Chapter 6 - How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is the ultimate energy source for life?
The sun

What are the two processes that continuously work together to transfer energy in cells?
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration
What type of process is photosynthesis?
Endergonic process
Where does photosynthesis occur?
In the chloroplast using chlorophyll
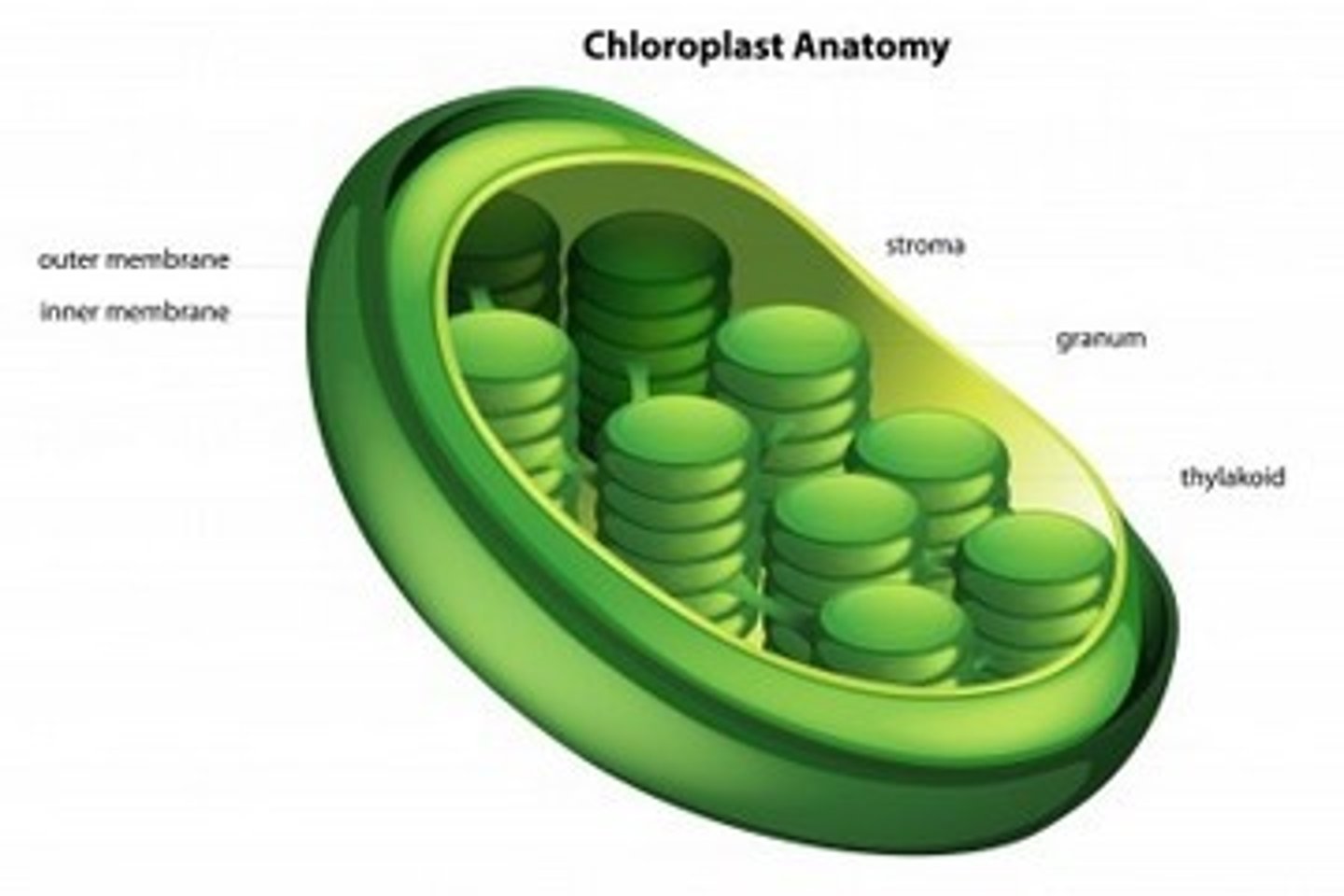
What are the reactants of photosynthesis?
CO2, H2O, and light energy
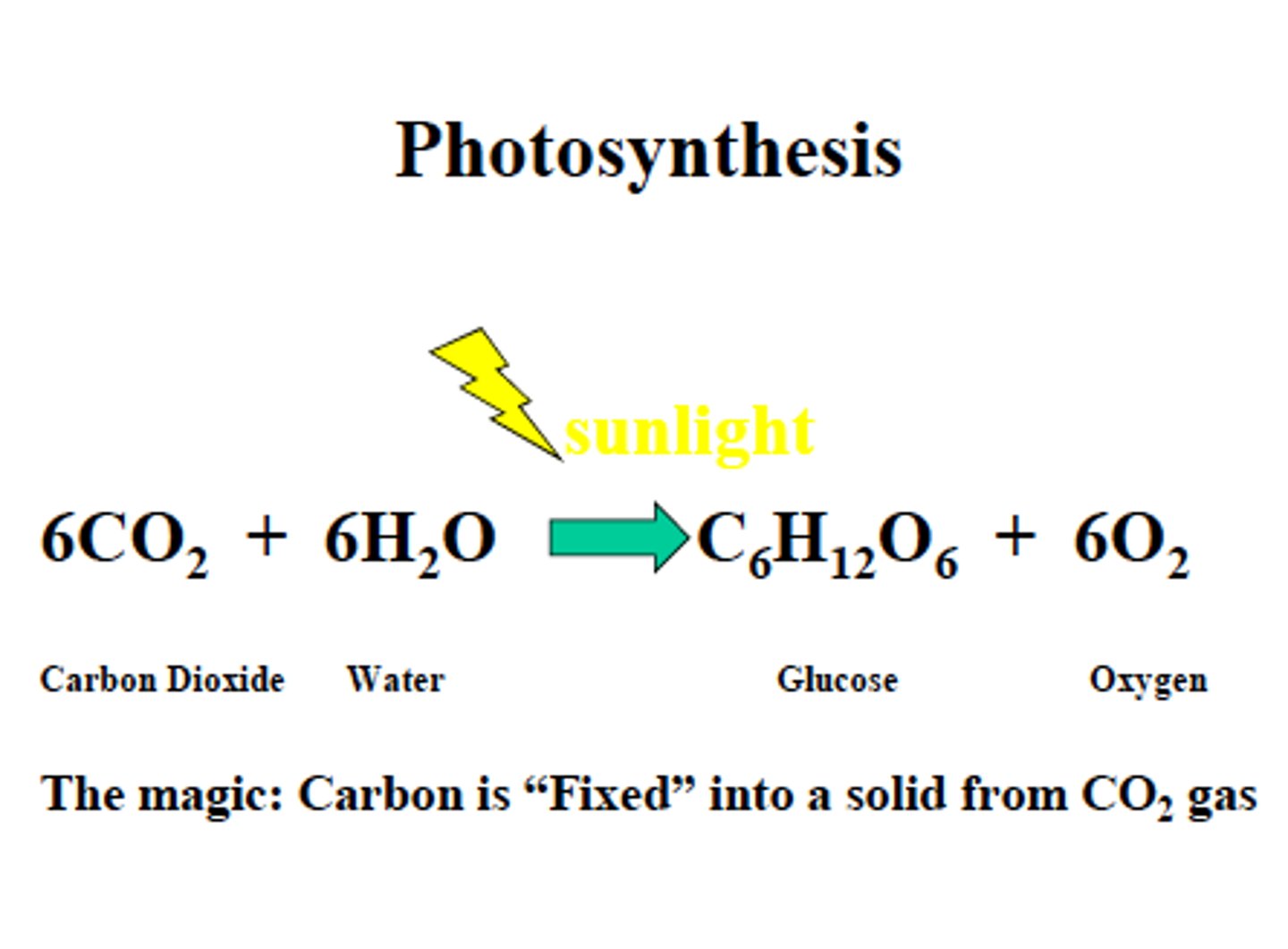
What are the products of photosynthesis?
Glucose and O2
What type of process is cellular respiration?
Exergonic process
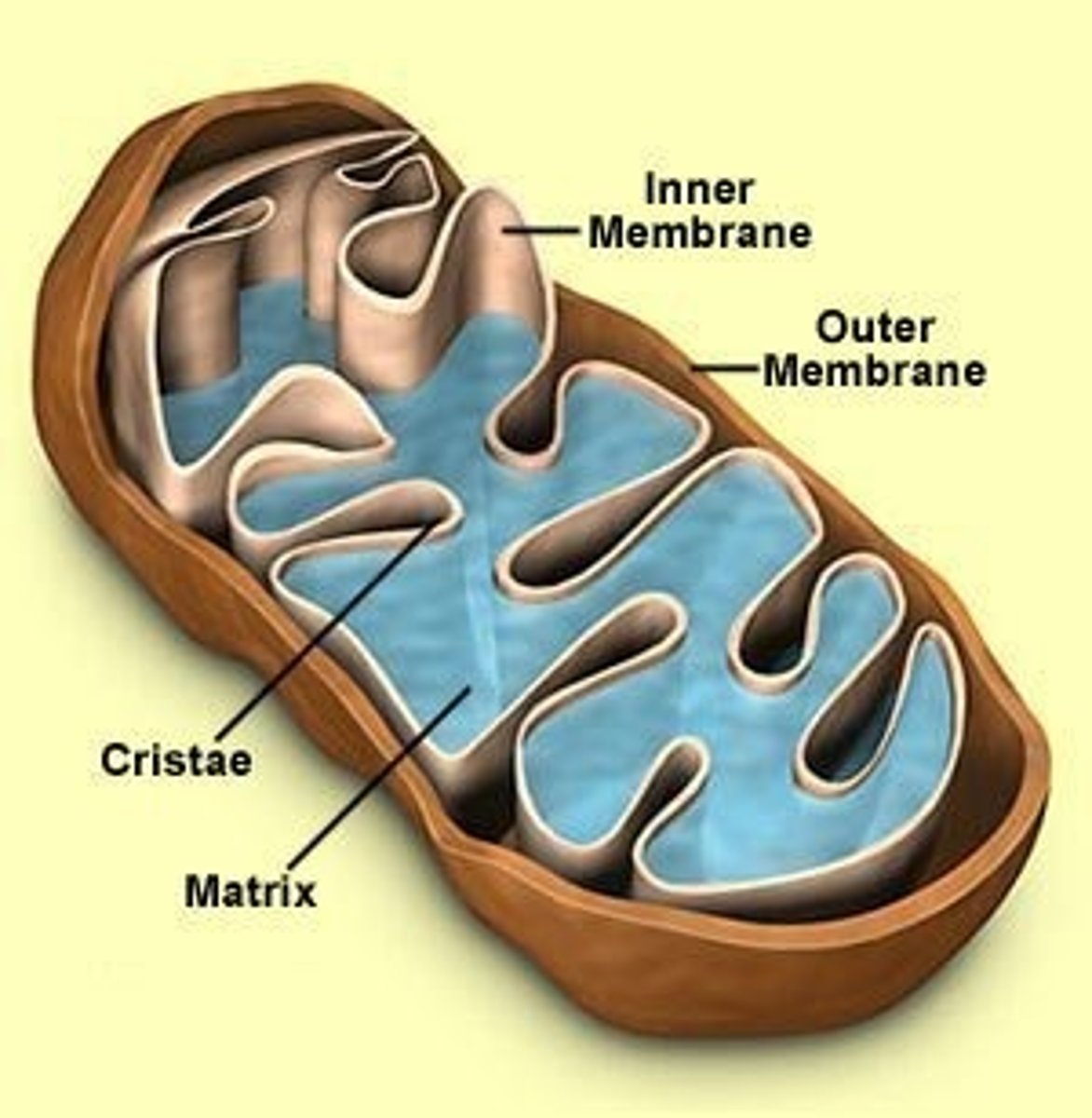
Where does cellular respiration occur?
In the mitochondria
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
Glucose and O2
What are the products of cellular respiration?
CO2, H2O, and ATP
What percentage of stored energy in glucose is converted to ATP during cellular respiration?
About 34%
What is the Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)?
The amount of energy needed to perform basic life-sustaining activities
What is the caloric value of carbohydrates per gram?
4 kcals
What is the caloric value of fats per gram?
9 kcals
What is the caloric value of proteins per gram?
4 kcals
What is the caloric value of alcohols per gram?
7 kcals
What are NAD and FAD in cellular respiration?
Coenzymes and electron carrier molecules, they allow cellular respiration to occur by constantly getting oxidized/reduced
What is glycolysis?
The first stage of cellular respiration that converts glucose into pyruvates, producing 2 ATP and 2 NADH
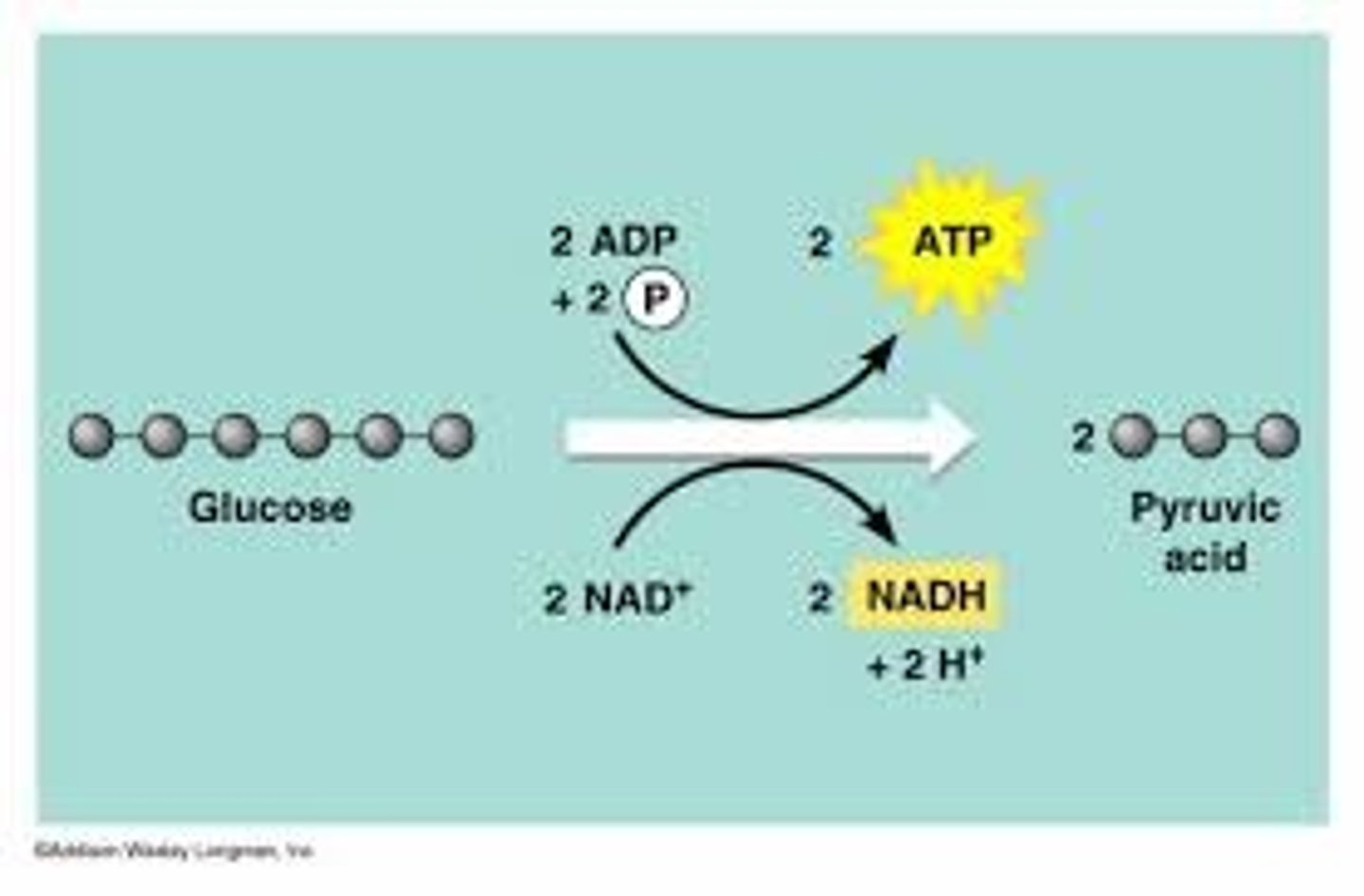
Where does glycolysis occur?
In the cytosol (cytoplasm)
What is the net ATP produced from glycolysis?
2 ATP
What is pyruvate oxidation?
The transition phase between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, producing acetyl CoA and NADH
What occurs during the Citric Acid Cycle?
Acetyl CoA is processed to produce CO2, GTP, NADH, and FADH2
What is the Electron Transport Chain (ETC)?
