310 Vaccines and Vectors
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
why no AIDS vaccine?
glycosylated gp120 and error-prone Reverse Transcriptase
ART (antiretroviral therapy)
a multidrug/combinatorial therapy against HIV. ART when taken correctly (PreP) can make the person unable to transmit HIV virus.
taken daily
GOALS: prevent more T cells from getting harmed; keep virus as provirus so viral load undetectable in blood; halt lytic cycle
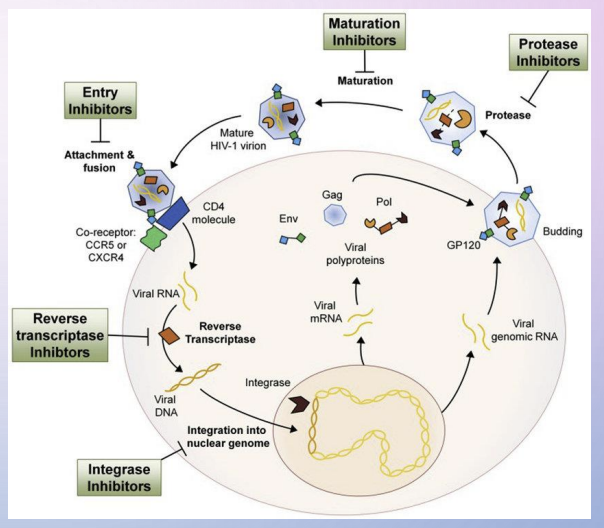
fusion/entry, RT nucleoside and direct, integrase, protease and maturation inhibitors are available
HIV
descendant of Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)
most cases in Africa
disease of poverty / access to care
HIV facts

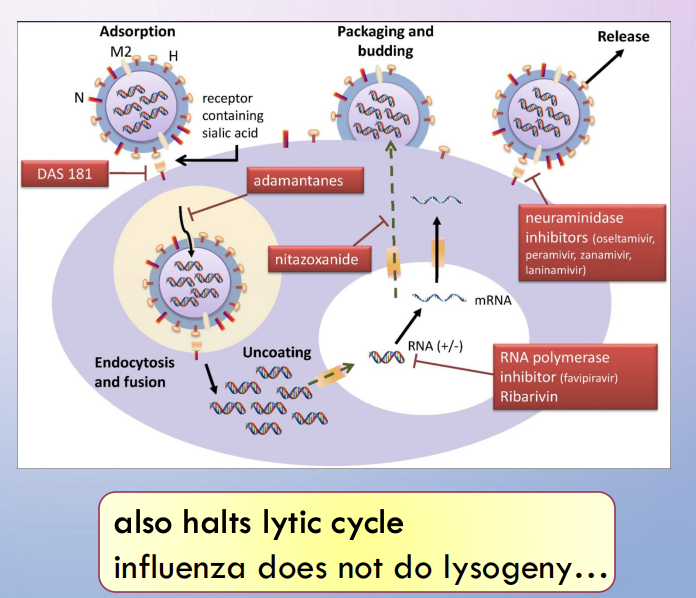
Tamiflu (antiviral against influenza)
neuraminidase inhibitor —> virions can’t leave cell. ALSO halts lytic cycle
type A and type B influenza
shortens symptoms by 1-2 days
may be important for older ppl (65+) and ppl with chronic conditions —> avoid complications like pneumonia
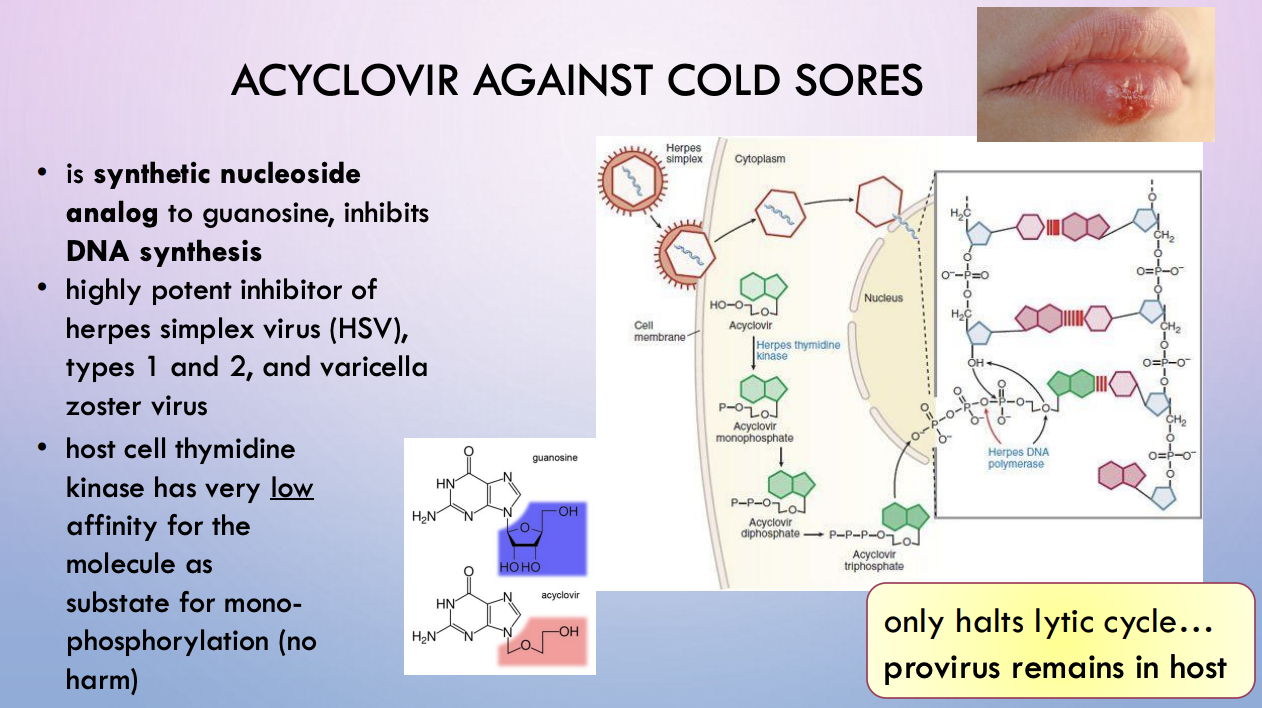
acyclovir
against cold sores / herpes
synthetic nucleoside analog to guanosine, inhibits DNA synth
highly potent inhibitor of herpes simplex virus (HSV), types 1 and 2, and varicella zoster virus
host cell thymidine kinase has very low affinity for the molecule as substate for monophosphorylation (no harm)
halts lytic cycle, but provirus remains in host
provirus
virus genome that is integrated into the DNA of a host cell
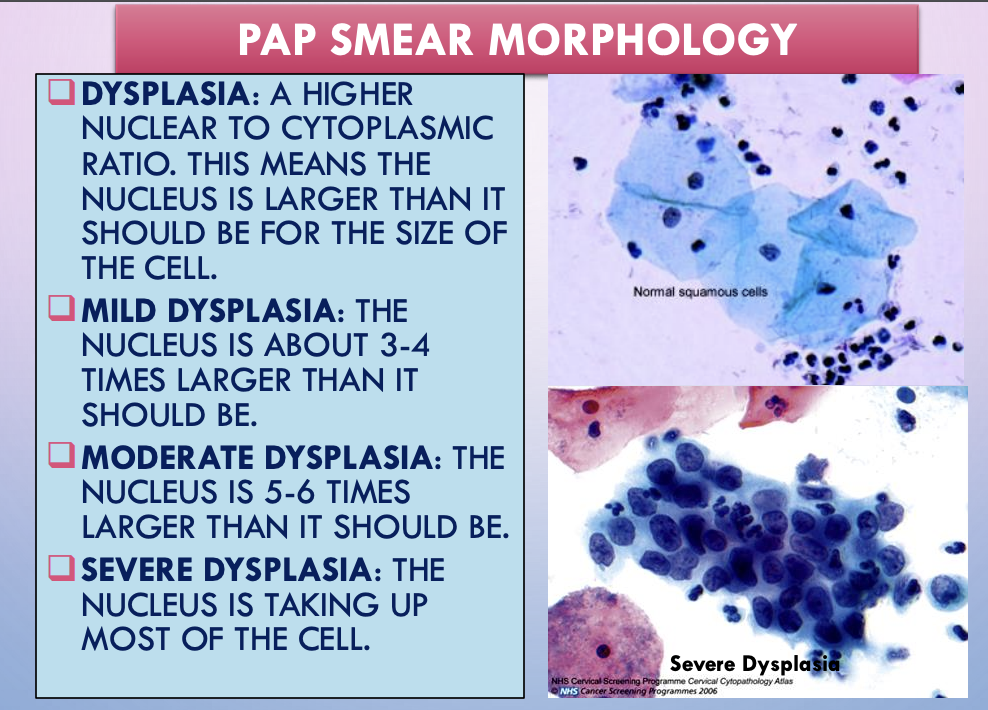
pap spear morphology
dysplasia - higher nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio
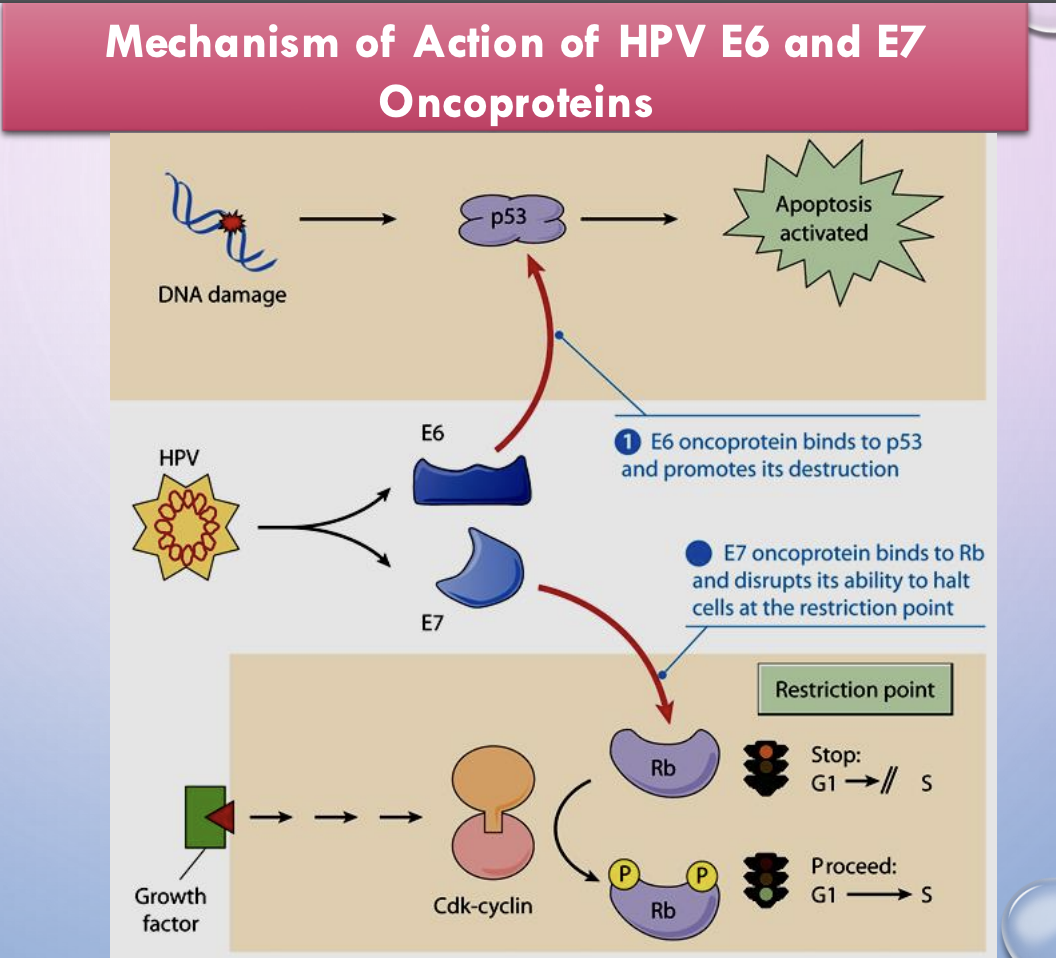
HPV - cervical cancer mechanism
infects epithelial cells in cervical mucosa —> HPV DNA integrates into cellular genome
E6 and E7 oncoproteins
E6 binds p53 —> destroys it —> cell can’t do apoptosis
E7 binds Rb —> can’t halt cells at G1/S restriction point
HPV virus
circular, double stranded DNA, protected by capsid proteins
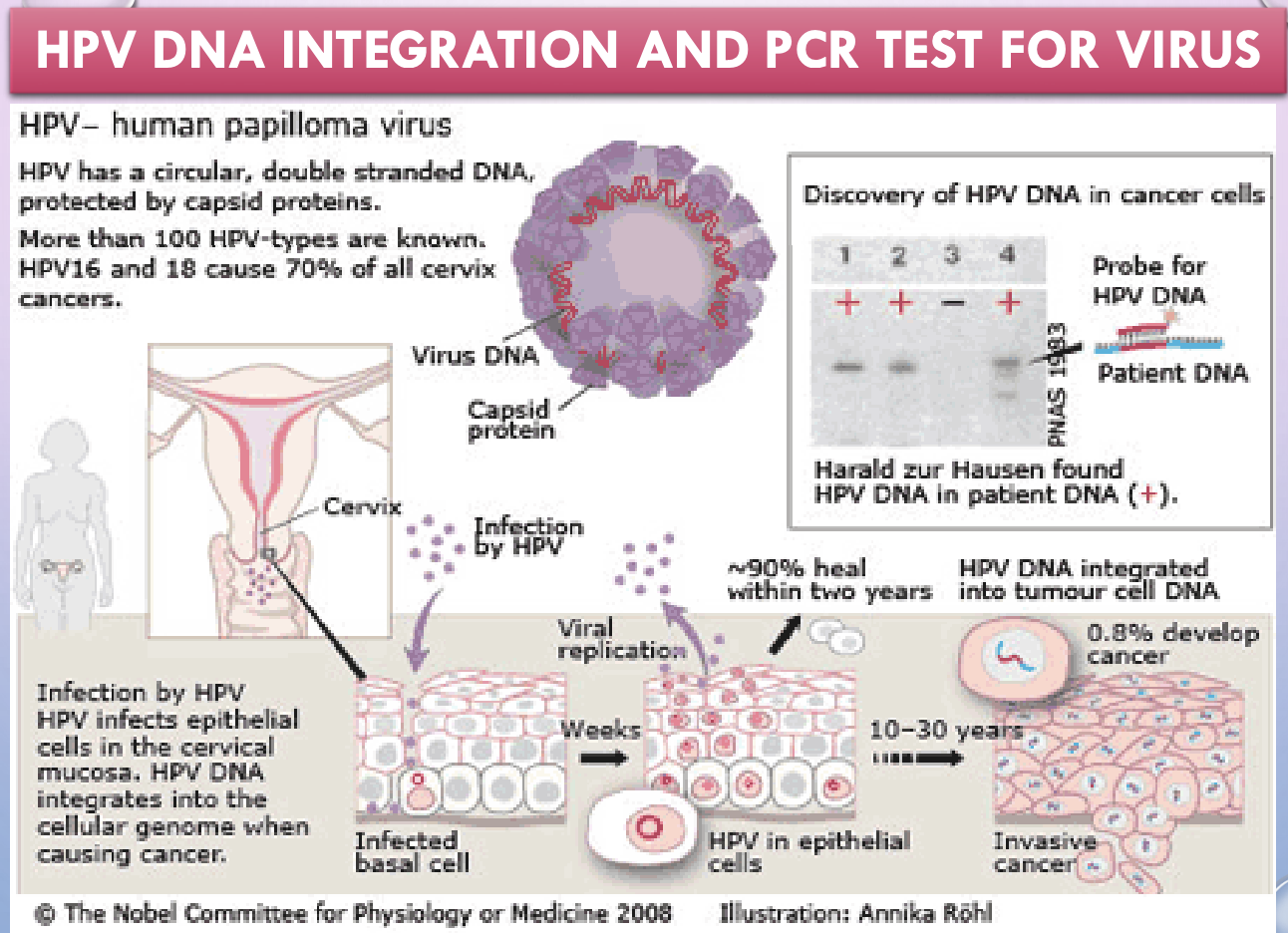
HPV facts

