CH 38 The Musculoskeletal System
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Musculoskeletal system
General function is to cause or control movement, more specifically: Support & maintain upright posture. It ALSO allows movement such as body transport & manipulates objects. AND lastly to PROTECT! What body system is this?
Hydrostatic pressure
Refers to the pressure that any fluid in a confined space exerts. Formed by a fluid-filled compartment within the body, called the coelom.
Compartment is under ____ because of the fluid, and supports the other organs of the organism.
Found in soft-bodied animals such as sea anemones, earthworms, Cnidaria, and other invertebrates.
Exoskeleton
consists of a hard encasement on the surface of an organism. Provides defense against predators, supports the body, and allows for movement through the contraction of attached muscles.
Arthropods such as crabs and lobsters have it & consists of 30–50% chitin, a polysaccharide derivative of glucose that is a strong but flexible material.
Because it’s acellular, arthropods must
periodically shed their exoskeletons because it does not grow as the organism grows.
Endoskeleton
Consists of hard, mineralized structures located within the soft
tissue of organisms. They provide support for the body, protect internal organs, and allow for movement through contraction of
muscles attached to the skeleton.
huma axial skeleton
skeleton consists of the bones of the skull, ossicles of the middle ear, hyoid bone, vertebral column, and rib cage.
skull
bones support the structures of the face and protect the brain.
cranial bones
Includes the frontal, parietal, and sphenoid bones which cover the top of the head. They are the facial bones of the skull from the face and provide cavities for the eyes, nose, and mouth.
appendicular skeleton
this skeleton is composed of the bones of the pectoral limbs (arm, forearm, hand), the pelvic limbs (thigh, leg, foot), the pectoral girdle, and the pelvic girdle.
upper limbs
consists of the humerus of the upper arm, the radius and ulna of the forearm, eight bones of the carpus, five bones of the metacarpus, and 14 bones of the phalanges.
Pevic girdle
To adapt to reproductive fitness, the (a) female pelvis is lighter,
wider, shallower, and has a broader angle between the pubic
bones than (b) the male pelvis.
Long bone
(a) Longer than wide
(b) Shaft with two ends
(c) Mostly compact
(d) Bones of limbs
is covered by articular cartilage at either end and contains
bone marrow (shown in yellow in this illustration) in the marrow cavity.
What type of bone is this?
Short bone
(a) Cube-like
(b) Mostly spongy
(c) Sesamoid—bones embedded in tendon
Patella
What type of bone is this?
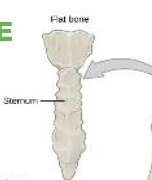
Flat bone
(a) Spongy bone embedded within parallel layers of thin compact bone
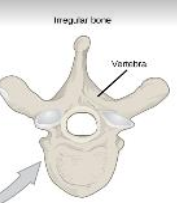
Irregular bone
(a) Vertebrae and hip bones
(b) Complicated shapes
(c) Mostly spongy with a thin covering of compact bone
What type of bone is this?
Lacunae:
cavities containing osteocytes
Canaliculi:
connect lacunae to each other and central canal
Trabeculae:
needle-like (flat) pieces
appear less organized than structures of
compact bone
(a) No osteon
(b) Organization is based on lines of stress
(c) Lamella and osteocytes are irregularly organized
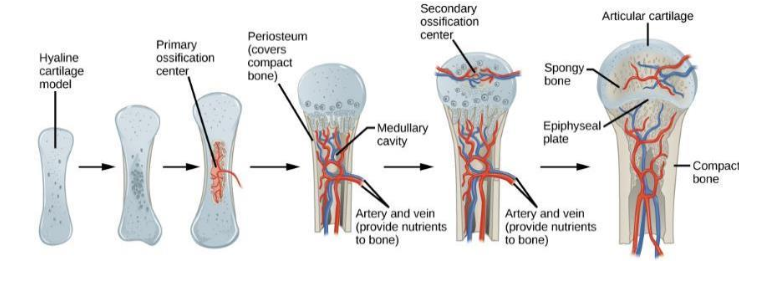
endochondrial ossification
Cartilage bone are used as a pattern for bone construction
(a) Primary ossification center at the center of the hyaline cartilage
intramembranous ossification
Ossification center forms in fibrous connective tissue membrane
Mesenchymal cells differentiate into osteoblasts
fibrous joints
are held together by fibrous connective tissue.
Cartilaginous joints
are joints in which the bones are connected by cartilage.
Synchondrosis
the bones are joined by hyaline cartilage & are found in the epiphyseal plates of growing bones in children.
Symphyses
hyaline cartilage covers the end of the bone but the
connection between bones occurs through fibrocartilage. They are found at the joints between vertebrae. Either type of
cartilaginous joint allows for very little movement.
synovial joints
are the only joints that have a space or “synovial cavity” in the joint. The cavity is filled with synovial fluid, which
lubricates the joint.
planar joints
The joints of the carpal bones in the wrist are examples of?
hinge joint
The elbow joint, where the radius articulates with the humerus, is an example of a?
pivot joint
The joint in the neck (between the C1 and C2 vertebrae) that allows the head to move back and forth is an example of a?
condyloid joints
The metacarpophalangeal or joints between the radius & carpal bones of the wrist in the finger are examples of?
saddle joints
The carpometacarpal joints in the thumb are examples of?
ball-and-socket joint
The shoulder joint or hip joint is an example of a ?
smooth muscle
cells are short, tapered at each end, and have only one plump nucleus in each. Involuntary
cardiac muscle
cells are branched and striated, but short. The cytoplasm may branch, and they have one nucleus in the center of the cell. Involuntary
skeletal muscle
surrounded by a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma with a cytoplasm called the sarcoplasm. A muscle fiber is composed of many fibrils, packaged into orderly units. Multinucleated, voluntary & striated