Nuclear Imaging Modalities for Cardiac Amyloidosis
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards on key vocabulary and concepts related to nuclear imaging modalities for cardiac amyloidosis.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Amyloidosis
A heterogeneous group of diseases characterized by the deposition of insoluble extracellular fibrillary proteins in the heart and other organs.
Cardiac Amyloidosis
The deposition of insoluble amyloid fibrils in the myocardium, leading to restrictive cardiomyopathy and heart failure.
Scintigraphy
A noninvasive imaging method used to diagnose cardiac amyloidosis and evaluate disease burden.
Endomyocardial Biopsy (EMB)
The gold standard procedure for the definitive diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis.
ATTRm Amyloidosis occurs
in an autosomal dominant fashion
ATTRm amyloidosis leads to
familial amyloidotic cardiomyopathy (FAC) or familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (FAP)
What is the exact prevalence of FAC
unknown the exact prevalence of FAC but pooled data shows up to 3.9% of African Americans are heterozygous carriers of the amyloidogenic allele, V122I, resulting in cardiac amyloid in an age-dependent penetrant manner.
what is ATTRwt cardiomyopathy (wild type transthyretin amyloidosis)
is underdiagnosed and has been shown to have a prevalence similar to autopsy studies with as many as 30% of patients with HFpEF ≥ 75 years
what causes primary AL amyloidosis (light chain)
deposition of monoclonal immunoglobulin light chains and is associated with plasma cell dyscrasias
What is the most frequently diagnosed amyloidosis
Primary AL amyloidosis
Tc-DPD mechanism
A bone-seeking radiotracer used for identifying cardiac amyloid deposition.
Tc-PYP mechanism
A bone-seeking radiotracer that distinguishes AL amyloid from ATTR amyloid, showing high sensitivity.
123I-MIBG
An imaging agent used to evaluate cardiac sympathetic innervation in heart failure patients with class II or class III and left ventricular ejection fraction <35%.
Does MIBG undergoes enzymatic degradation
yes
Metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) is an analog to what
norepinephrine
what do MIBG and norepinephrine have in common
similar uptake and storage in sympathetic nerve endings
When I231 is coupled with MIBG what is possible
evaluation of cardiac sympathetic function
18F-Fluorbetapir
An FDA-approved tracer for imaging β-amyloid plaques, currently being studied for cardiac amyloidosis.
Myocardial Uptake Patterns
Categories that include absent, focal, diffuse, or focal on diffuse uptake of radiotracers in cardiac imaging.
Amyloid can infiltrate the heart resulting in what
restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and atrial and ventricular arrhythmias
True or False: planar or SPECT can be used for amyloid image
true
are there approved cardiac amyloid tracers
no
what does cardiac amyloidosis invlove
deposition of insoluble fibrils in the myocardium and is an underdiagnosed cause of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
What are the most clinically relevant cardiac involvement occurs in what
primary light-chain (AL) amyloidosis
familial transthyretin amyloidosis (mutant transthyretin, ATTRm)
senile transthyretin amyloidosis (wild-type transthyretin, ATTRwt)
Other forms of systemic amyloidosis including secondary AA amyloidosis rarely affect the heart
What do nuclear imaging modalities for cardiac amyloid allow for
for noninvasive identification of myocardial involvement
differentiating amyloid subtypes
monitoring disease burden, disease progression, and potential response to therapy
After diagnosis for cardiac amyloid what is done
additional testing with immunohistochemistry and/or sequence analysis by mass spectroscopy can identify the precursor protein.
