CP317 Test 2 - Software Engineering
1/197
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Shaun Gao - Spring 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
198 Terms
Association
When objects are related to one another, the relationship is called ______ among the objects
Types of associations
Aggregation
Composition
Aggregation
a special form of association where all objects have their own lifecycle but there is ownership
Composition
a technique to combine objects or data types into more complex one
Inheritance
an "is-a" relationship
Composition
is a "has-a" relationship
SOLID
the most popular sets of design principles in object-oriented software
SOLID
makes software designs more understandable, flexible and maintainable
Single Responsibility Principle (SRP)
a computer programming principle that states that every module, class, or function should have responsibility over a single part of the functionality provided by the software
Single Responsibility Principle (SRP)
This principle is closely related to the concepts of coupling and cohesion
Single Responsibility Principle (SRP)
One (module, class, or function) should have single responsibility
Open-Close Principle (OCP)
states that software entities (classes, modules, functions, etc.) should be open for extension, but closed for modification. That is, such an entity can allow its behaviour to be extended without modifying its source code
Characteristics of a poor design
- Single change results in cascade of changes
- Program is fragile and unpredictable
Characteristics of good design
- Modules never change
- Extend Module's behavior by adding new code, not changing existing code
Liskov substitution principle (LSP)
Let Φ(x) be a property provable about objects x of type T. Then Φ(y) should be true for objects y of type S where S is a subtype of T
Liskov substitution principle (LSP)
a way of ensuring that inheritance is used correctly
Liskov substitution principle (LSP)
If _____ is not maintained, class hierarchies would be a mess, and if a subclass instance was passed as parameter to methods, strange behavior might occur
Liskov substitution principle (LSP)
If ______ is not maintained, unit tests for the base classes would never succeed for the subclass
Interface segregation principle (ISP)
states that no client should be forced to depend on methods it does not use
Interface segregation principle (ISP)
Splits interfaces that are very large into smaller and more specific ones so that clients will only have to know about the methods that are of interest to them
Dependency inversion principle (DIP)
states that high-level modules should not depend on low-level modules. Both should depend on abstractions (e.g. interfaces)
Dependency inversion principle (DIP)
states that abstractions should not depend on details. Details (concrete implementations) should depend on abstractions
Dependency inversion principle (DIP)
a specific form of decoupling software modules
SOLID
Ensures high cohesion and low coupling
Incorrect coding
can cause severe accidents, create system vulnerabilities
Fail-safe default
states that unless a subject is given explicit access to an object, it should be denied access to that object
Coding Standards
a set of guidelines, rules, programming styles and conventions that software developers adhere to when writing source code for a project
Benefits of using coding standards
- Improve software quality
- Quicker to debug code
- Easier to code review work
- Avoid conflict
- Code is easier to collaborate on
Software code/version control
the management of changes to documents, computer programs, and other collections of information
Comment
a note written in source code by the programmer to describe or clarify the code
Benefits of comments
- easy to understand the code
- easier maintenance
Side effects
software has THIS if it modifies global variables or has an observable interaction with the outside of its scope
Defensive programming
the process of designing and implementing software so that it continues to function when it is under attack
Defensive programming
you should expect erroneous input to your functions, or methods
Offensive programming
It departs from defensive principles when dealing with errors resulting from software bugs
Offensive programming
It adds an explicit priority of NOT tolerating errors
Exception
an unexpected event (could be either inside or outside) that happens while a program is running
Buffer
a region of a physical memory storage used to store data
Buffer overflow
an occurrence when a process or program writes more data into a buffer than the buffer can hold
Stack overflow
an undesirable condition in which a particular computer program tries to use more memory space than the stack size
Memory leak
a particular type of memory consumption by running software where the software fails to release memory when it is no longer needed
Safety critical systems
a system whose failure or malfunction may result in serious injury or even death of people
Real-time operating systems
processes data and executes tasks within strict time constraints and with a high degree of reliability and precision
Redundancy
In software engineering, it is a design method in which a component is duplicated so if it fails there will be a backup
System redundancy
a widely used method of improving the reliability of computerized systems
Constructors
only perform necessary initialization including resource allocations
Destructors
Focus on releasing resources that have been allocated in heap
Destructors
The general rule is: never allow exceptions to leave _____.
