UNIT 1: BIOCHEMISTRY
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Why is water cohesive/adhesive
Water’s hydrogen bonds cause a high level of polarity (and strong attractive partial charges) which allows for bonding with other water molecules and other polar molecules.
Why does water have a high specific heat capacity.
Water’s strong hydrogen bonding and as you must break those bonds to heat it up, a lot of energy must be used
Why is water the perfect solvent
Water is highly soluble because polar molecules can easily ionize with the positive and negative ions of other molecules
Why is ice less dense than water
Ice is less dense than water because when water freezes, the molecules slow down and their tetrahedral position becomes fixed, leaving empty space within the barriers of the molecules and decreasing its densit
Why is carbon so fundamental
Can make 4 bonds
Large and stable molecules can be formed
Formed stable bonds at moderate energy levels that won’t be broken spontaneously
Relatively small amount of energy is needed to break and reform bonds
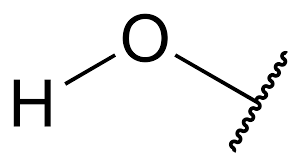
Hydroxyl
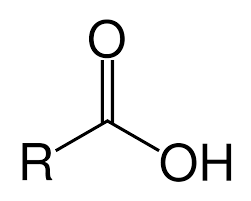
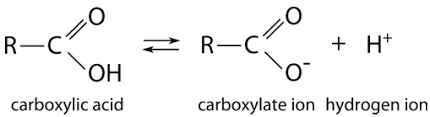
Carboxyl
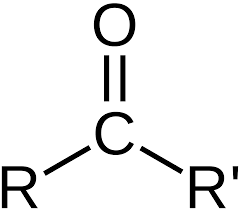
Carbonyl
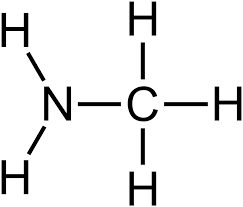
Amino