Gardasil
HPV vaccine
recombinant virus-like particle - 9 antigens correspond to most oncogenic HPV variants
T/F: 50% of the sexually active population will be infected with oncogenic versions of HPV
true
HPV stats
cause most warts (not toads) including genital warts
is a sexually transmitted virus that at leads to the majority of cervical, anal, vulva and orthopharnygeal (throat) cancers
best cancer screening test for HPV
pap smear
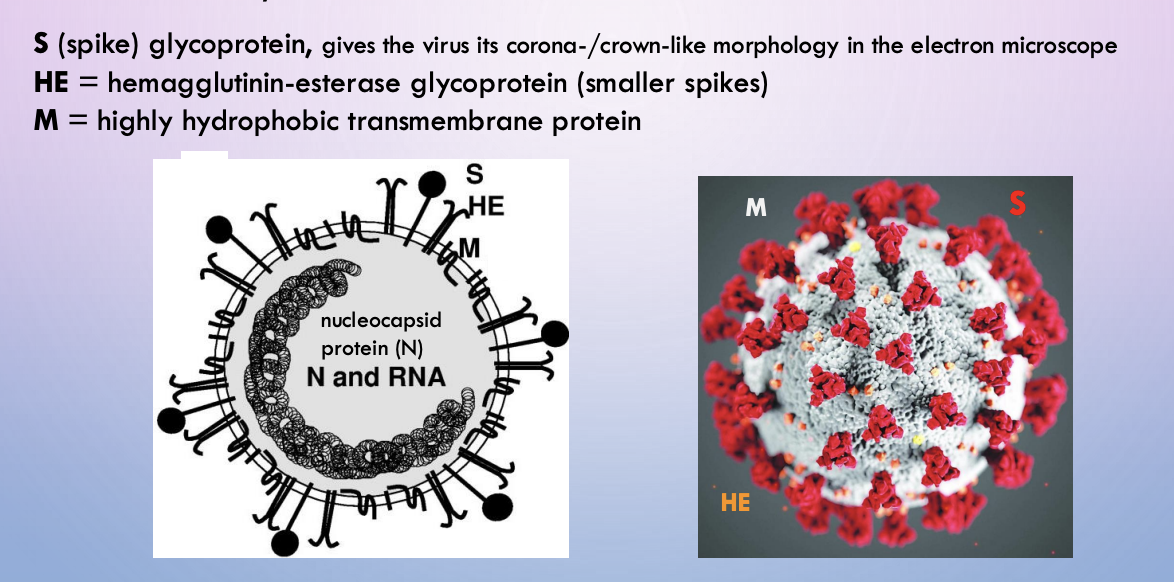
COVID-19 (Sars-Cov-2) - envelope structure
S, HE, M
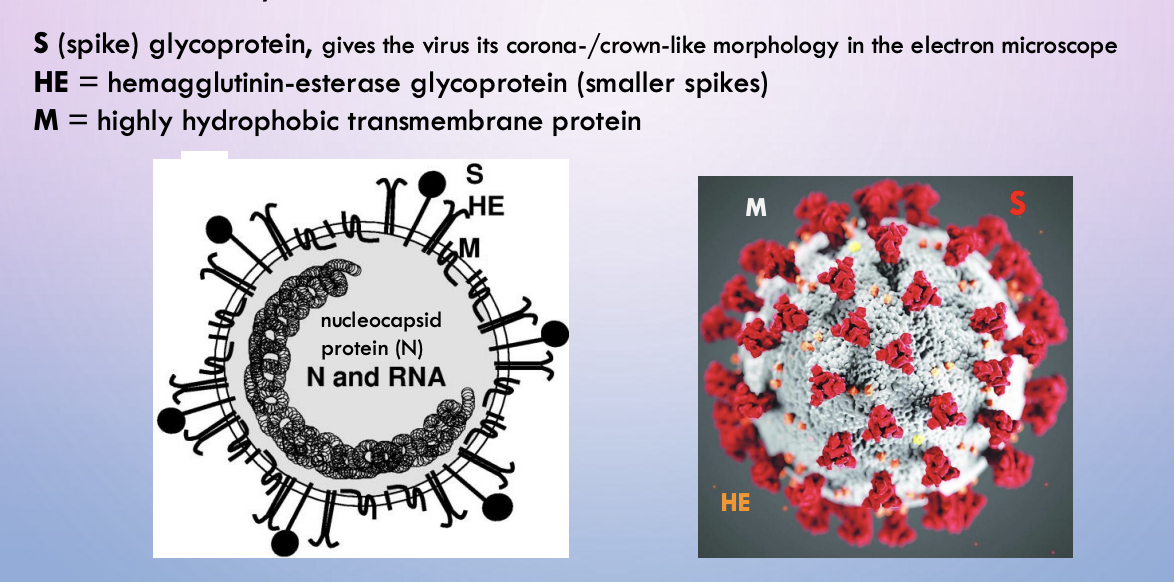
COVID - S
spike glycoprotein. Gives the virus a corona/crown-like morphology in electron microscope
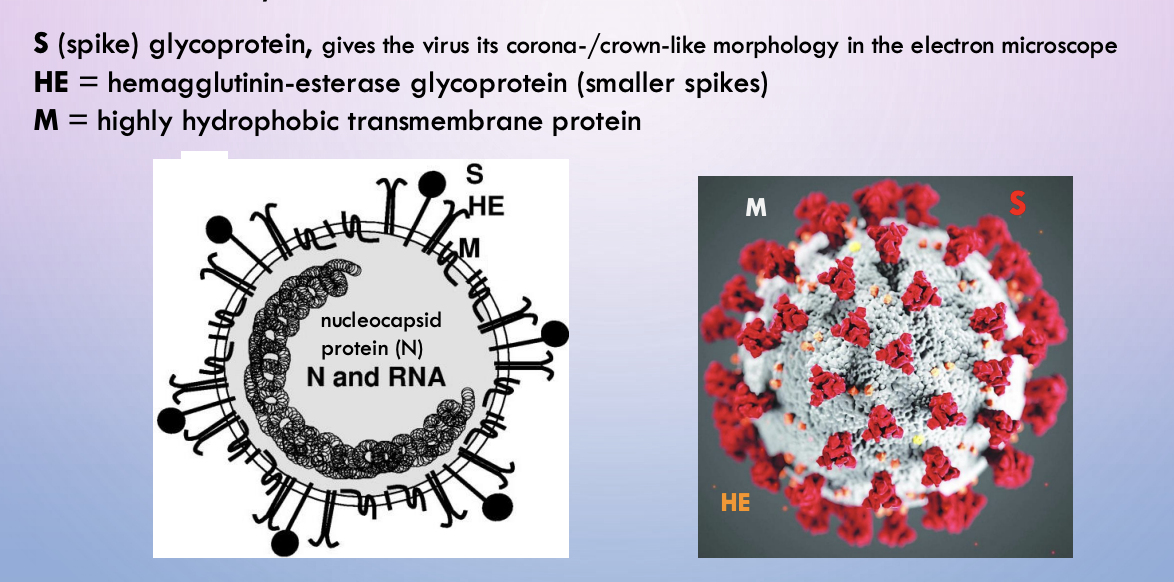
COVID - HE
hemagglutinin-esterase glycoprotein (smaller spikes)
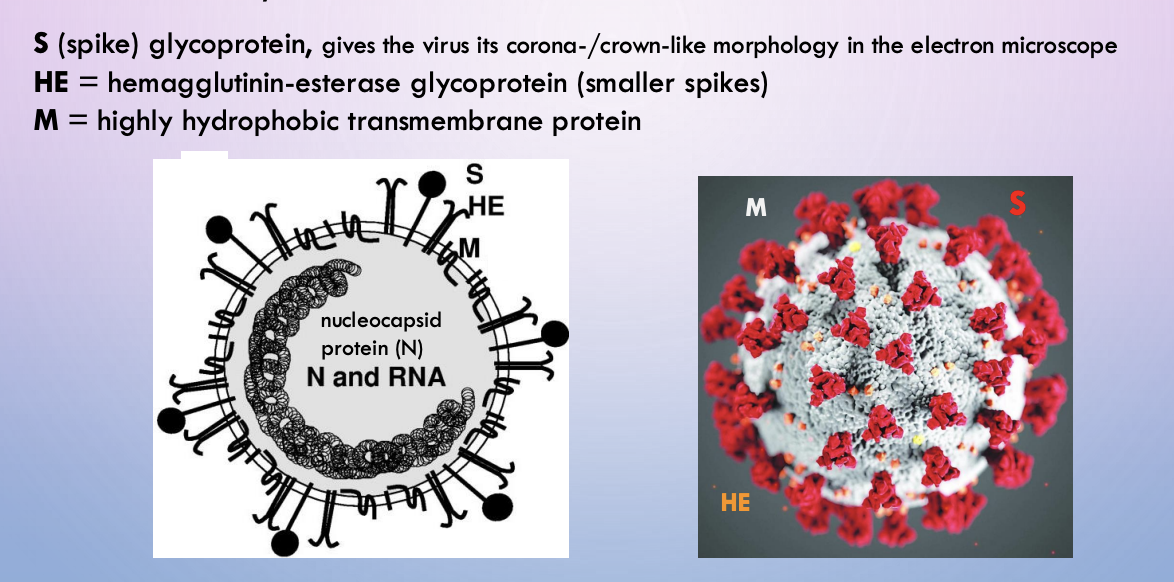
COVID - M
hydrophobic transmembrane protein
ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme II)
cell receptor for SARS-CoV, and for some SARS-like bat coronavirus.
Receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 has even higher binding affinity than SARS-CoV