Software testing
to evaluate the software against requirements gathered from users and system specifications
Types of testing
- unit testing
- integration testing
- regression testing
- system testing
Software test plan
a document describing software testing scope and activities
Test case
a specification of the inputs, execution conditions, testing procedure, and expected results that define a single test to be executed to achieve a particular software testing objective, such as to exercise a particular program path or to verify compliance with a specific requirement
Unit testing
a method by which an individual unit (method or function) of source code is tested to determine if it behaves correctly
Test coverage
a measure used to describe the degree to which the source code of a program is executed when a particular test suite runs
Integration testing
the phase in software testing in which individual software modules are combined and tested as a group
Top-down approach
an integration testing technique that is used in order to simulate the behaviour of the lower-level modules that are not yet integrated
Fault localization
it identifies the reason for the error that can best explain the observed defects
Bottom-up approach
a testing strategy in which the modules at the lower level are tested with higher modules until all the modules and aspects of the software are tested properly
Regression testing
Testing of the previously tested program following modification to ensure that defects have not been introduced in the unchanged areas of software due to the changes made.
Retesting
The rerunning of tests that failed earlier in order to verify the success of corrective action
System testing
testing conducted on a complete integrated system to evaluate the system's compliance with its specified design requirements
Acceptance testing
formal testing with respect to user needs, requirements, and business processes conducted to determine whether a system satisfies the acceptance criteria and to enable the user, customers or other authorized entity to determine whether the system is accepted
Black-box testing
a method of software testing that examines the functionality of software without peering into its internal structures or workings
White-box testing
a method of software testing that tests internal structures or workings of software as opposed to its functionality
Test driven development
a technique for building reliable software that guides software development by writing tests
Test driven development
about design, where design is evolved through refactoring
Benefits of test driven development
- Early problem discovery
- Facilitates change
- Simplifies integration
- Self documentation
- Visualises the design
Software development
all of the activities that make a new or new version of software system available for use
Deployment strategies
- Cutover
- Stage development
- Gradual cutover
- Incremental
- Parallel
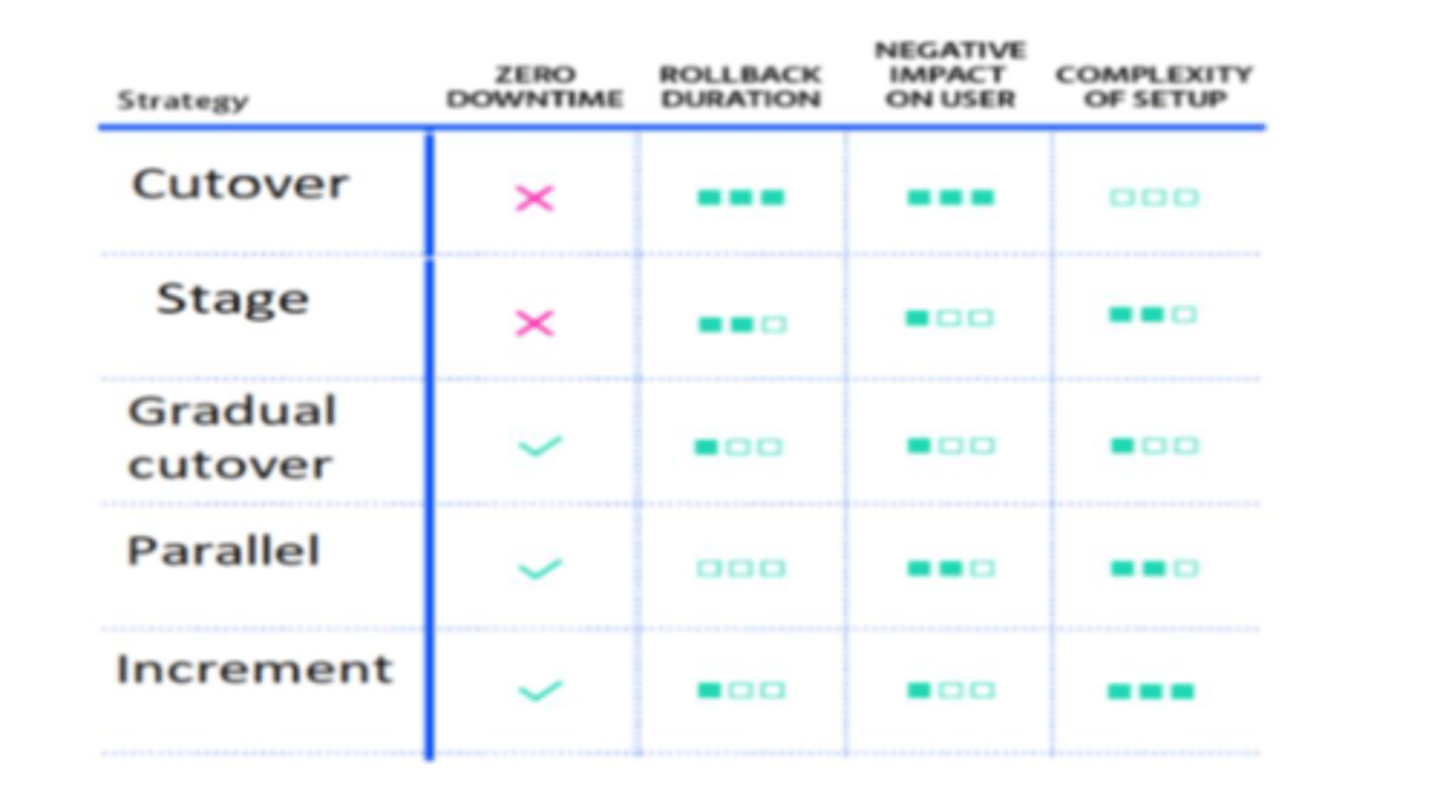
Software deployment plan
defines the scope, approach, and execution for the deployment of a software product
Software deployment strategy
a way to change or upgrade software. The aim of software deployment strategy is to make the change without downtime in a way that the user barely notices the improvements