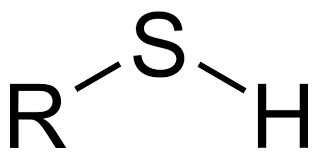
Sulfhydryl
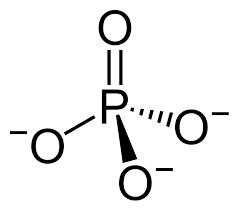
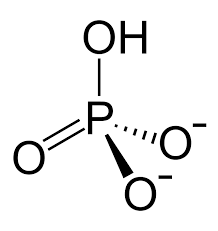
Phosphate
Properties of hydroxyl
Polar covalent
Soluble in water
Properties of carboxyl
Weakly ionic
Acidic
Soluble
Properties of carbonyl
Weakly polar
Soluble in water
Properties of aminos
Ionic
Basic
Soluble
Properties of sulfhydryls
Non-polar
Insoluble in water
Properties of phosphates
Ionic
acidic
soluble in water
single unit of molecule
monomer
repeated string of monomers (100s-1000s)
polymers
oligomers
short polymers (≈3-20)
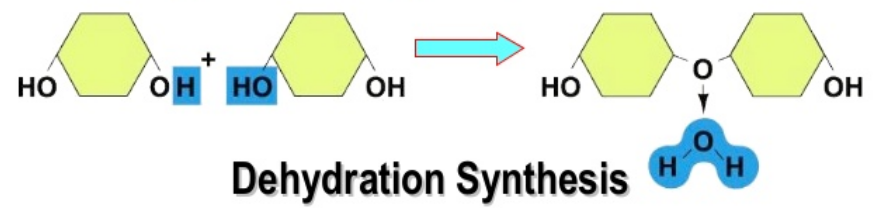
how do you build polymers
condensation or dehydration synthesis
removing water from two monomers
each monomer joins at hydroxyl
h from one monomer attaches to oh from second creating water and a greater string of monomers
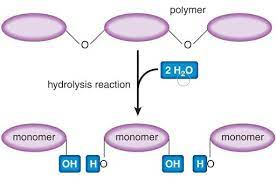
how do you break up polymers
hydrolysis
adding water to split polymers
h goes to one string of monomers and oh goes to other string
what basic biomolecule does not have true monomers
lipids
What is the typical molar ratio of a carbohydrate
CH2O or 1:2:1
What are the elements of carbohydrates
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
What are some structures/functions of carbohydrates
Suitable for energy storage
Play a structural role in the cell wall of plants
What is the monomer of a carbohydrate
monosaccharides
What are some key features of monosaccharides
Small
Polar (water soluble)
Rich in chemical energy
Form ring structures in solution
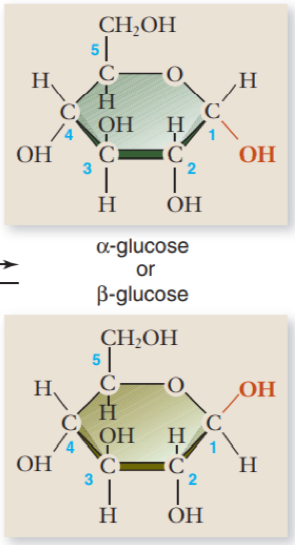
What differentiates α-glucose and β-glucose
α-glucose
hydroxyl group points down
used for energy
β-glucose
hydroxyl group points up
used for structure
What are the benefits of disaccharides
Twice as much energy per molecule of monosaccharide
Less osmosis which disrupts cell processes
What are the common disaccharides
Maltose
Lactose
Sucrose
What are the common monosaccharides
Glucose
Galactose
Frutose
What are the characteristics of polysaccharides
Good for long-term energy storage
Insoluble due to shape
What are the α-glucose polysaccharides
Amylose
Amylopectin
Glycogen
What are the β-glucose polysaccharides
Cellulose
Chitlin

What are the characteristics of amylose
Helix shape
Made by plants for energy
Starch
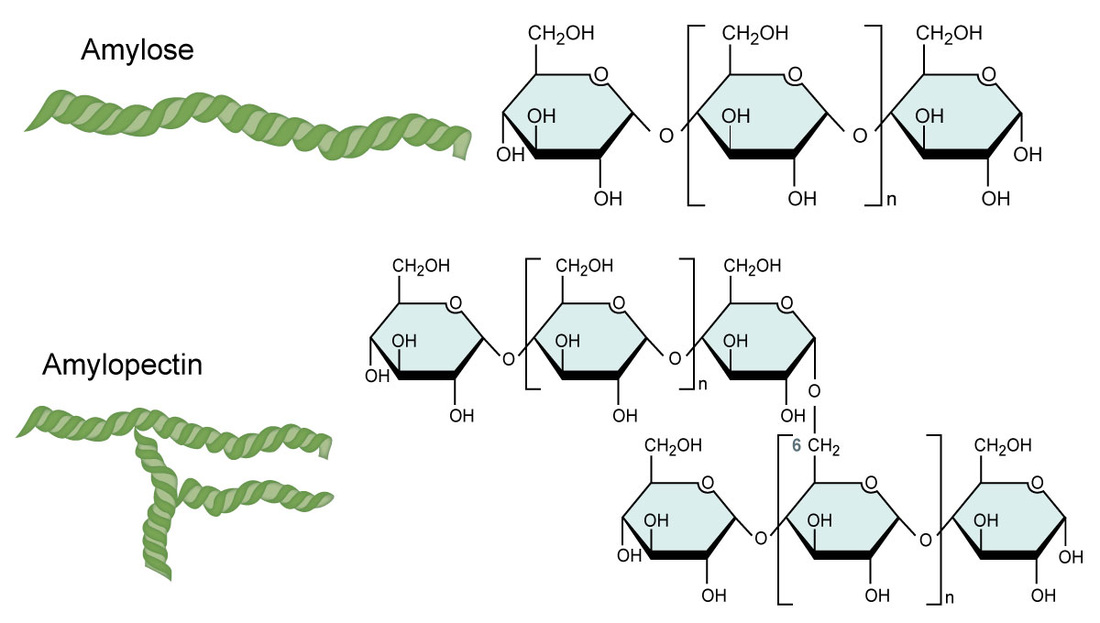
What are the characteristics of amylopectin
Helix shape (w additional branches from 1,6 glycosidic bond)
Made by plants for energy
Even more starch than amylose
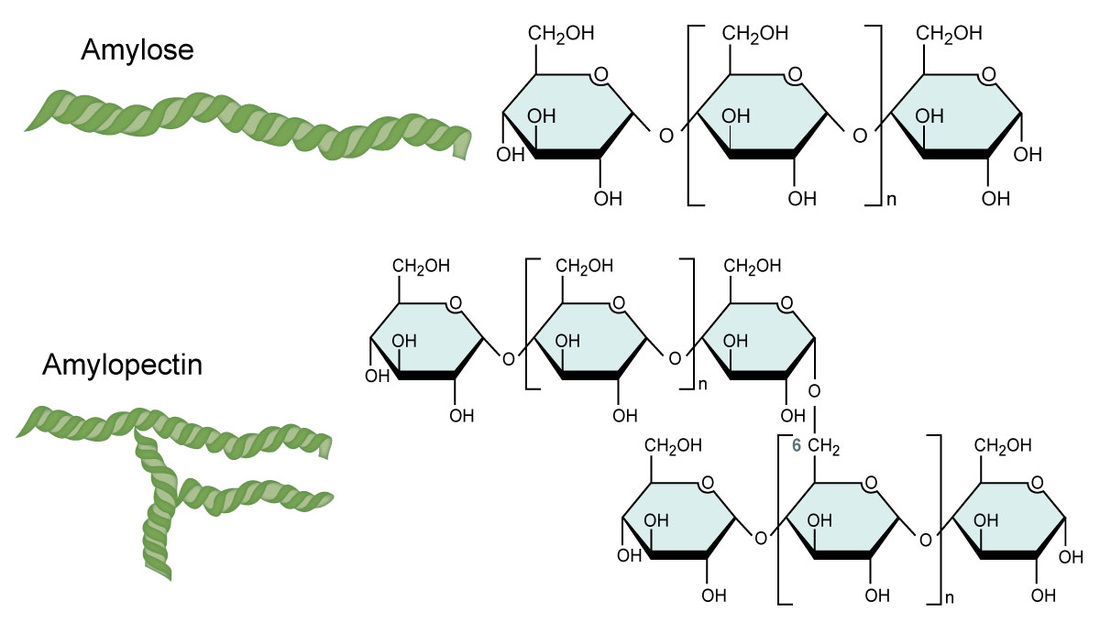
What are the characteristics of glycogen
Helix shape with many branches
Animal starch stored in liver and skeleton
Breaks down faster as it has increased surface area
What are the characteristics of cellulose
Strong and rigid
In the cell walls of animals/plants
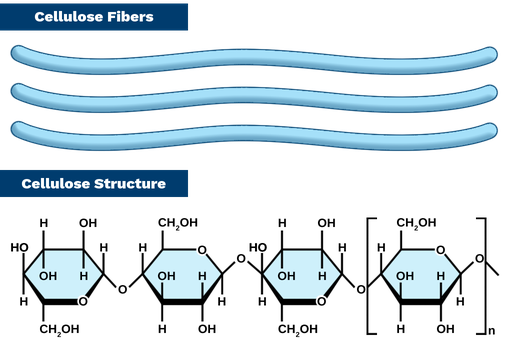
What are the characteristics of chitin
Heightened strength due to additional amino groups
In exoskeletons of insects/bugs
Extra H bonds

What are the characteristics of lipids
CHO
less oxygen and more CH than carbs
2x as much usable energy as carbs (reserve of stored energy)
non polar (insoluble in water)
What are the functions of lipids
Waterproof (hydrophobic because of non-polarity)
Protect vital organs
Insulation (strong insulators against heat and electricity)
Long-term energy storage (2x as much usable energy as carbs)
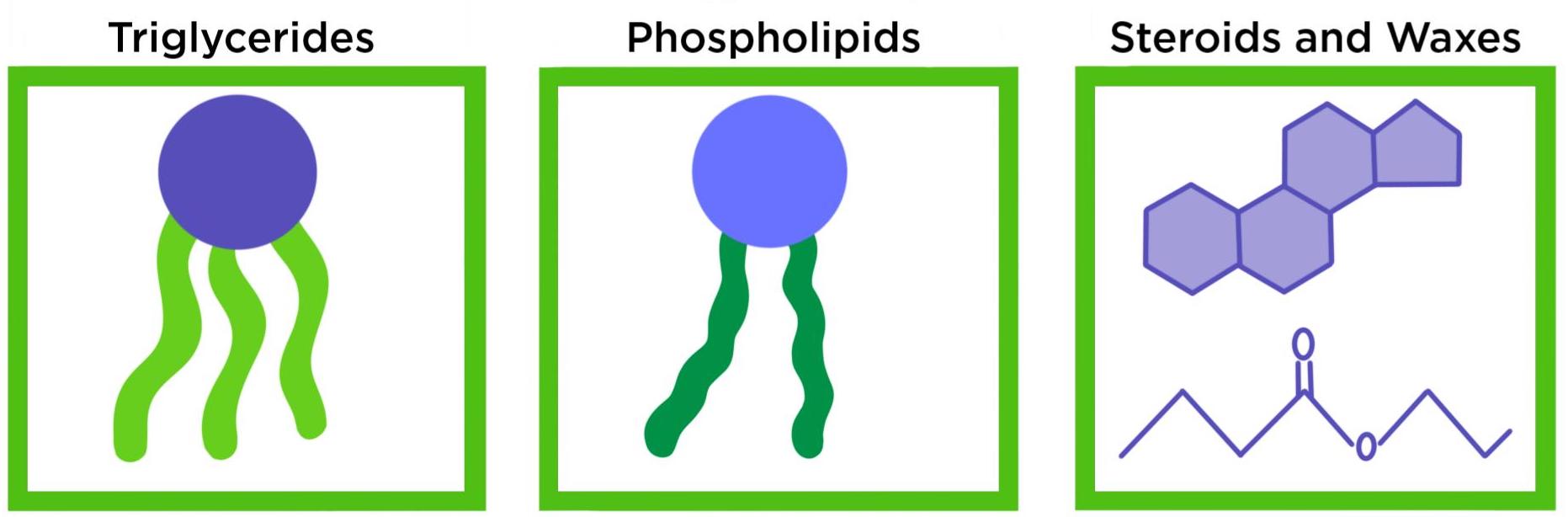
What are the types of lipids and how do you distinguish them
Triglycerides
Glycerol condensed with 3 fatty acids
Phospholipids
Two fatty acids attached to a phosphate group and a polar head
Wax
Ester with long chain alcohol bonded to fatty acid (H’s are removed in the bond)
Steroids
3 hexagons and 1 pentagon
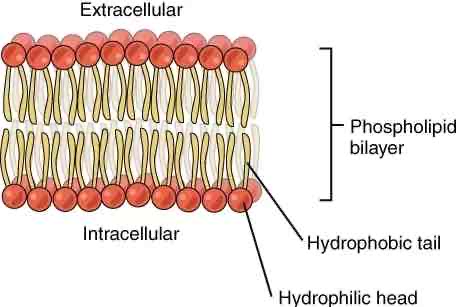
What is a membrane?
A barrier that separates aqueous cell contents from the environment
Made up of phospholipids
What are the types of membrane transport
Passive (including facilitated)
Active
How does regular passive transport work?
