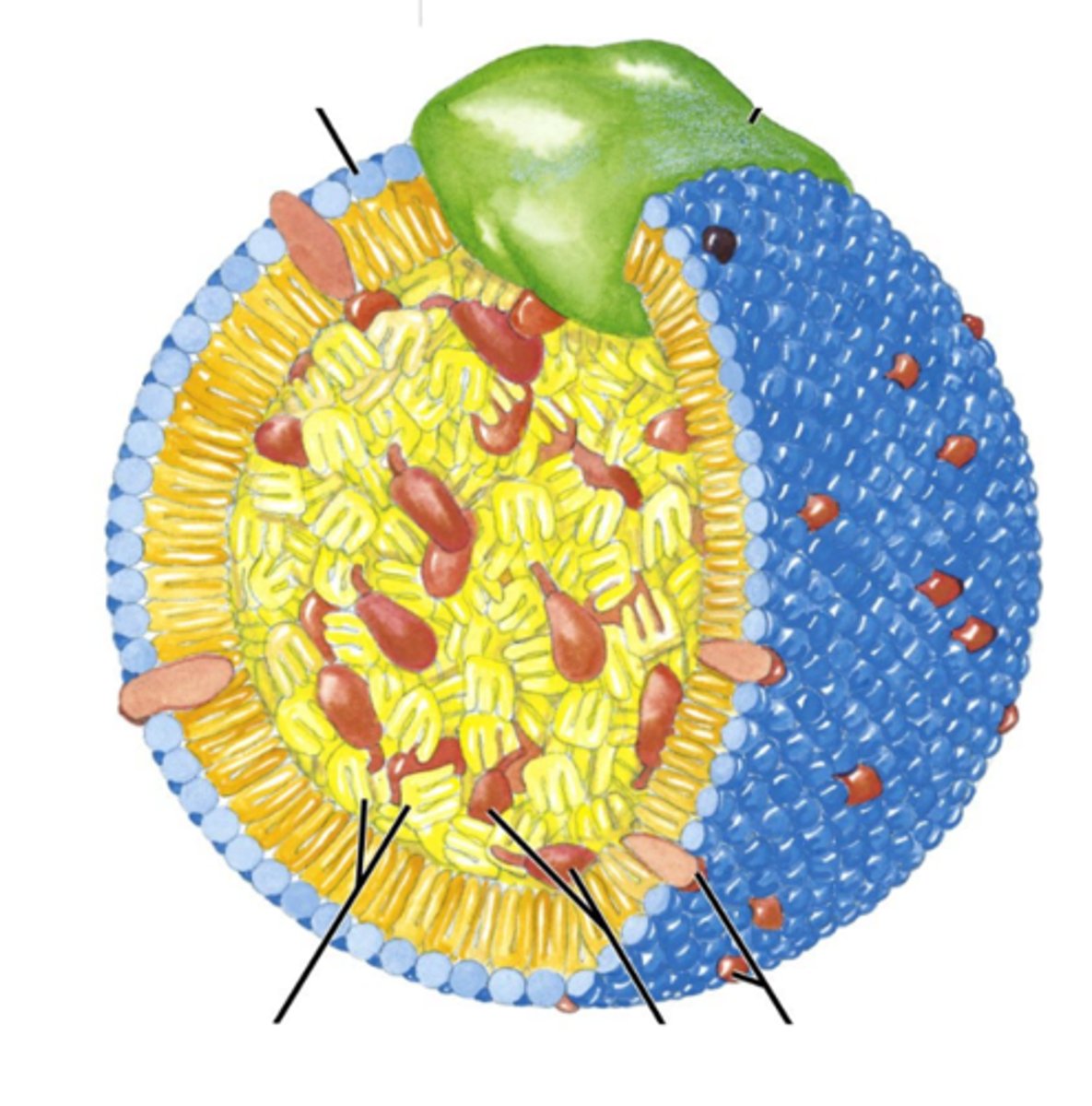
In this picture, is the blue shell a phospholipid bilayer?
No
Why does blood plasma appear cloudy/milky a couple of hours after consuming a fatty meal?