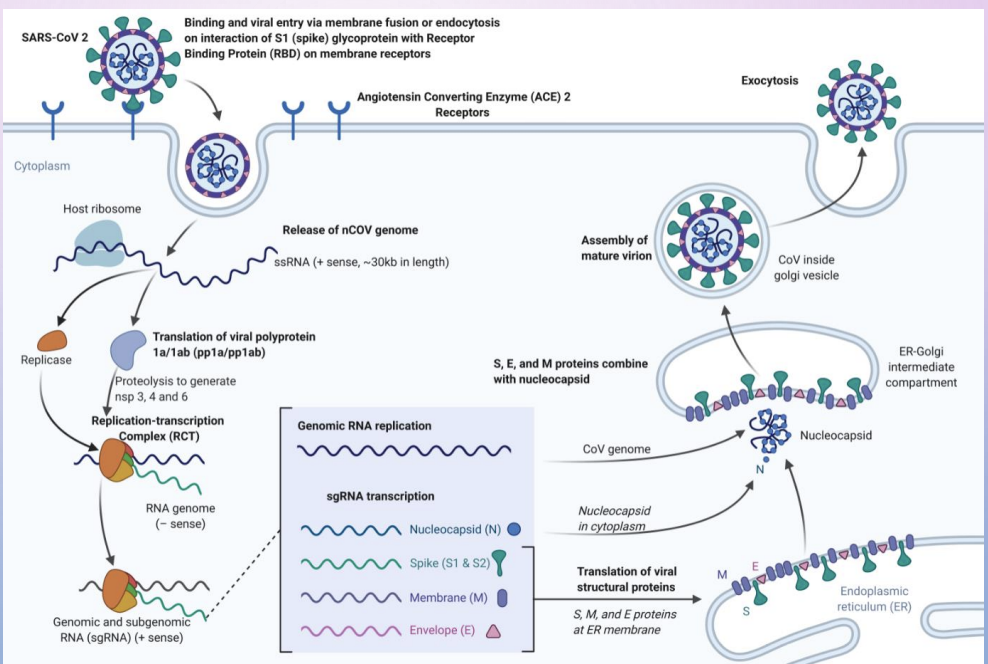
ACE2 target
certain progenitor cells that normally develop into respiratory tract cells lined with cilia that sweep mucus and bacteria out of the lungs
paxlovid
antiviral treatment for Sars-Cov-2 (COVID19)
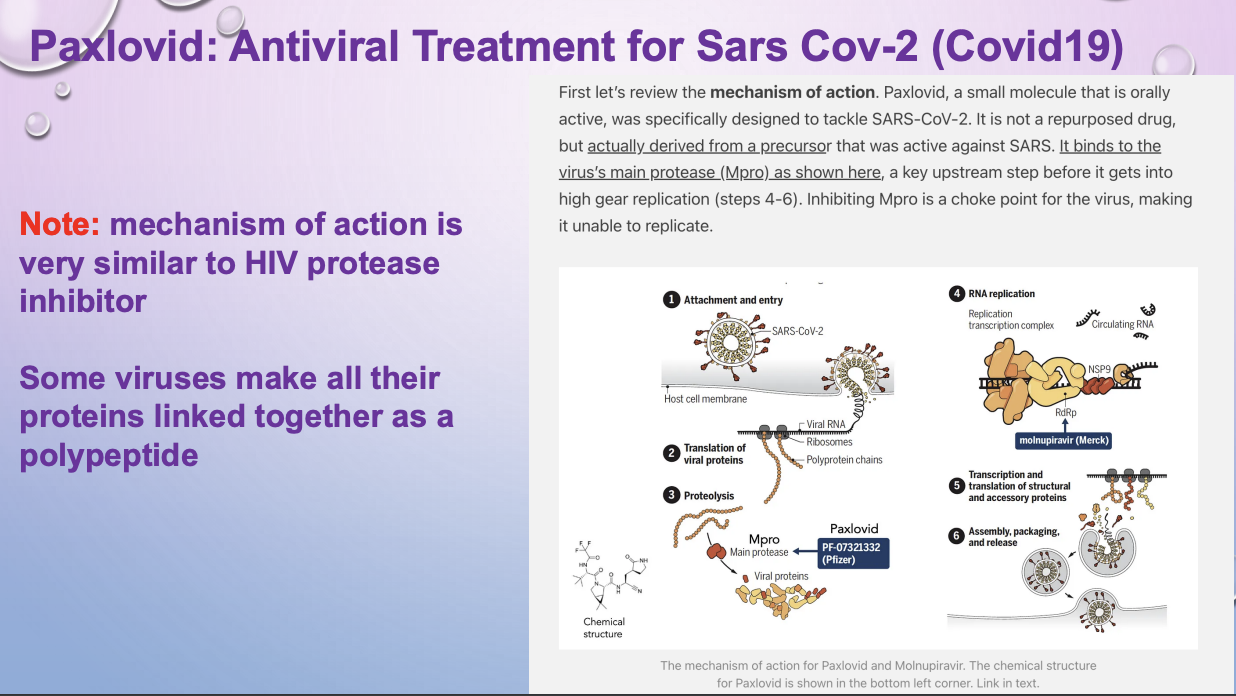
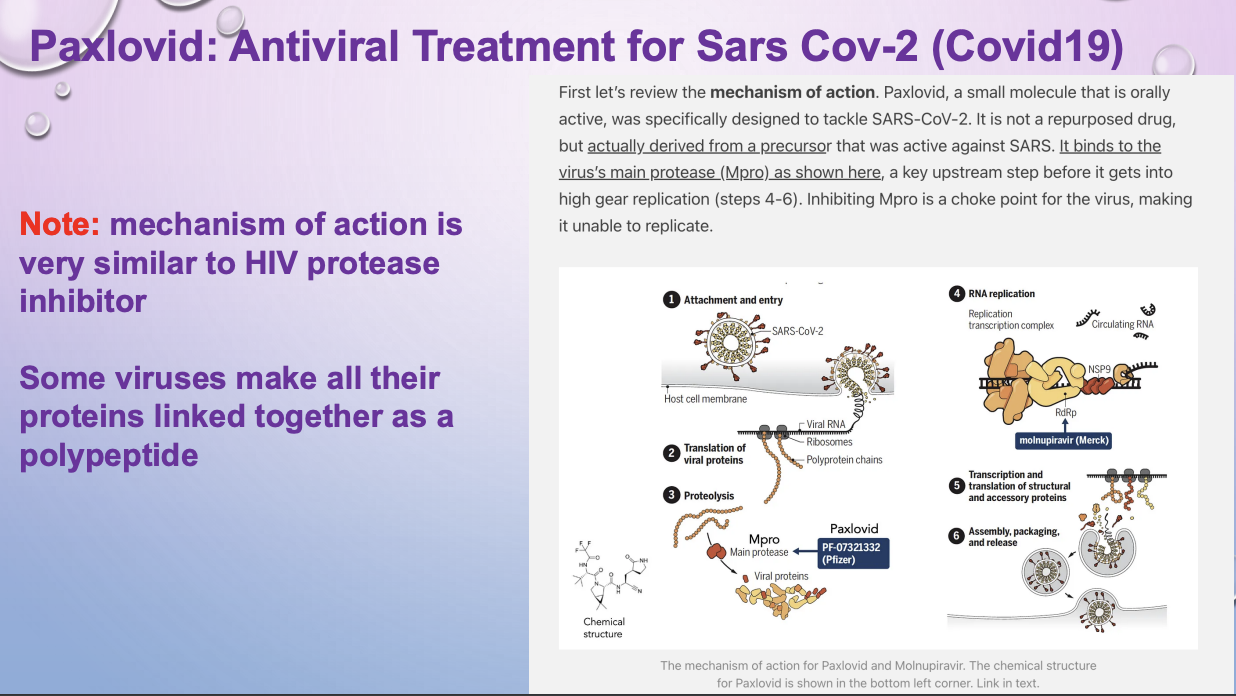
paxlovid - mech of action
like HIV protease inhibitor. Some viruses make all their proteins linked together as a polypeptide
makes virus unable to replicate
long COVID
“sequela” of COVID - sequela is a condition or complication that occurs after an injury, disease, therapy, or other trauma. The word comes from the Latin word meaning "sequel".
possible symptoms:
neurologic and mental health conditions
kidney failure
musculoskeletal conditions
cardiovascular conditions
respiratory conditions
blood clots and vascular tissues
chronic fatigue
long COVID - stats
Worldwide: 650 Million Covid infections
incidence = 10-30% of non-hospitalized cases
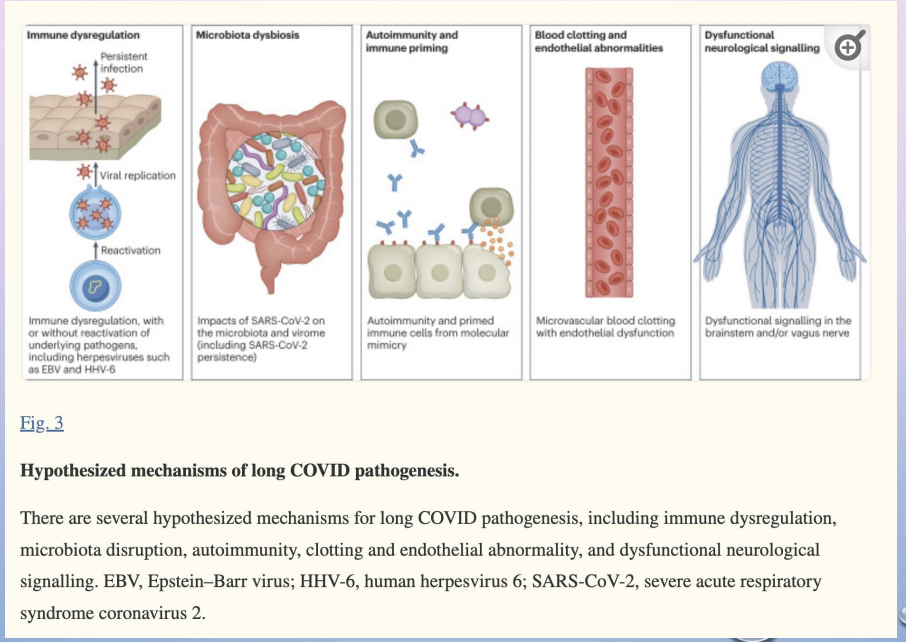
long COVID - mechanisms
immune dysregulation
microbiota dysbiosis
