Malnutrition and Body Weight Concerns (Test 2)
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
malnutrition
-state of nutrient imbalance
-can be undernutrition to overnutrition
-inadequate vitamins or minerals (can occur in overweight, normal weight, and underweight people)
1.9 billion
How many people are overweight or obese per WHO?
462 million
How many people are underweight per WHO?
-starvation
-chronic disease
-acute disease
What can malnutrition be related to?
no
Is there inflammation present in starvation-related malnutrition?
acute and chronic disease-related malnutrition
Inflammation is present in what type of issue related to malnutrition?
marasmus
malnutrition syndrome characterized by the wasting or withering of body tissues, particularly muscles and subcutaneous fat, as a result of severe restrictions in energy intake
long-term
For marasmus you have to have ______________ (months to years) deprivation of energy and nutrients. (all body fat stores have been exhausted)
children <5 yrs old because of their increased caloric requirements and increased susceptibility to infections
Is Marasmus most likely to occur in adults or children?
marasmus signs/symptoms
•Emaciated, loose skin from loss of subcutaneous adipose
•Weak
•Lethargic
•Weak with muscle wasting
•Bradycardia, hypotension, and hypothermia
•Can also occur in patients with anorexia nervosa, depression/anxiety, and malabsorption syndromes
grade 1 muscle wasting
wasting of the axilla and groin
grade 2 muscle wasting
wasting of the thighs and buttocks
grade 3 muscle wasting
wasting of the chest and abdoment
grade 4 muscle wasting
wasting of facial muscles
kwashiorkor
malnutrition syndrome characterized by near normal weight but bilateral edema, as a result of inadequate protein intake
areas of famine or with limited food supply (corn, rice, beans)
Where does kwashiorkor typically occur?
kwashiorkor signs/symptoms
-Skin lesions
-Dry, brittle, hypopigmented hair
-Distended abdomen
Hepatomegaly
-Edema precipitated by a combination of low serum albumin, increased cortisol, and inefficient antidiuretic hormone
grade 1
pedal edema in kwashiorkor
grade 2
facial edema in kwashiorkor
grade 3
chest and paraspinal edema in kwashiorkor
grade 4
ascites in kwashiorkor
malnutrition etiology
-marked by the signs of inflammation and injury
-acute and chronic
acute malnutrition
- < 3 months
-Critical illness, major infection/sepsis, ARDS, SIRS, severe burns, major abdominal surgery, multitrauma, and closed head injury
chronic malnutrition
•IBD, CVD, CHF, CF, RA, chronic pancreatitis, cancers, DM, Mets, CVA, dementia, COPD, organ failure/transplant, etc
overall energy balance
What is body weight driven by?
Total Energy Expenditure (TEE)
is equal to basal energy expenditure (BEE)* activity factor
TEE>BEE*AF
underweight, wasting, and stunting occur
TEE
overweight and obesity occur
BMI equation
What are these?