Increased levels of lipoproteins (mainly chylomicrons) - which transport dietary fats through bloodstream.
Eventually, the ability of beta-cells to respond to a glucose load, referred to as glucose stimulated insulin secretion or GSIS, can become so diminished and this blunted ineffective response ultimately leads to X. What is X?
Insulin resistance
- Beta cells are making a lot of insulin, but the tissues are no longer responding to insulin and cannot maintain blood-glucose concentration.
What is the role of chylomicrons in fat metabolism?
Responsible for transporting dietary lipids from the intestines to other parts of the body.
What is the importance of cholesterol in a cellular membrane?
Balance membrane fluidity and integrity
How does nitrogen metabolism interact with energy metabolism under conditions of starvation?
Amino acids are catabolised to produce energy and maintain glucose levels.
What is the most important metabolic function of a cell?
Maintaining ATP levels
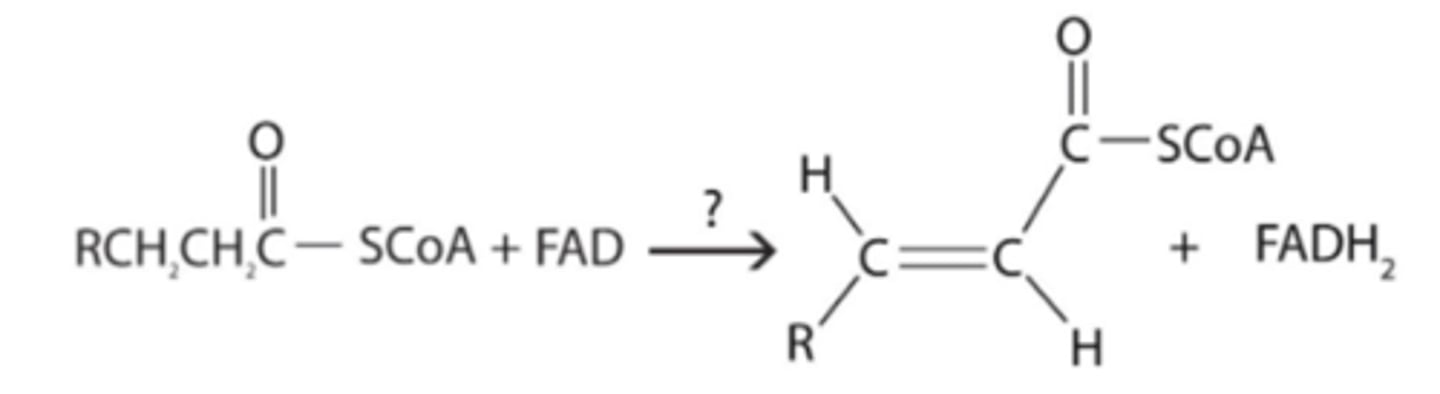
What type of enzyme catalyses the reaction shown below?
Dehydrogenase
-> Substrate-H2+FAD→Product (double bond)+FADH2
-> Substrate loses 2 hydrogens (characteristic of beta-oxidation)
How many acetyl CoA, FADH2 and NADH are formed by the complete beta-oxidation of an 18-carbon saturated fatty acid?
9 acetyl CoA
8 FADH2
8 NADH
Which of the following does happens when the uncoupler DNP is added to muscle tissue performing oxidative phosphorylation coupled to the oxidation of fatty acids?
- Proton gradient dissipates
- Rate of ATP synthesis decreases
- Rate of beta oxidation increases
When the uncoupler DNP is added to muscle tissue performing oxidative phosphorylation coupled to the oxidation of fatty acids, does the rate of oxygen consumption stop?
No
What are the rules regarding oxidative phosphorylation and ATP synthesis?
- When protons re-enter the matrix through ATP synthase, ADP is consumed.
- Proton re-entry into the matrix and ATP synthesis must occur at the same time.
- Movement of hydrogens/electrons down the electron transport chain can only occur if protons are simultaneously being pumped through the matrix.
True or false (regarding oxidative phosphorylation): The higher the proton gradient, the faster electron transport occur.
False
What factors improve an athlete's sprinting ability?