What are some complication form EMB (endomyocardial biopsy)
include arrhythmia
perforation with pericardial tamponade
accidental arterial puncture
pneumothorax
What is the percent of EMB complication
6%
The prognosis of AL amyloidosis is related to what
the number and severity of organs involved with cardiac involvement carrying the worst prognosis
What is more progressive AL cardiac amyloidosis, ATTRm or ATTRwt
AL cardiac amyloidosis
What are the advantage of Tc-DPD
distinguish Al from ATTR amyloid
most useful at extremes of spectrum (intense uptake or absent uptake)
what are the disadvantage of Tc-DPD
not available in the US market
intermediate myocardial uptake concluded to be indeterminate significance
not useful for AL amyloid
What is the imaging modality for Tc-DPD
planer or SPECT
What is the sensitivity for Tc-DPD
100%
What is the specificity for Tc-DPD
88%
What are the advantage of Tc-PYP
potentially distinguish AL from ATTR amyloid
what are the disadvanages of Tc-PYP
limited number of studies validating use
not useful in Al amyloid
what is the sensitiivity of Tc-PYP
97%
what is the specificity of Tc-PYP
100%
what imaging modality is used for Tc-PYP
planar or SPECT
What is the mechanism for 11C-PIB
amyloid deposits
what are the advances for 11C-PIB
currently experimental and further studies warranted
what are the disadvantages of 11C-PIB
more studies needed to validate used
short half life requiring on site cyclotron and limiting use to specialized centers
What image modality is used for 11C-PIB
PET/CT
what is the mechanism of 18F-florbetaplr
amyloid deposits
what are the advantages of 18F-florbetaplr
FDA approved for identifying amyloid plaques in the brain high affinity and specificity for B-amyloid
what are the disadvantages of 18F-florbetaplr
fole in cardiac amyloidosis not established and currently in trail
what is the imaging modality used for 18F-florbetaplr
PET/CT
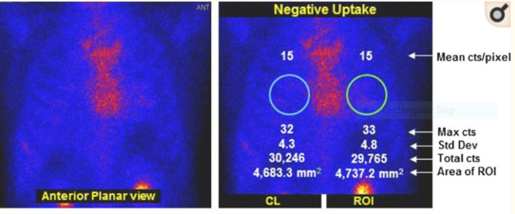
does this image show negative or positive uptake
negative
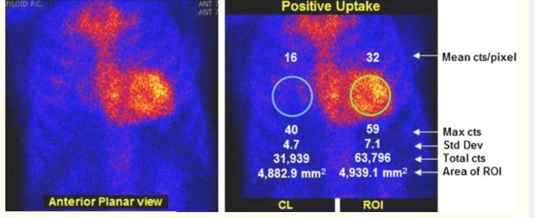
does this image show negative or positive uptake
positive
True or False: 99m Tc-PYP is readily available
true
99m Tc-PYP is available as what
unit doses from commercial radiopharmaceutical distributors or as kits for preparation
what is the total body effective does for 99m Tc-PYP
15mCi or 3.2mSv
99m Tc-PYP kits contain - or - single use vails
5 or 30
99m Tc-PYP kits are approved for
bone
cardiac (for the detection of myocardial infarction)
blood pool (radionuclide ventriculography and GI bleeding)
how much ml are in each vail for 99m Tc-PYP
10ml
99m Tc-PYP vails contain —- mg of sodium pyrophosphate and —- mg of stannous chloride and —- mg of total tin
11.9mg
3.2mg
4.4mg
is there test preparation required
no
what images are reconstructed and reviewed in standard cardiac imaging planes using commercial software
anterior and lateral planar images
rotating projection images
reconstructed SPECT images
how are myocardial 99m Tc-PYP uptake patterns categorized
absent, focal, diffuse or focal on diffuse
scans with focal 99m Tc-PYP uptake could represent what
rib fracture or previous myocardial infraction
after myocardial infraction, how long will myocardial 99m Tc-PYP uptake be positive for
7 days
What are the two approaches to quantification
quantitative
semi-quantitative
what is the quantitative approach
myocardial to contralateral lung ratio of uptake at 1 hour
the quantitative approach includes what
Circular target regions of interest (ROI) are drawn over the heart on the planar images and are mirrored over the contralateral chest to account for background and ribs (see Figure 1)
Total and absolute mean counts are measured in each ROI. A heart to contralateral (H/CL) ratio is calculated as the fraction of heart ROI mean counts to contralateral chest ROI mean counts.