Regular:
When molecules are small and non-polar enough they diffuse naturally (eg. O2 and CO2)
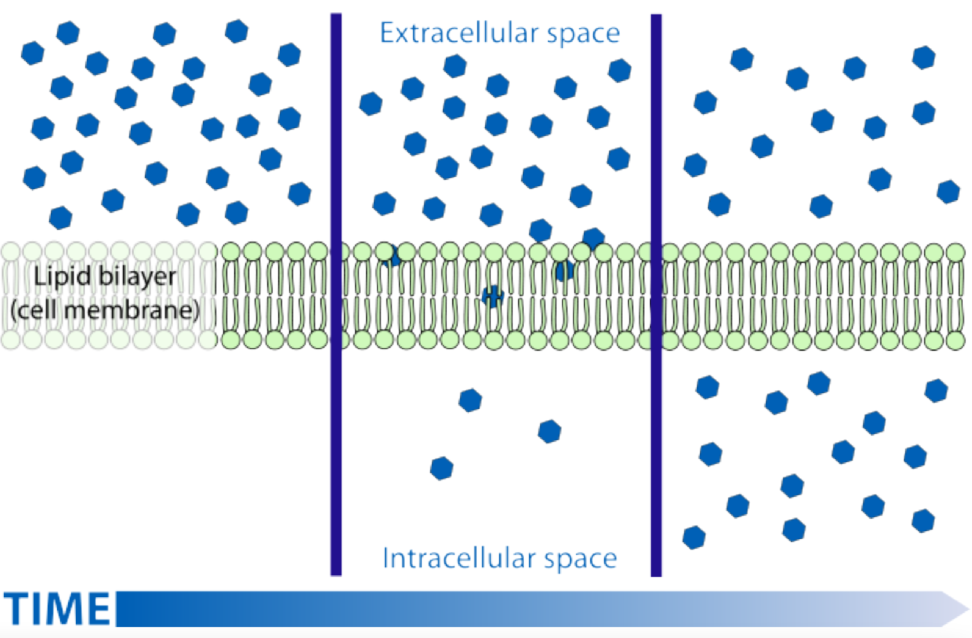
How does active transport work.
Active transport goes against the concentration gradient and uses ATP to change protein shape
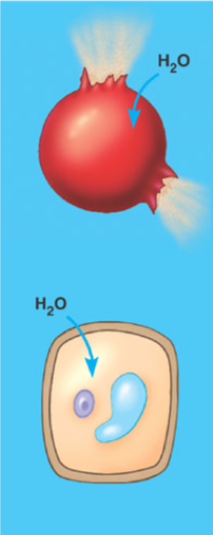
What is a hypotonic solution?
A solution with a low amount of solute relative to the other side of the membrane and a positive net movement of water
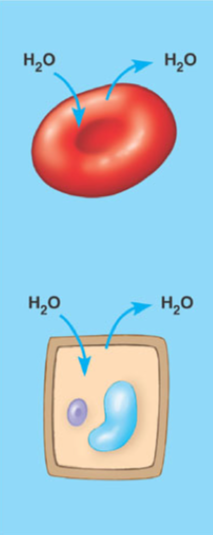
What is an isotonic solution
A solution with an equal amount of solute as the other side of the membrane and no net movement of water
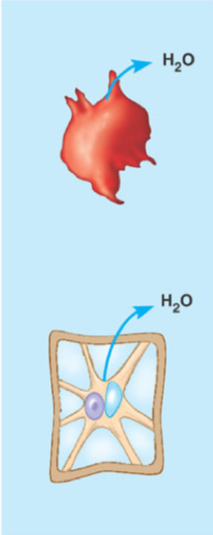
What is a hypertonic solution
A solution with a high concentration of solute relative to the other side of the membrane and therefore a negative net movement of water
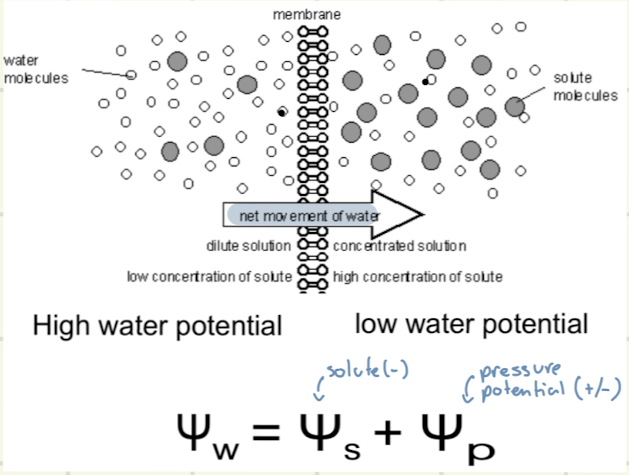
How does osmosis work
Water molecules go from a dilute solution with a low concentration of solute to a concentrated solution with a high concentration of solute, leading to a positive net movement of water
What is bulk transport
Taking many things and moving them across the membrane (the membrane uses ATP to change shape to facilitate this)
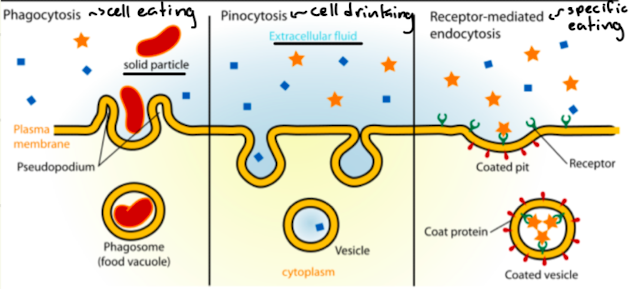
What is endocystosis and three main types
Bulk transport into the cell
Phagocytosis - cell eating (plasma membrane absorbs cells)
Pinocytosis - cell drinking (plasma membrane absorbs extracellular fluid)
Receptor-mediated endocytosis - specific eating (plasma membrane absorbs specific particles)
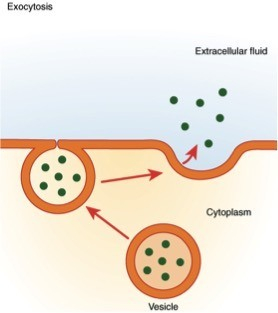
What is exocytosis
Bulk transport out of the cell
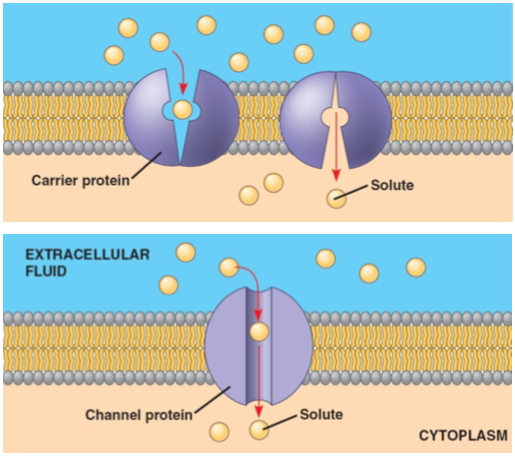
How does facilitated passive transport work
Facilitated:
Go through proteins
Channel protein is opening for molecules to go through
Carrier proteins change shape for molecules
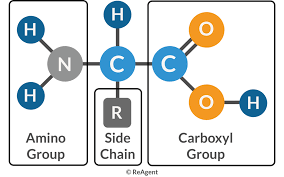
What is a protein
Polymer of amino acids with complex 3-dimensional folding
What is the monomer of a protein
Amino acid
What are the key defining features of amino acids
An amino
Carboxyl
R group
How does polymerization of amino acids work
2 amino acids link by the oh of the carboxyl on one and the H of the amino on the other to form a a peptide bond.
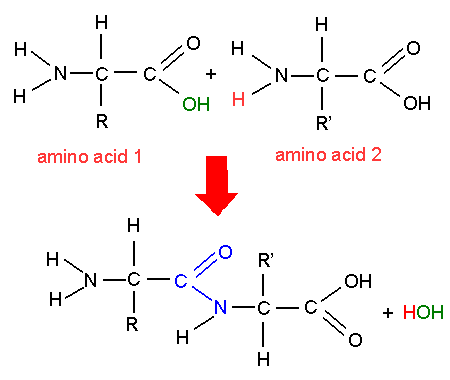
What is the difference between a polypeptide and a protein
Any protein is a polypeptide but polypeptides are only called proteins if they have a specific function
What is the primary polypeptide structure
A sequence/chain of amino acids
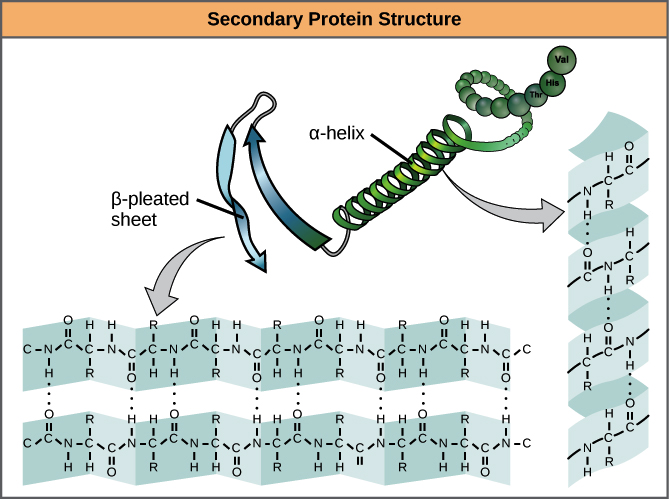
What is the secondary polypeptide structure
When hydrogen bonds in the peptide chain interact causing folding in a repeated pattern
What is the tertiary polypeptide structure
When interactions between remote R groups based on charges, attraction to water, size and shape
This is when they are called proteins (typically in a globular form)
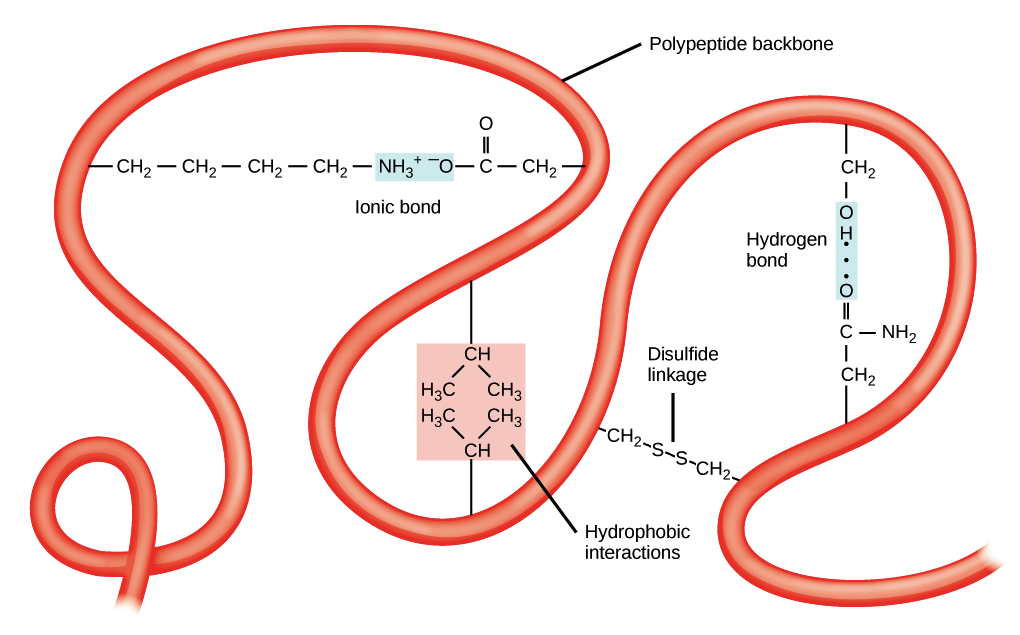
What types of interactions cause tertiary folding
Hydrophobic exclusion
Hydrogen bond