- Efficient release of lactate into the blood
- Increased endogenous glycogen availability
- Increased levels of glycolytic enzymes
Would an increased number of mitochondria in muscle cells improve an athlete's fast sprinting ability?
No
Humans produce heat using which natural uncoupling agent?
Thermogenin (UCP-1) - found only in brown adipose tissue.
Is lactate formed ONLY under aerobic or anaerobic conditions?
No - can occur in both aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis depending on the cell's energy needs and environment.
The NAD+ generate to keep glycolysis going is generated by transporting pyruvate into the mitochondria. True or false.
False - transporting pyruvate into the mitochondria does not regenerate NAD+.
Cells that lack mitochondria (such as red blood cells) are unable to convert pyruvate to lactate. True or false?
False - RBCs must convert pyruvate to lactate in order to produce energy and regenerate NAD+.
Which of the following statements about glycolysis is true?
- In the absence of oxygen, the formation of lactate is essential to keep glycolysis going.
- Needs NADP+ in the cytoplasm - cannot move it in and out of the mitochondria. Only way to acquire more NADP+ is by reducing pyruvate to lactate - helps oxidise NADH back into NAD+.
The rate of fuel oxidation in the Krebs Cycle is mostly influenced by...
The cellular demand for ATP.
An anabolic pathway uses compounds "X" and "Y" to produce compounds "A" and "B". Which of the following statements is true?
The conversion of A & B to X & Y would be a catabolic pathway.
What is most likely to limit the rate of fuel oxidation in resting muscle tissue?
The availability of oxidised NAD+
Compared to resting muscle cells, actively contracting muscle tissue has:
A higher rate of NAD+/NADH turnover.
After consuming a meal containing carbohydrates, glucose is taken up into tissues via:
Movement of GLUT-4 transporters to the cell surface in white adipose tissue.
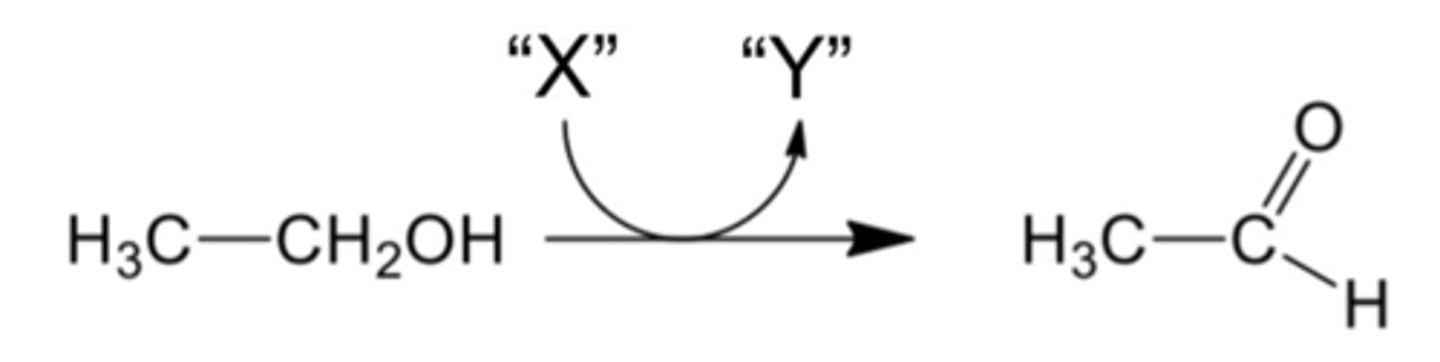
What cofactors are represented by "X" and "Y" in the reaction shown below?
NAD+ and NADH.
