Chap 9A - Acid-base equilibria A
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Describe arrhenius theory
(Def.): An acid is a substance that has H in its formula and dissociates in water to yield H3O+ and A base is a substance that has OH in its formula and dissociates in water to yield OH
Eg. HCI, NaOH
Chemists use H+(aq) and H3O+(aq) interchangeably = solvated H+ ion
Limitation: restricted to aqueous solutions
Rationale:
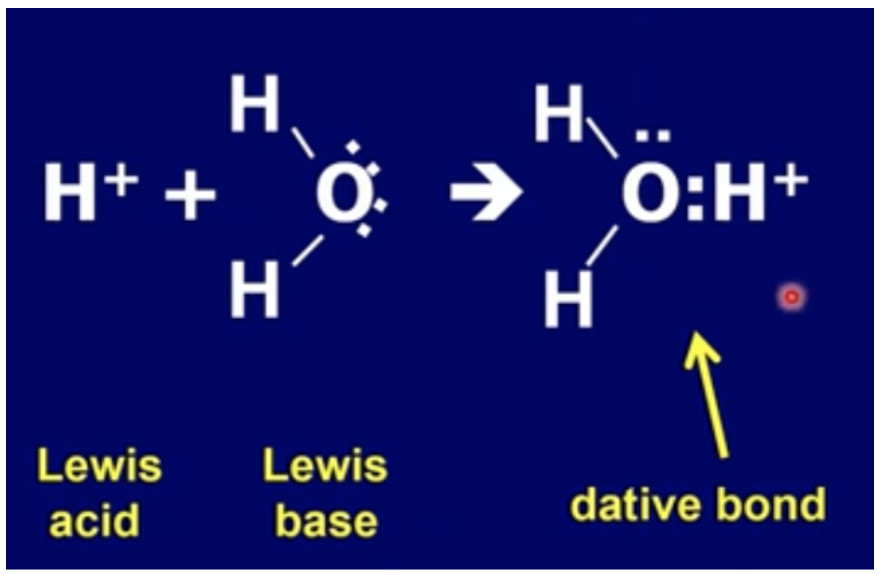
H+ is a bare proton -> very small and has a relatively high charge density -> attracts any molecule with lone pair of electrons such as H2O
In aqueous solution, a water molecule forms a dative covalent bond (coordinate bond) to the H+ ion to produce hydronium ion, H3O+
H2O(l) + H+(aq) -> H3O+(aq)
Describe bronsted-lowry theory
Acid : Any species which donates a proton , must thus contain H in its formula
Base : Any species which accepts a proton, H+ , must contain a lone pair of electrons to bind the H+ ion
A Bronsted-Lowry acid-base reaction involves the transfer of a proton from an acid to a base (can occur between gases too)
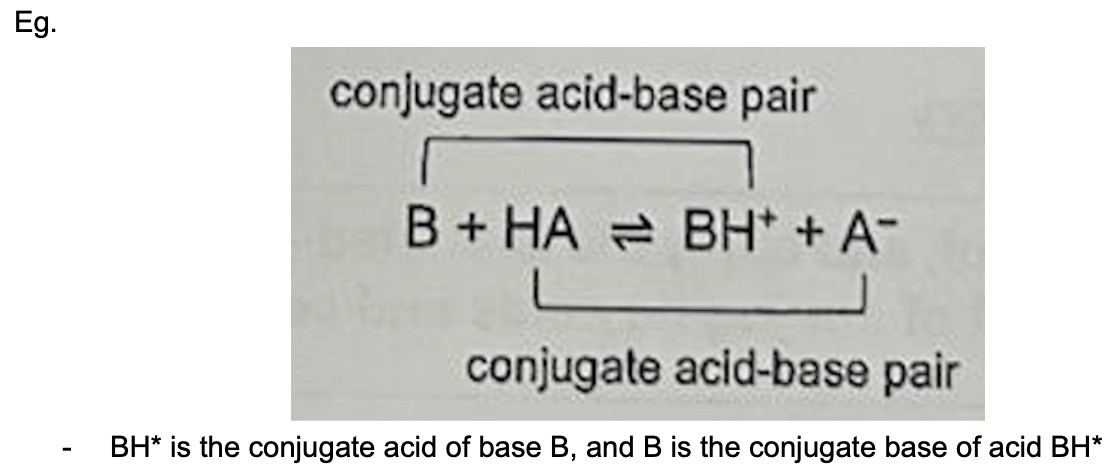
Describe conjugate acid and base
Conjugate base: Species formed after acid has donated its proton
Conjugate acid: Species formed after base has accepted a proton
Conjugate acid-base pair: 2 species that differ from each other by 1 proton
Describe lewis theory Eg. Ai(OH)3 + OH- -> Ai(OH)4
Acid : species that accepts an electron pair
Base : species that donates an electron pair
A Lewis acid-base reaction can be viewed as a transfer of a pair of electrons from the base to the acid
Ai(OH)3 + OH- -> Ai(OH)4-
AI(OH)3 accepts a lone pair of electrons from OH- to form AI(OH)4- -> AI(OH)3 is a lewis acid
NOTE:
Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis theories are often used to describe specific acid-base reactions whereas Arrhenius theory is used to describe whether isolated substances are acids, bases or neither
An Arrhenius acid / base also be a Bronsted-Lowry acid / base
A Bronsted-Lowry acid / base also be a Lewis acid / base
Draw formation of H3O+ from H+ and H2O
Describe degree of dissociation and state its equation
Strong acid and base: a = 1 (normal arrow in equation)
Weak acid and base: a < 1 (reversible arrows in equation)

Define pH and state its equation
pH (Def.): negative logarithm to base 10 of H3O+ concentration in mol dm^-3, it is the measure of the contentation of H3O+ ions in a solution (no units)

Define pOH and its equation
pOH (Def.): negative logarithm to base 10 of OH- concentration in mol dm^-3, it is the measure of the contentation of OH- ions in a solution (no units)
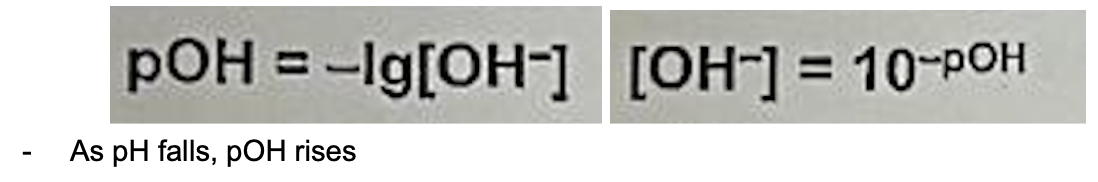