The final stage of cellular respiration where ATP is produced using the energy from redox reactions
What is chemiosmosis?
The process where a proton gradient is created, allowing ATP synthesis through ATP synthase
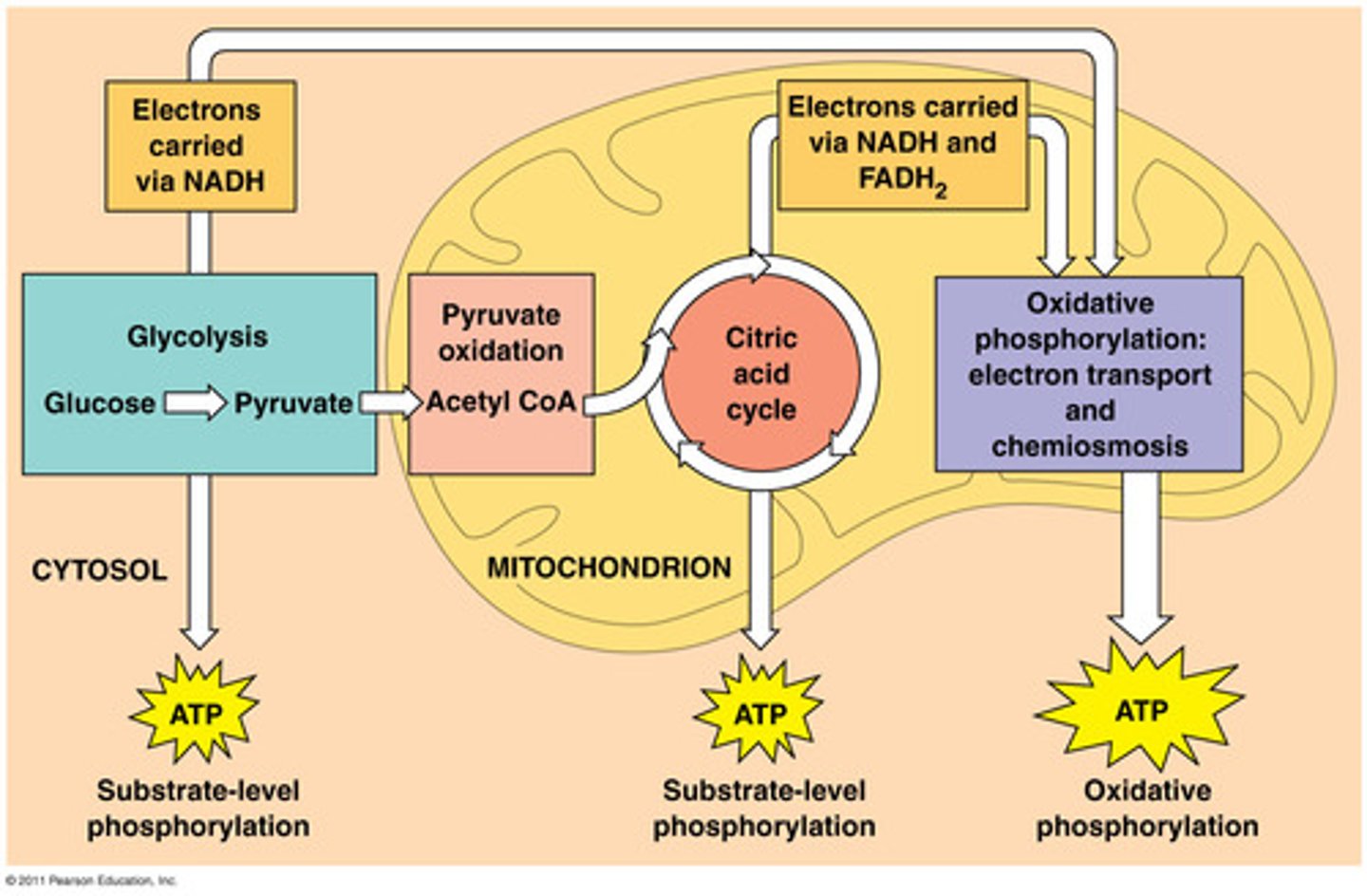
What is substrate-level phosphorylation?
The formation of ATP by directly adding a phosphate group during glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
What is fermentation?