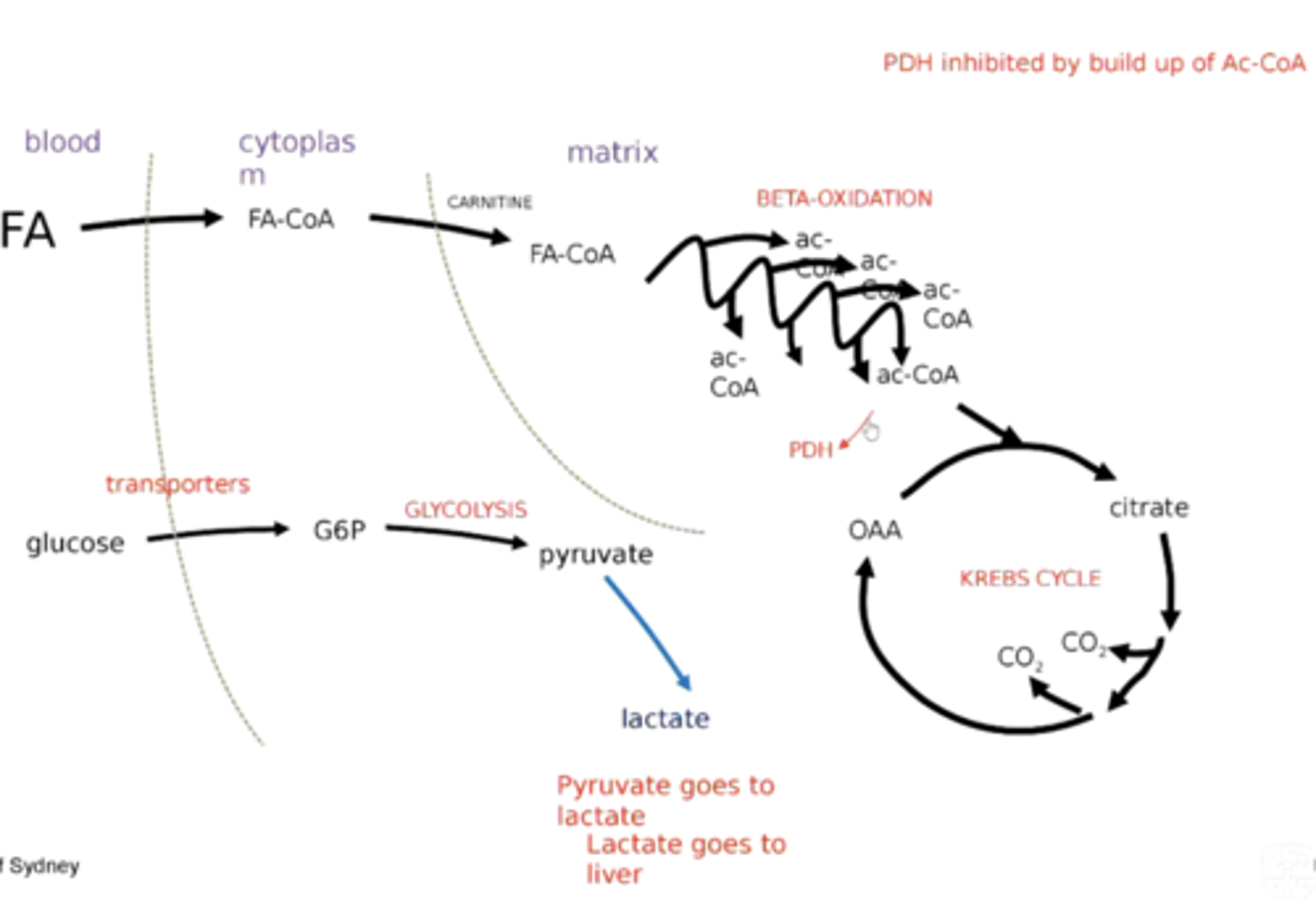
Fatty acids and carbohydrates are two major fuels that can undergo complete oxidation to form CO2. What is common to both processes?
- Acetyl CoA is an intermediate in the oxidation pathway
- Requires availability of NAD+
- Trapped in the cytoplasm following transport from the bloodstream
Fatty acids and carbohydrates are two major fuels that can undergo complete oxidation to form CO2. Is direct generation of ATP in the cytoplasm common to both?
No:
- Carbohydrates (via glycolysis) generate ATP in the cytoplasm through substrate-level phosphorylation.
- Fatty acid oxidation occurs entirely in the mitochondria - thus does not produce ATP directly in the cytoplasm.