Cutover
the process of deploying new or new version software to all devices at the same time
Pros of Cutover
- Easy to setup
- Software state entirely renewed
Cons of Cutover
- High risks
- High impact on customers
- Expect downtime: system reboot
Staged deployment
a strategy for deployment that has exactly functional production environments for practicing deployment.
Pros of Staged deployment
- Low risks
- Software state entirely renewed
Cons of Staged deployment
- Expensive
- Expect downtime: system reboot
Gradual Cutover
the process of installing new software into some users' machines while other machines continue working with existing software
A pro of Gradual Cutover
Low risks
A con of Gradual Cutover
Difficult to configure
Parallel deployment
a strategy for software deployment where a new software system slowly assumes the roles of the older software system while both software systems operate simultaneously
Pros of Parallel deployment
- Different versions run in parallel
- Zero down-time release
A con of Parallel deployment
Difficult to configure for online releases
Incremental deployment
the process of releasing the new features of software to the user machines gradually
A pro of Incremental deployment
Low risks
Cons of Incremental deployment
- Slow rollout
- Does not work with monolithic software
Deployment mistakes
- Assume everything will work
- Have no rollback plan
- Allow insufficient time
- Skip staging
- Install lots of updates all at once
- Use an unstable environment
Software metric
the measurement of software characteristics which are measurable or countable. They're valuable for many reasons, including measuring software performance, planning work items, measuring productivity, and many other uses
Software metrics
good for comparative study of various design methodologies of software systems
Software metrics
good for comparing and evaluating the capabilities and productivities of team members
Software metrics
Help to prepare software quality specifications
Software metrics
It gets an idea about the complexity of the software code
Software metrics
It provides feedback to software engineers and managers about the progress and quality during various phases of the software development life style
Product metrics
describes the characteristics of the product such as size, complexity, design features, performance, and quality level
Software metrics measurements
- size, line of code (LoC)
- Complexity
- Performance
- Usability
- Security
Process metrics
standard measurements that are used to evaluate and benchmark the performance of software engineering processes
Process metrics measurements
- Efficiency
- Productivity
- Error rate
- Cost effectiveness
Project metrics
describe the project characteristics and execution such as resources, cost, and productivity
Defect analysis
part of the continuous quality improvement in which defects are classified into different categories and are also used to identify the possible causes in order to prevent the problems from occurring again
Ishikawa diagrams
causal diagrams created by Kaoru Ishikawa that show the causes of a specific event. To figure out in which category a defect belongs