UTA Microbiology Chapter 9: Microbial Growth
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
182 Terms
Binary Fission
most common form of bacterial reproduction
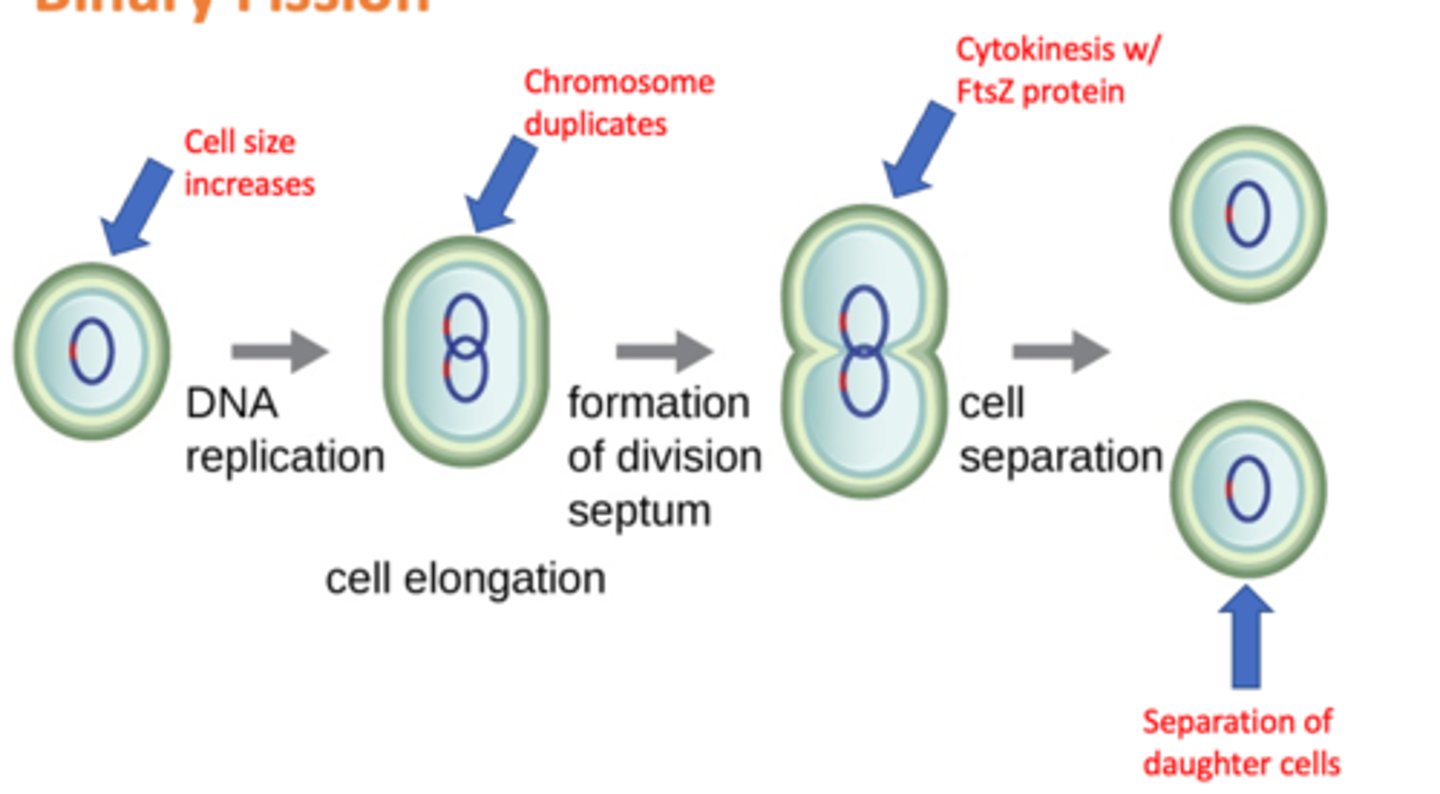
4 Basic Steps of Binary Fission
1. growth of cell size and increase in cell components
2. replication of DNA
3. division of the cytoplasm (cytokinesis
4. septum formation and division of daughter cells
What protein directs cytokinesis?
FtsZ
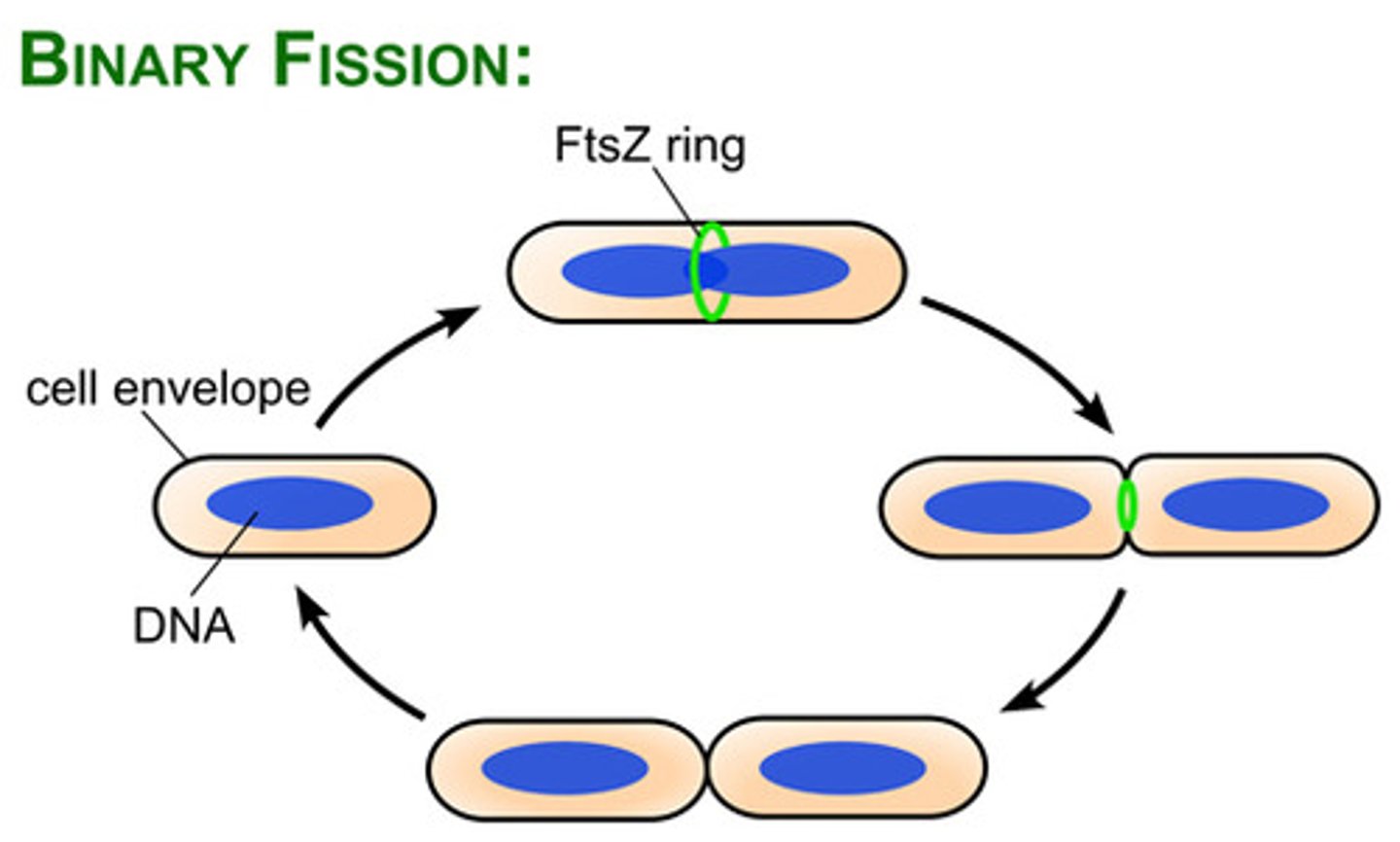
What does the FtsZ assemble to form divisome?
Z ring
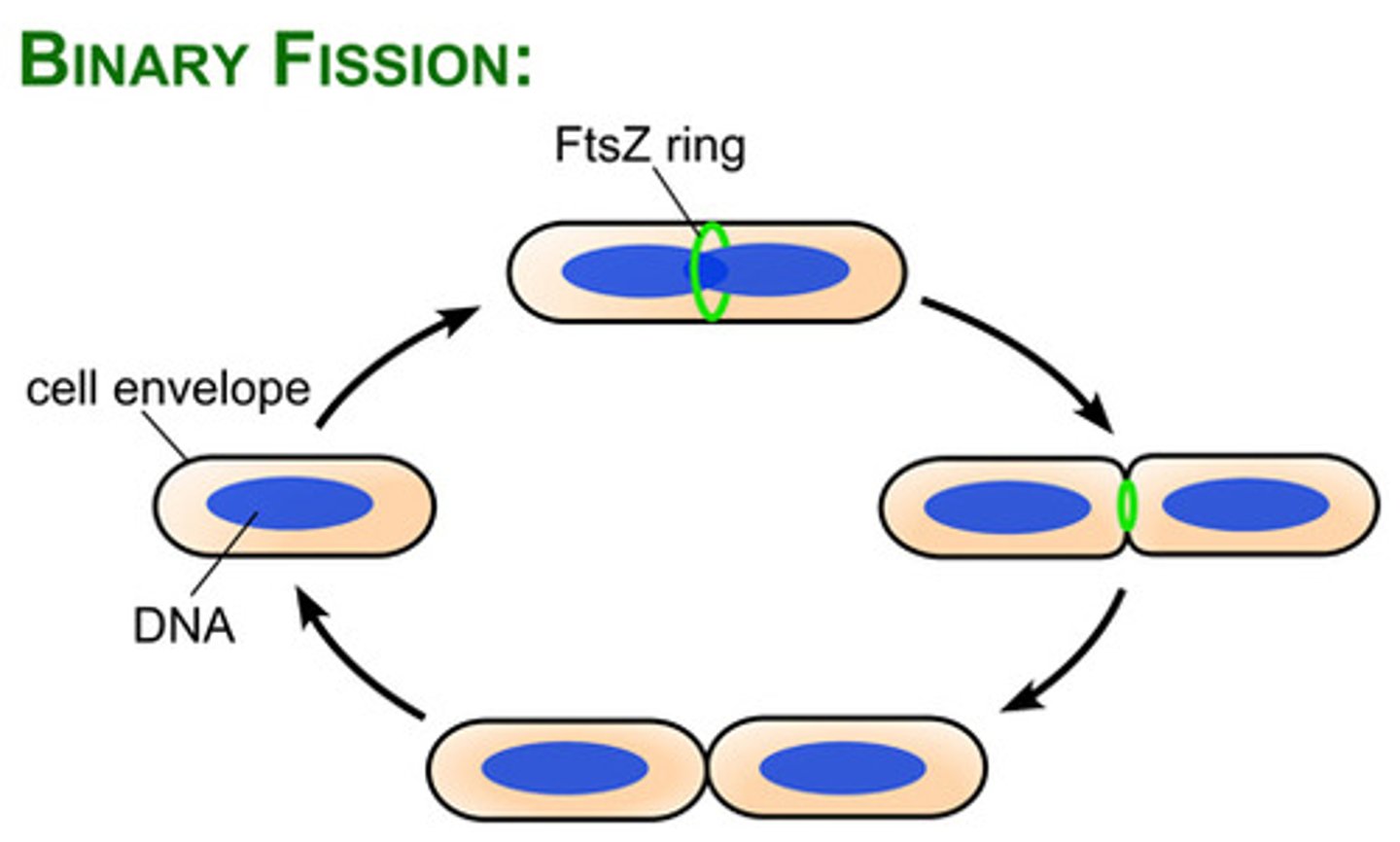
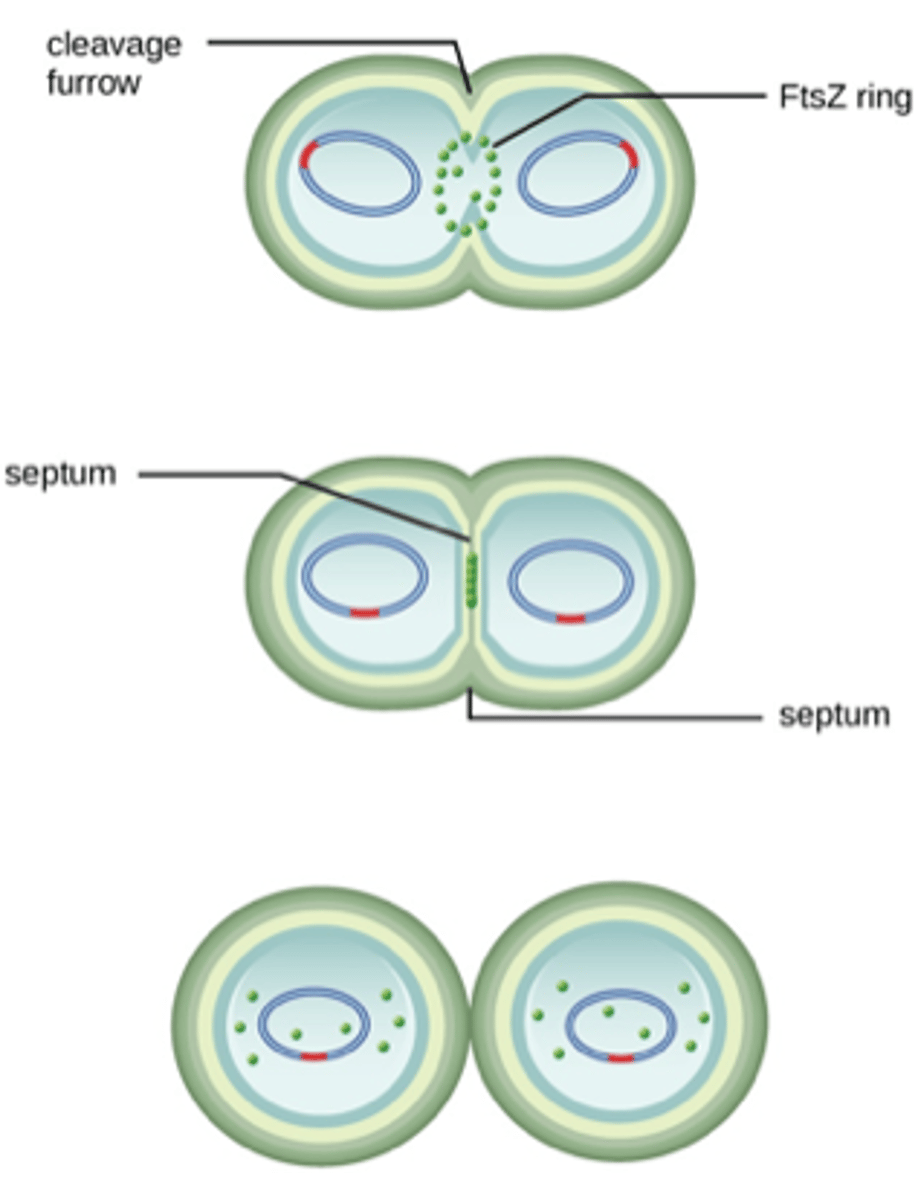
Divisome activates the production of (2)
peptidoglycan and septum
Generation Time
the time it takes to double a population
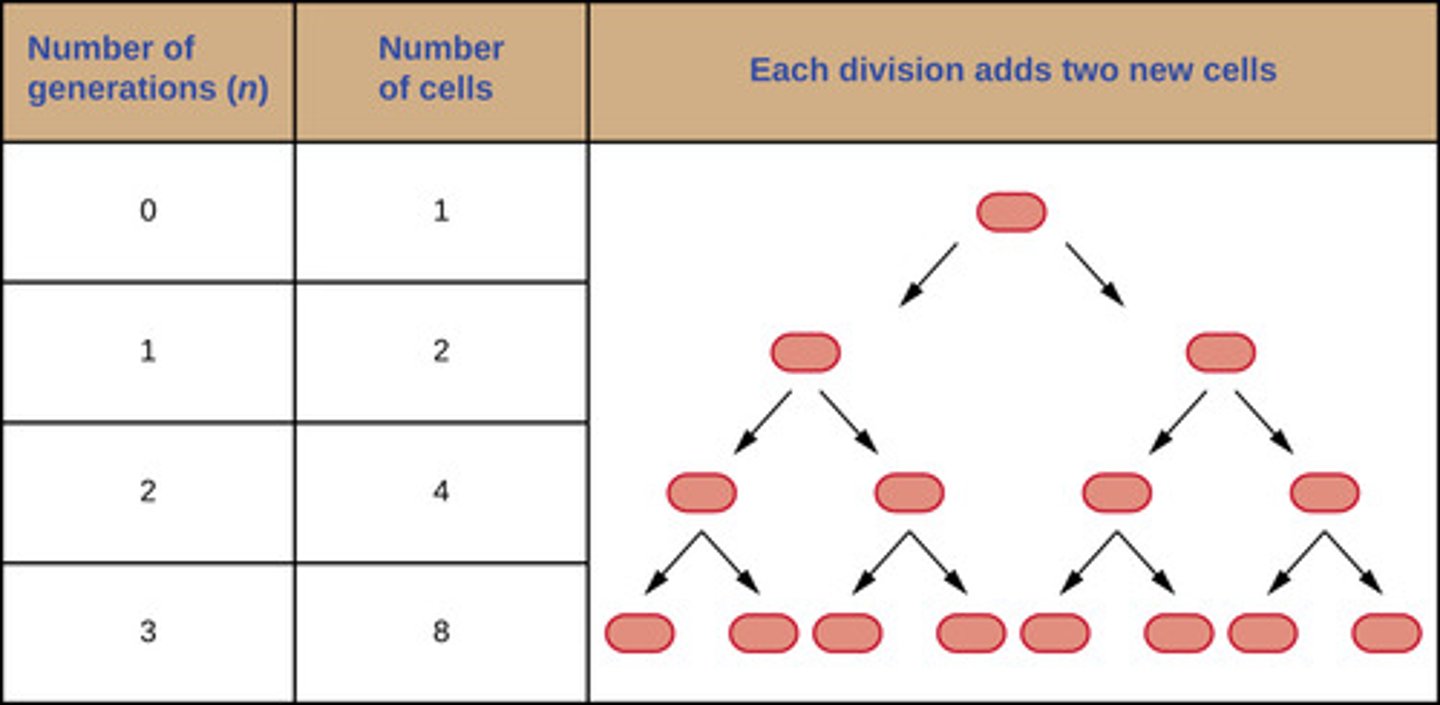
What is the generation time for E. coli?
20 minutes
What is the generation time for B. subtilis?
120 minutes
What is the generation time for S. aureus?
30 minutes
What is the generation time for M. tuberculosis?
15-20 minutes
Eukaryotic Organisms Generation Time
the time between the same points of the life cycle in two successive generations
Prokaryotic Organisms Generation Time
the time it takes for the population to double through one round of binary fission
Calculating Population Size Formula
Nn=number of cells at generation n
n=number of generations
N0=initial number of cells
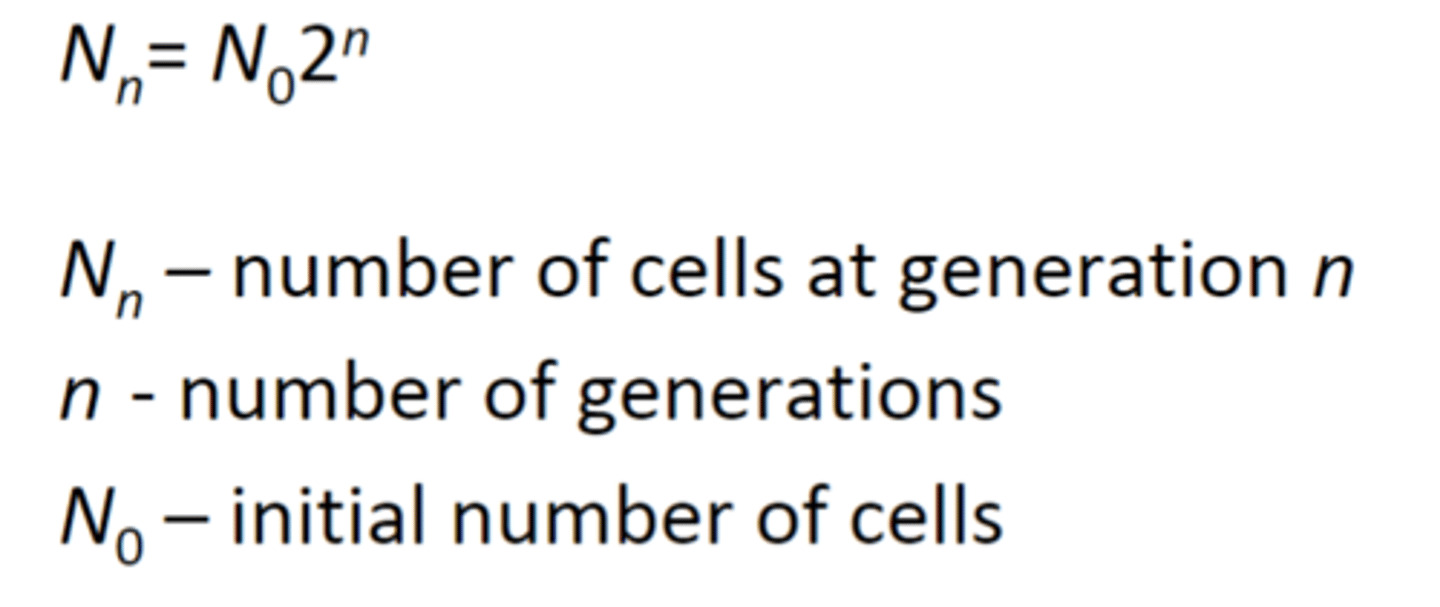
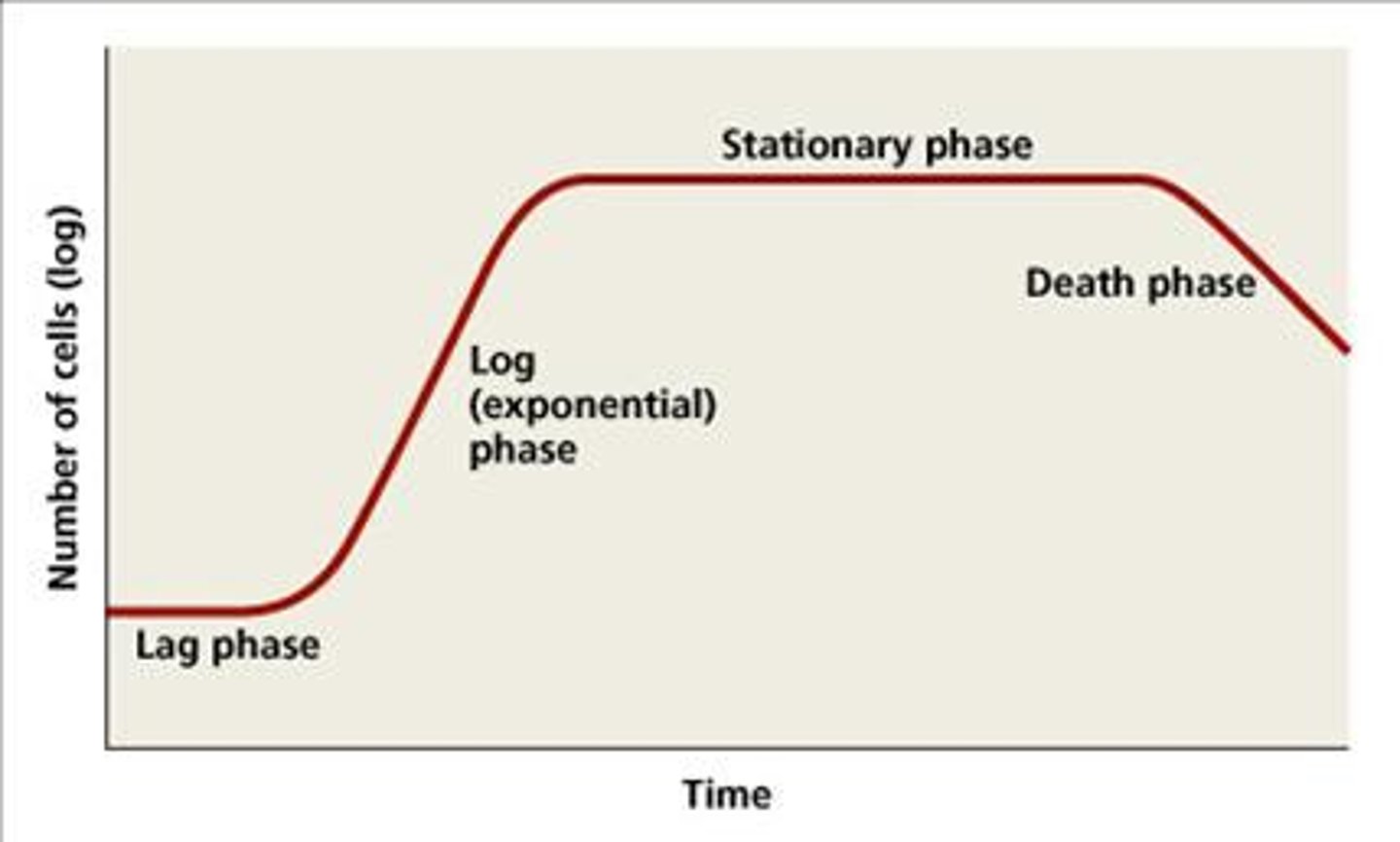
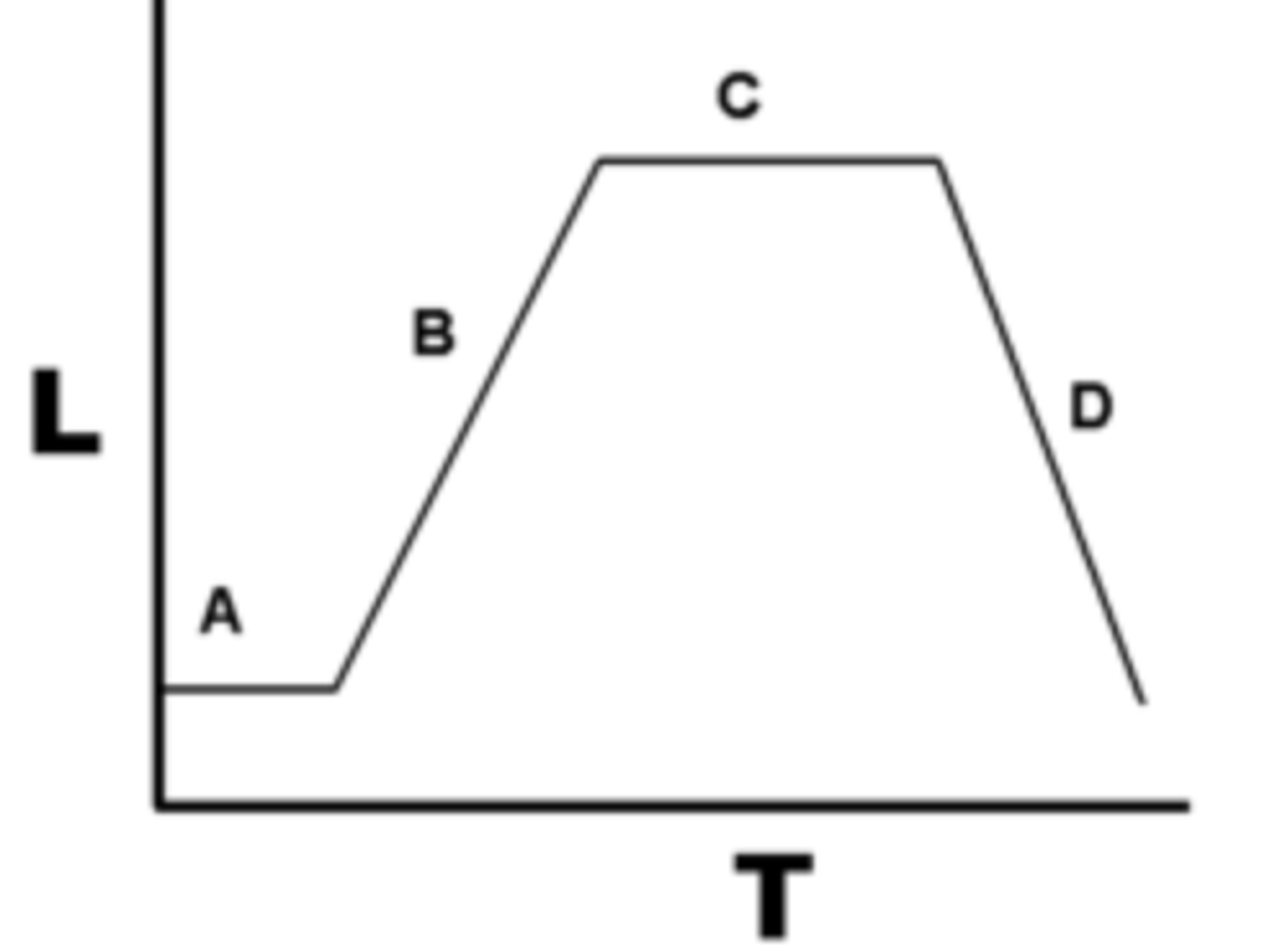
What are the 4 phases that make up the Growth Curve?
Lag phase
Log phase
Stationary phase
Death phase
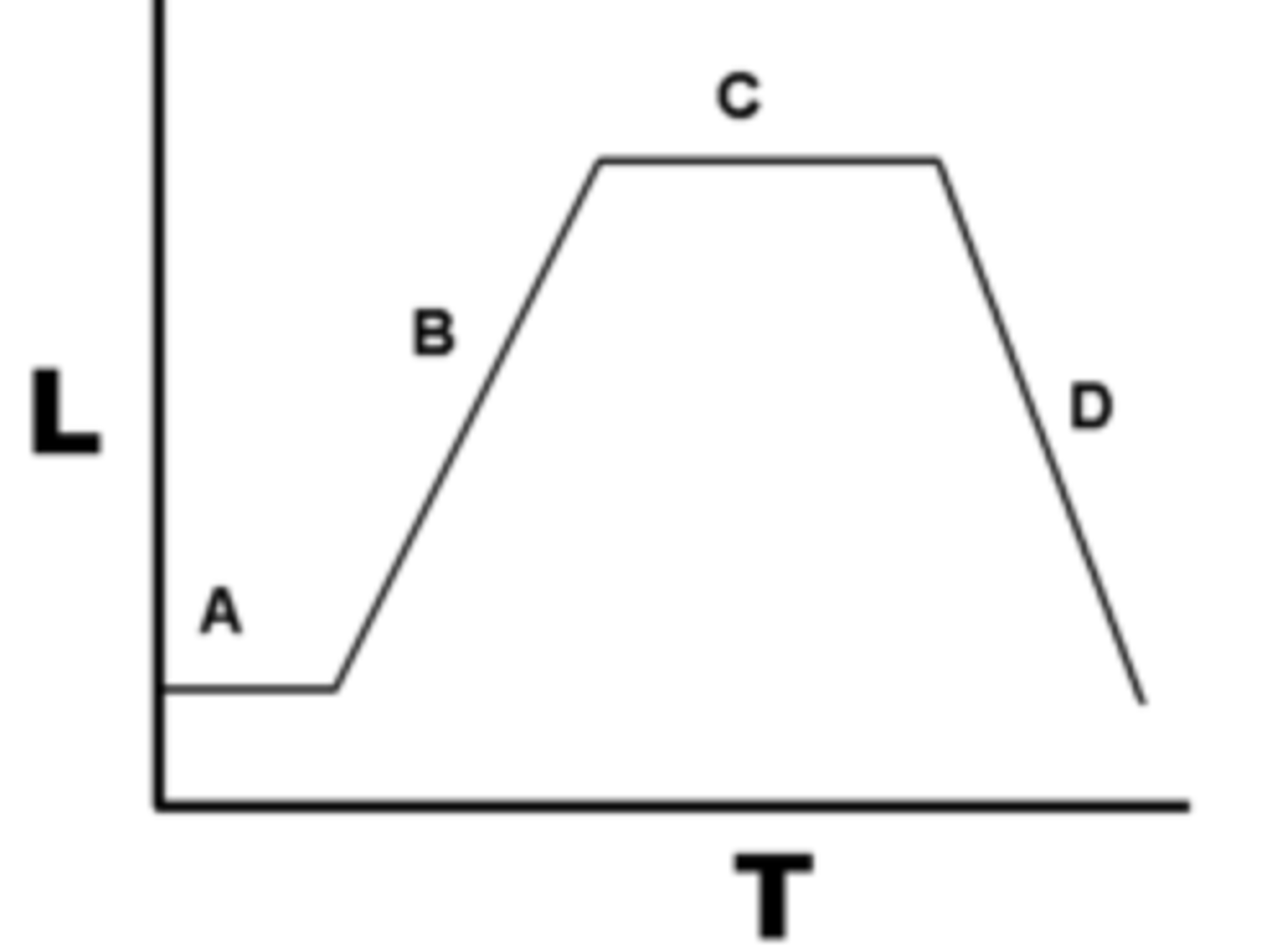
Lag Phase
(A) inoculum cells added and adjust to culture medium; no change in population
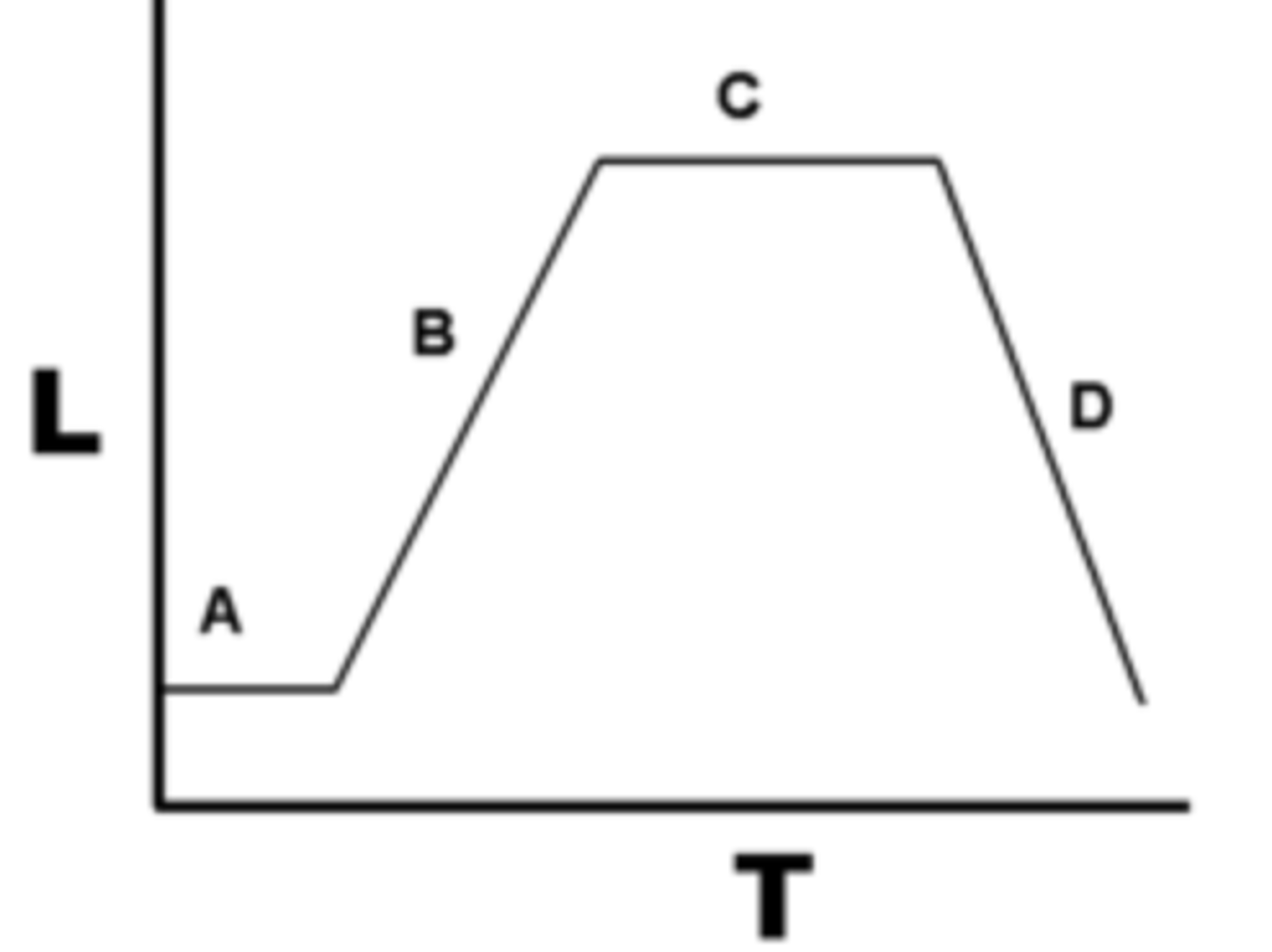
Log (exponential) Phase
(B) binary fission occurs; cell replication is greater than cell death
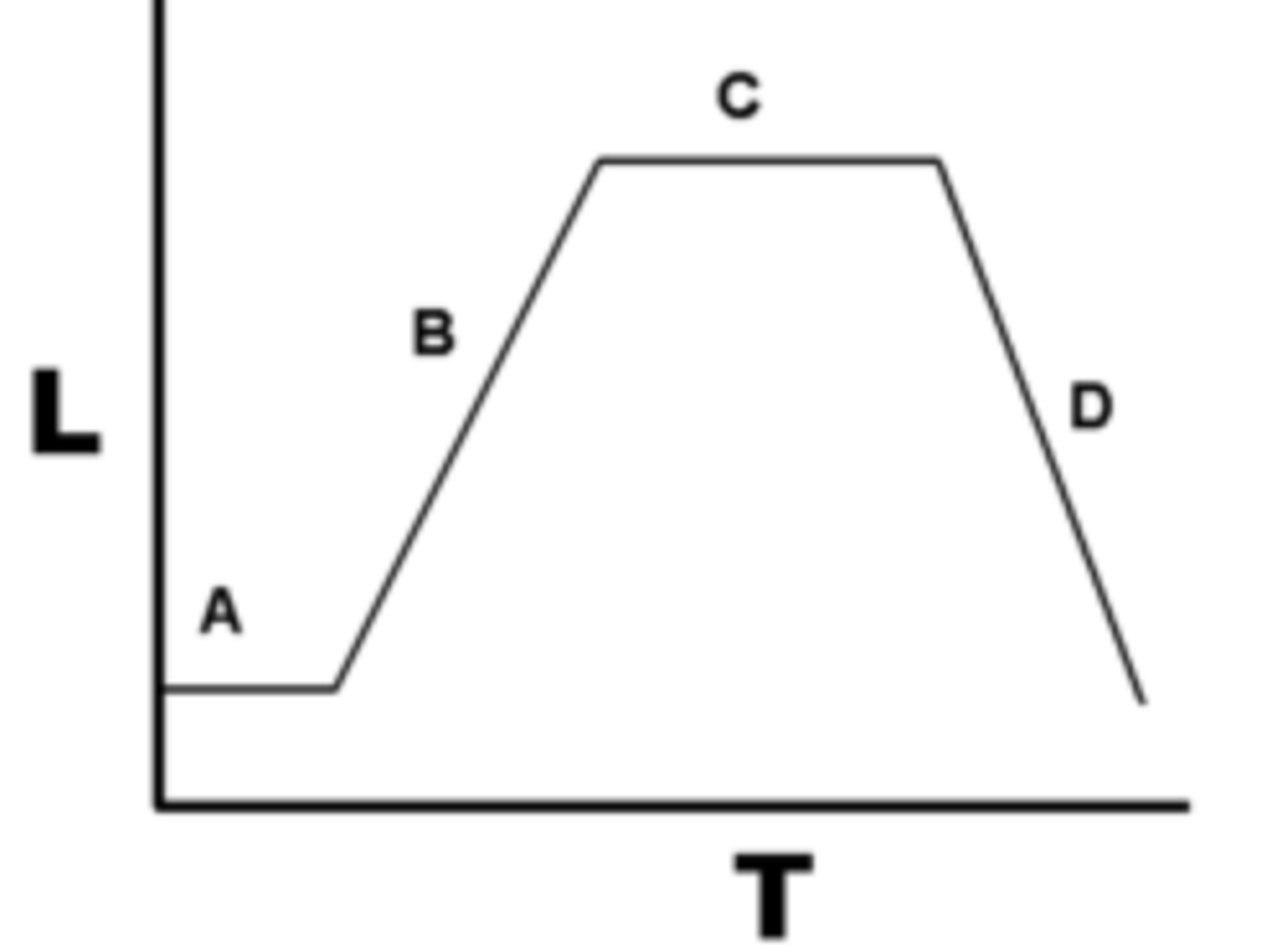
Stationary Phase
(C) resources become depleted, cell replication=cell death
Death Phase
(D) endospores can form cell replication is less than cell death
What happens during the Lag phase?
initial cell numbers do not change, cells grow larger; metabolically active, and damaged or shocked cells undergo repair
Duration of the lag phase is determined by factors including: (3)
genetic makeup
media composition
initial inoculum size
The generation time for the Log phase is
genetically determined (intrinsic growth rate)
Which growth curve phase is it when time vs # of cells is exponential?
Log phase, semilog displays linear
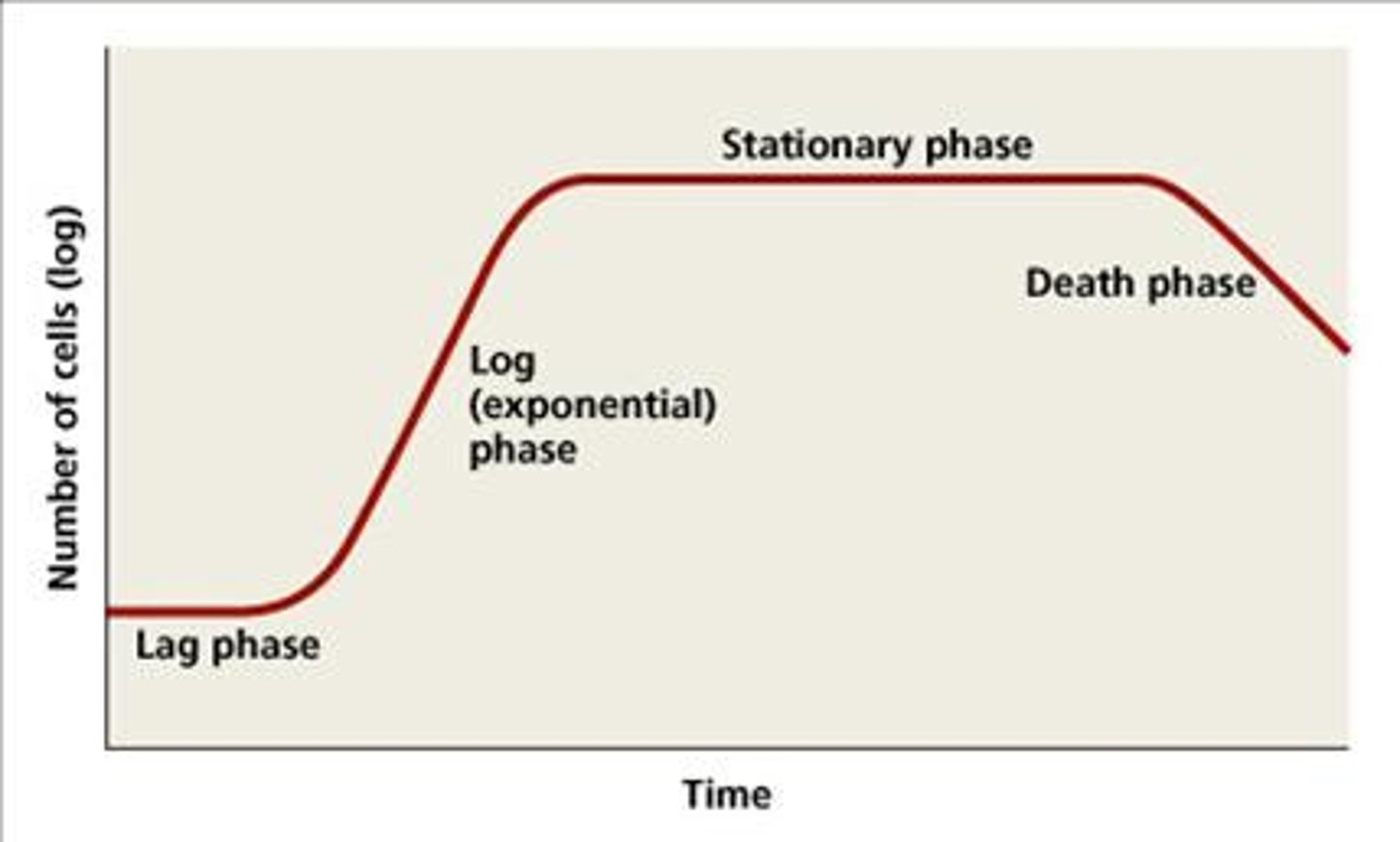
This growth curve phase has constant growth and uniform metabolism which is good for industrial applications
Log phase
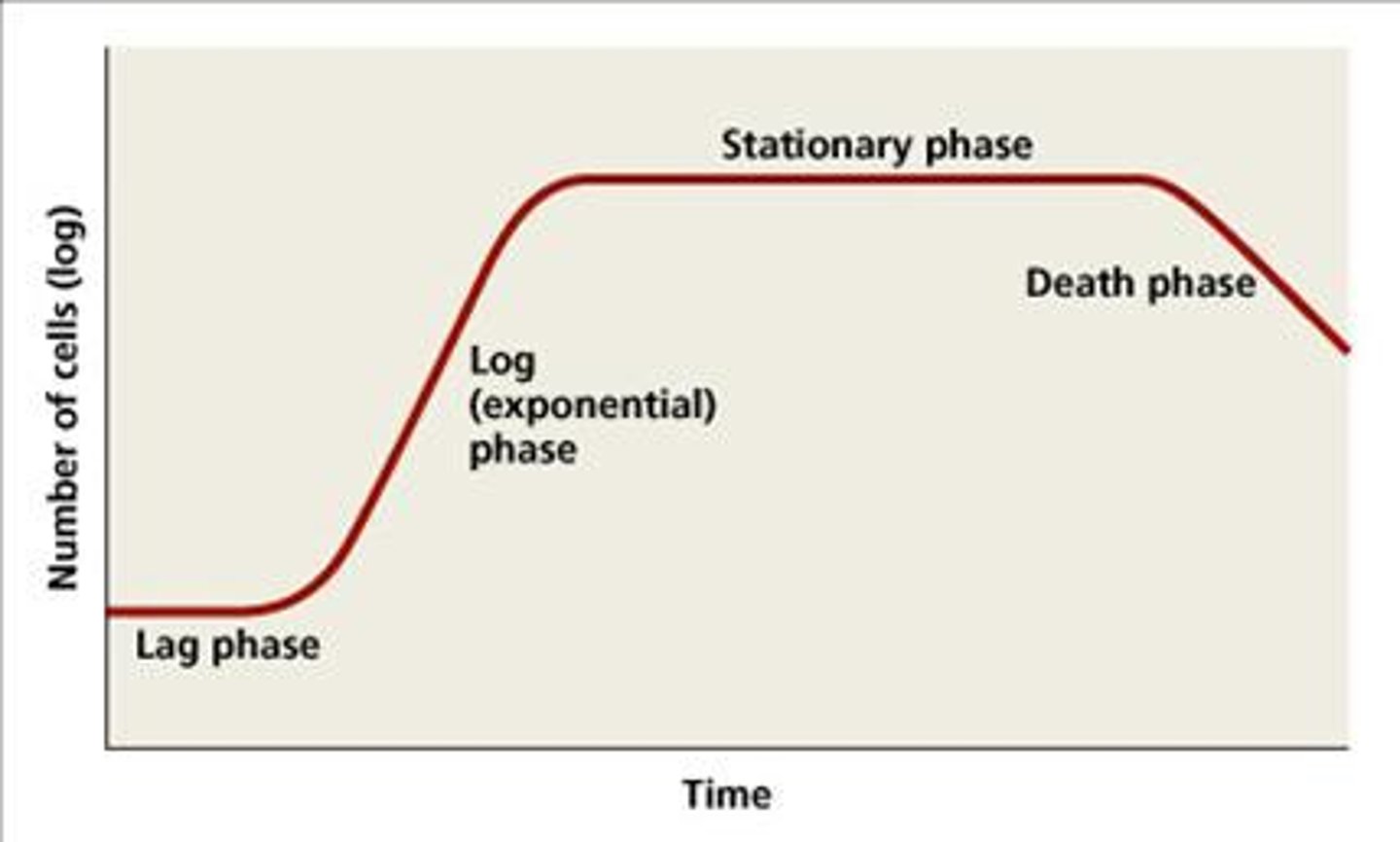
What growth curve is most susceptible to disinfectants and antibiotics that affect protein, DNA and cell-wall synthesis?
Log phase
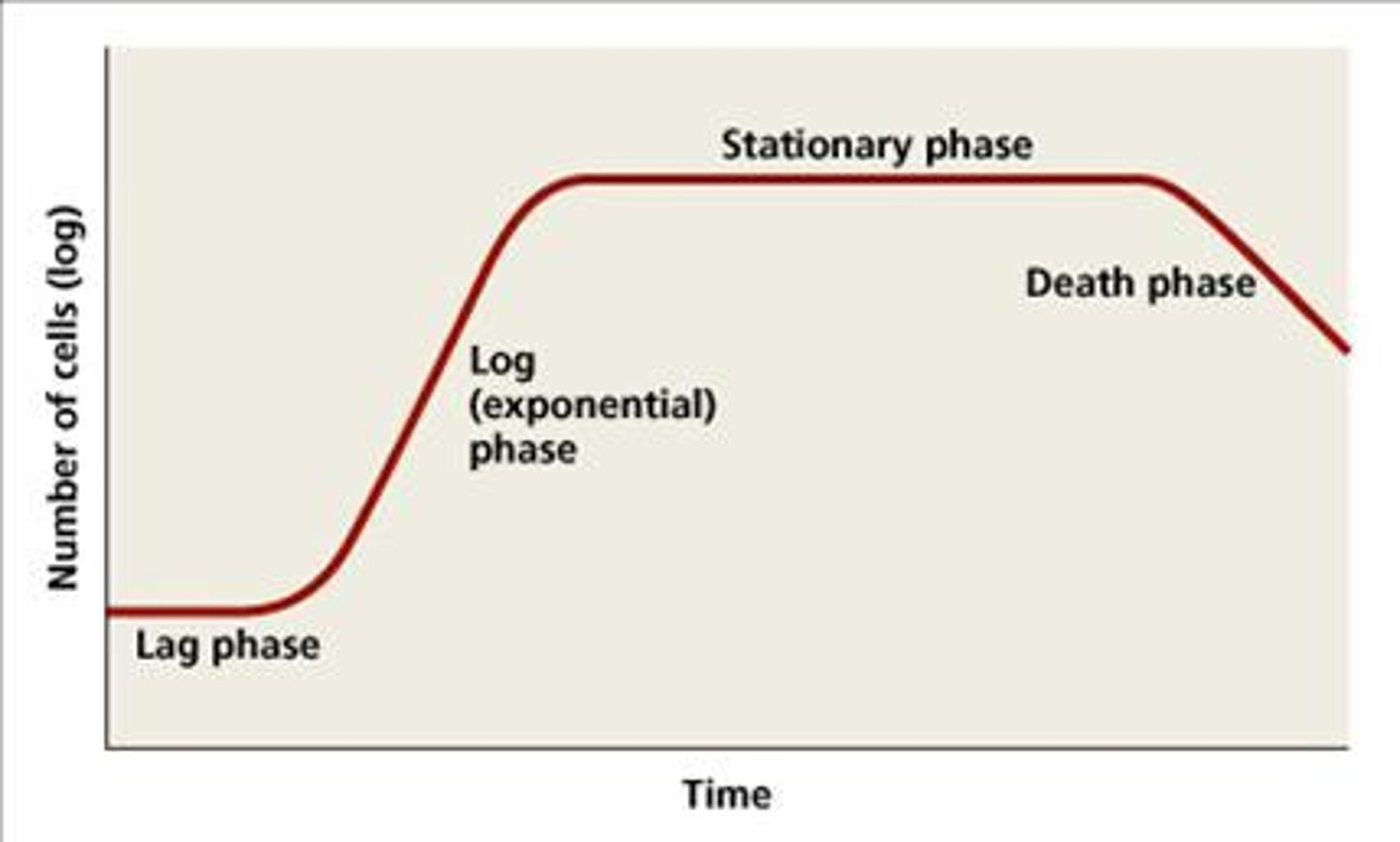
Waste accumulating and nutrients gradually being used up in during which phase of the growth curve?
stationary phase
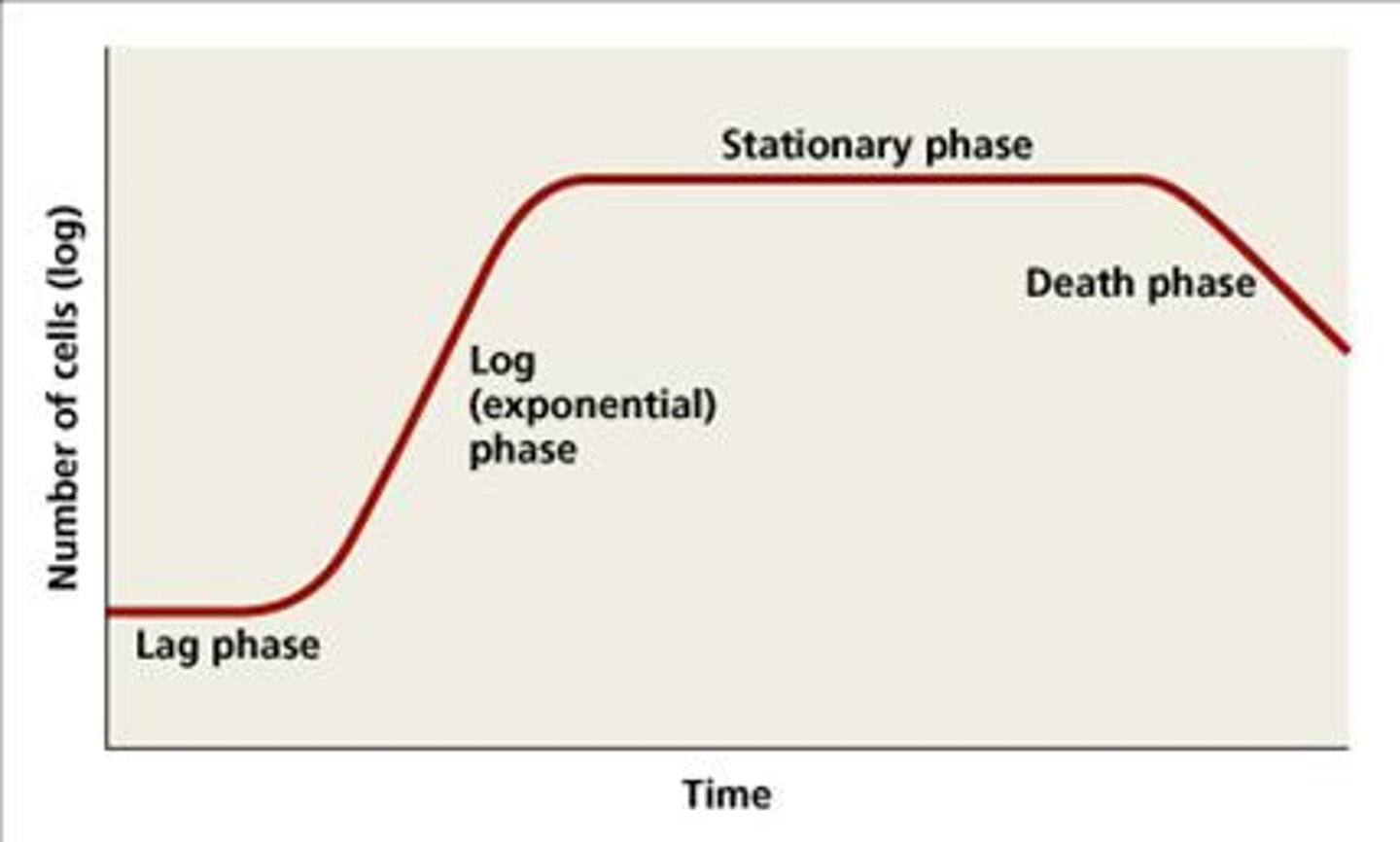
Culture density if constant during which growth curve phase?
stationary phase
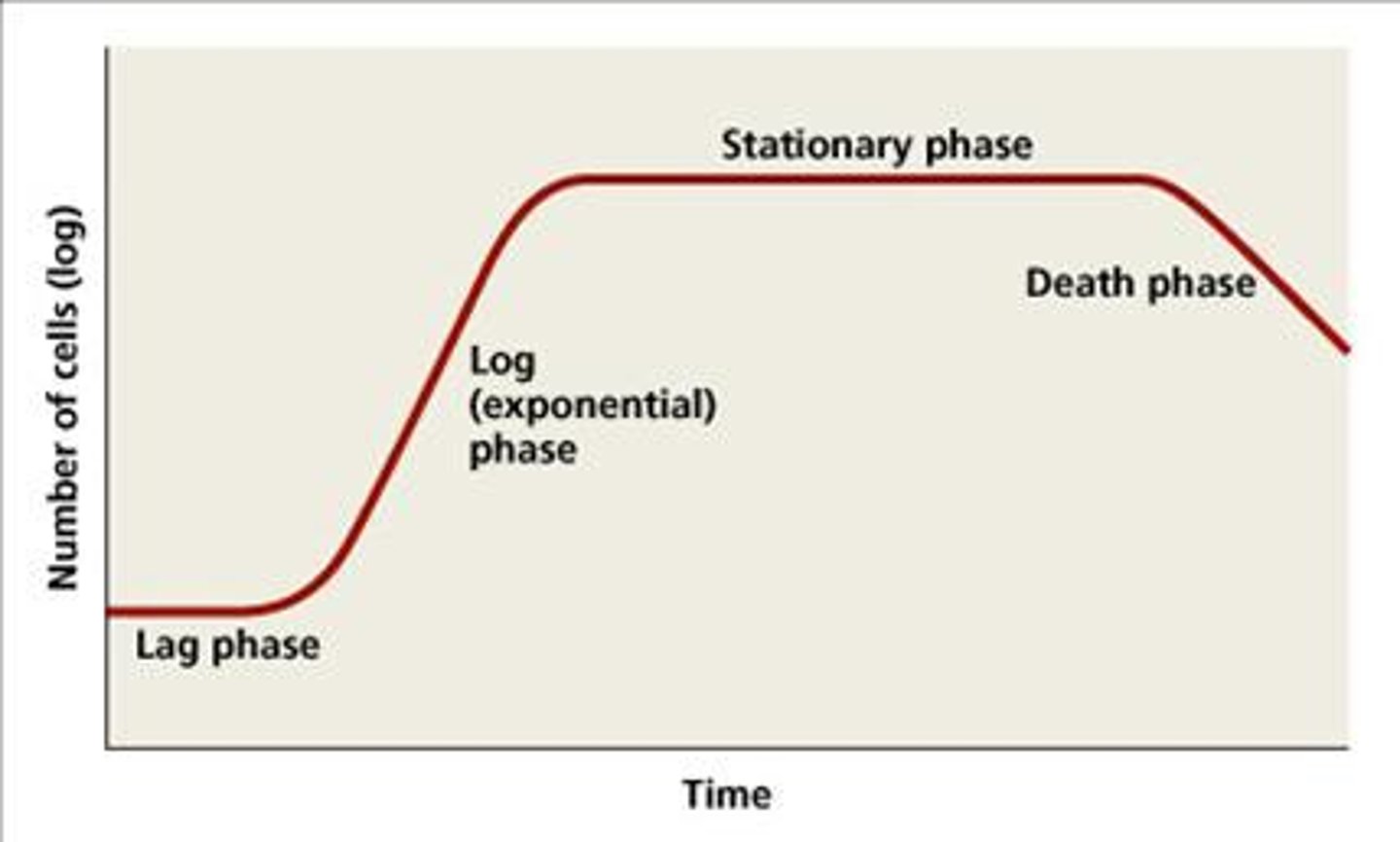
Which growth curve phase includes the cell entering survival mode, synthesis slowing down, and the cell being less susceptible to antibiotics?
stationary phase
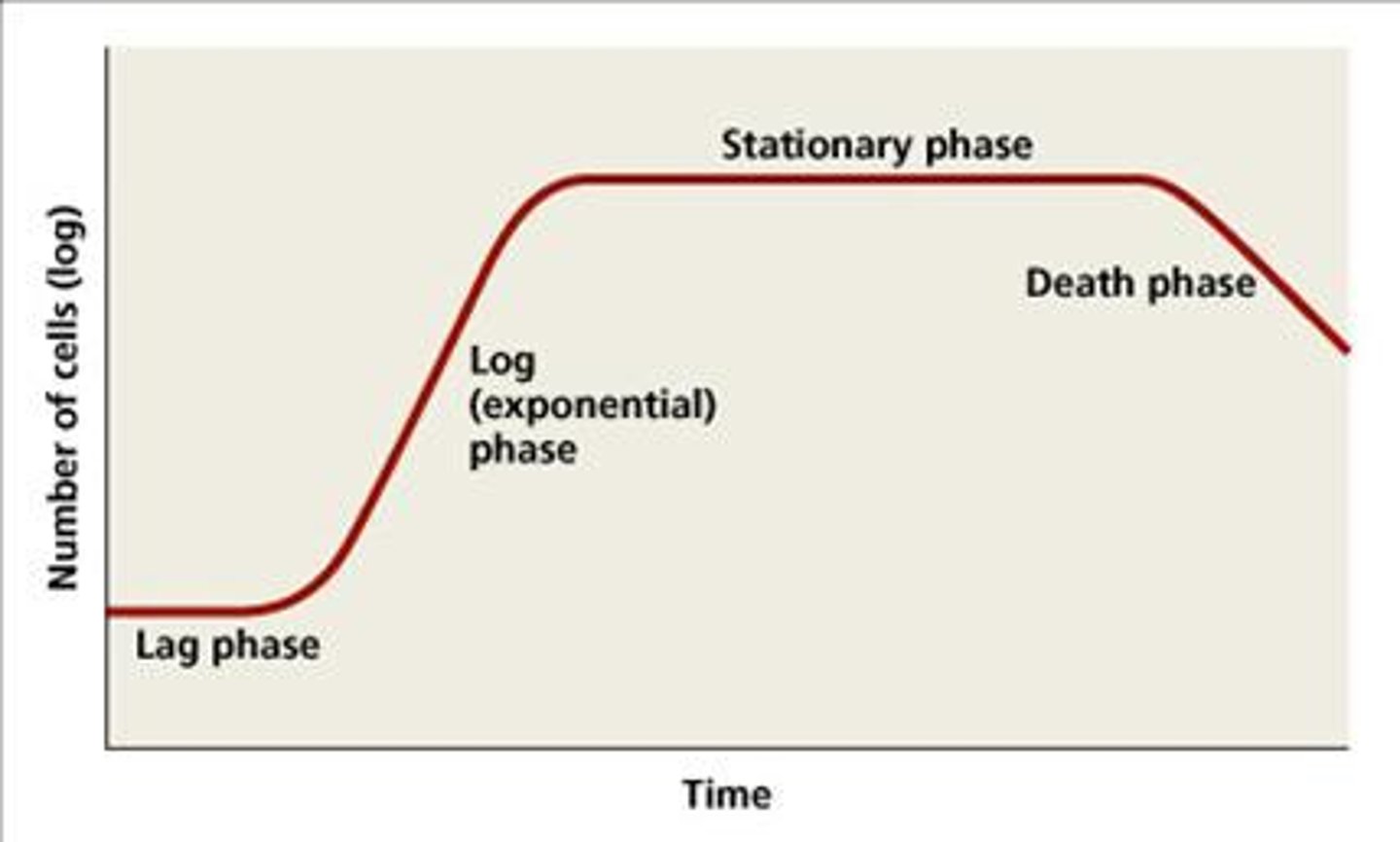
During the __________ phase of the growth phase, cells undergo sporulation for endospore-formers.
stationary phase
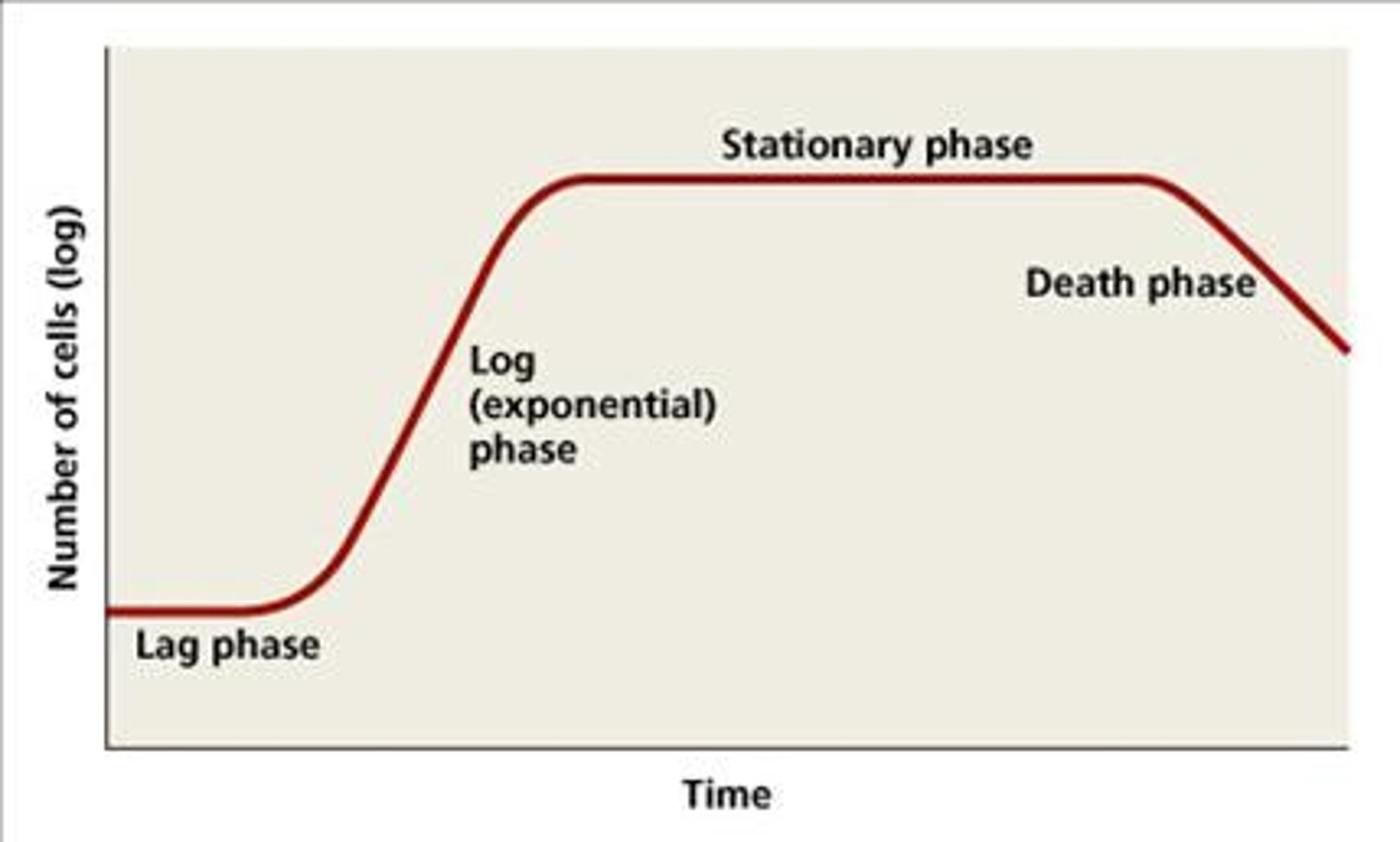
This growth curve phase includes expression of virulence factors and secondary metabolites
stationary phase
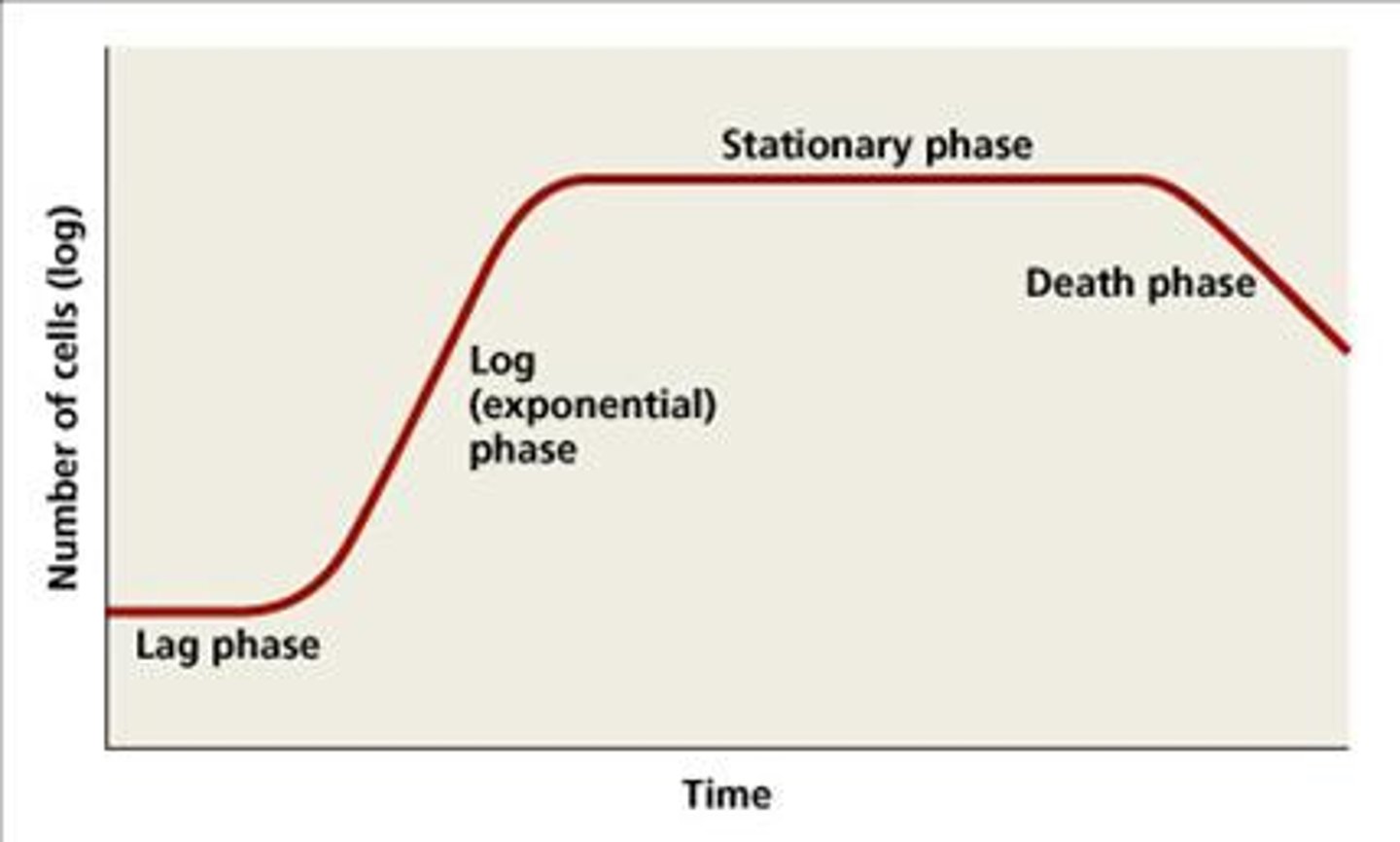
Which phase of the growth curve includes toxic waste accumulation and the nutrients being exhausted?
death phase
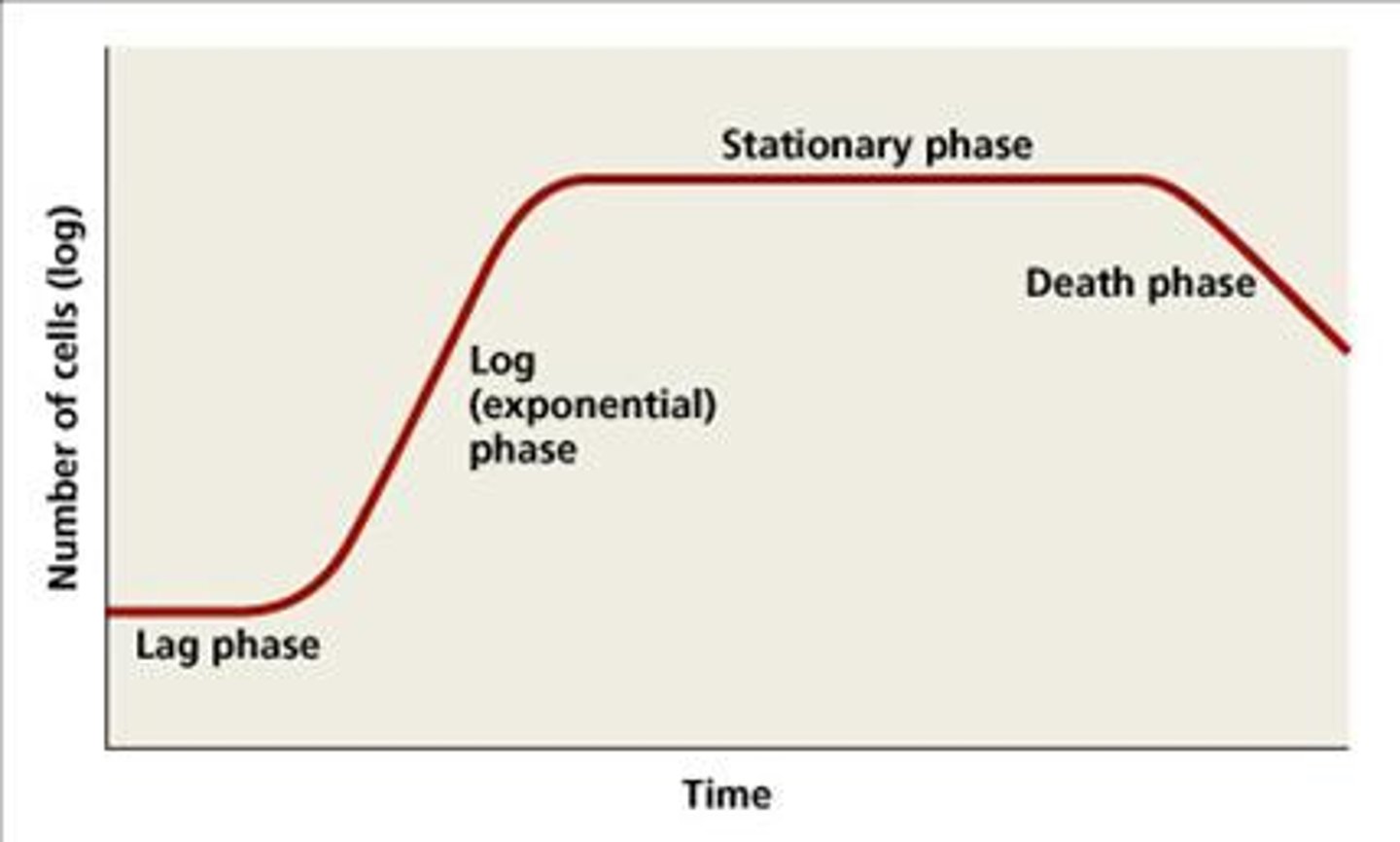
Which growth curve phase is happening if the cells lyse and release nutrients for surviving cells and endospore-formers?
death phase
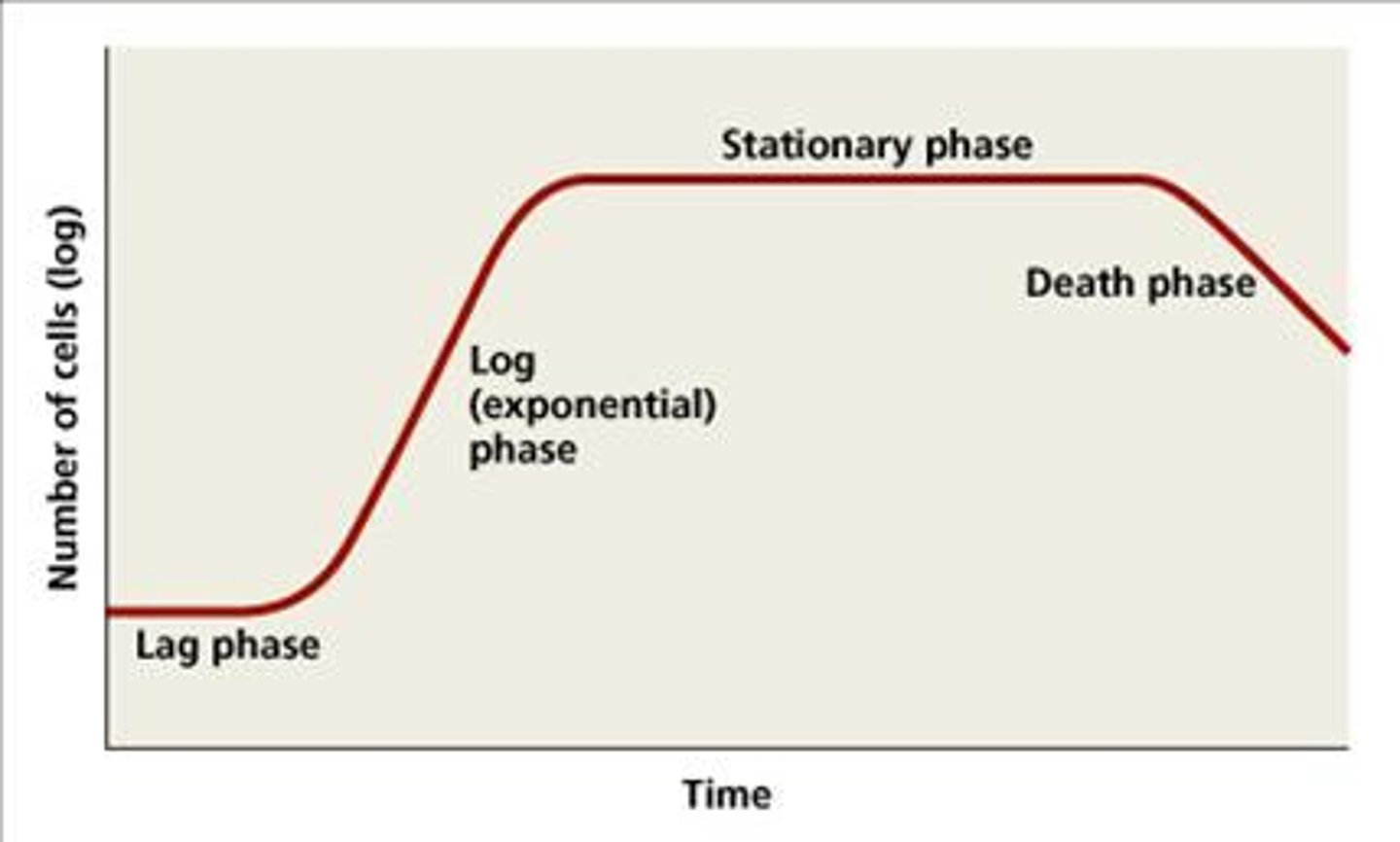
During the Death Phase, __________ are the surviving cells with slow metabolism.
persisters
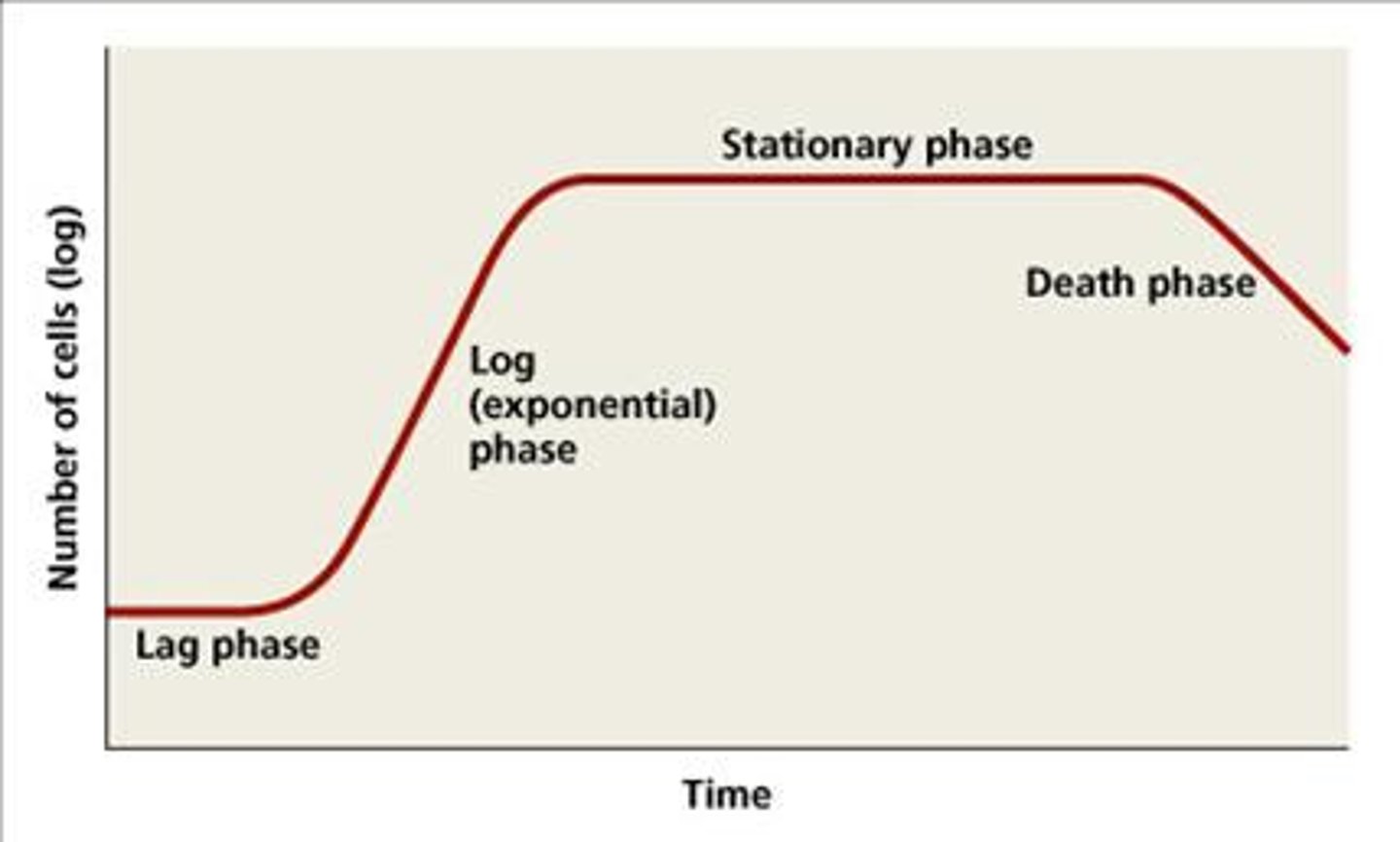
Persister cells are medically important because they are associated with certain chronic infections that do not respond to antibiotic treatment such as
tuberculosis
A chemostat is a
culture vessel fitted with an opening to add nutrients (feed) and an outlet to remove contents (effluent), effectively diluting toxic wastes and dead cells.
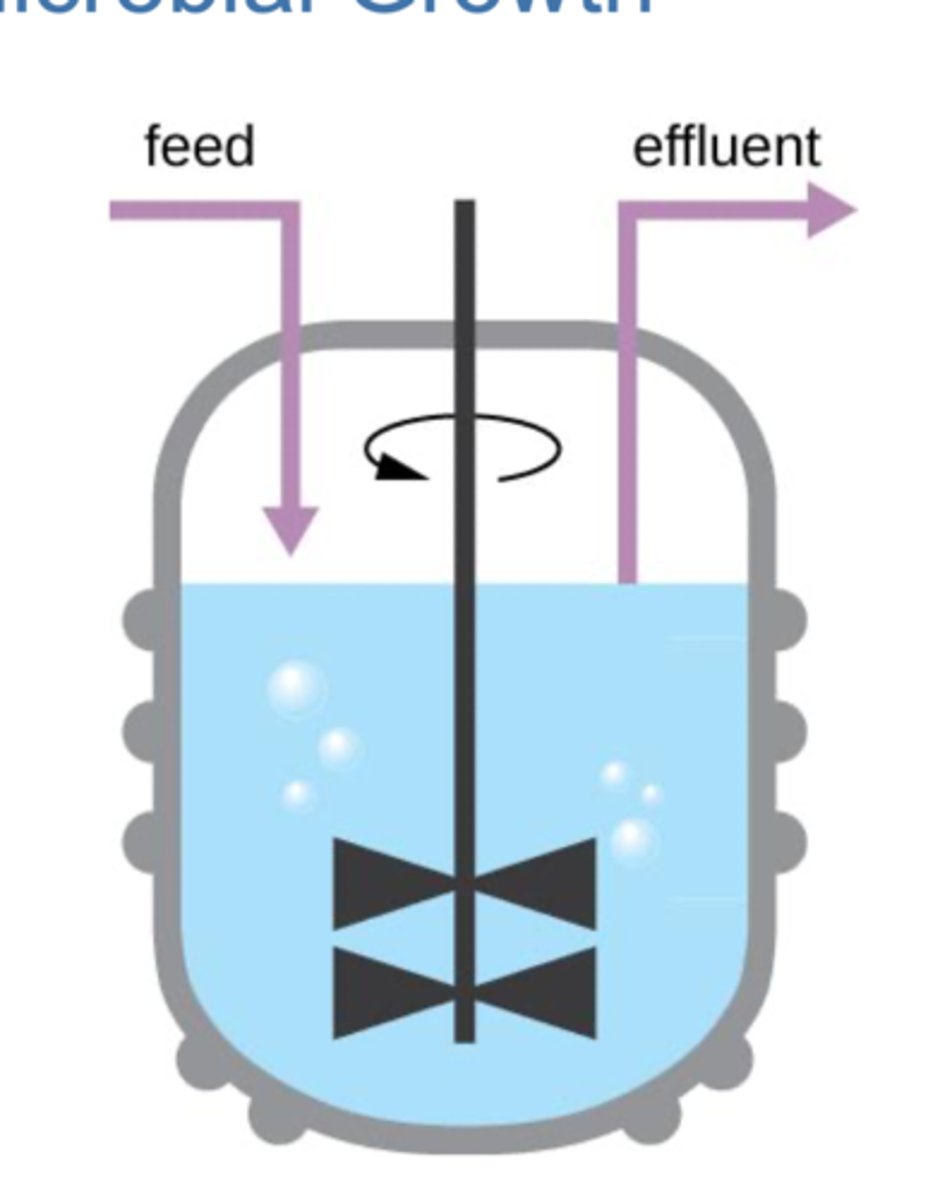
Sustainable Growth
-open system culture have infinite resources
-nutrients and air are replenished
-dead cells and waster are removed
-beneficial for industrial microbiology
How is the Direct Microscopic Cell Count method used to measure growth?
cells are counted under a microscope
In Direct Microscopic Cell Count, what is the known volume that is transferred to a calibrated slide to be manually counted called?
Petroff-Hausser chamber
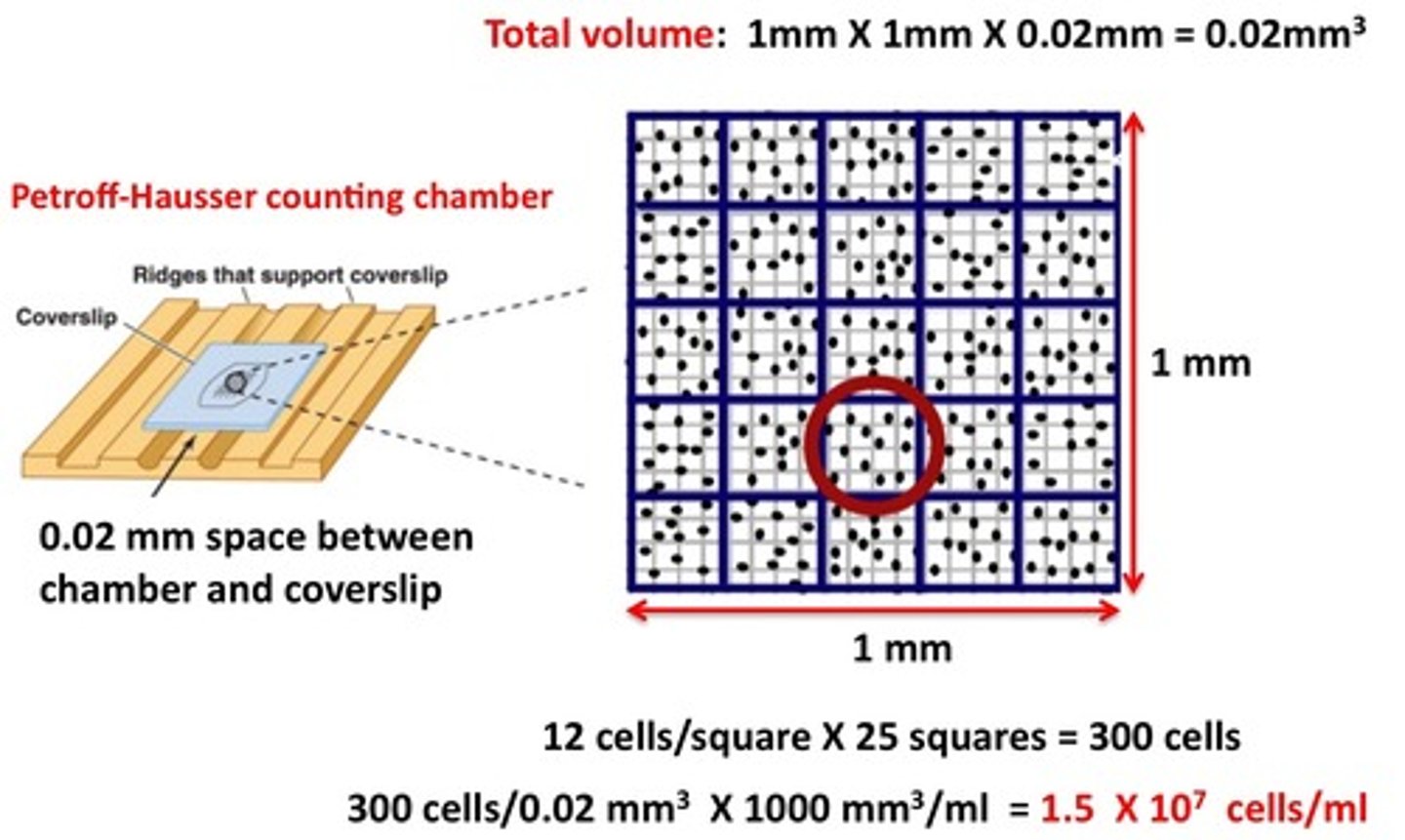
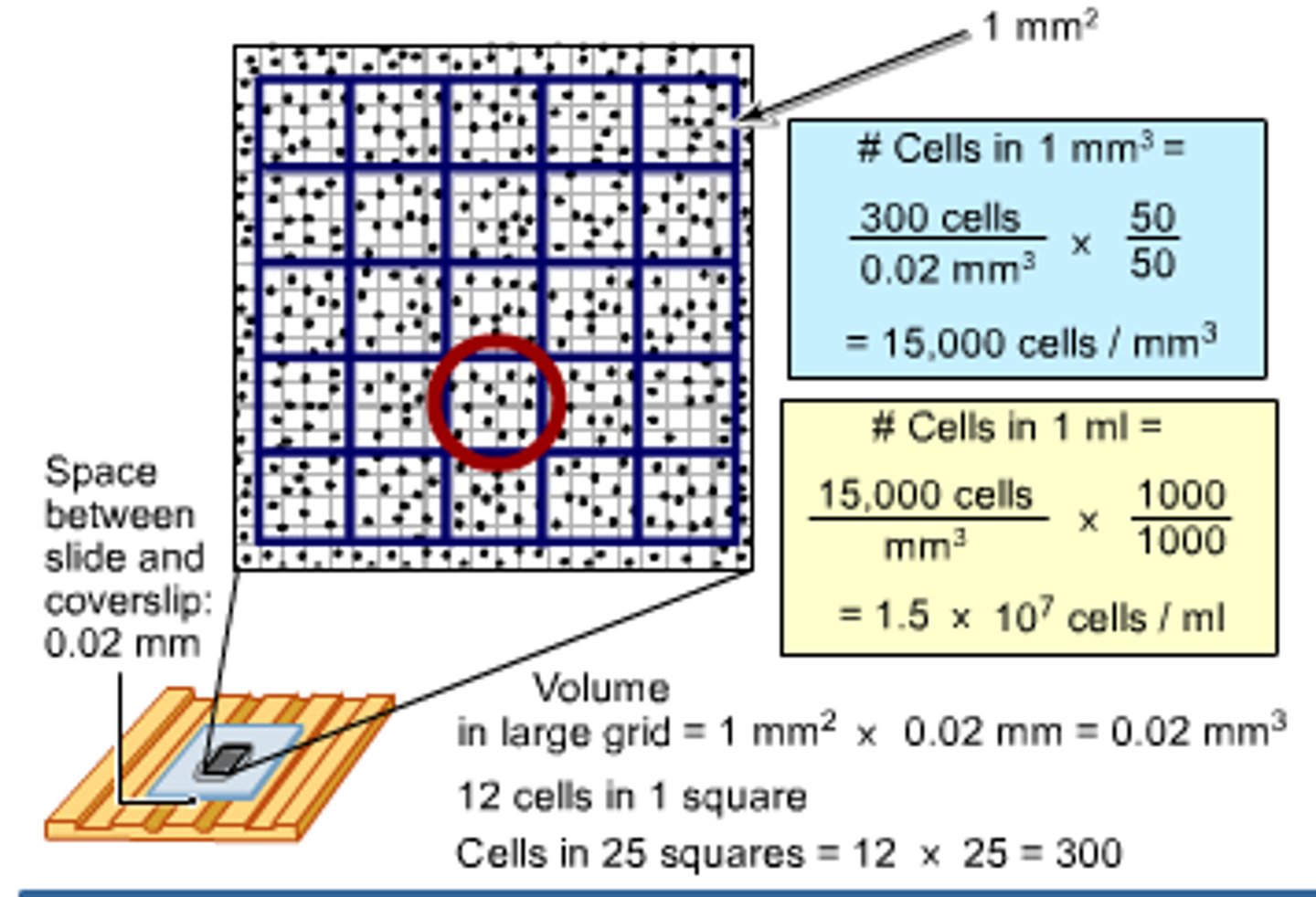
What is a limitation of the Direct Microscopic Cell Count method used to measure growth?
They cannot distinguish between live vs. dead cells
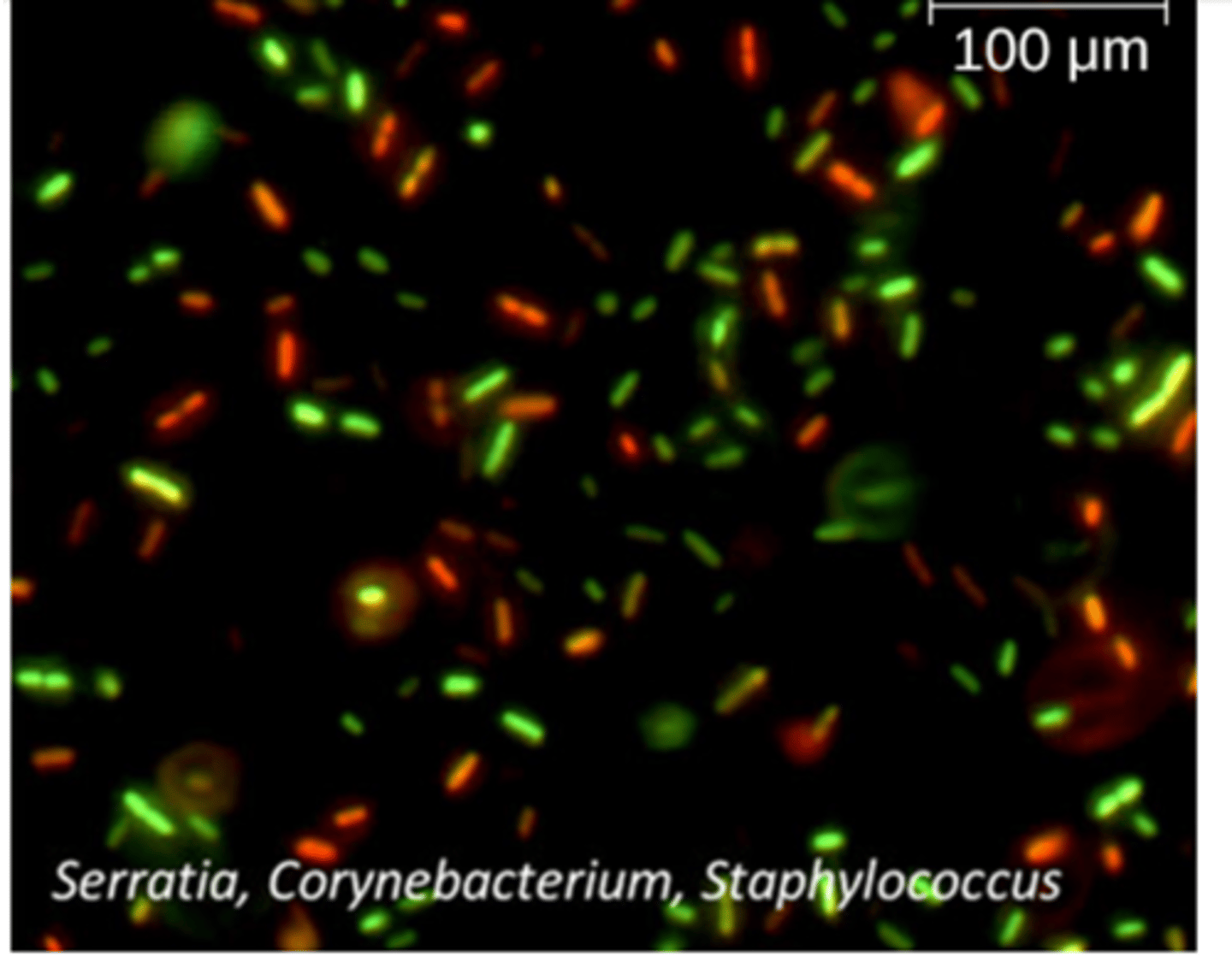
How is the Fluorescence Staining method used to measure growth?
cells are counted under a microscope or flow cytometer, the red stain binds to damaged cells to indicate dead cells
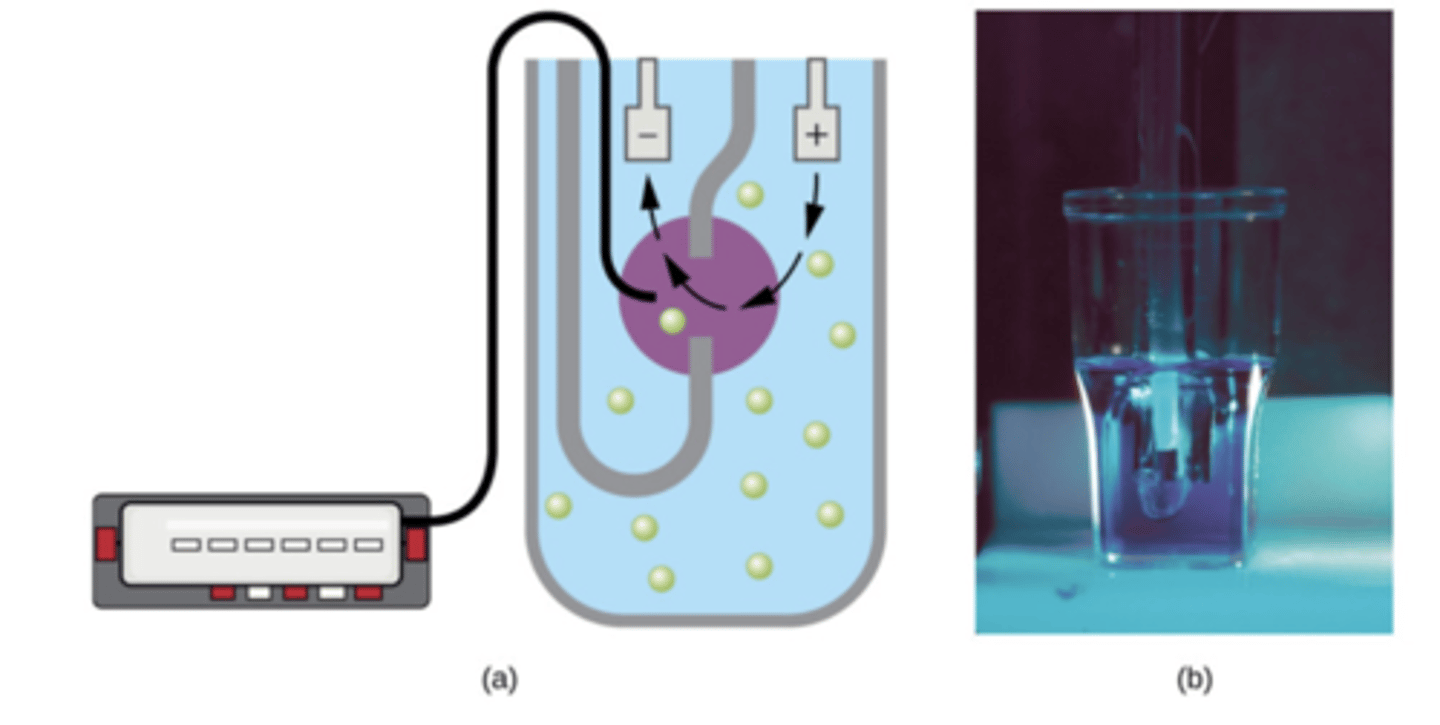
How is the Coulter Counter method used to measure growth?
it detects electrical resistance change due to cell density
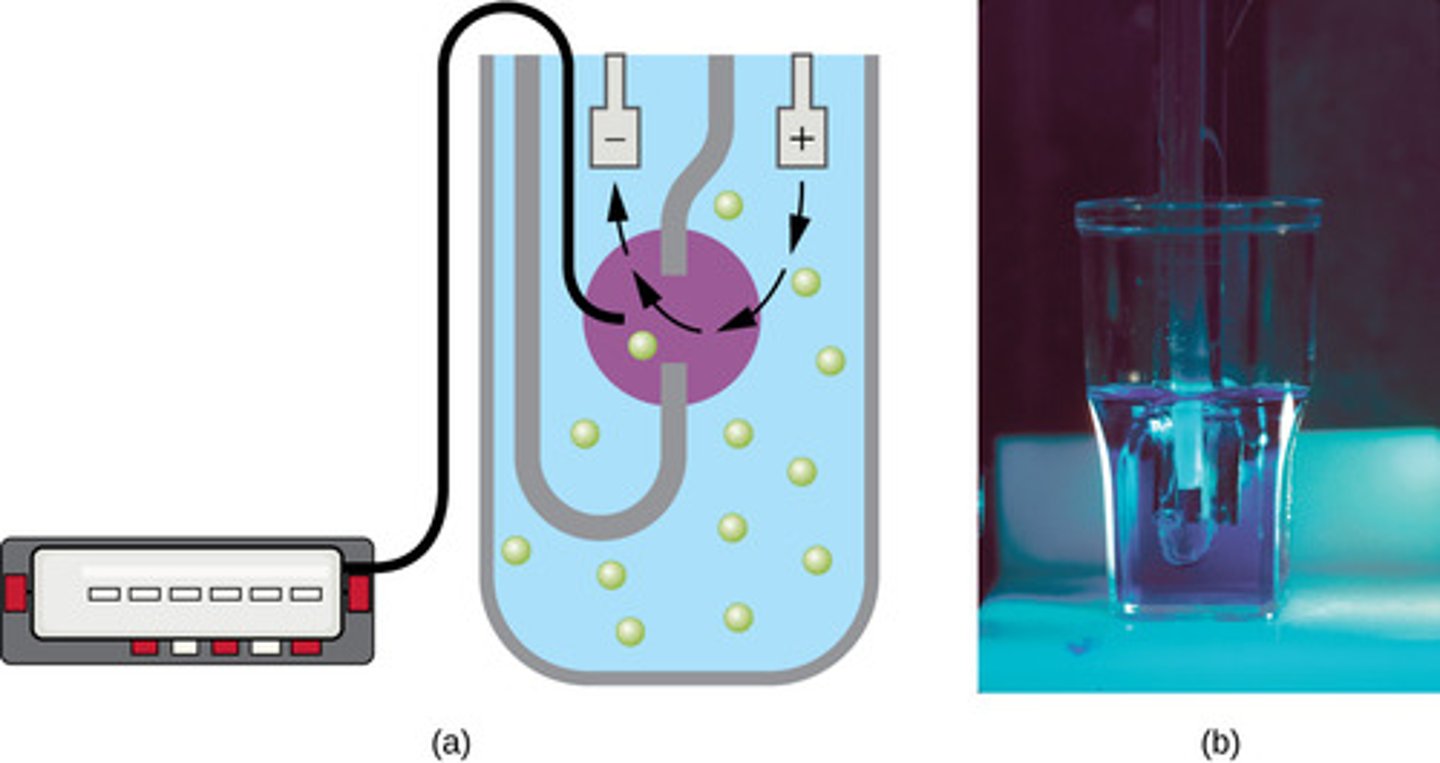
What is the limitation to the Coulter Counter Method?
it does not differentiate between live and dead cells
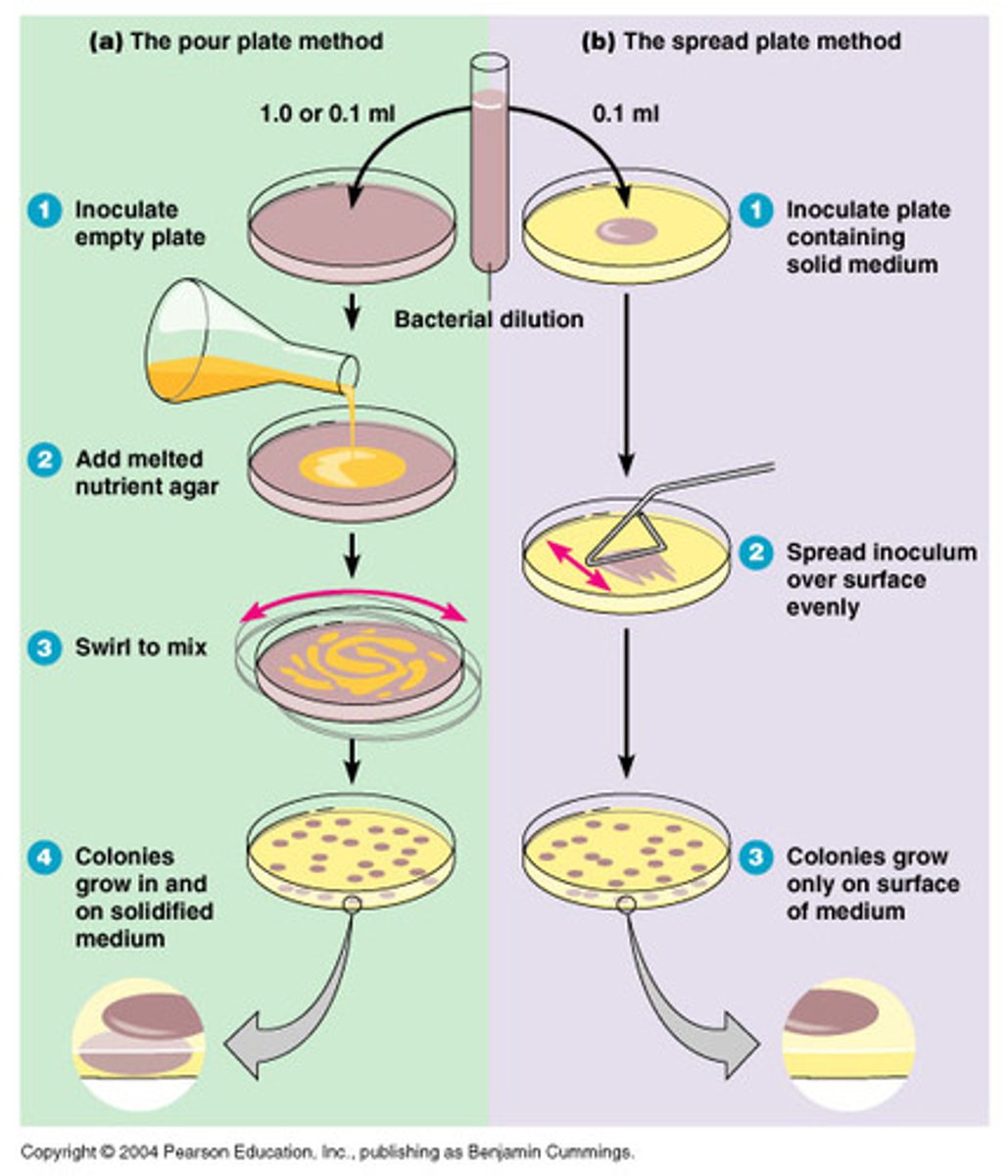
How is the Viable Plate Count method used to measure growth?
count of viable cells; samples are diluted and grown on solid media
How are the results expressed for the Viable Plate Count?
in colony forming units per volume (CFU/mL)
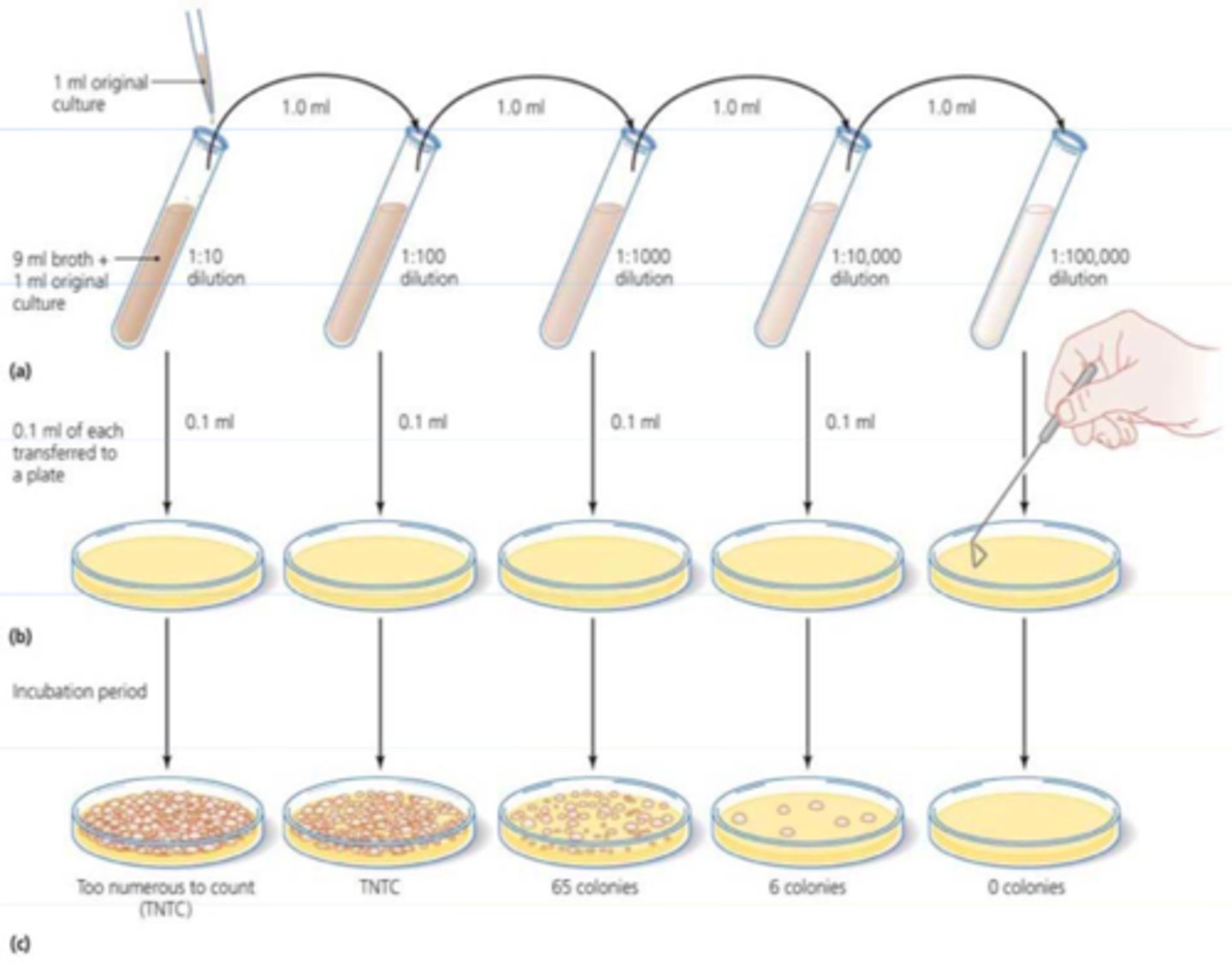
What is the limitation for the Viable Plate Count method?
it is limited only to easily cultured species
Serial Dilution if plated and counted via (2)
pour plate or spread plate technique
The countable range is traditionally
30-300 CFU/mL because it is statistically most accurate
TFTC
too few to count; Less than 30
TNTC
too numerous to count; more than 300
If there is a very dilute sample that may not contain enough organisms to use for the plate count methods, what technique can be used to concentrate the sample before plating?
membrane filtration technique
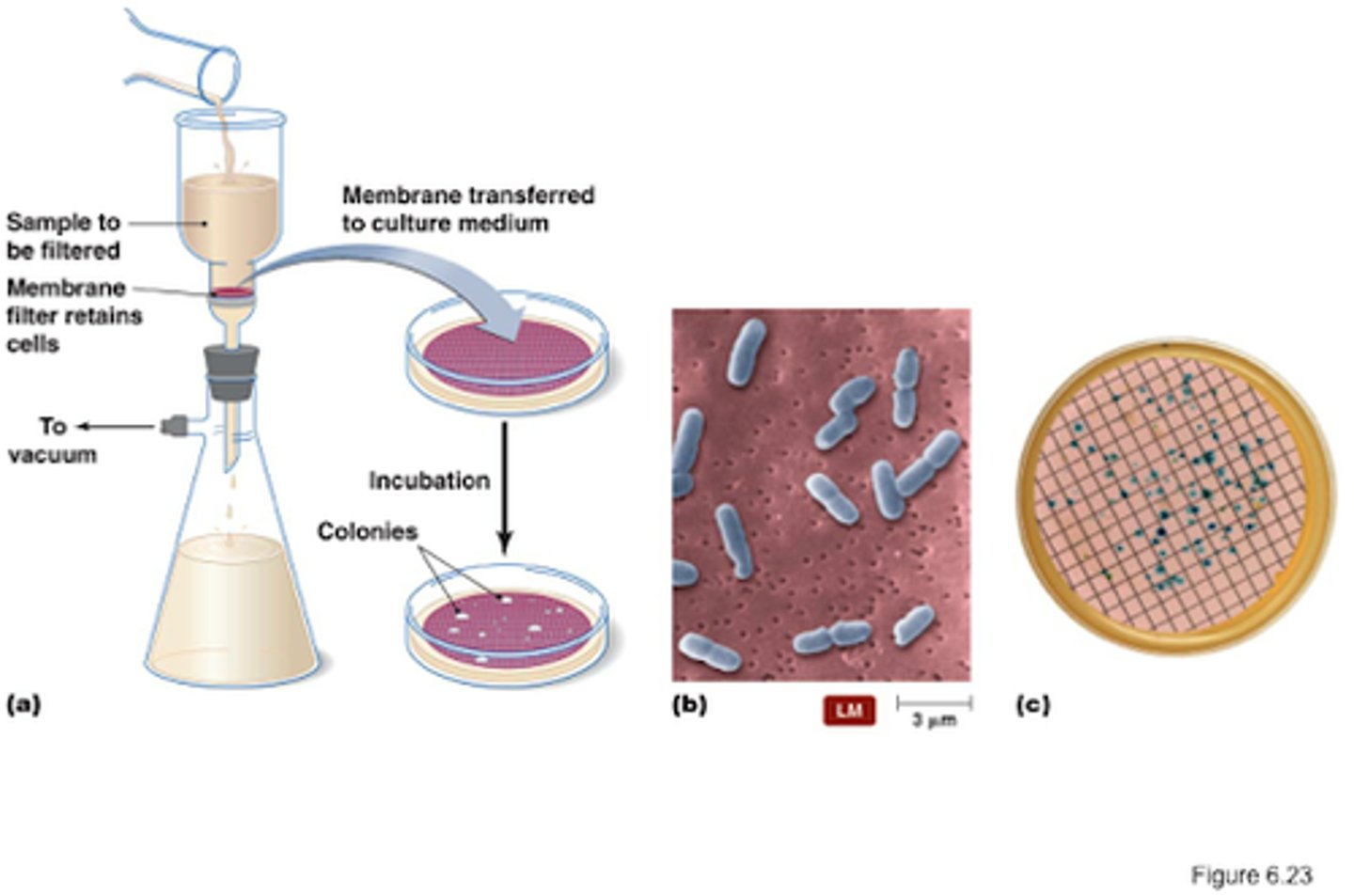
Membrane filtration technique
known volume filtered through a membrane; membrane plated and colonies counted
most probable number (MPN) method
a statistical procedure for estimating of the number of viable microorganisms in a sample when counts are very low. Often used for water and food samples
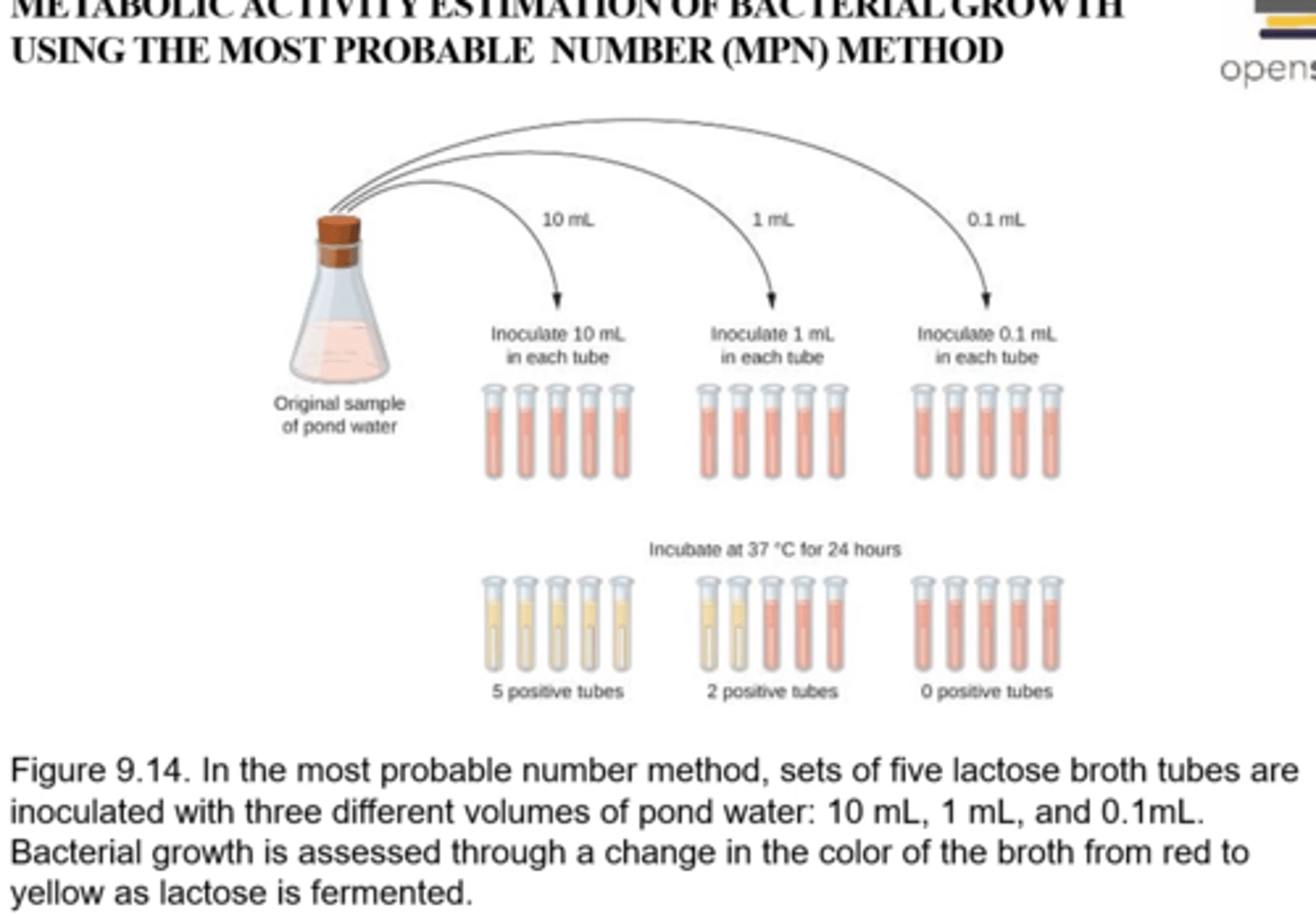
Procedure for MPN
-Uses 3 log dilutions (1/1, 1/10, 1/11) grown in 3-5 replicates
-growth is determined positive or negative
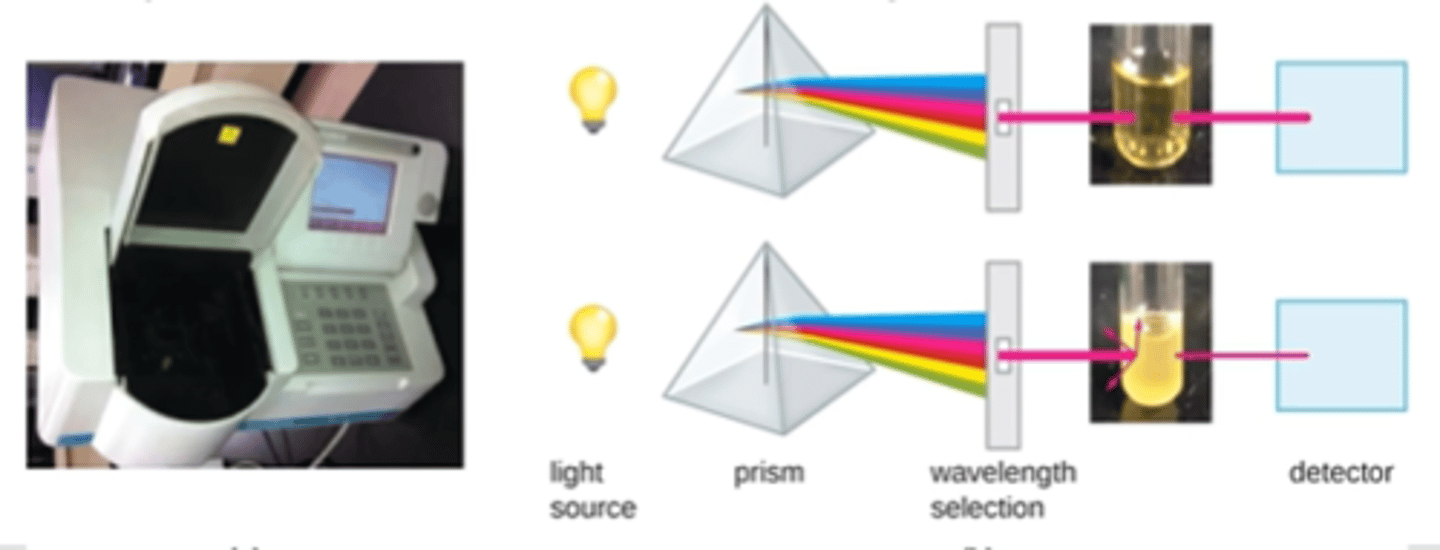
Optical Density (Turbidity)
measured with spectrophotometer, light is passed through the culture measured on other side, population increase=turbidity increase
Some cells divide asymmetrically through (2)
budding or fragmentation
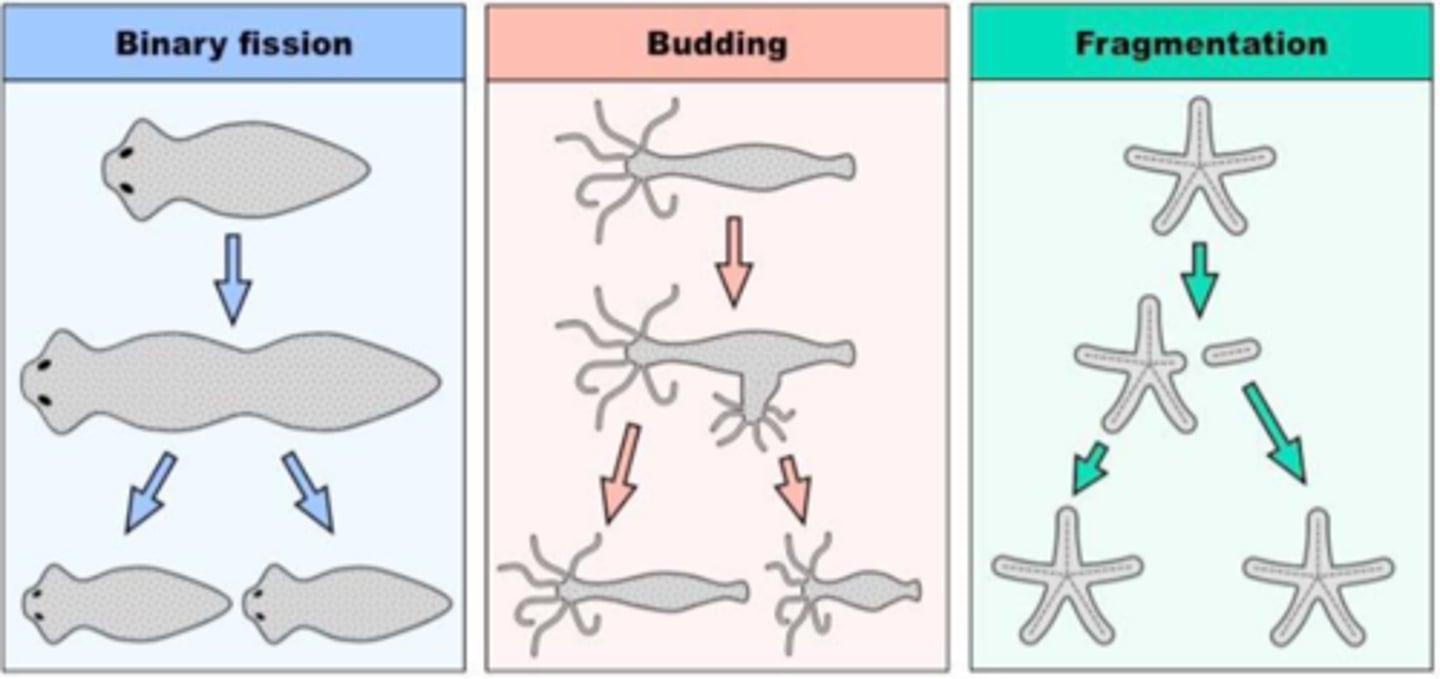
Fragmentation
The new cells often split from the parent filament and float away in a process called
Budding
Other species may for ma long narrow extension at a one pole in a process called
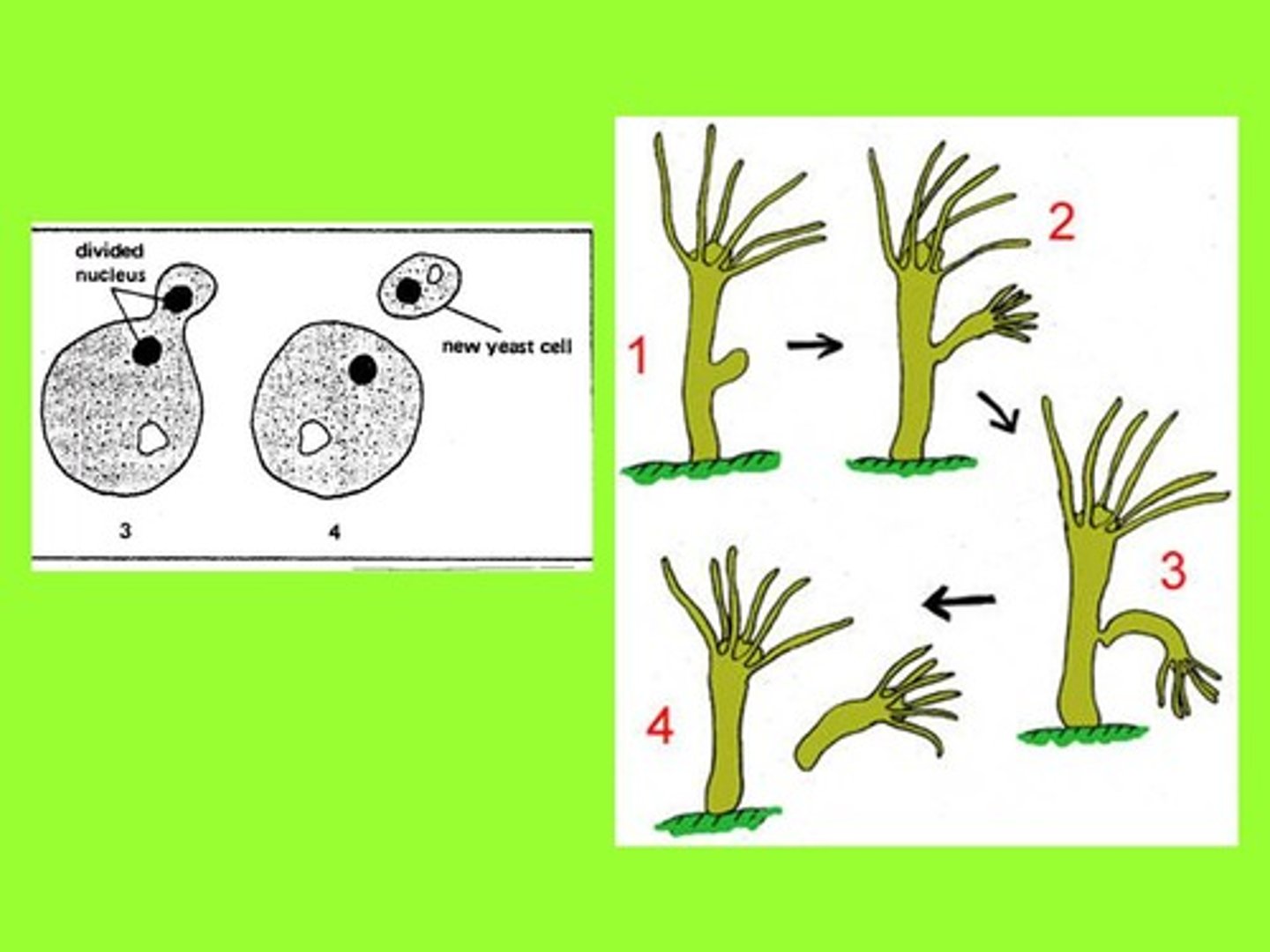
Biofilm Formation
Micro ecosystem of one or more species that can provide protection, forms mostly in liquid environments (rivers, pipelines, oral cavity, etc.)

Biofilm Structure
clusters of microbes in a matrix, filamentous biofilms called streamers

Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS)
extracellular matrix secreted by organisms in biofilm, hydrated polysaccharide gel with other macromolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, and lipid
Planktonic Cells
free-floating microbial cells that live in an aquatic environment
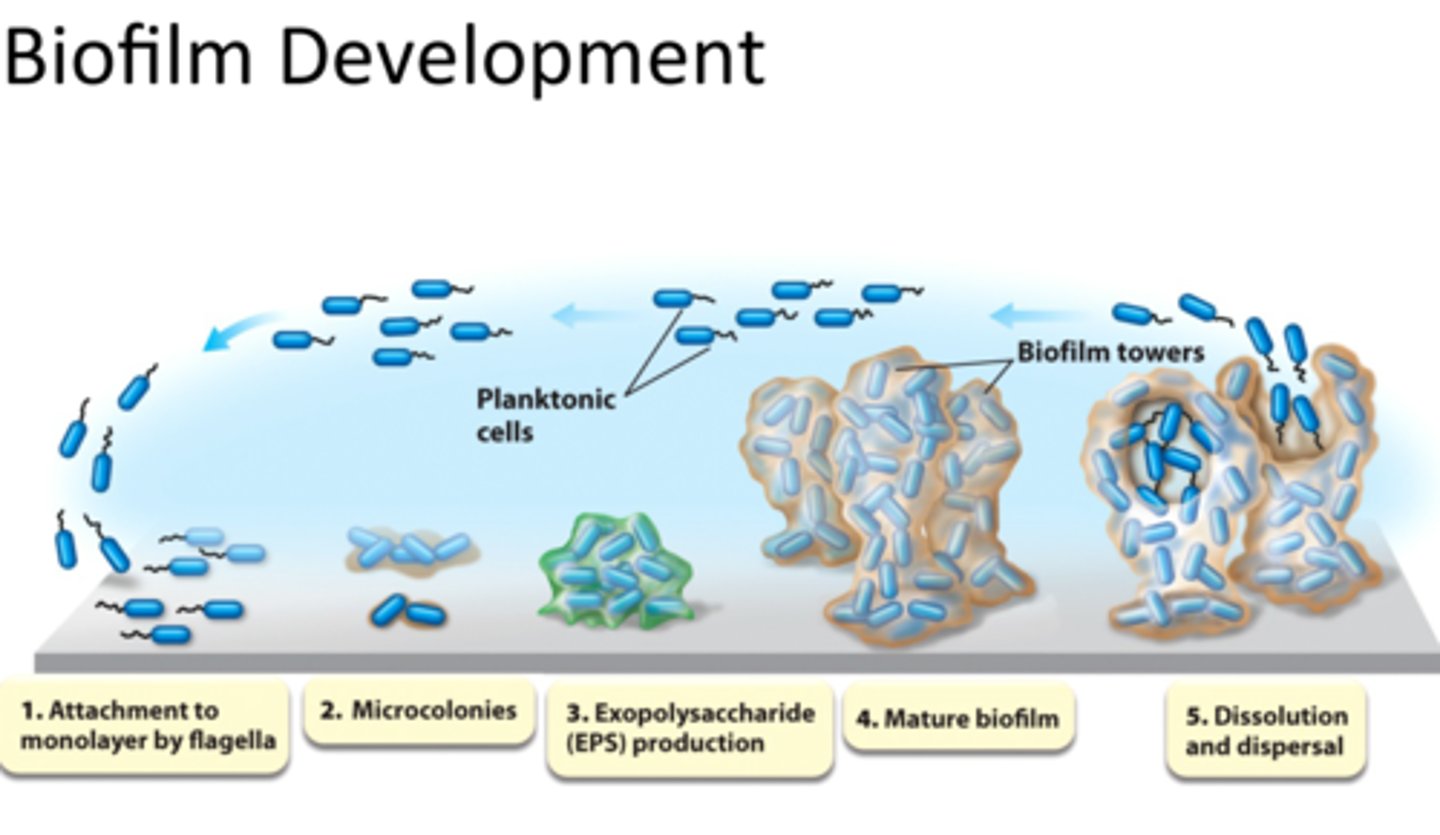
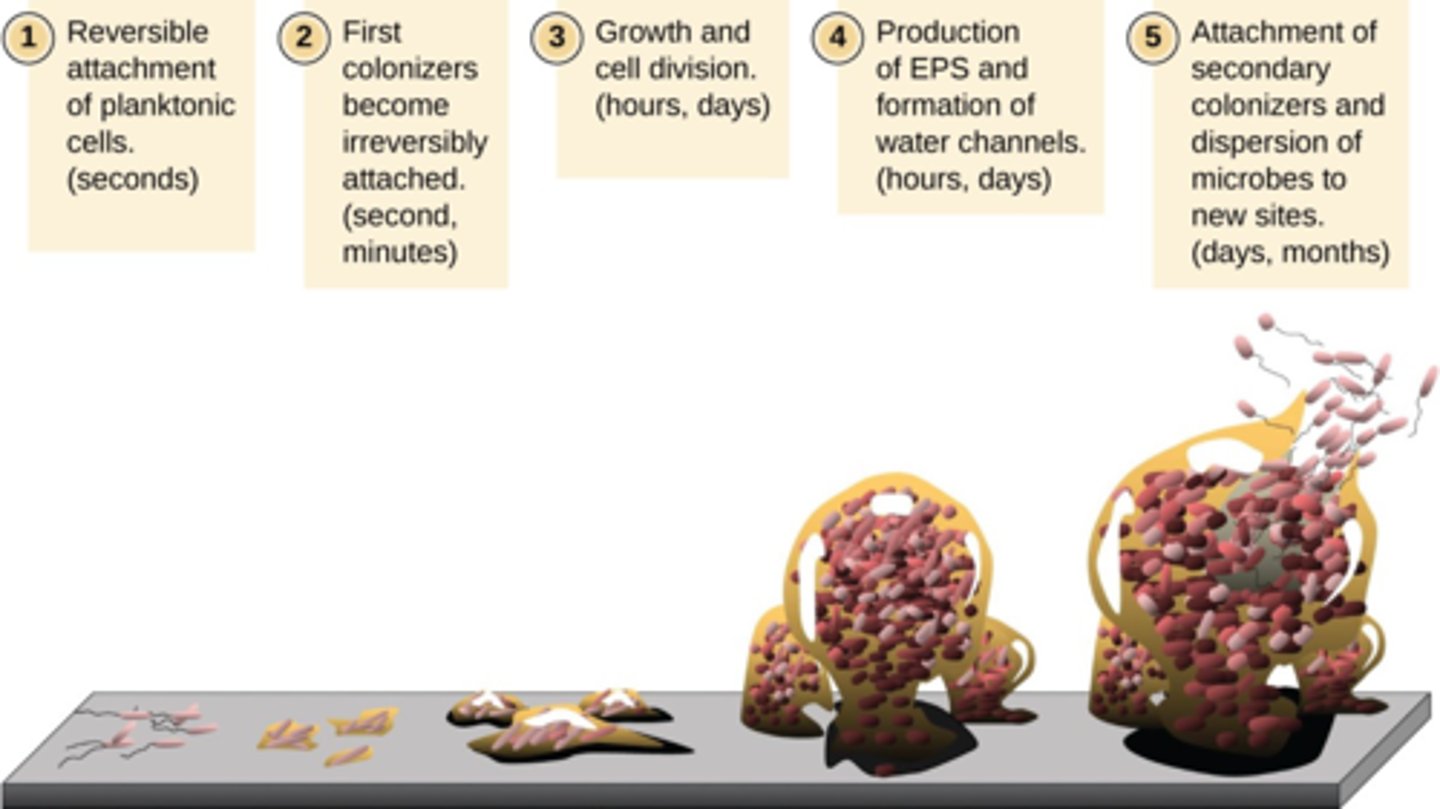
Steps of Biofilm Formation
1. Attachment of planktonic cells to a substrate
2. Attachment becomes irreversible; cells become sessile
3. Growth and division on substrate
4. Production of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS)
5. Attachment of secondary colonizers and dispersion of microbes to new locations
What is Biofilm formation formed through?
Quorum sensing, or cell to cell communication
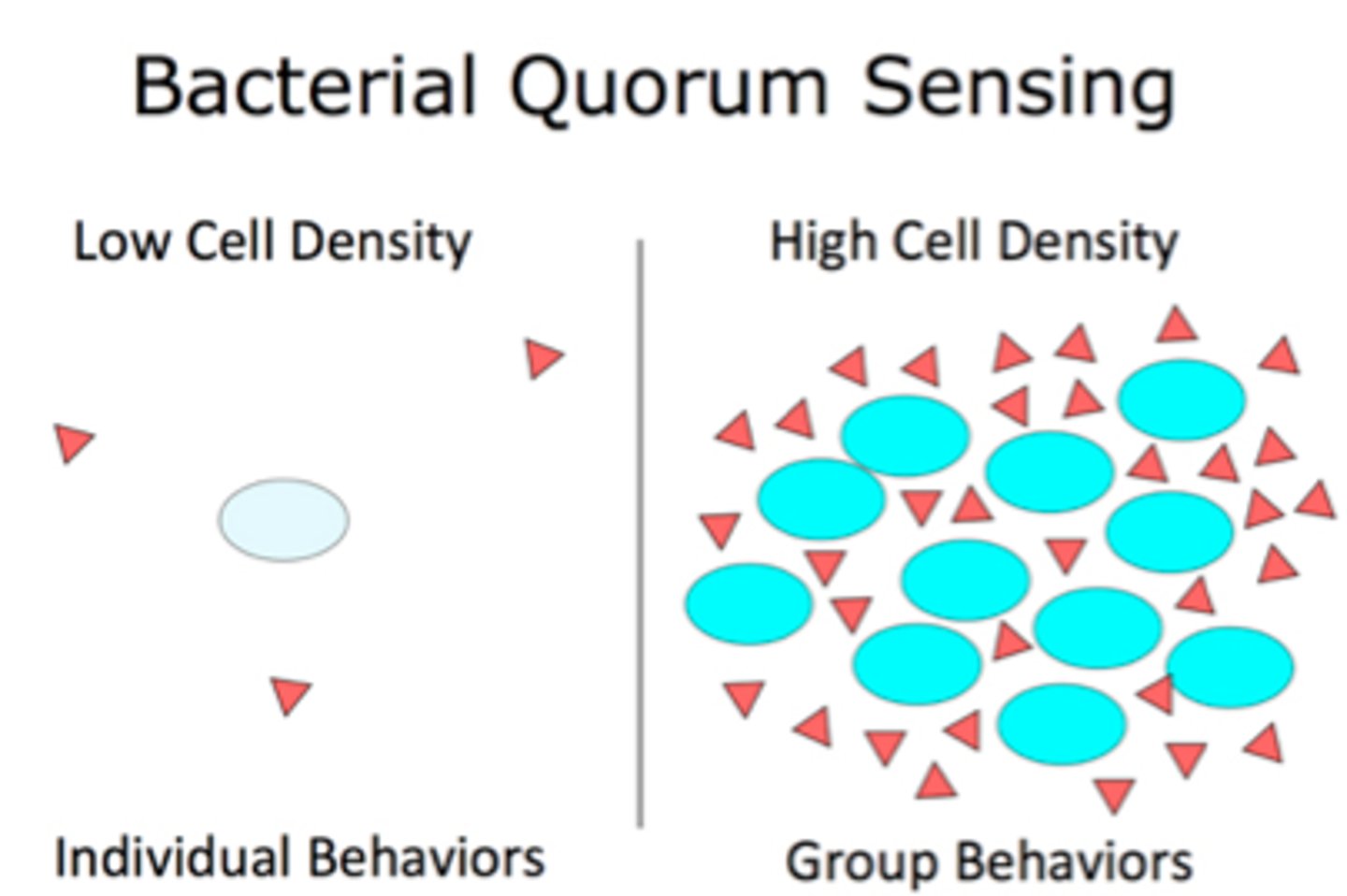
Quorum Sensing
How cells coordinate their activities in response to environmental stimuli
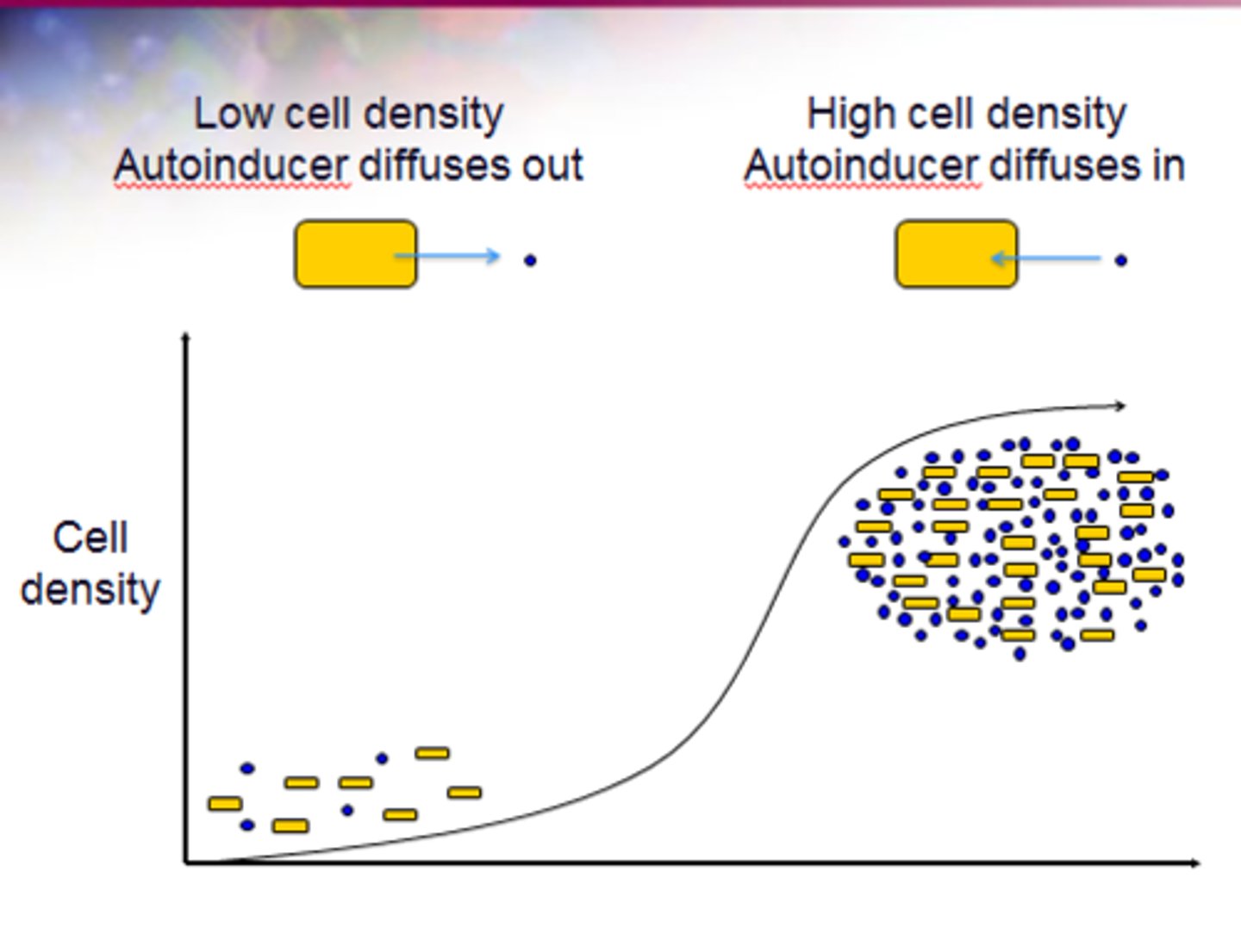
Autoinducers
small molecules produced by cells to induce various actions such as detecting their cell density and binding
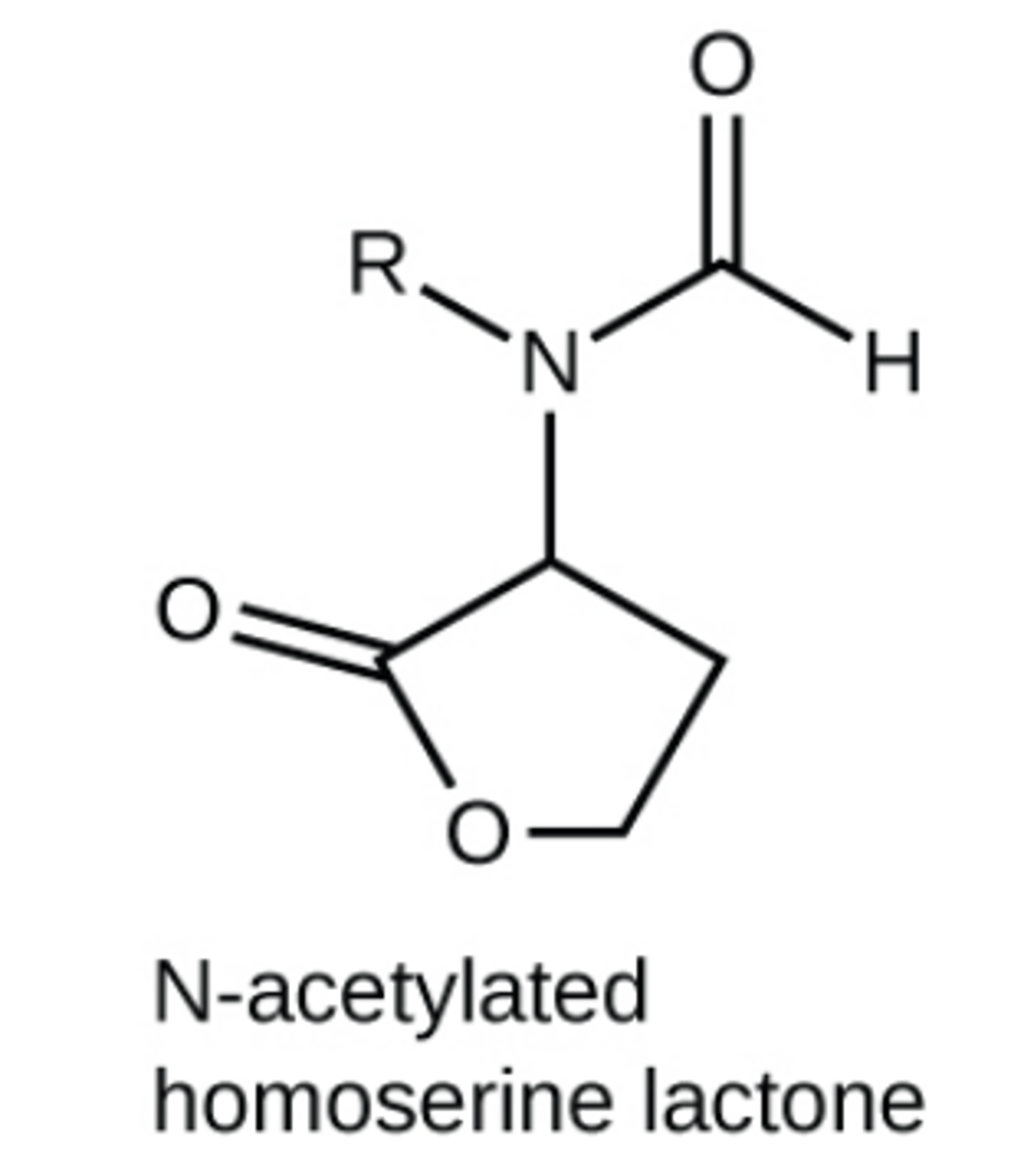
The signaling molecules in quorum sensing belong to two major classes which are
gram negative bacteria and gram positive bacteria
In quorum sensing, gram negative bacteria communicate mainly using
N-acetylated homoserine lactones
In quorum sensing, gram positive bacteria communicate mainly using
small peptides
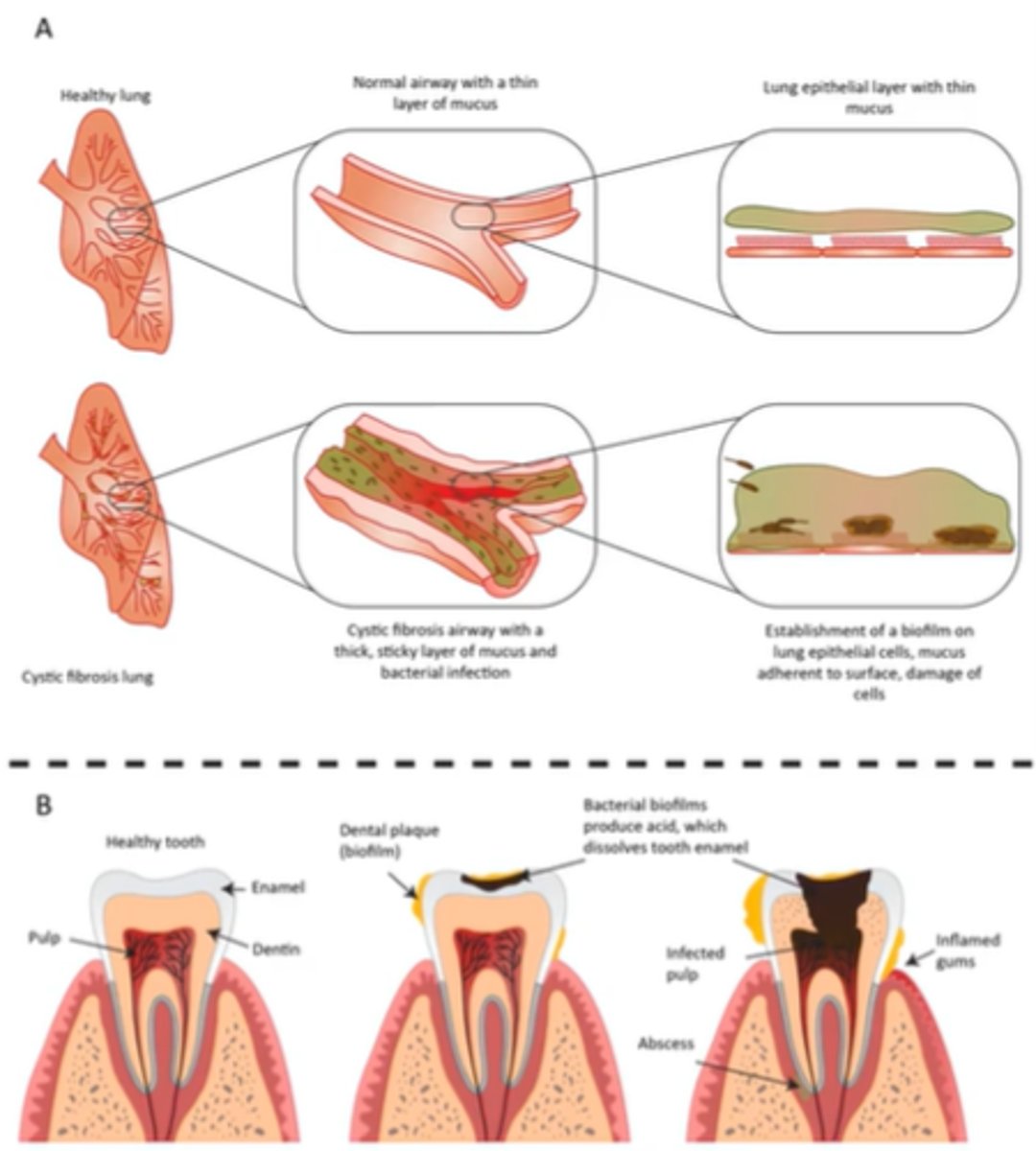
Biofilm and Human Health
Some are beneficial (normal biota in lungs) and some are not (plaque formation on teeth)
Biofilms often provide resistance to antibiotics
1. cells in deep layers may be metabolically inactive
2. EPS may slow diffusion of biocidal agents
3. provide optimal environment for sharing of plasmids
Main Factors that affect growth:
1. oxygen level
2. pH
3. Temperature
4. Osmotic pressure
5. Barometric pressure
Many environments do not have, need, or tolerate O2 such as
anaerobic environments
Optimal Oxygen Concentration
ideal concentration of O2
Minimum Permissive Oxygen
lowest O2 concentration allowing growth
Maximum Permissive Oxygen Concentration
highest O2 concentration allowing growth
Obligate
must have
Facultative
can do both
Aerotolerant
tolerant
Aerobe
prefers O2
Anaerobe
prefers other than O2
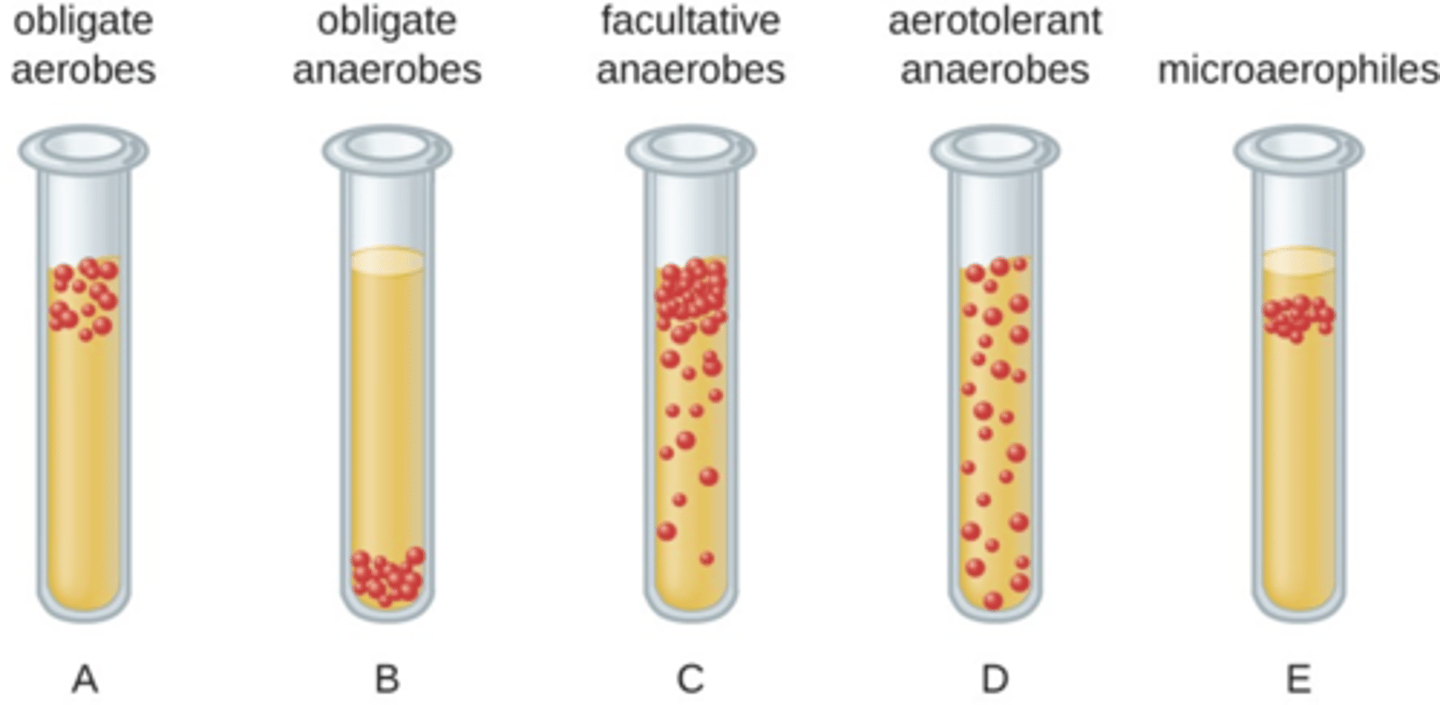
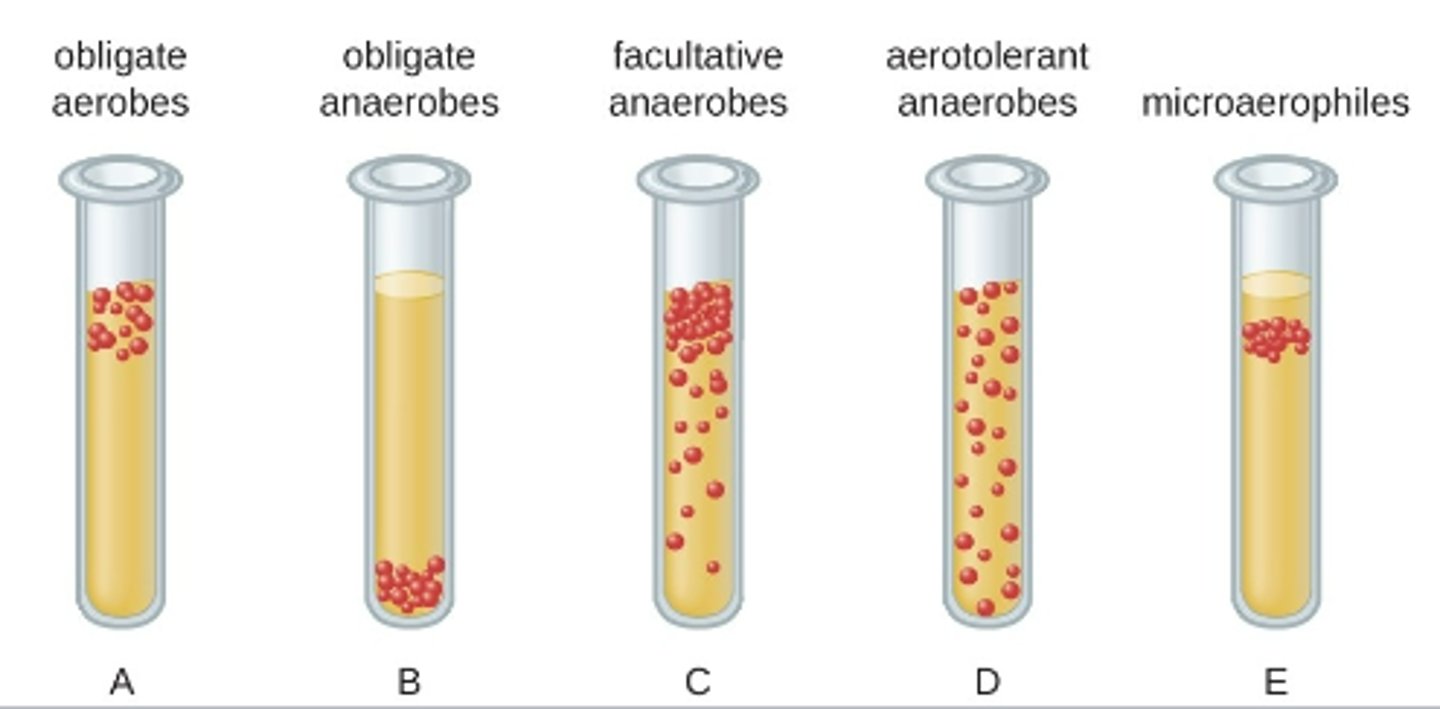
Obligate Aerobe and Examples
need oxygen, Micrococcus luteus Mycobacterium tuberculosis
N. gonorrhea
N. meningitidis

Obligate Anaerobes and Examples
must not have oxygen,
Baceroides
Clostridioides
Clostridium
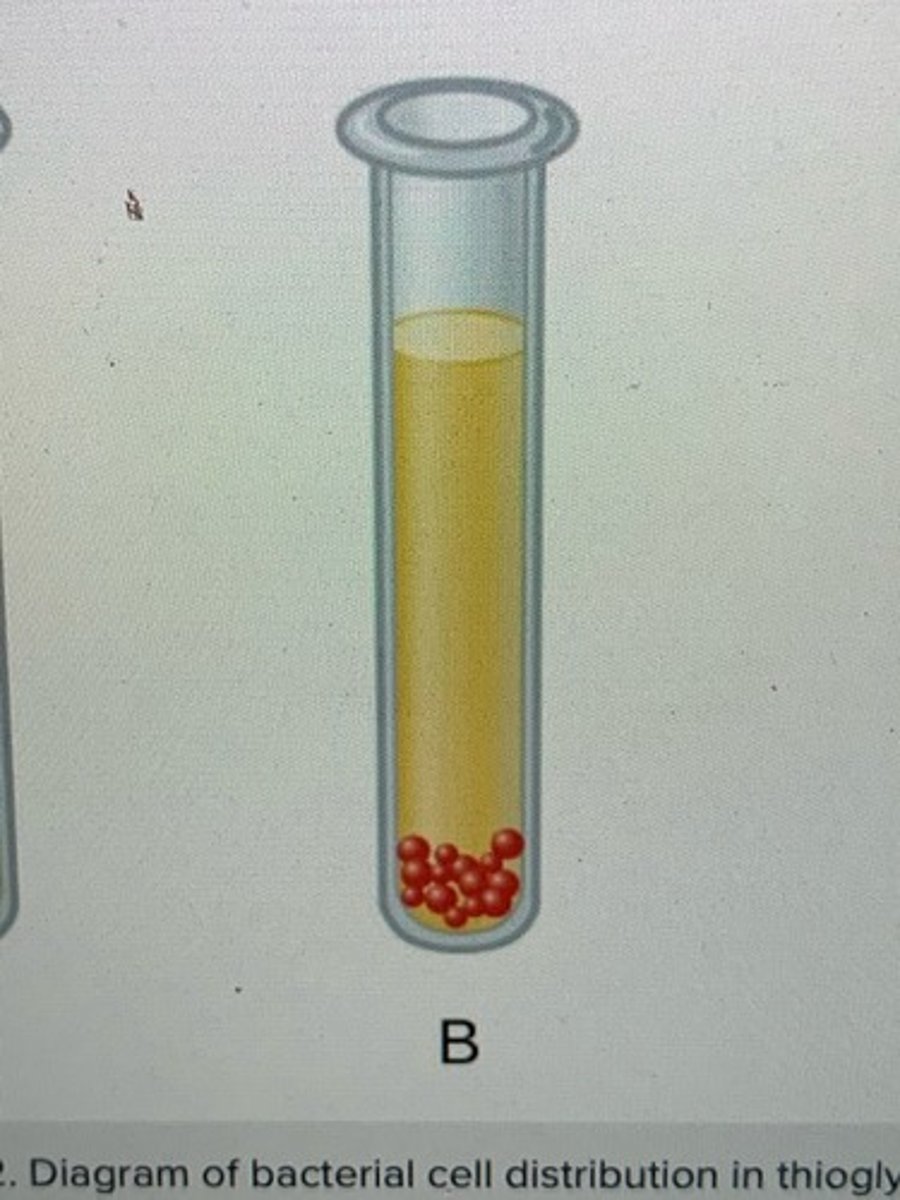
Facultative anaerobes and Examples
can live with or without oxygen,
Staphylococci
Enterobacteriaceae
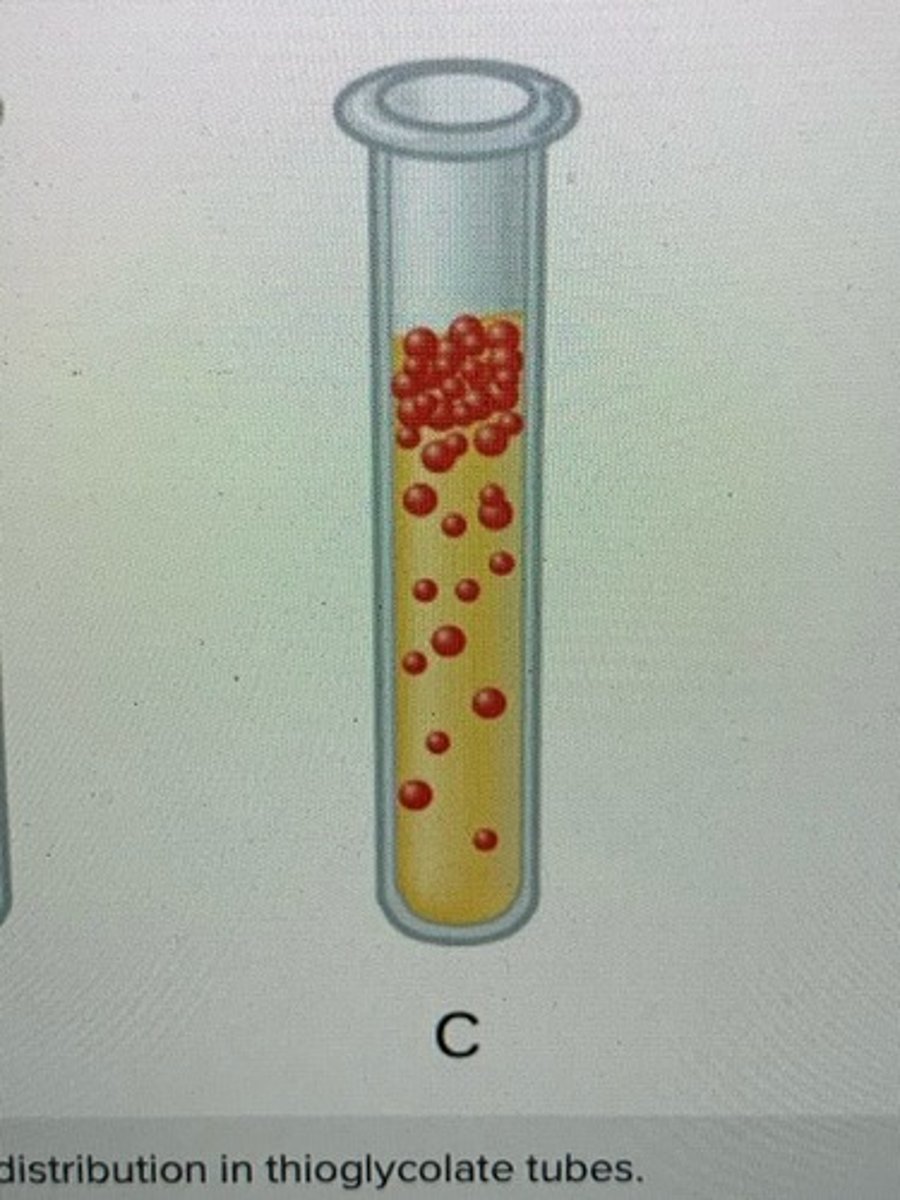
Aerotolerant Anaerobes and Examples
can grow in the presence of oxygen but can produce ATP without oxygen,