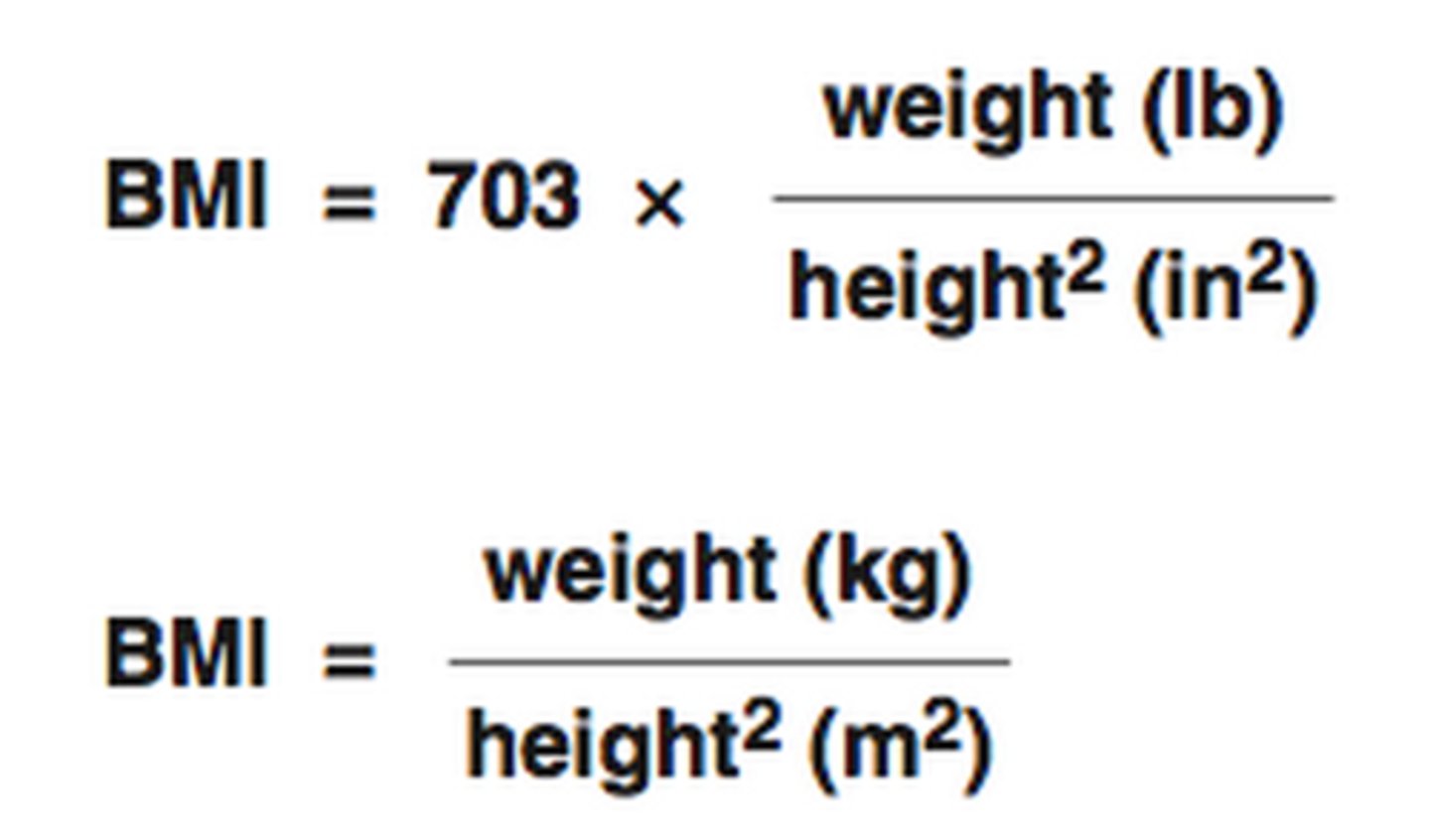
underweight
BMI<18.5
normal
BMI 18.5-24.9
overweight
BMI 25-29.9
obese
BMI greater than or = to 30
class 1 obesity
BMI 30-34.9
Class 2 obestiy
MBI 35-39.9
Class 3 obesity
BMI greater than or equal to 40
2.2
1 kg = ____ lbs
0.035
1 g= __________ oz
0.394
1 cm = _________ in
484
1 lb = _________ g
28.4
1 oz = _______ g
0.394 in
1 cm = ________ in
IBW for Males
50 kg + (2.3 * inches over 5 ft)
IBW for Females
45.5 kg + (2.3 * inches over 5 ft)
AdjBW
IBW + 0.4(TBW-IBW)
-conserves energy by reducing energy expenditure
-restricts growth
-converts and burns stored fat
-utilizes muscles for amino acids, pyruvate, and lactate (which depletes muscle mass)
When energy intake is reduced our body does what?
consequences of wasting
•Reduction in energy availability lowers the efficacy of the sodium pumps that regulate cell membrane permeability, leading to systemic imbalances in sodium and potassium
•Immune system
•Cardiovascular system
•Nervous system
•Digestive system: (effects also contribute)
Hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, hypernatremia
When you have cachexia you can have a reduction in energy availability that lowers the efficacy of the sodium pump leading to what?