autoimmunity and immune priming
blood clotting and endothelial abnormalities
dysfunctional neurological signalling
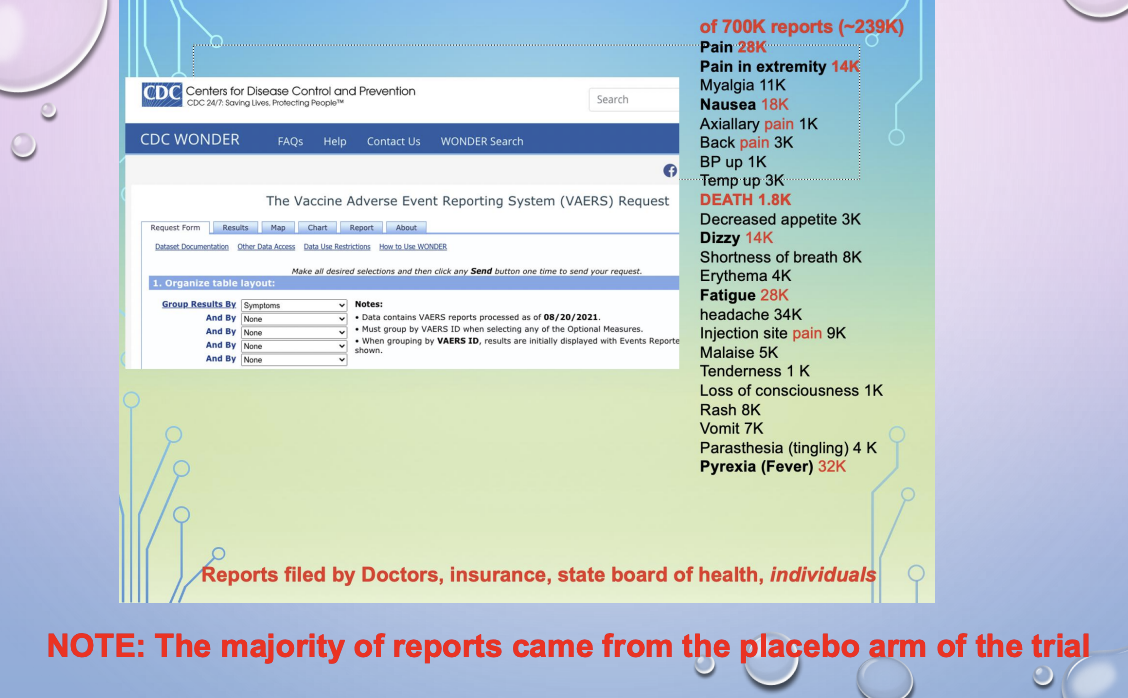
placebo arm of vaccines trial
most reports of symptoms come during the placebo arm of trial!
things like pain in extremity, nausea, fatigue, dizziness
filed by doctors, insurance, state board of health, individuals
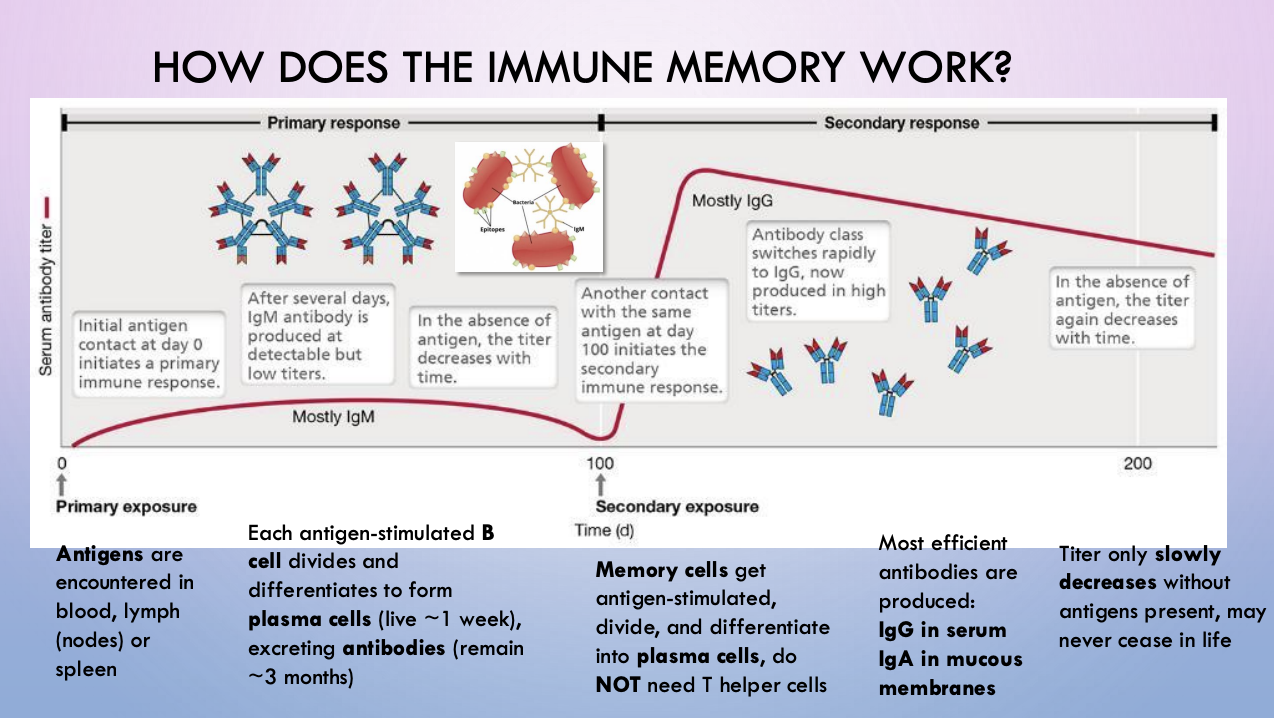
immune memory
vaccination - polyclonal antibodies
after vaccination, our body produces polyclonal antibodies
each phagocyte presents different epitopes of the spike protein —> variety of B cells are activated, each one recognizing a different epitope of the spike protein antigen
slight mutations should still allow adequate memory/immunity; DNA-containing vs. RNA-containing pathogens
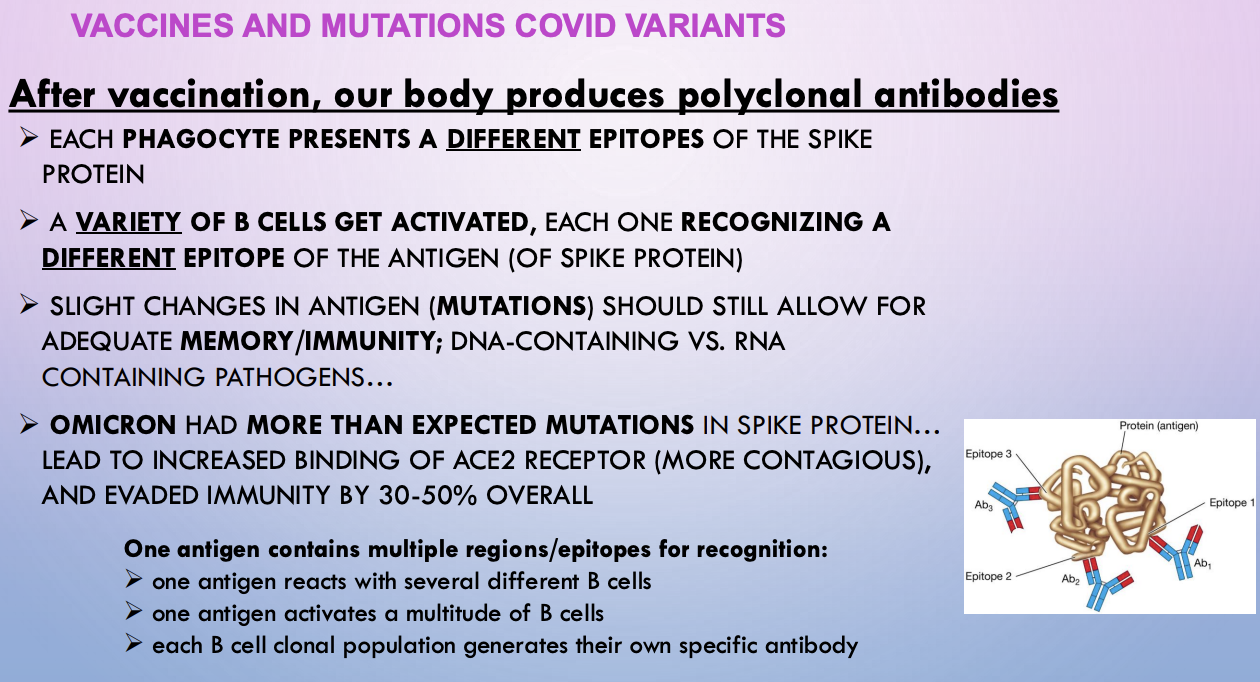
Omicron
had more than expected mutations in spike protein —> increased binding of ACE2 receptor (more contagious), immunity evasion 30-50%
epitopes
One antigen contains multiple regions/epitopes for recognition
one antigen reacts with several different B cells
one antigen activates a multitude of B cells
each B cell clonal population generates their own specific antibody
vaccine strategies
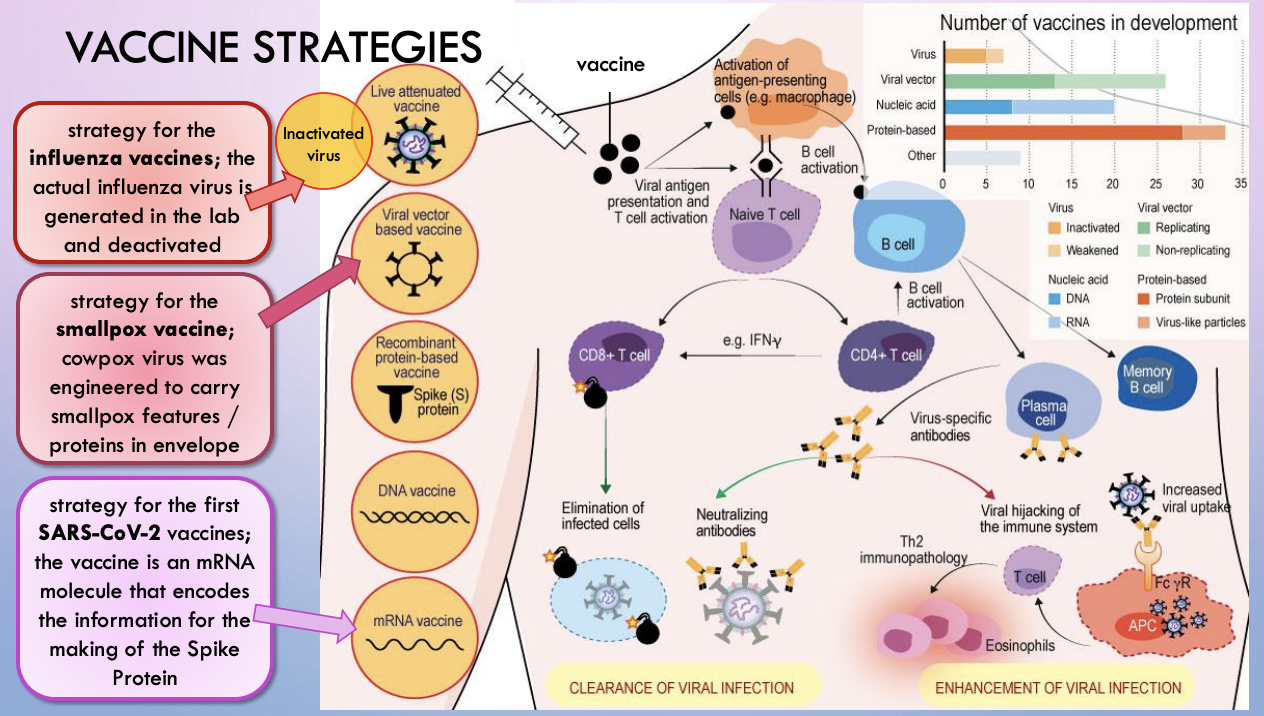
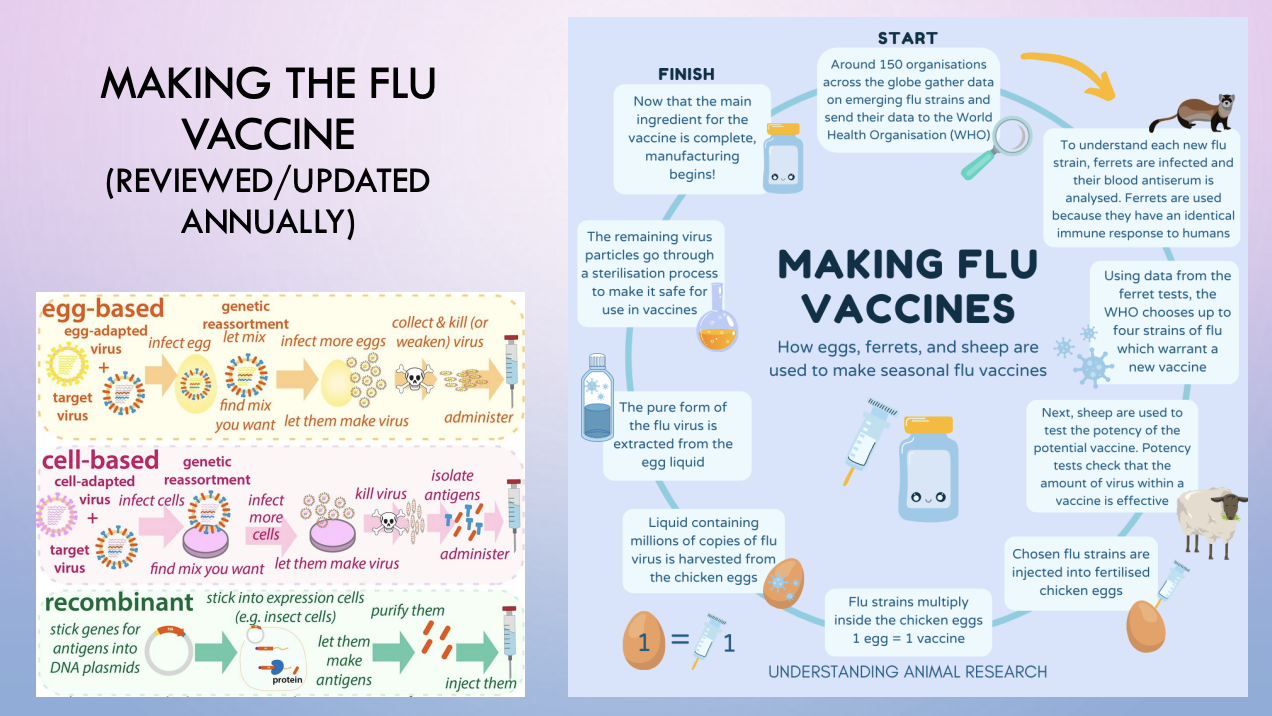
influenza vaccine - development
live attenuated vaccine - actual influenza virus is generated in the lab and deactivated
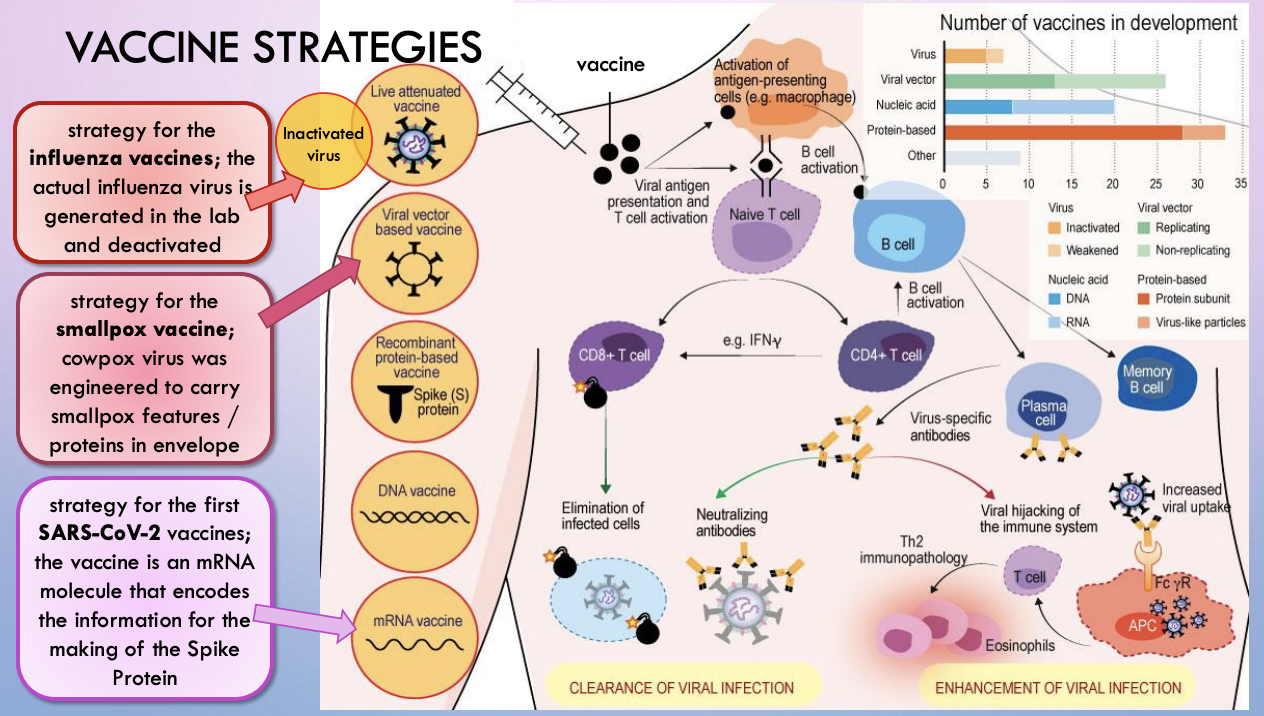
smallpox vaccine - development
viral vector based vaccine - cowpox virus was engineered to carry smallpox features / proteins in envelope
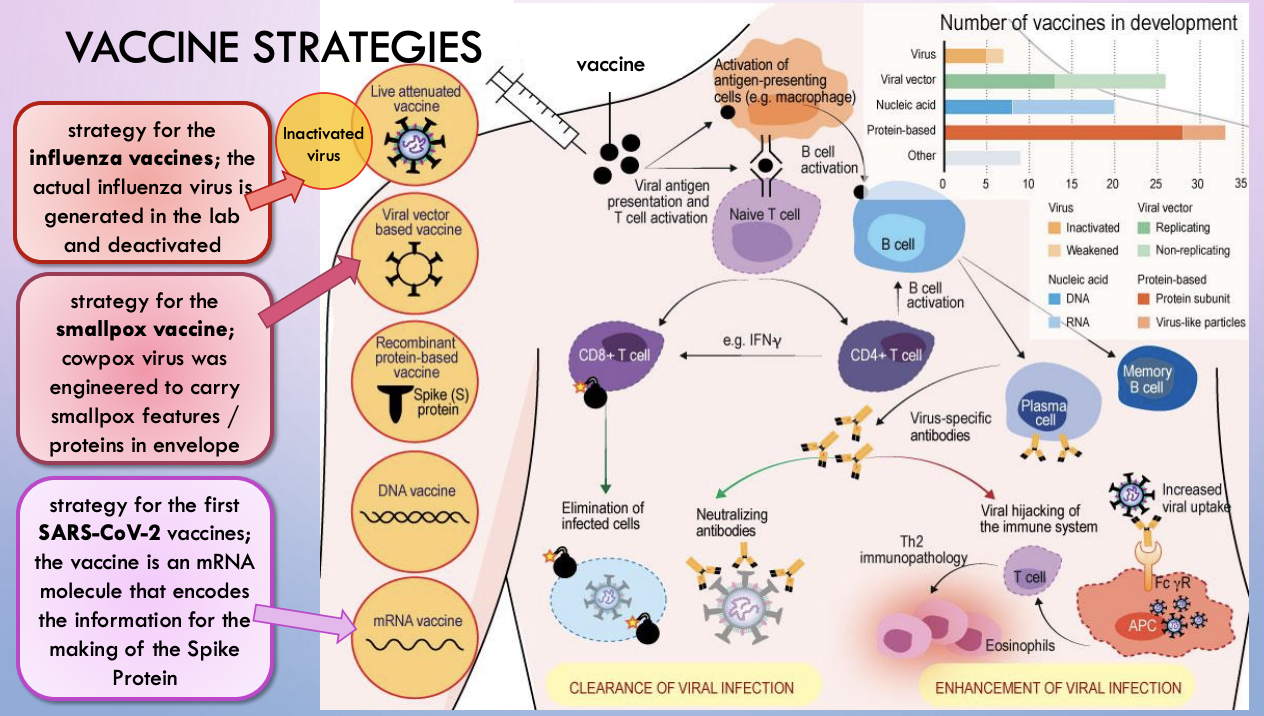
first SARS-Cov-2 vaccines - development
mRNA vaccine - vaccine is mRNA that encodes info for making Spike protein
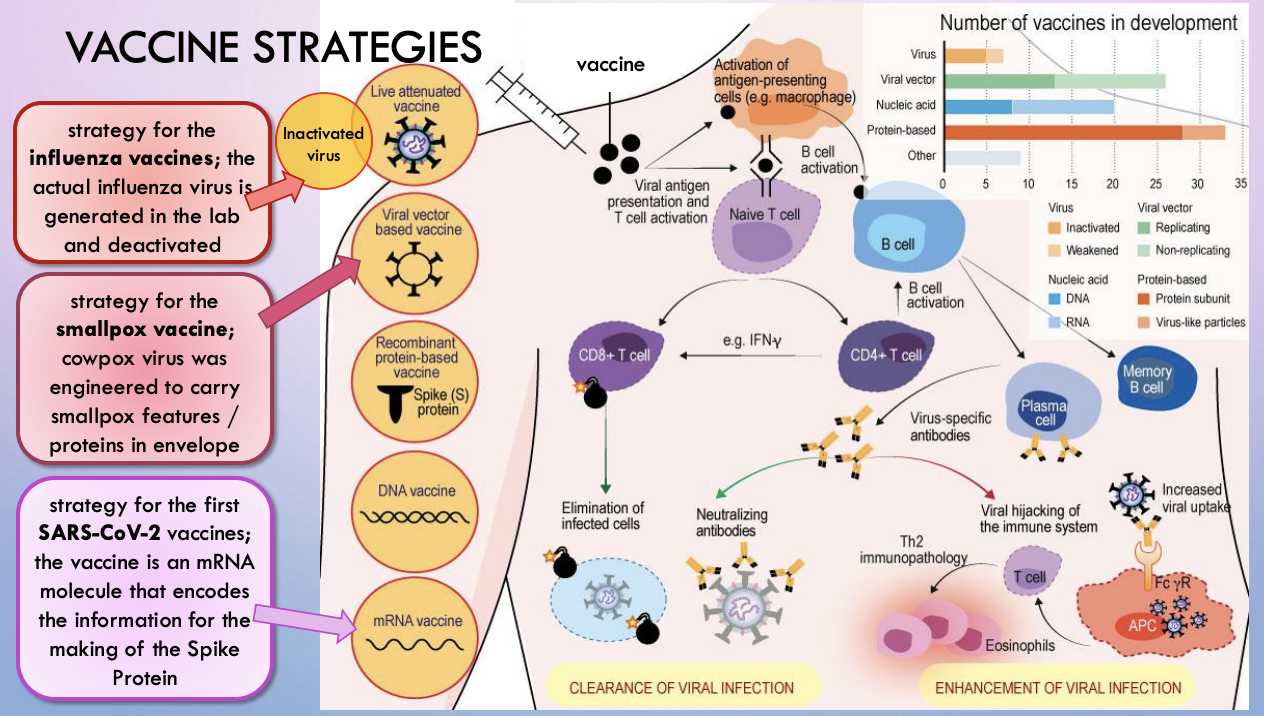
mRNA vaccines
no need to cross nuclear membrane for expression; no risk of viral genes integrating into host DNA (there’s no DNA)
problem: high natural destruction rate, low uptake/transfection efficacy by euk cells
Lipid coat to get in; RNA backbone chemistry to let them last longer
mRNA vaccines mechanism
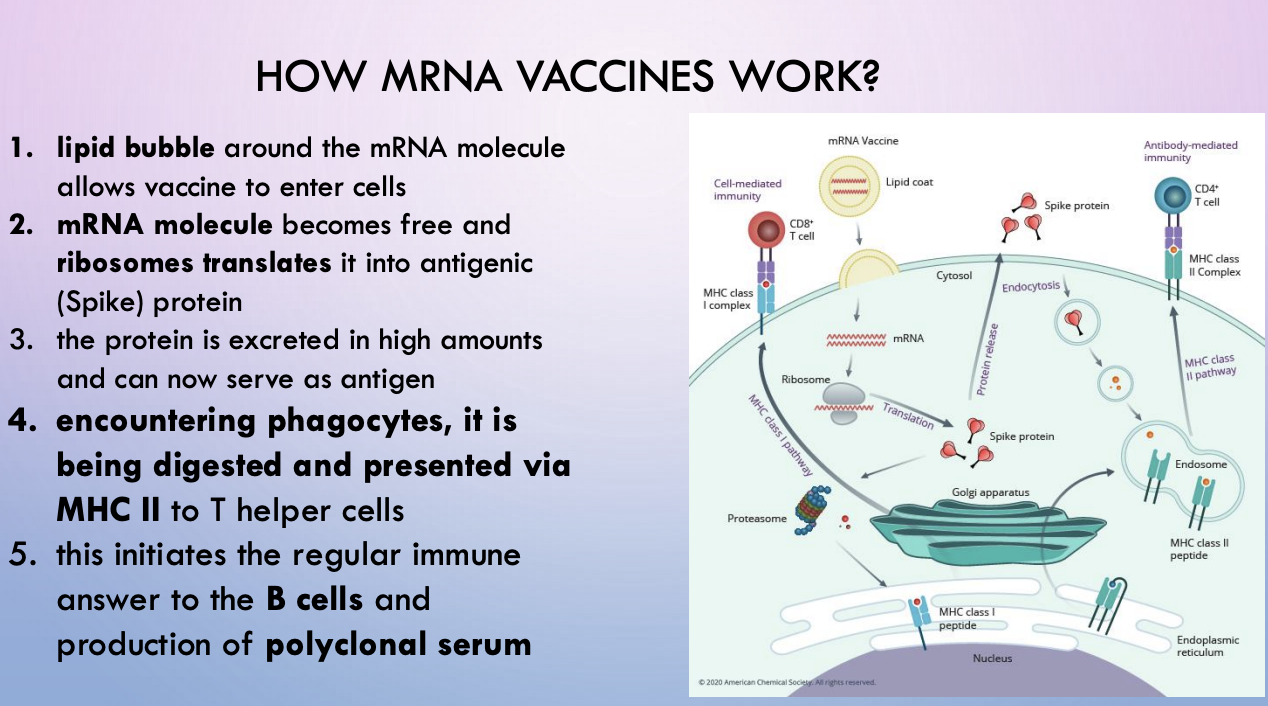
why were first COVID vaccines mRNA based?

making the flu vaccine
1.) egg-based
2.) cell-based
3.) recombinant
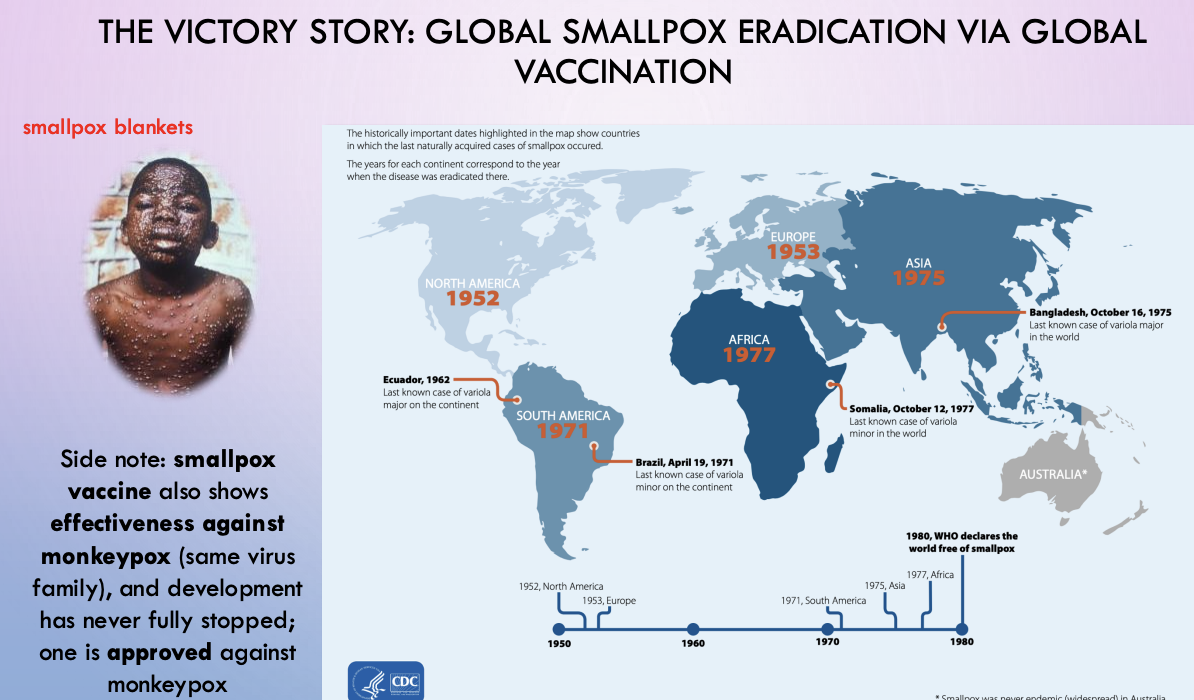
smallpox eradication via global vaccination
smallpox vax also effective against monkeypox. There is a monkeypox vaccine too (same family of virus)
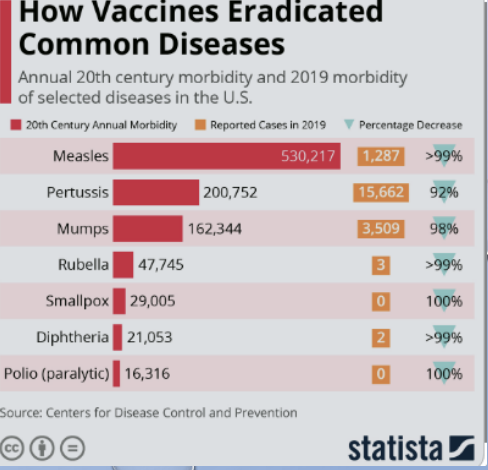
vaccines to eradicate disease
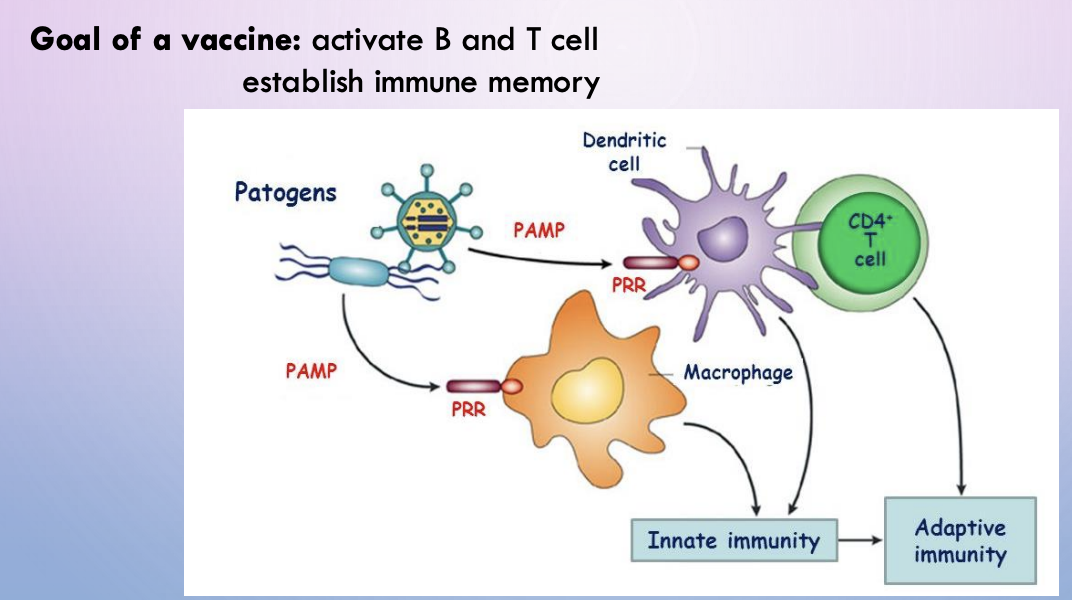
vaccine goals
1.) activate B and T cell
2.) establish immune memory
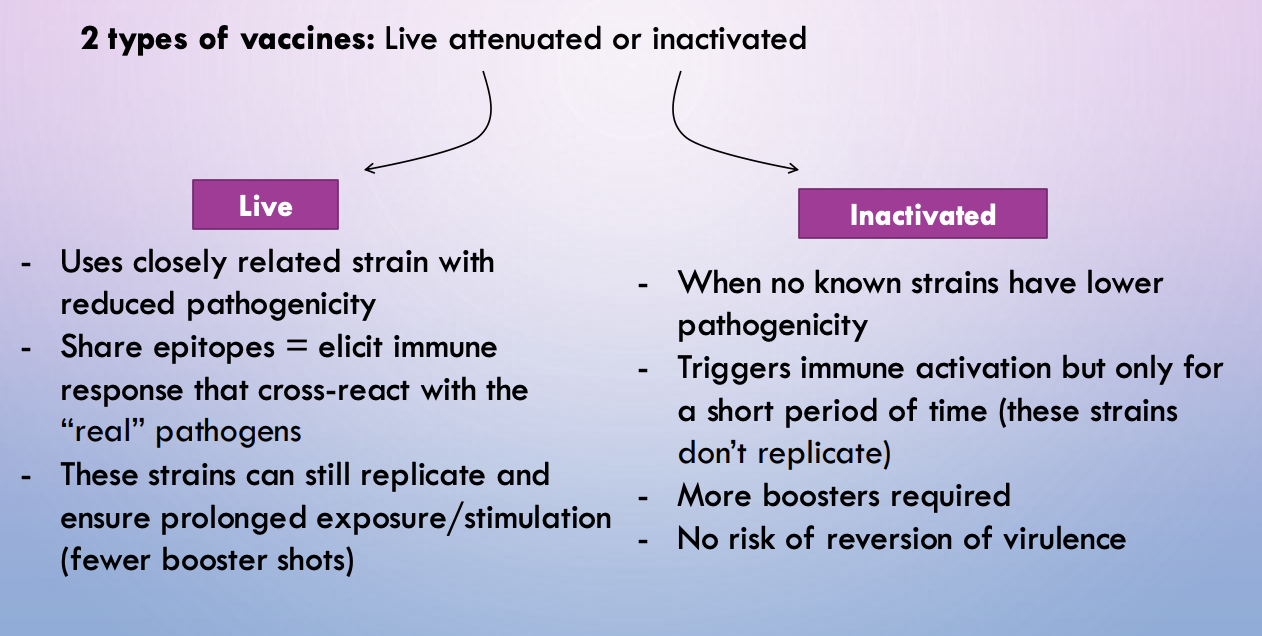
live attenuated vs. inactivated vaccine
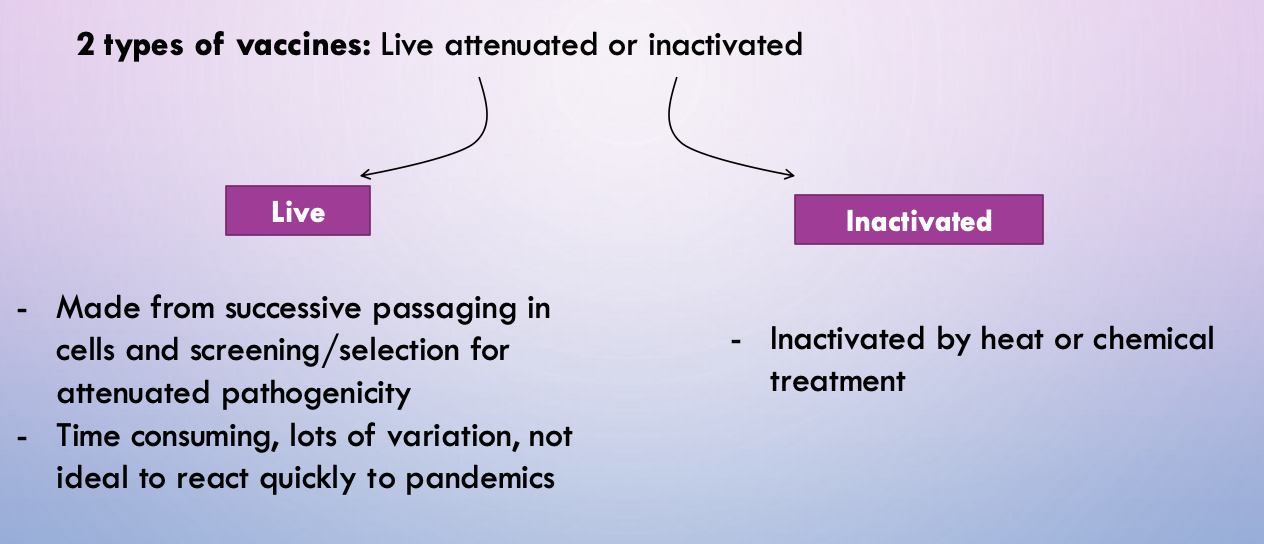
live attenuated vs. inactivated vaccine - development
live attenuated vaccines - example
MMR, OPV (oral polio vaccine), chicken pox

