Biogeochemistry of Wetlands and Soil Properties
1/225
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
226 Terms
Soil Taxonomy
Classification system for soil types and properties.
Andisols
Soils formed from volcanic ash, high in nutrients.
Alfisols
Soils with clay-rich horizons, fertile for agriculture.

Aridisols
Soils in arid regions, often saline or alkaline.
Entisols
Young soils with minimal horizon development.
Gelisols
Soils in cold climates, permafrost present.
Histosols
Organic soils, rich in decomposed plant material.
Inceptisols
Soils with weakly developed horizons, transitional.
Mollisols
Dark, fertile soils, rich in organic matter.
Oxisol
Highly weathered tropical soils, low in nutrients.
Wetland Types
Coastal and inland wetlands with distinct characteristics.
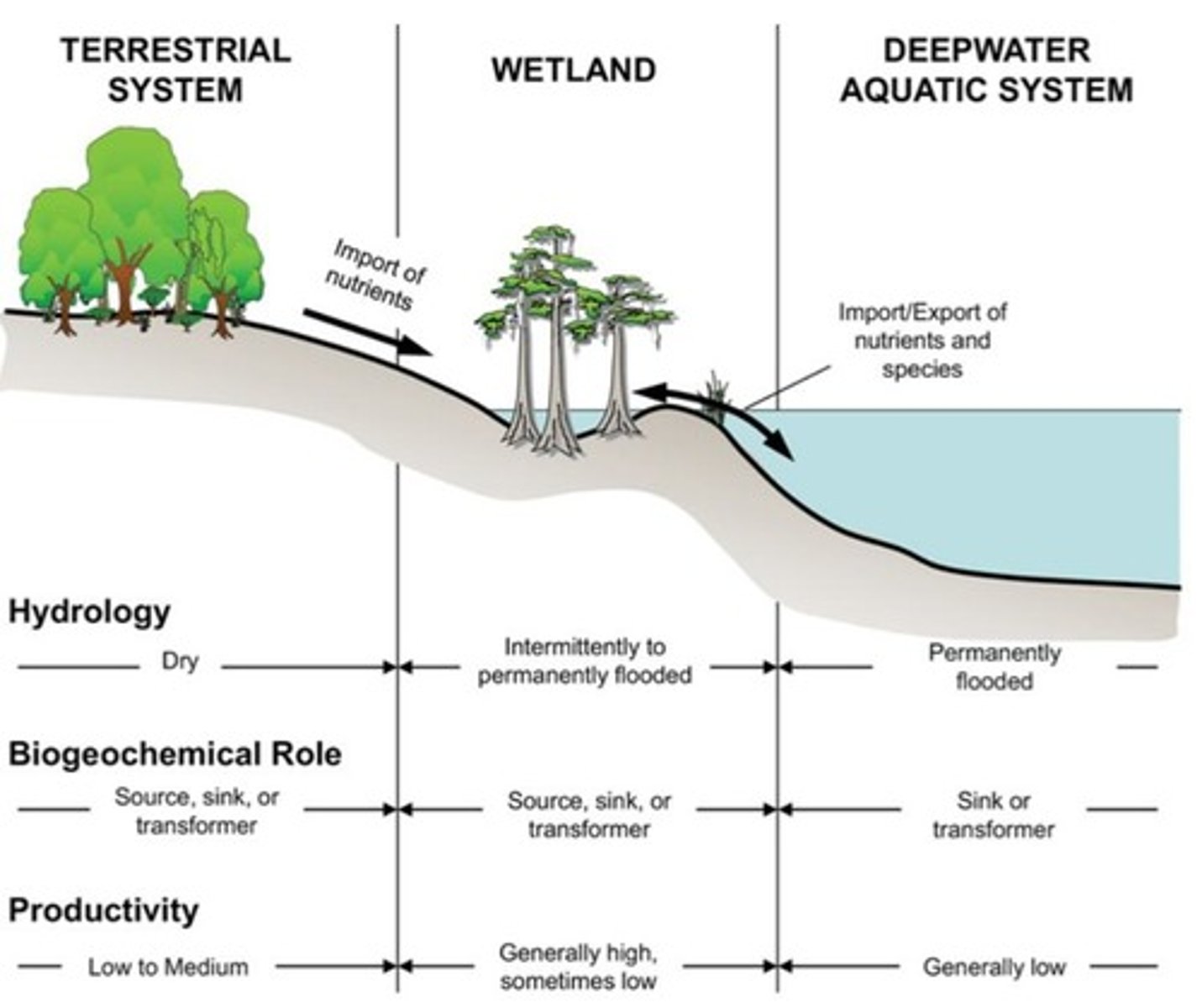
Hydric Soils
Soils saturated with water, supporting wetland vegetation.