-Cardiac myofibrils are thinned with impaired contractility
-Cardiac output is reduced, noted bradycardia and hypotension
-Risk of arrhythmia due to cardiac changes as well as electrolyte imbalances predisposes
What happens to the cardiovascular system with cachexia?
reduction in neurons/synapses which leads to delays in motor function, memory, and other mental responses
What happens with the nervous system in patients with cachexia?
•Atrophy of the intestinall villi
•Pancreatic atrophy
•Dysbiosis of microbiome
What happens to the digestive system with patients with cachexia?
T2DM, CVD, HTN, stroke
What are the serious health tissues that overweight and obese people can get?
chromium deficiency
Impaired glucose/protein utilization, peripheral neuropathy, weight loss, increased LDL (cholesterol), increased free fatty acid concentrations
copper deficiency
Neutropenia, hypochromic anemia, pallor, dermatitis, neurological dysfunction, osteoporosis, myopathy, thrombocytopenia, decreased bone mineralization
iodine deficiency
Hypothyroid goiter, neuromuscular impairment, deaf-mutism, increased embryonic and postnatal mortality, cognitive impairment, impaired fertility, congenital hypothyroidism
iron deficiency
Microcytic, hypochromic anemia, glossitis, headache, dysphasia, nail changes, gastric atrophy, paresthesia, decreased cognitive function
manganese deficiencies
Nausea; vomiting; dermatitis; hair color changes; hypocholesterolemia; growth retardation; defective carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism
molybdenum deficiency
Tachycardia, tachypnea, altered mental status, visual changes, headache, nausea, vomiting
selenium deficiency
Muscle weakness or pain, cardiomyopathy, skin and hair pigmentation changes, macrocytosis, alopecia and growth retardation
zinc deficiency
Dermatitis, stomatitis, glossitis, mouth and tongue ulcers, altered taste and smell, alopecia, diarrhea, apathy, depression, growth retardation, impaired wound healing, anorexia, confusion, immunosuppression, delayed sexual maturation, hypogonadism
Thiamine Deficiency (B1)
Anorexia, fatigue, depression, impaired memory or concentration, N/V/D, nystagmus
Beriberi: heart failure, edema, neurological deficits (Wernicke’s, Korsakoff’s psychosis, neuropathy)
Riboflavin (B2) deficiency
Mucositis, dermatitis, glossitis, photophobia, corneal vascularization, lacrimation, decreased vision, impaired wound healing and growth, normocytic anemia
Niacin deficiency
Pellagra: dermatitis, dementia, glossitis, diarrhea, memory loss, headaches
Folic acid deficiency
Macrocytic anemia, diarrhea, glossitis, cheilosis, angular stomatitis, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, headache, palpitations, shortness of breath, heart failure, tachycardia, postural hypotension, lactic acidosis, neural tube defects, impaired cellular immunity, paranoid behavior
cyanocobalamin (B12) deficiency
Pernicious (megaloblastic) anemia, glossitis, spinal cord degeneration, peripheral neuropathy, paresthesias, pancytopenia, personality changes, dementia, depression, psychosis
biotin deficiency
Dermatitis, depression, lassitude, somnolence
Ascorbic acid (C) deficiency
Enlargement or keratosis of hair follicles, impaired wound healing, anemia, lethargy, depression, bleeding, ecchymosis, scurvy
Vitamin A deficiency
Dermatitis, night blindness, xerophthalmia, pruritus, follicular hyperkeratosis, excessive deposition of periosteal bone, hair changes, poor growth and wound healing, impaired resistance to infection
Vitamin D deficiency
Rickets, osteomalacia, osteoporosis, muscle weakness, poor growth, hypocalcemia, immune dysfunction, cardiomyopathy
alpha-Tocopherol (E) deficiency
hemolysis
Vitamin K deficiency
bleeding (ecchymosis, petechiae, hematoma)