If a patient has a genetic defect in the carnitine shuttle system, what would be the most immediate metabolic consequence?
Decreased fatty acid oxidation.
Which of the following best explains why muscle cells preferentially use fatty acids over glucose for ATP production during moderate exercise?
Fatty acids are providing more acetyl-CoA than is being demanded in the Kreb's cycle under these conditions.
How do alternative pathways of electron transfer, such as those involving the glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle, contribute to cellular metabolism?
They provide the means to regenerate NAD+ in the cytosol.
What is lipogenesis?
Formation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA
Lipogenesis, like other anabolic pathways, needs ATP. However, it also needs something else. What is that thing and where does it come from?
NADPH from the Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Which fact about PDH and lipogenesis is INCORRECT?
a) PDH is stimulated when insulin binds to fat cells
b) PDH provides thesubstrate for lipogenesis
c) PDH is active when it is phosphorylated
d) Insulin stimulates PDH phosphatase
c) PDH is active when it is phosphorylated
Correct answer - PDH is active when it is dephosphorylated.
Eukaryotic genomes have higher proportions of protein coding genes. True or false?
False
Only eukaryotic cells have ribosomes. True or false?
False
Only eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. True or false?
True
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes have different building blocks of DNA. True or false?
False
What happens in cells during genetic information flow?
DNA → DNA (Replication)
DNA → RNA (Transcription)
RNA → DNA (Reverse transcription — in viruses)
RNA → RNA (RNA replication — in RNA viruses)
RNA → Protein (Translation)
Can synthesis of protein from a DNA template occur in cells?
No - DNA needs to be copied into RNA copy of DNA. RNA needs to be processed before it is made into protein.
Can the synthesis of RNA from a protein template occur?
No
Which RNA is the most abundant in the transcriptome by weight?
Ribosomal RNA
What are the base pairs found in DNA?
Adenine-Thymine (2 H bonds)
Guanine-Cytosine (3 H bonds)
What are the interactions between complementary bases in DNA?
Hydrogen bonds - between base pairs
Where are phosphodiester bonds present in DNA?
- Present in backbone of DNA (holds strand together).
- These are covalent bonds
Where are ionic interactions present in DNA?
Around the phosphate backbone - not the bases.
Are these molecules hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Ring structure with conjugated double bonds = hydrophobic.
Is glucose hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Glucose has a ring structure, but not double bonds.
Thus is hydrophilic.
Are the bases in DNA and RNA joined by phosphodiester bonds?
No - phosphodiester bonds join the sugars in the sugar-phosphate backbone.
What does accessing genetic information in DNA rely on?
- The specificity of base pairing
- Backbone structure
- Ability to separate and re-anneal strands
Why is it important that DNA strands are antiparallel?
Crucial for replication and enzyme activity.
Where are nucleotides added during DNA or RNA synthesis?
To the 3′ OH group of the growing strand
What happens to the phosphates during nucleotide addition?
Two phosphates are released as pyrophosphate, which is hydrolyzed to release energy - to support unfavourable reaction.
What provides the energy for nucleotide addition?
Hydrolysis of pyrophosphate provides the energy for this unfavourable reaction
How is the lagging strand synthesised?
In Okazaki fragments, in the direction opposite to the replication fork
What happens to DNA when it is unwound?
It creates positive supercoiling, which inhibits replication
How is positive supercoiling relieved during replication?
By Topoisomerase II
Why is fidelity important during replication?
To ensure accuracy, using proofreading to prevent mutations
Why must the genome be copied only once?
To preserve genetic stability and prevent duplication errors
What is a key property of RNA in cells?
RNA is short-lived and only transcribed when needed
Which enzyme separates the two DNA strands at the replication fork?
Helicase
Which enzyme synthesises RNA primers during DNA replication?
Primase
hich enzyme adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strand during replication?
DNA Polymerase III - adds DNA nucleotides to the 3′ end of the new strand
What ensures the separated single DNA strands remain stable and open?
Single-stranded-binding proteins (SSB) bind and stabilise exposed DNA strands
Which enzyme relaxes DNA supercoiling as it unwinds ahead of the fork?
Topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase)