Lab 3: Blood Analysis and Typing Techniques
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Plasma
Liquid component, 55% of blood volume.
Albumin
Maintains osmotic pressure in capillaries.
Globulin
Transport proteins and antibodies in plasma.
Fibrinogen
Protein essential for blood clot formation.
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells, carry oxygen via hemoglobin.
Platelets
Cell fragments crucial for blood clotting.
Leukocytes
White blood cells, true cells, fight infections, <1% of blood.
Hematocrit
Percentage of blood volume occupied by red cells.
Leukopoiesis
Production of white blood cells in bone marrow.
Diapedesis
Movement of WBCs out of blood vessels.
Granulocytes
WBCs with granules, multi-lobed nuclei.
Neutrophils
Most abundant WBC, 50-70% of leukocytes, first responders, White blood cells involved in fighting infections
Eosinophils
1-4% of WBCs, involved in allergic responses and parasites attacks; combat parasites + parasitic worms, moderate the inflammatory process
Basophils
<1% of WBCs, release histamine and heparin; increases inflammation, releases chemotaxis factors
Lymphocytes
20-30% of WBCs, involved in immune responses.
T-cells and B-cells, smallest WBC
T-cells (Killer t-cells)
Attack viruses, part of adaptive immunity, attacks antigens during the immune response, mainly viruses and tumor cells
B-cells
Produce antibodies that are released into the blood, target bacteria.
Monocytes
3-8% of total WBC count, Largest WBC, involved in chronic infection cleanup; differentiate into macrophages in the lymph tissues, activate lymphocytes during the immune response
ABO System
Blood typing system based on antigens present.
Type A Blood
Has A antigen, B antibody in plasma.
Type B Blood
Has B antigen on RBC, A antibody in plasma.
Type O
No antigens on RBC, both antibodies present, Universal donor
Agglutination
Clumping of blood cells due to antibodies. shows incompatible blood types.
Rh+
Rh antigen present on RBC, 85% prevalence.
Rh-
Rh antigen absent on RBC, 15% prevalence.
Blood Typing Test
Agglutination indicates positive blood type result.
WBC Types
Five distinct types of white blood cells.
Differential WBC Count
Counting each WBC type in a sample; Percentage breakdown of different white blood cells.
Total RBC Count
Average male count: 5-6 million cells/µL.
Average female count: 4-5 million cells/µL.
Total WBC Count
Average count: 5000-10000 cells/µL.
Leukocytosis
WBC count above 11,000/µL, possible immune response.
Leukopenia
WBC count below 4,800/µL, indicates bone marrow damage.
Hematocrit Calculation
(Length of RBC/Total length) x 100.
Normal Hematocrit Ranges
Male: 44-52%, Female: 38-48%.
Anemia
Reduced O2 delivery due to low RBC or hemoglobin.
Polycythemia
Abnormally high RBC density, risks heart strain.
Biohazard
Biological substance posing risk to health.
ABO blood typing
Determines blood type using specific antibodies.
Lancet
Device used to puncture skin for blood.
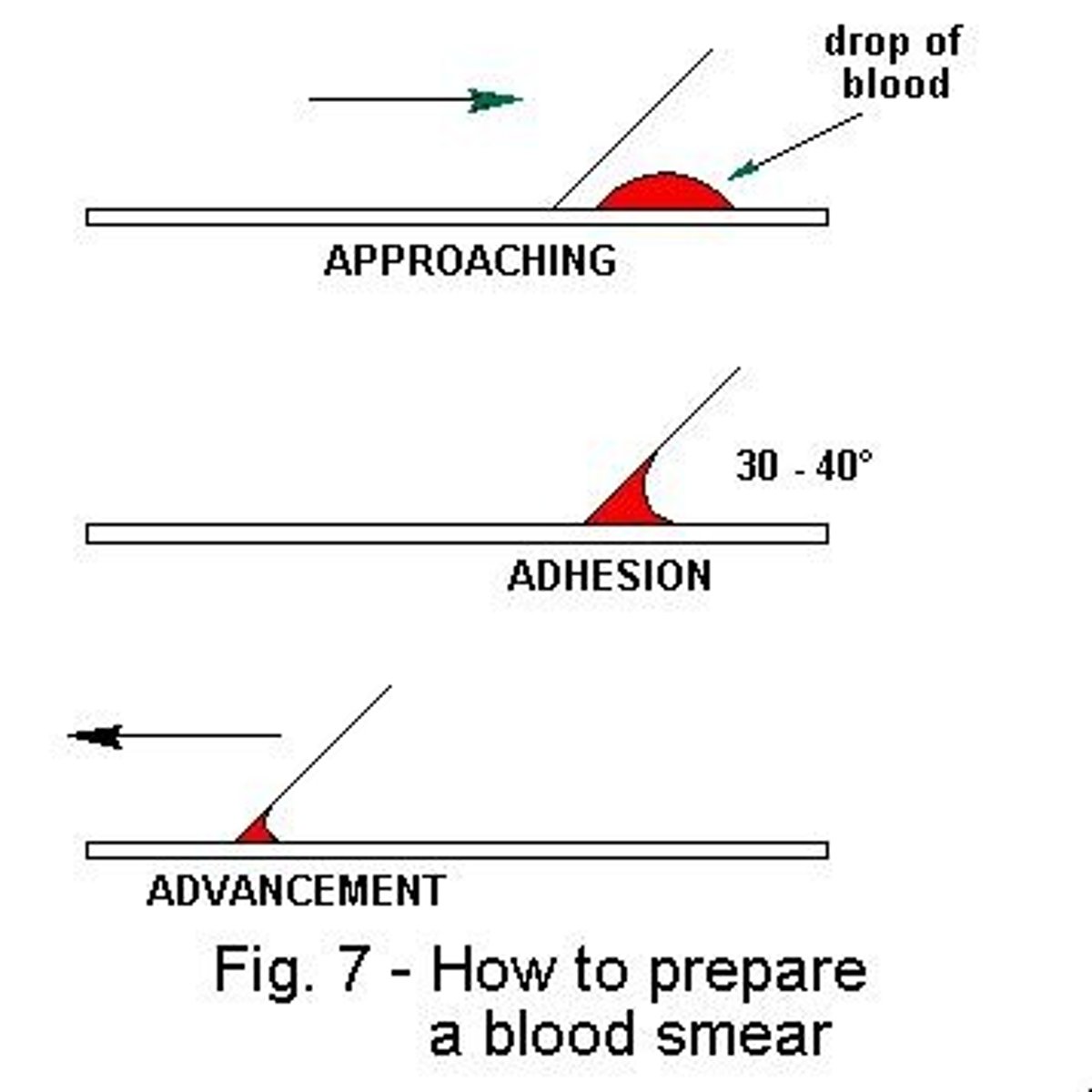
Blood smear
Thin layer of blood for microscopic examination.
Wright's stain
Stain used to visualize blood cells under microscope.
Safety precautions
Measures to prevent accidents and exposure to blood.
Capillary tubes
Small tubes used for collecting blood samples.
Alcohol swab
Used to disinfect skin before blood draw.
Blood typing card
Card with antibodies for blood type testing.
Biohazard bags
Containers for safe disposal of hazardous materials.
Sharp's container
Container for disposing sharp objects like lancets.
Instructor supervision
Requirement to have instructor present before procedures.
Blood flow technique
Method to enhance blood flow from finger.
Smear technique
Process of spreading blood on a slide.
Color-coded antibodies
Antibodies marked by colors for identification.
Finger selection
Choosing a finger for blood collection.
Air drying
Process of drying the blood smear before staining.
Mixing sticks
Colored toothpicks used for mixing blood and antibodies.
Light-headedness response
Sit down and notify lab partners if feeling dizzy.
Wright's Stain
Stain used for fixing blood cells.
Hematocrit Tube
Tube used to measure blood cell volume.
Centrifuge
Device to separate components of blood.
Physioex Program
Software for simulating blood analysis activities.
Rh Factor
Protein determining blood type positivity or negativity.
Bibulous Paper
Absorbent paper used to dry slides.
40X Objective Lens
Microscope lens for viewing blood smears.
Blood Type AB
Universal recipient, contains both A and B antigens.
Rh Incompatibility
Concern during pregnancy if mother is Rh-.
Acute Bacterial Infections
Condition often indicated by increased neutrophil count.