A process that produces ATP without the need for oxygen, occurring after glycolysis
What occurs during lactic acid fermentation?
Pyruvates from glycolysis are converted into lactate
What occurs during alcoholic fermentation?
Pyruvates from glycolysis are converted into ethanol and CO2
What is the chemical formula for glucose?
C6H12O6 (numbers are subscripts)
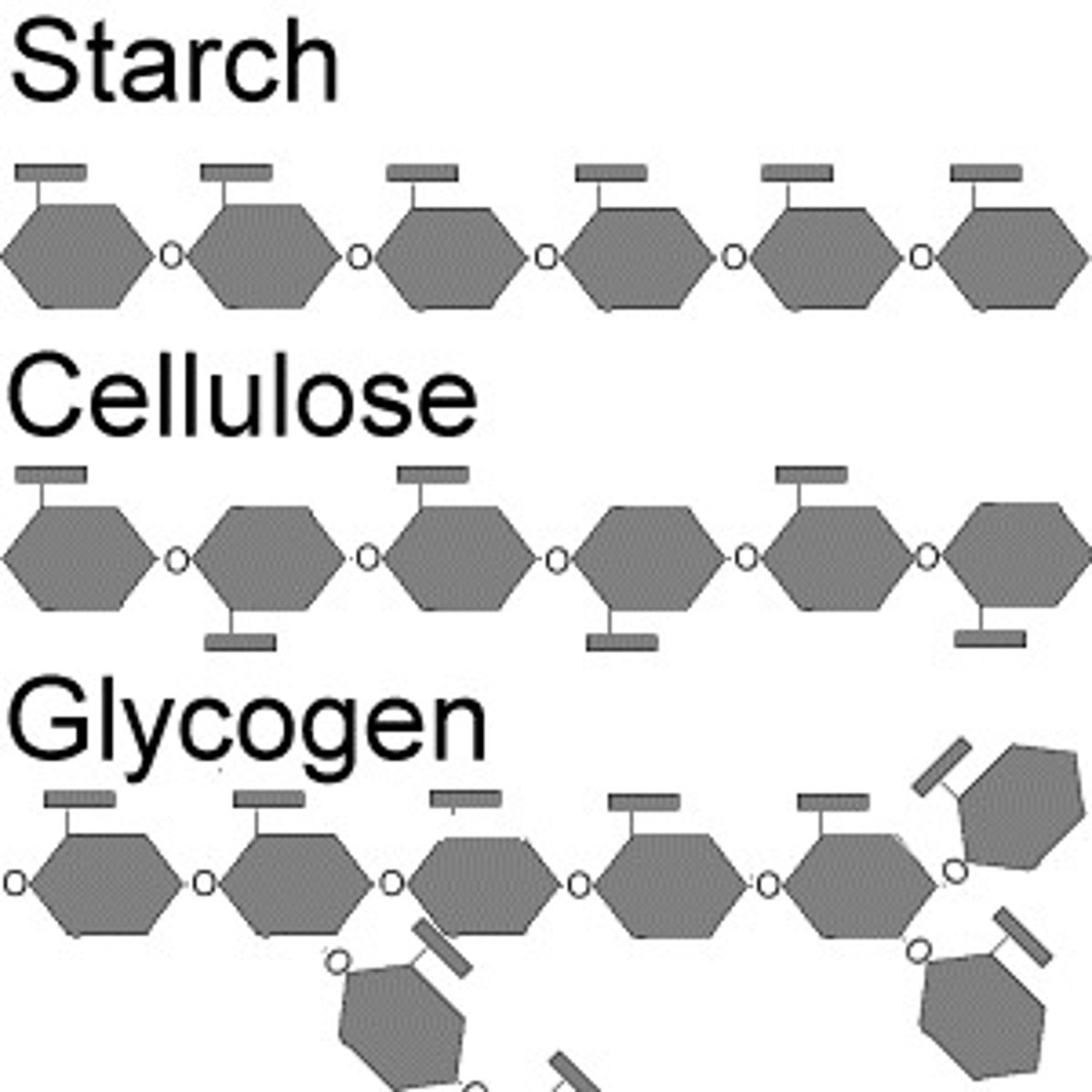
Plants convert glucose to _______ for storage
starch
Animals convert glucose to _____ for storage
glycogen
The human body uses energy from _______ to power all its cellular reactions
ATP
List the 3 major steps in cellular respiration:
1. Glycolysis
2. Citric Acid Cycle
3. Electron Transport Chain
What does aerobic mean?