Disulfide bridge
Ionic bond
van der Waals interaction
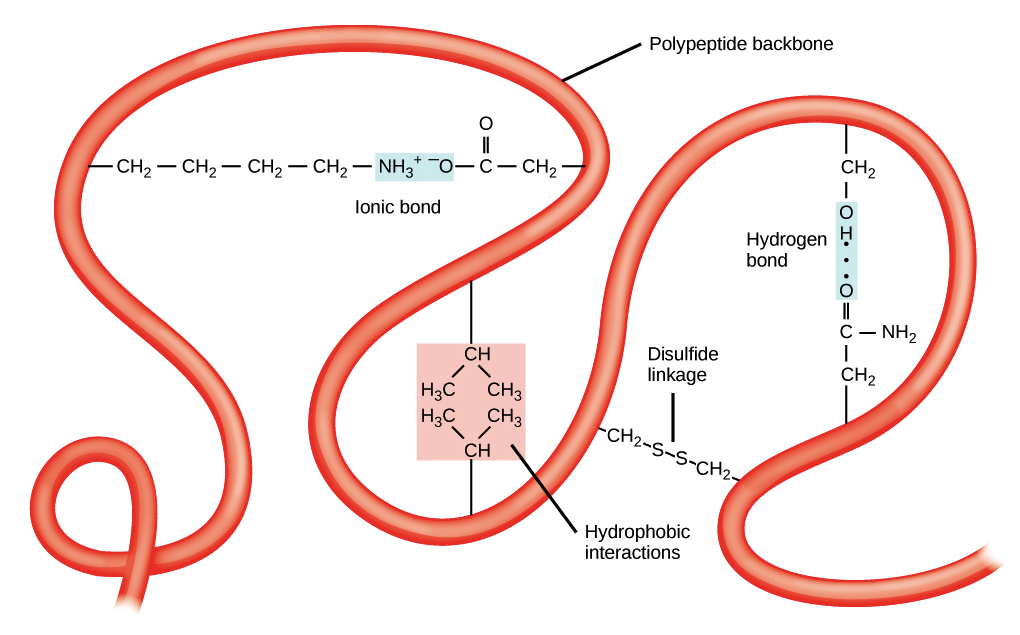
What is hydrophobic exclusion
When non-polar hydrophobic R groups cluster together in the inside of the protein leaving hydrophilic amino acids to bond with water on the outside)
How does hydrogen bonding affect protein shape
Some polar R groups can undergo hydrogen bonding, bending their respective polypeptide chains
What is a disulfide bridge
Covalent links between the sulfur-having side chains of the R group cysteine (strongest of all the bonds that contribute to tertiary structures)
How do ionic bonds affect protein shape
R groups with different charges can undergo ionic bonding, bending their respective polypeptide chains
What is a van der Waals interaction
When two molecules come very close to each other inducing electrical charges
What is a quartenary polypeptide structure
When multiple amino chains (typically secondary) attach
What kind of things can change the shape of a protein
Any change in environment (eg. temperature or pH)
What is an enzyme and how does it work
A protein that acts as a catalyst for a chemical reaction
Each protein has an ‘active site‘ that is shaped for a substrate and therefore binds to it
After they bind, the enzyme typically bends the substrate contorting the bonds and making them weaker/easier to break
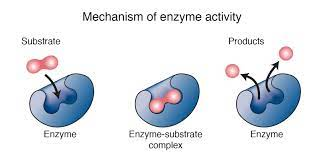
What is the typical naming structure of an enzyme
(thing it breaks up/builds up)-ase
What are the key features that must be in the naming of a protein