Waterlogged Soils
Soils with excess water, affecting oxygen availability.
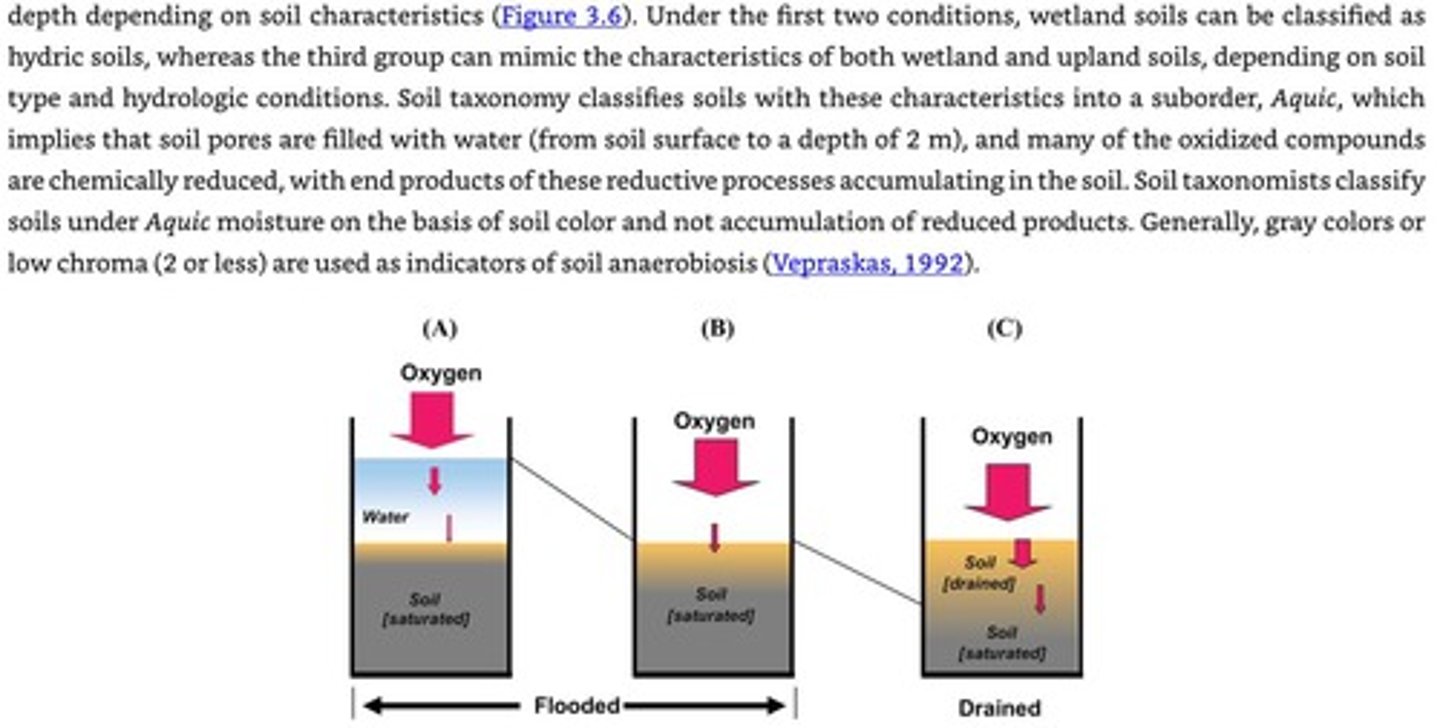
Flooded Soil
Soil submerged in water, anaerobic conditions prevail.
Upland Soils
Soils found in elevated areas, well-drained.
Biogeochemical Cycles
Recycling of nutrients between living and non-living.
Microbes
Microorganisms playing key roles in soil health.
Acrobes
Microbes requiring oxygen for survival.
Facultative Anaerobes
Microbes that can survive with or without oxygen.
Anaerobes
Microbes that thrive in oxygen-free environments.
Organic Soils
Soils containing significant amounts of organic material.
Peatlands
Wetlands with accumulated peat, rich in carbon.
Chemical Reactions
Transformations involving reactants to products.
Proton Exchange
Reactions where protons (H+) are transferred.
Electron Exchange
Reactions where electrons (e-) are transferred.
Proton and Electron Transfer
Reactions involving both protons and electrons.
Oxidation
Loss of electrons from an atom or molecule.