for quantitative approach H/CL ratios > 1.5 at one hour indicate what
ATTR positive
or quantitative approach H/CL ratios <1.5 indicate what
ATTR negative
what is semi quantitative
visual comparison to bone(rib) uptake at 3 hours
how is cardiac uptake of 99m Tc-PYP evaluated
semiquantitative visual scoring method in relation to bone uptake
visual scores greater than or equal to 2 on planar or SPECT images at 3 hours indicate what
ATTR positive
scores less than 2 indicate what
ATTR negative
grade 2-3 or H/CL > 1.5 uptake suggest what
ATTR amyloidosis
any degree of 99mTc-PYP uptake can also be seen in AL amyloidosis, and as such a complete evaluation is warranted to exclude this diagnosis.
Semi quantitative visual grading of myocardial 99m Tc-PYP uptake by comparison to bone (rib) uptake grade 0 indicates what
no uptake and normal bone uptake
Semi quantitative visual grading of myocardial 99m Tc-PYP uptake by comparison to bone (rib) uptake grade 1 indicates what
uptake less than rib uptake
Semi quantitative visual grading of myocardial 99m Tc-PYP uptake by comparison to bone (rib) uptake grade 2 indicates what
uptake equal to rib uptake
Semi quantitative visual grading of myocardial 99m Tc-PYP uptake by comparison to bone (rib) uptake grade 3 indicates what
uptake greater than rib uptake with mild/absent rib uptake
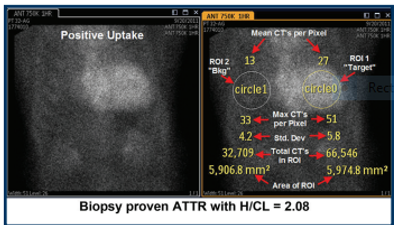
what quantifying method was used in this image
quantitation of cardiac 99m Tc-PYP uptake using heart to contralateral lung (h/CL) ratio
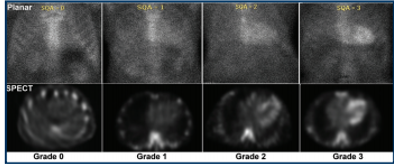
what quantifying method was used in this image
grading 99m Tc PYP uptake on planar and SPECT images
What is the patient preparation using 99m Tc-PYP
none
what scan is being done using 99m Tc-PYP
rest scan
what is the dose for 99m Tc-PYP
10-20mCi intravenously
what is the recommended time between injection and acquisition using 99m Tc-PYP
1 hour for SPECT and planar
3 hour SPECT and planar optional
what is the field of view for 99m Tc-PYP
recommended: cardiac or chest
optional: whole body planar
imaging type for 99m Tc-PYP
cardiac or chest SPECT and planar imaging
patient position for 99m Tc-PYP
supine
what is the energy window for 99m Tc-PYP
140keV, 15-20%
what collimator is used for 99m Tc-PYP
low energy, high resolution
what is the matrix size for 99m Tc-PYP
64×64
what is the pixel size for 99m Tc-PYP
3.5-6.5mm
what views are being taken using 99m Tc-PYP for planar
anterior. lateral, and left anterior oblique
what is the detector configuration for 99m Tc-PYP planar images
90 degrees
image duration (number of counts) for 99m Tc-PYP planar images
750,000 counts
what is the magnification for 99m Tc-PYP planar images
1.46
what is the angular range for 99m Tc-PYP SPECT imaging
360 degrees
what is the detector configuration for 99m Tc-PYP SPECT imaging
189 dregrees
what is the ECG gating for 99m Tc-PYP SPECT imaging
off: nongated imaging
number of views/detector for 99m Tc-PYP SPECT imaigng
40
time per stop for r99m Tc-PYP SPECT imaging
20 seconds
what is the magnification for 99m Tc-PYP SPECT imaging
1.0