Polarity (non-polar or polar)
Charge (negative or positive charge)
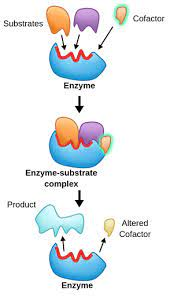
What are cofactors/coenzymes
Things that bind to the active site to create a better fit and facilitate the building up or breaking down of molecules
cofactors are typically metal ions while coenzymes are organic molecules
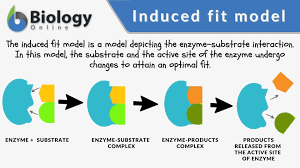
What is induced fit
When an enzyme slightly changes shape to better bind to substrates
What structure can form enzymes
At least tertiary structure is needed
What are the types of enzymes and what do they do
Hydrolase: catalyzes hydrolysis
Lyase: cleaves covalent bonds (without hydrolysis)
Ligase: combines 2 molecules
Transferase: transfers functional groups between molecules
Isomerase: catalyzes spatial rearrangement of substrate
Oxidoreductase: transfers electrons between molecules
What are the 6 components of membranes and what do they do?
Phospholipids
Provides permeability barrier and matrix for protein
Transmembrane proteins
Active and passive transport and transmission of information into cell
Interior proteins:
Determines the shape of cells and act as anchor sites for proteins
Glycoproteins:
Self recognition (your cells are your cells)
Glycolipids:
Tissue recognition
Cholesterol:
Membrane fluidity
What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of water through the membrane
Diffusion is the movement of a solute in solution through the membrane
Which molecules can typically undergo diffusion?
oxygen
carbon dioxide