lec 11.1 - eukaryotic transcription regulation (copy)
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
RECALL: levels of transcription control in prokaryotes
Transcription initiation
Post-transcriptional processes
RNA stability
Translation
Protein modification
Protein transport
Protein degradation
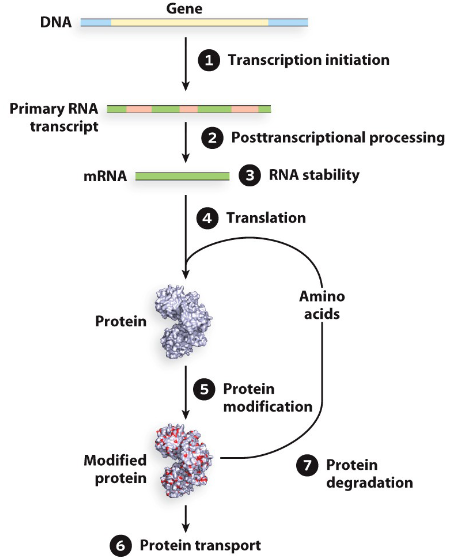
when is gene expression principally controlled?
at the initiation of transcription
what is an additional control level found in eukaryotes?
Activation of gene structure: epigenetics to open/close chromatin
Chromatin structure can persist through cell division, called the epigenetic state
how are genes turned on?
first mechanism
first mechanism: When replication disrupts chromatin structure, after the Y fork has passed, either chromatin can reform or transcription factors can bind and prevent chromatin formation
transcription factors bind promoters to keep open access to the genes and prevent nucleosomes from reforming
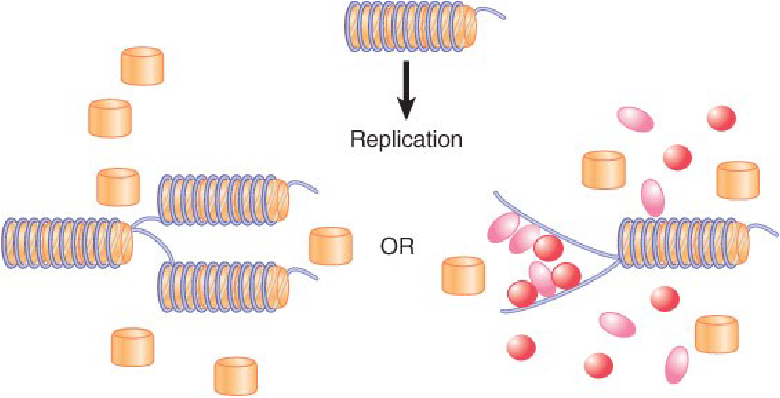
how are genes turned on?
second mechanism (briefly describe)
second mechanism: transcription factors can bind to DNA on outside of histones and recruit histone modifiers to go open up gene region: either uni or bi directionally until it reaches an insulator (Boundary element)
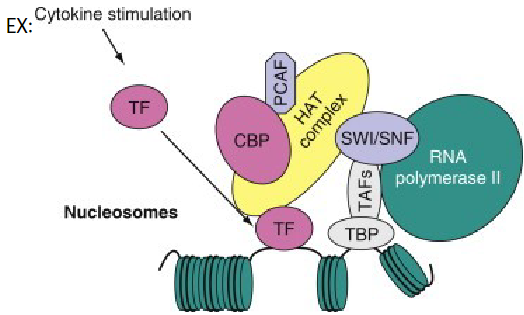
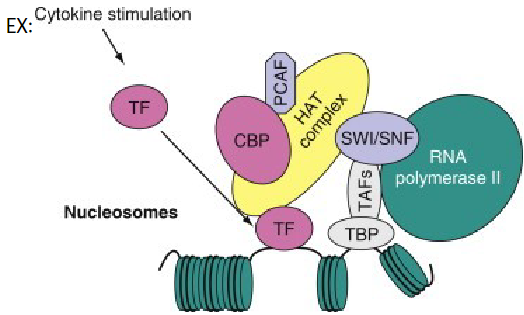
what are the components of the second mechanism?
TAF – transcription activating factors
TBP – TATA binding factor
TF - transcriptional factor - activated by a cell or env’t signal and recruits the CBP-PCAF-HAT complex which binds to the SWI/SNF complex which is an ATP- dependent chromatin remodeling complex and brings RNA polymerase to region to start transcription
HAT complex: histone acetyl transferase transfers acetyl groups onto histones to hide their positive charge (makes them less attracted to DNA which is negative)
SWI/SNF: moves histones to get better access
activator
a molecule that determines the frequency of
transcription – usually upregulation
repressor
A protein that inhibits expression of a gene.
It may act to prevent transcription by binding to a regulator site (e.g. promoter to block access) in DNA or by preventing translation by binding to RNA.
downregulation
positive control
The default state of genes that are under positive control is that they cannot be expressed unless a positive regulator is bound
need inducer
true activator
A positive transcription factor that functions by
making contact, direct or indirect, with the basal apparatus to activate transcription.
binds to DNA and activates RNA pol