killed vaccines - example
inactivated influenza, IPV (inactivated polio vaccine)

subunit vaccines - example
subunit vaccines don’t stress the animal as much as live, and only have concentrated amounts of the target antigen (which aren’t destroyed like in killed) —> thus do a better job of disease prevention. SAFE and EFFECTIVE
ex: Hib (Haemophilus influenzae type b), HepB, HepA, Pneumococcal conj. vaccine

rabies
cause - rhabdovirus (ssRNA)
pathology - carriers = racoon, etc. Transmit by saliva in wounds or mucous membranes. Infect CNS and brain especially
symptoms - fever, restlessness, spasms, salivation, paralysis
diagnosis - symptomatic, tissue examination for virus (fluorescent immunostaining)
treatment - none for animals; purified human antibodies (passive) and vaccine (active)

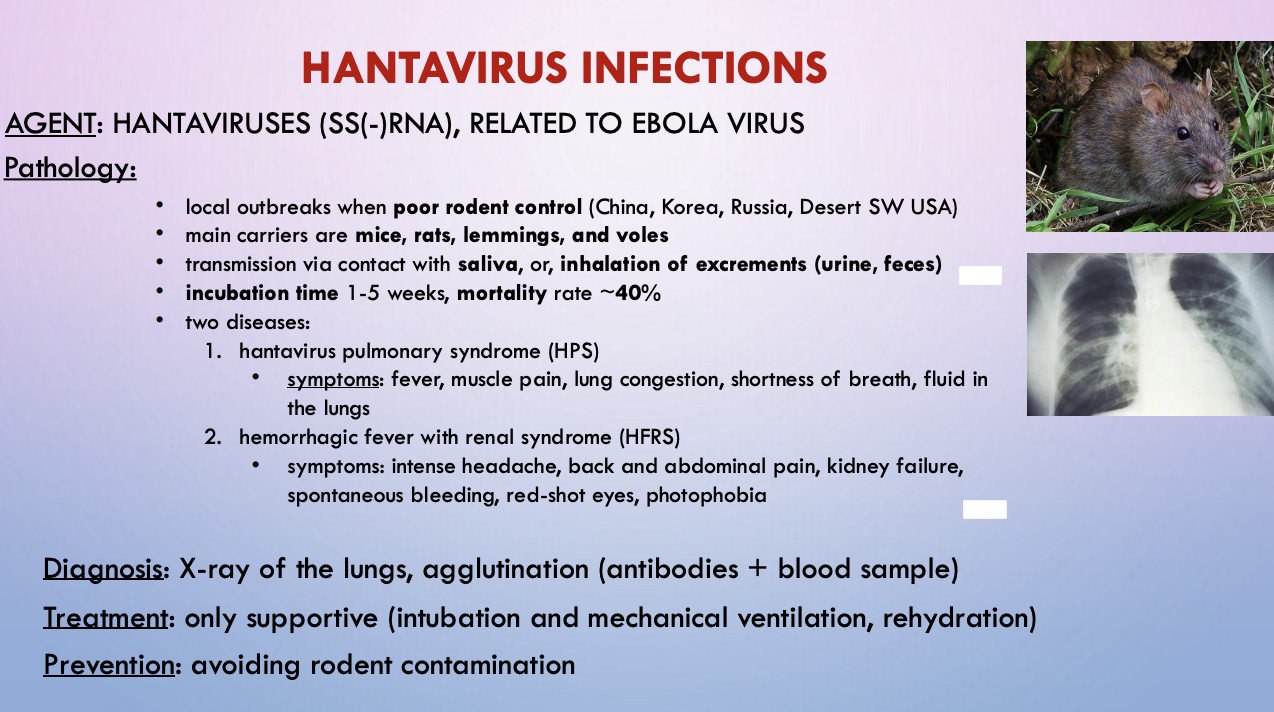
hantavirus
cause - hantavirus (ssRNA), related to ebola virus
pathology - poor rodent control. Mice, rat, lemming, vole. Transmit via saliva or inhaling excrements
symptoms - 2 diseases w diff symptoms, HPS and HFRS
diagnosis - lung X ray, agglutination (antibodies + blood sample)
treatment - only supportive (intubation and mechanical ventilation, rehydration)
prevention - avoiding rodent contamination
hantavirus meme