Reduction
Gain of electrons by an atom or molecule.
Oxidizing Agent
Substance that accepts electrons in a reaction.
Reducing Agent
Substance that donates electrons in a reaction.
Nernst Equation
Calculates redox potential based on concentration.
Redox Potential (Eh)
Measure of tendency to gain or lose electrons.
pH
Measure of acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
Redox Couples
Pairs of oxidizing and reducing agents.
Soil Oxygen Demand
Amount of oxygen required for microbial activity.
Specific Conductance
Ability of water to conduct electricity.
Diel Changes
Daily fluctuations in environmental conditions.
Electrochemical Properties
Characteristics related to electron transfer reactions.
Wetland Soils
Soils saturated with water, influencing redox reactions.

Combustion Reaction
Exothermic reaction producing heat and light.
Displacement Reaction
One element replaces another in a compound.
Synthesis Reaction
Two or more substances combine to form one.
Decomposition Reaction
Single compound breaks down into two or more products.
Aerobic Respiration
Process of producing cellular energy with oxygen.
Oxidation
Loss of electrons in a chemical reaction.
Reduction
Gain of electrons in a chemical reaction.
Oxidant
Substance that gains electrons, causing oxidation.
Reductant
Substance that loses electrons, causing reduction.
Nernst Equation
Calculates electrode potential based on concentration.
Eh
Electrode potential measured in volts.
Eo
Standard electrode potential under standard conditions.
Faraday's Constant
Amount of charge per mole of electrons.
Gas Constant
Constant relating energy, temperature, and volume.
Oxidation-Reduction Potential
Measure of tendency to gain or lose electrons.
Nitrate Respiration
Process of reducing nitrate to nitrogen gas.
Sulfate Respiration
Process of reducing sulfate to sulfide.
Anaerobic Conditions
Environment lacking oxygen, promoting reduction reactions.
Aerobic Conditions
Environment with oxygen, promoting oxidation reactions.
Wetland Soil
Soil type characterized by water saturation.
Drained Soil
Soil that has been dried out.
Electron Donors
Substances that donate electrons in reactions.
Electron Acceptors
Substances that accept electrons in reactions.
Energy Release
Energy produced during oxidation-reduction reactions.
Hydrogen Ion (H+)
Proton involved in acid-base reactions.
Temperature (T)
Measured in Kelvin for Nernst equation.
Oxides
Compounds formed by oxygen and another element.
Mn(IV)
Manganese in the +4 oxidation state.
Fe(III)
Iron in the +3 oxidation state.
Electrode Potentials
Voltage associated with half-cell reactions.
Ease of Reduction
Relative ability of a substance to gain electrons.
Oxidation-Reduction
Reactions involving electron transfer between species.
Mn4+
Manganese ion in the +4 oxidation state.
Mn2+
Manganese ion in the +2 oxidation state.
Se(0)
Elemental selenium in its neutral state.
SeO4
Selenium in the +6 oxidation state.
Redox Potential (mV)
Measure of tendency to gain or lose electrons.
Iron Redox Couple
Equilibrium between Fe2+ and Fe3+ states.
Eh
Redox potential measured in millivolts.
Nitrate Reduction Zone
Soil layer where nitrate is reduced.
Sulfate Reduction Zone
Soil layer where sulfate is reduced.
Methanogenesis
Anaerobic process producing methane from organic matter.
Electron Acceptors
Substances that gain electrons during redox reactions.
Electron Donors
Substances that lose electrons during redox reactions.
Redox Gradients
Variations in redox potential with depth in sediments.
Flooded Organic Soils
Soils saturated with water affecting redox processes.
Sediment Microbial Fuel Cell
Device converting chemical energy to electrical energy using microbes.
Regulators of Eh
Factors influencing redox potential in environments.
Redox Potential
Measure of electron transfer tendency in reactions.
Equilibrium
State where reactants and products remain constant.
Platinum Electrodes
Electrodes used for reversible redox reactions.
pH
Measure of acidity or alkalinity in solutions.
H2CO3
Carbonic acid formed from CO2 and water.
HCO3-
Bicarbonate ion, a key buffer in solutions.
Fe(OH)3
Iron(III) hydroxide, involved in redox reactions.
Flooding Effect
Impact of water saturation on soil properties.
Clay Loam
Soil type with balanced clay and silt content.
Ionic Strength
Concentration of ions in a solution.
Aerobic Respiration
Process converting glucose and oxygen to energy.
Gr (Gibbs Free Energy)
Energy change during a chemical reaction.
C6H12O6
Glucose, a primary energy source for organisms.