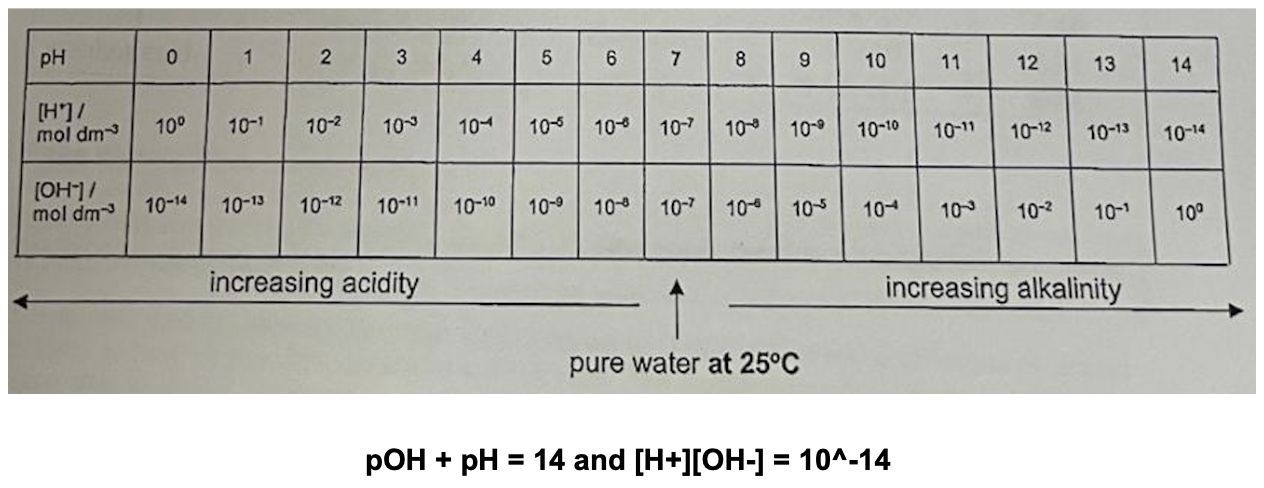
Describe relationship between pH, H+ and OH-
Describe pH meter
Electronic instrument that measures the potential difference (voltage) between a reference electrode and an electrode whose voltage varies with the concentration of H+ (aq) in an aqueous solution
The measured voltage is converted to pH values so that the scale of the meter can be read directly in pH
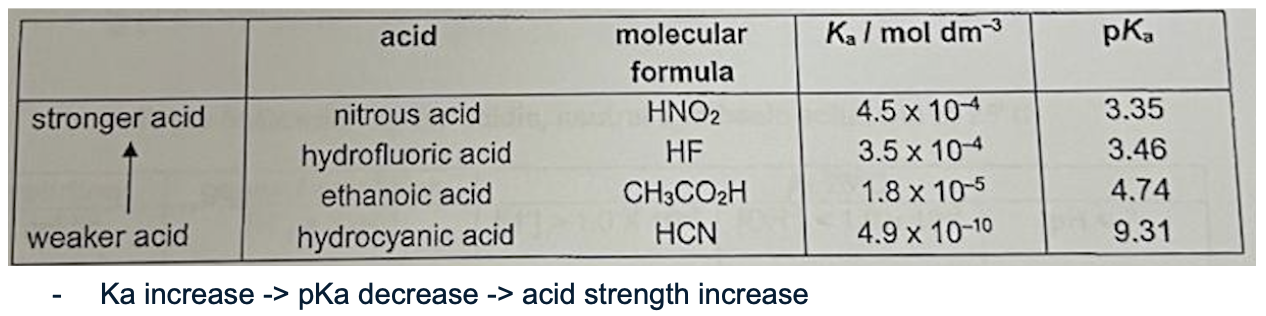
Describe Ka and state its equation
Units: mol dm^-3
Constant at constant temperature
Measures strength of acid
Larger the Ka (smaller the pKa) -> stronger the acid

Describe [H2O] in dilute aq solutions
[H2O] is constant (~55.6 mol dm^-3) in dilute aqueous solutions and has been incorporated into the equilibrium constant Ka -> omitted from the equilibrium constant expression
Describe Ka and the 4 acids u need to know
Describe Kb and its equation
Units: mol dm^-3
Constant at constant temperature
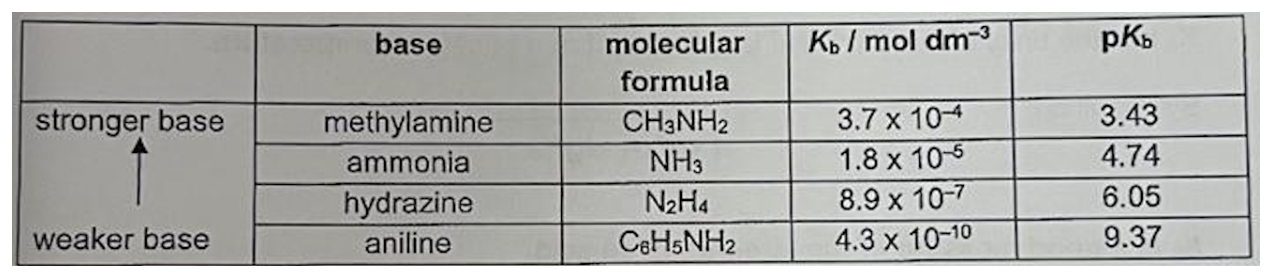
Measures strength of base
Larger the Ka (smaller the pKa) -> stronger the base
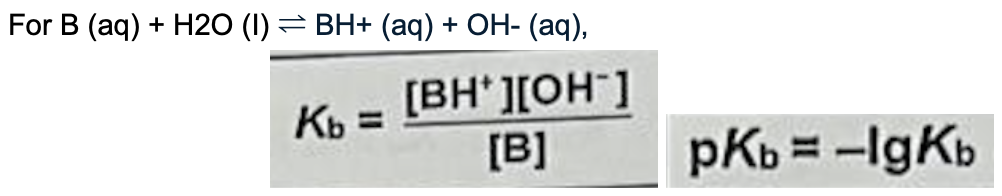
Describe Kb and the 4 bases u need to know
Is pH or Ka/Kb more reliable?
Kb and Ka more reliable method of finding strength of acid or base than pH: pH changes with concentration, Kb and Ka constant at all dilutions (only affected by temperature)