The reaction requires oxygen
How much ATP will 1 NADH molecule produce?
2.5 ATP
How much ATP will 1 FADH2 molecule produce?
1.5 ATP
Where does the citric acid cycle take place?
mitochondrial matrix (inner mitochondrial membrane)
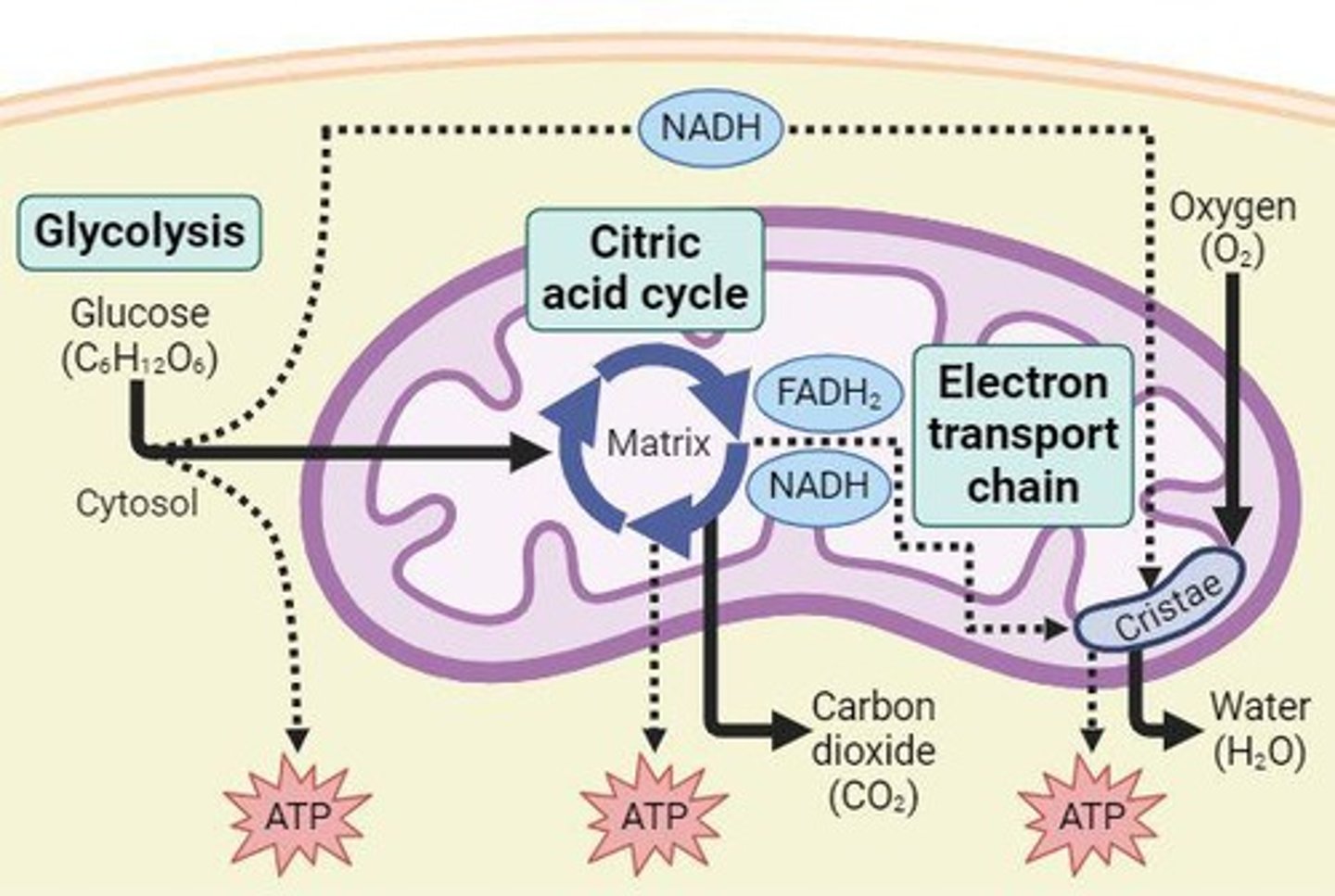
How much ATP will one glucose molecule produce overall?
32 ATP