Lactobacillus
streptococci
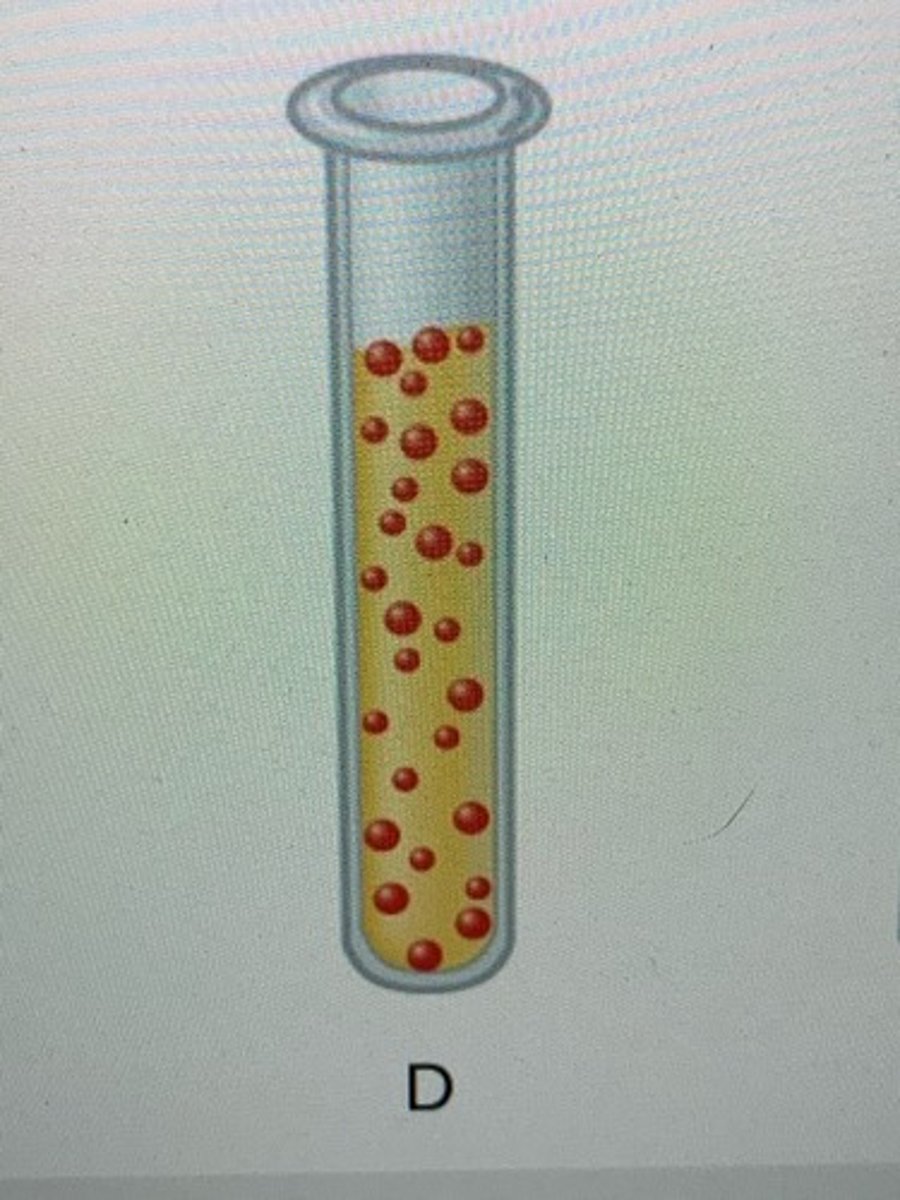
Microaerophiles and Examples
require a minimum levels (1%-10%) of oxygen for growth,
Campylobacter
Fluid Thioglycolate Medium (FTM)
low percentage agar tube that has a gradient of oxygen
Aerotolerance is determined by
location of growth
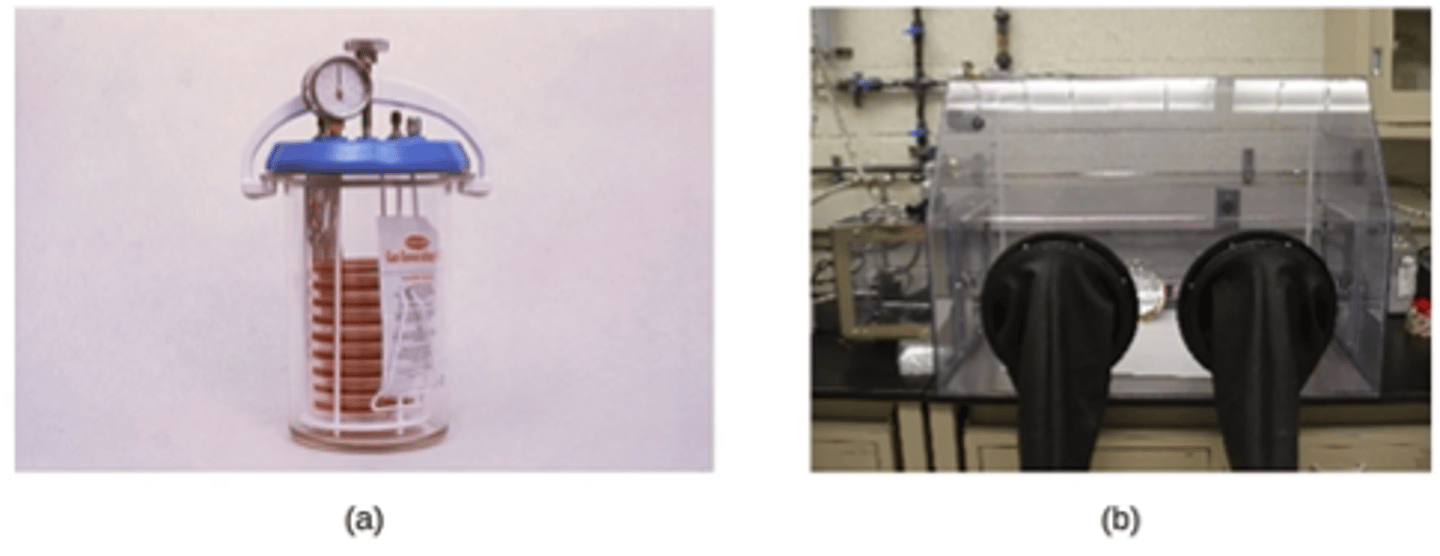
Studying obligate anaerobes requires special equipment such as (2)
anaerobic jars or anaerobic chambers
pH can affect efficacy of macromolecules, the most vulnerable are
proteins
Acidic
environments of a pH below 7.0
Basic
environments of a pH above 7.0
Fermenters are adapted to
acidity

Optimal growth pH
most favorable pH for growth
Minimum growth pH
lowest pH for growth
Maximum growth pH
highest pH for growth
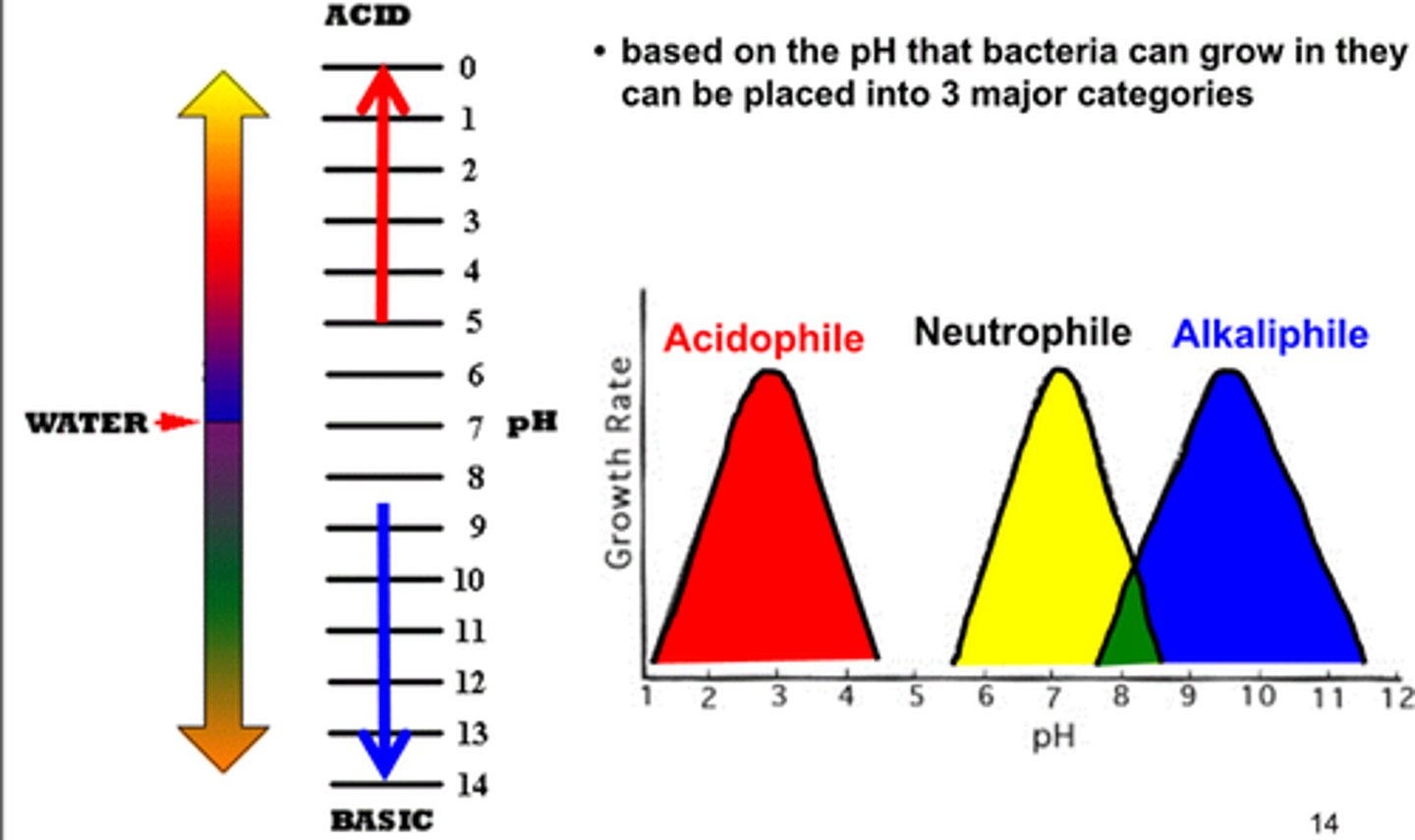
pH groups (3)
neutrophiles
acidophiles
alkaliphiles
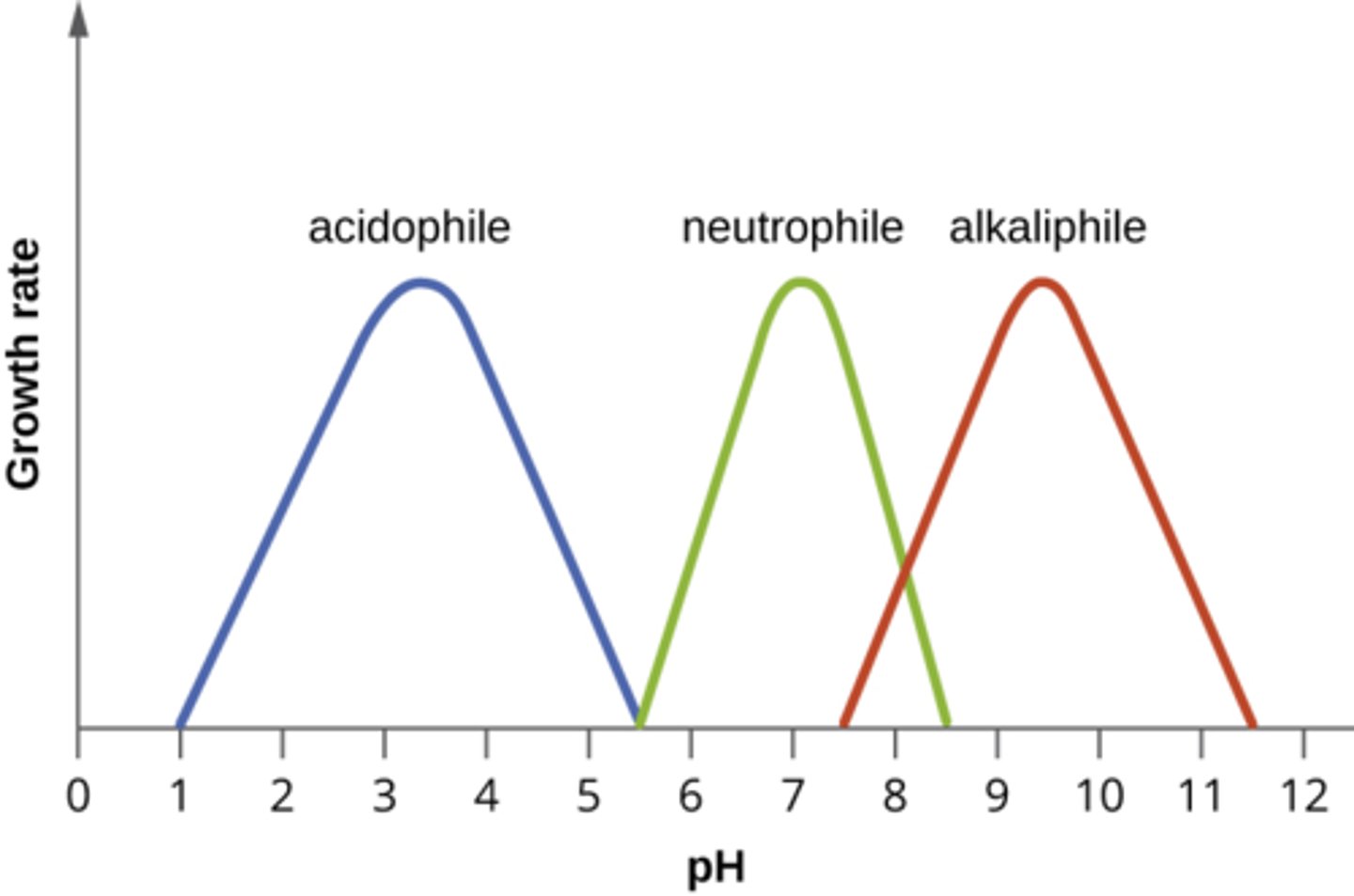
neutrophiles
grow optimally at a pH within one or two pH units of the neutral pH of 7
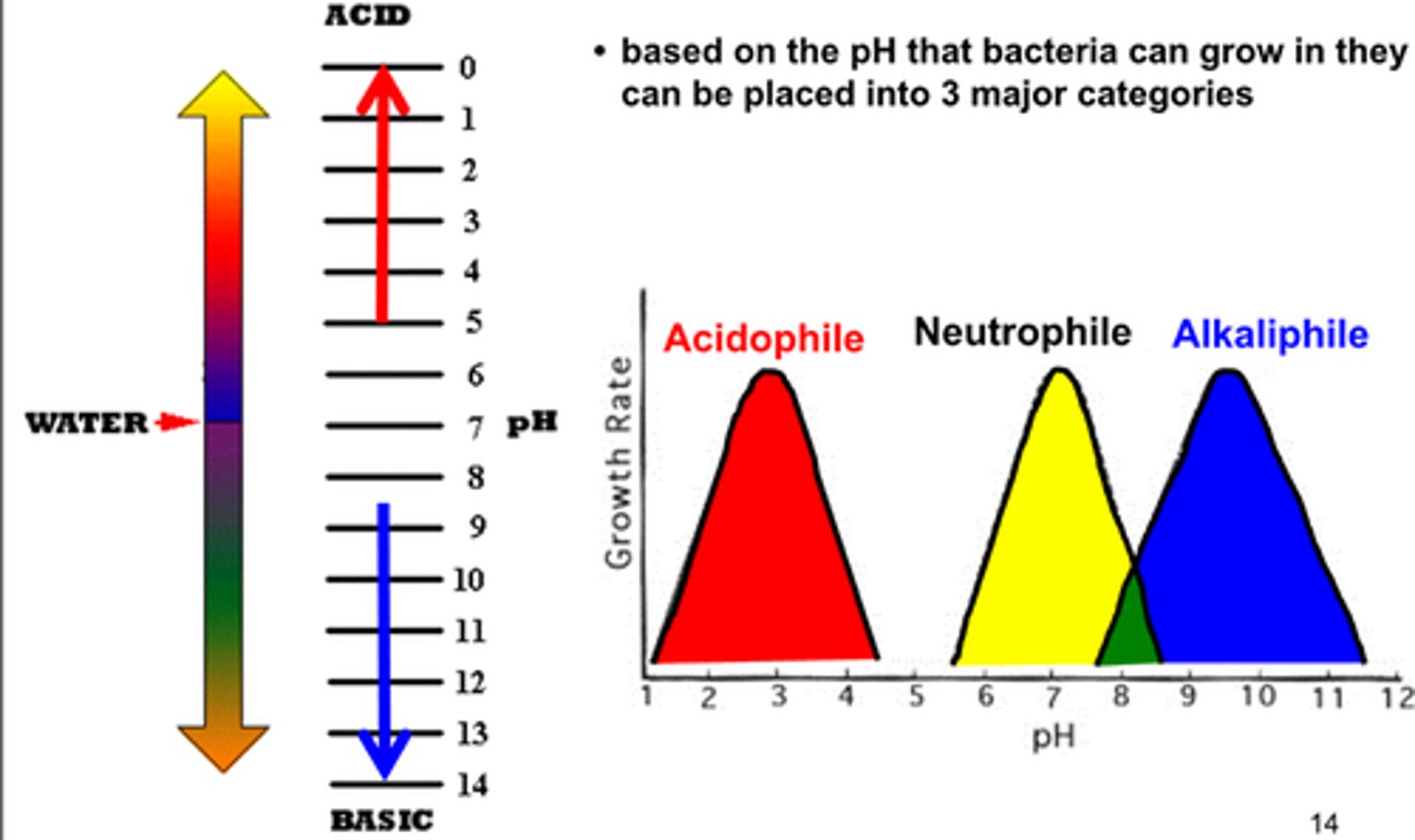
acidophiles
microorganisms that grow optimally at pH less than 5.55
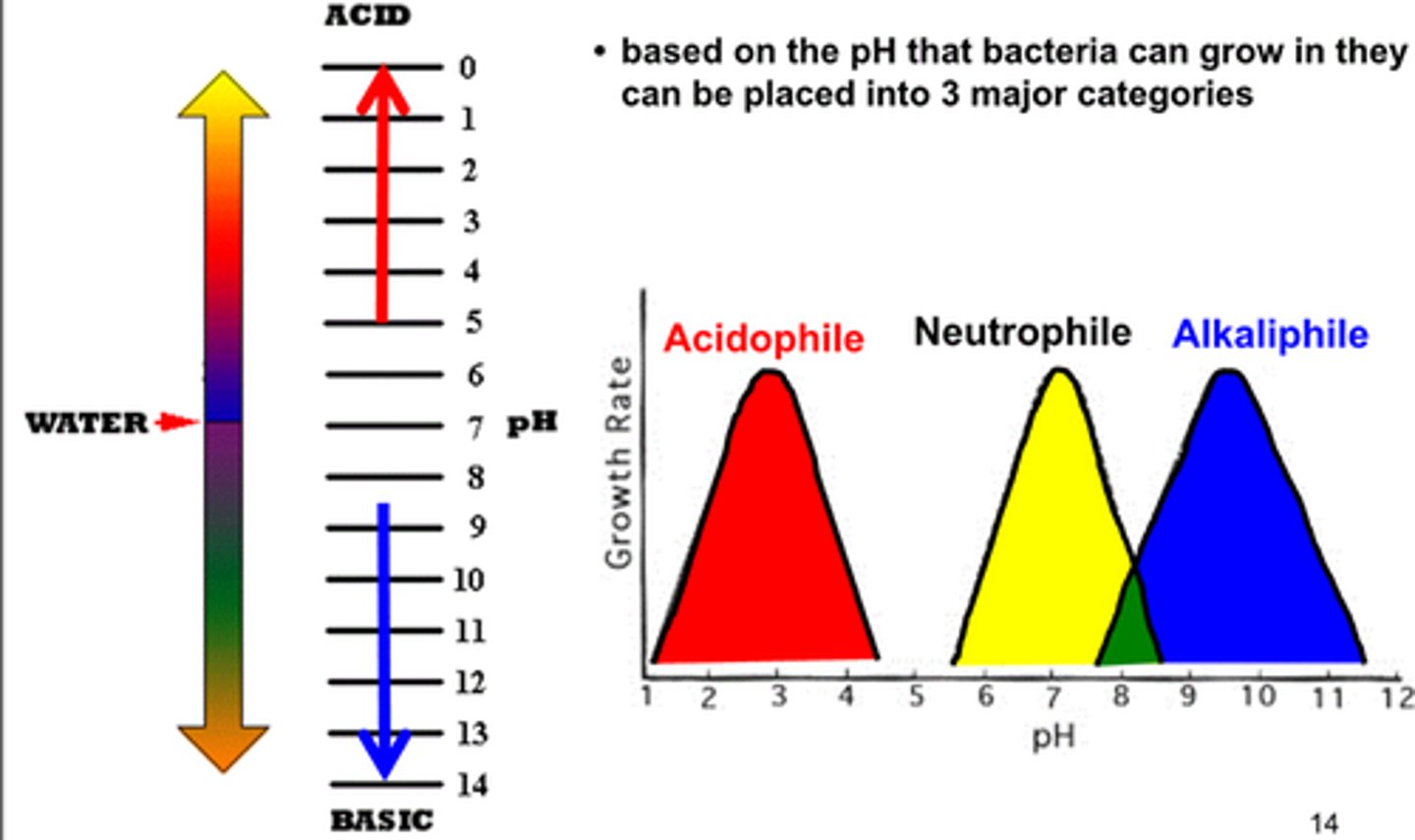
alkiliphiles
micoorganisms that grow best at pH between 8.0 and 10.5
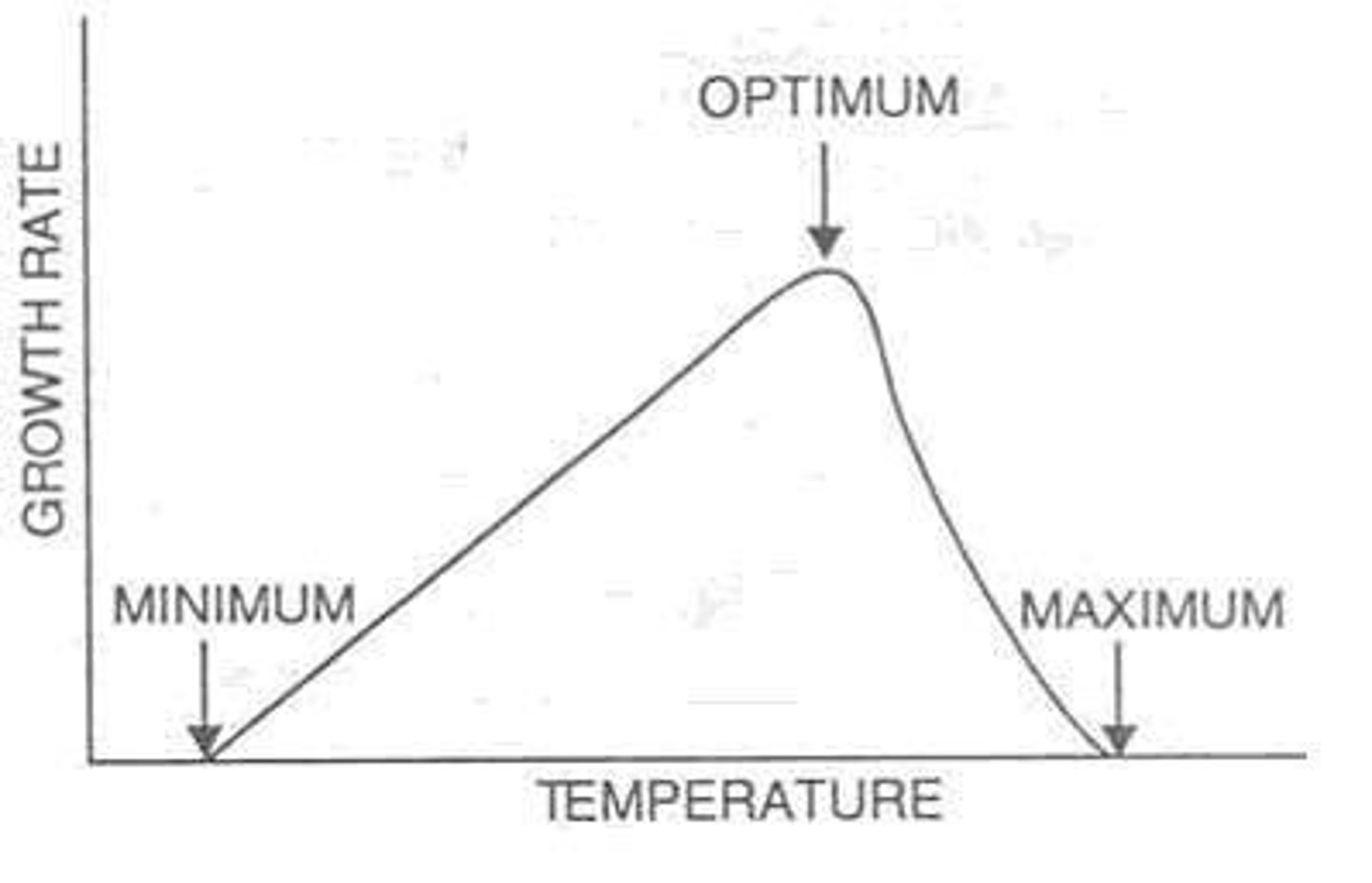
optimum growth temperature
growth rates are the highest for organisms at this temperature
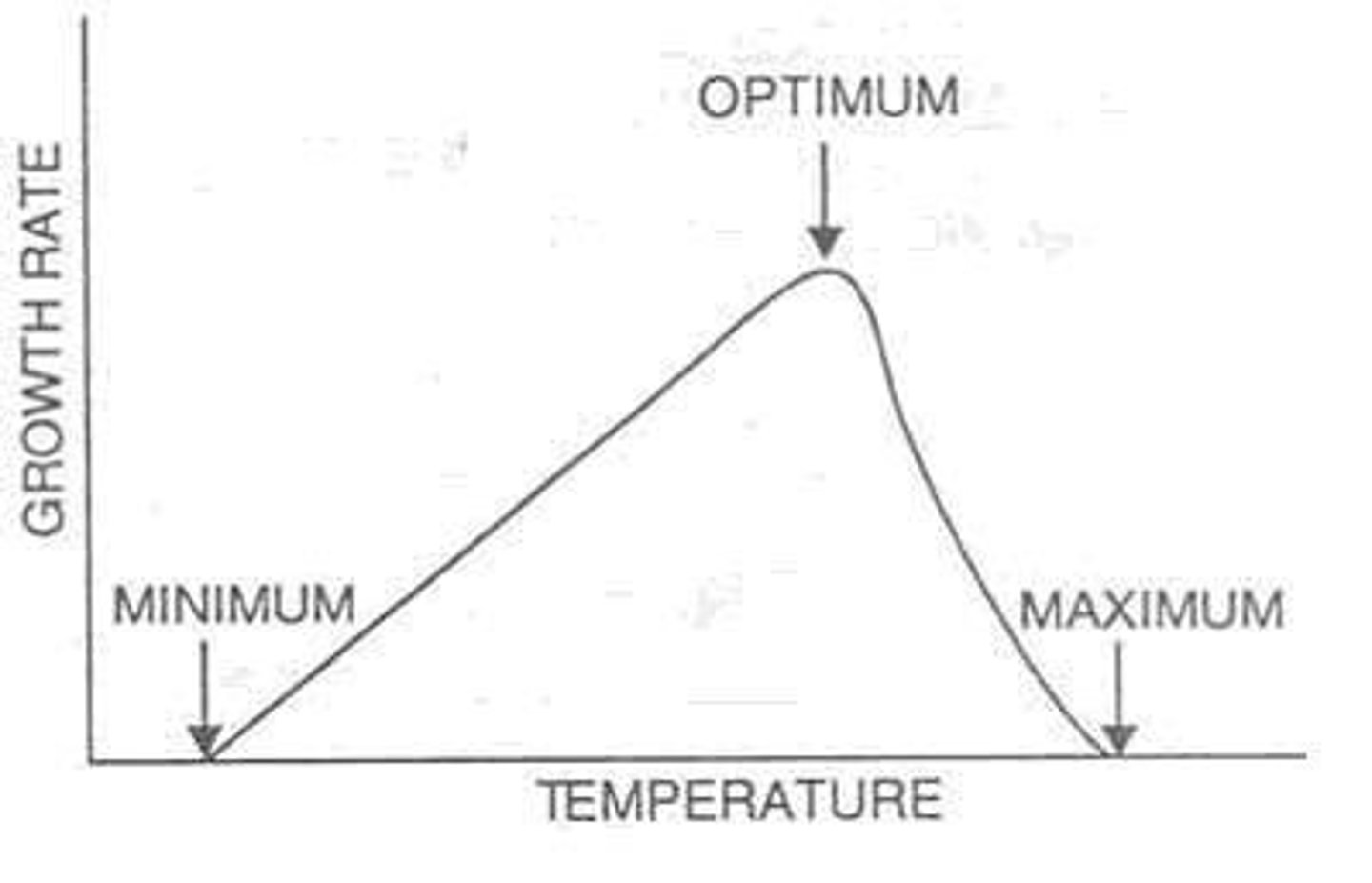
minimum growth temperature
lowest temperature at which the organisms can survive and replicate