diseases via arthropods (insects, spiders, crustaceans)
transmission via bites, with humans = accidental hosts
diseases often devastating, fatal.
bacterial examples: rickettsial diseases (typhus, RMSF) - lyme disease - plague
viral examples: yellow fever, Zika

Rickettsiales
obligate parasites (bacterial)
can replicate inside macrophages; associated with fleas, lice, ticks (blood-sucking arthropods)
3 group: thyphus group, spotted fever group, erlichiosis group

lone star tick
Rickettsiales
can cause meat allergy (allergy to alpha gal)
Lone star ticks can have alpha-gal in their guts and saliva. When a lone star tick bites someone, it can pass alpha-gal to the person in its saliva. This can trigger the individual's immune system to respond by producing antibodies (known as immunoglobulin E, or IgE) against alpha-gal.

lyme disease
agent - borrelia burgdoferi
pathology - ticks, esp very small deer ticks. Bacteria infect CNS, can stay dormant and cause muscle, vision, or nerve damage, or seizures. If untreated —> chronic (arthritis, neurological probs, heart damage)
symptoms - headache, back pain, chills, fatigue
diagnosis - bull’s eye rash ( <65%), fluorescent immunostain
treatment - antibiotics in first 1-2 weeks
prevention - removal of ticks before they bite, DEET insect repellent

typhus
agent - rickettsia prowazekii
pathology - body or head lice, bite wound gets infected with lice feces. Bact replication inside cells lining small blood vessels. Hurts CNS, lungs, kidneys, heart. 30% mortality
symptoms - fever, headache, weakness, rash in armpits that spreads (everywhere except head)
diagnosis - fluorescence immunostain on skin biopsy from rash
treatment - antibiotics
prevention - vaccination, but only when traveling to endemic regions

rocky mountain spotted fever
agent - rickettsia rickettsia
pathology - dog tick saliva. Southeast US
symptoms - fever, severe headache, followed by systemic rash, GI problems (diarrhea, vomiting). Damage of blood vessels, post-infection amputation, paralysis
diagnosis - symptomatic, blood testing poor, takes weeks
treatment - antibiotics
prevention - removal of ticks before they bite, DEET insect repellent

plague
agent - yersinia pestis
pathology - fleas of rats, cells rep in lymph nodes, capsule protects from phagocytosis. Bact fill lymph nodes (=bubonic plaque) —> enter blood stream and cause septicemia, bleeding - dark blotches on skin (=”black death”). >90% mortality after 48 hrs
symptoms - tissue necrosis, delirium, dark blotches on skin
diagnosis - sample from swollen lymph nodes, agglutination test, culturing
treatment - antibiotics
prevention - good sanitation and rodent control, quarantine (droplet infection)

yellow fever
agent - flavivirus (ss(+)RNA), related to Dengue fever, West Nile, Zika.
pathology - mosquito in tropical and subtropical climate (Latin/South America, Africa). Virus replicates in imm sys cells in lymph nodes, travels to liver
symptoms - : headache, mild fever and chills, backpain, nausea
1 in 5 enter “toxic phase”: jaundice (yellow coloring of skin, eyes, and mucous membranes due to bilirubin, formed when red blood cells break down), bleeding from mouth, eyes, and gastrointestinal tract, bloody vomit, multiple organ failure
diagnosis - antibody detection in blood sample
treatment - supportive, and, isolation of patient so no mosquitoes can transfer the virus
prevention - vaccination, recommended when travelling to endemic regions

Zika
agent - flavivirus (ssRNA)
pathology - vector is mosquito. Virus infects cells in special brain region. Causes microcephaly in newborns = smaller head —> intell. disabilities and speech delay
symptoms - mild = fever, backpain, joint pain, red eyes, rash. Very severe for pregnant women (or wanting to get pregnant)
diagnosis - symptomatic, RT-PCR from blood or urine in pregnant women
treatment - self-healing for ppl and unborns
prevention - insect repellents, general measures to avoid mosquito bites

soilborne diseases
direct contact or aerosolized; soil particles with attached bacteria. Animal fur or hides in ground
bact often free-living, don’t need host
Ex: anthrax, tetanus, gas gangrene

tetanus
agent - clostridium tetani, endospore
pathology - soil-contaminated wound. Bacteria germinate and grow, but are non-invasive. Produce exotoxin “tetanus toxin” —> prevent inhibitory signalling in nervous sys
symptoms - paralysis of voluntary muscles (face first = lockjaw). Proceeding spasms and body paralysis, respiratory failure; mortality 10-50%
diagnosis - symptomatic, rarely blood or tissue tests
treatment - antibiotics; vaccine; antitoxin (cannot un-paralyse)
prevention - routine vaccination

water/vehicle-borne cholera
agent - vibrio cholerae; salt tolerant
pathology - undercooked shellfish. Cells attach to epithelial cells in small intestine, produce AB-toxin / enterotoxin —> secrete fluid into intestinal lumen (block Na+ transporters). Mortality 25-50% by dehydration
symptoms - pandemic proportions! must get high dose of bact bc must survive stomach acid. Diarrhea, dehydration
diagnosis - culturing on special medium with bile salts and citrate
treatment - antibiotics, rehydration drink (glucose, NaCl, NaHCO3 , KCl)
prevention - adequate sewage treatment & drinking water purification procedures

water/vehicle borne legionellosis
agent - legionella pneumophilia; resistant to chlorine and heating
pathology - #1 disease-causing agent linked to US drinking water. aerosoles in showers, evap cooling systems. Invade lungs, grow in microphages
reservoir - freshwater and soil, warm stagnant water tanks, biofilms in pipes
symptoms - healthy ppl are mild (sore throat, headache fever), elderly pneumonia
diagnosis - immunostaining of bronchial washings or pleural fluid
treatment - antibiotics
prevention - major problem, heating water above 63℃

norovirus
agent - norovirus (ssRNA)
pathology - feces-contaminated food or water. Leading cause of GI illness. Person-to-person or fecal-to-oral route. Cruises, nursing homes
symptoms - short but intense vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue (24 hr bug)
diagnosis - symptomatic, RT-PCR, enzyme immunoassay of vomit or feces
treatment - none (necessary), rehydration/electrolytes
prevention - good sanitary behavior, boiling water, wash/heat foods

CRISPR-Cas9 gene resistance?
mutation at exon 5 site, but no resistance. Harder to replace a missing exon
Cas9 resistant variants but don’t block GENE DRIVE

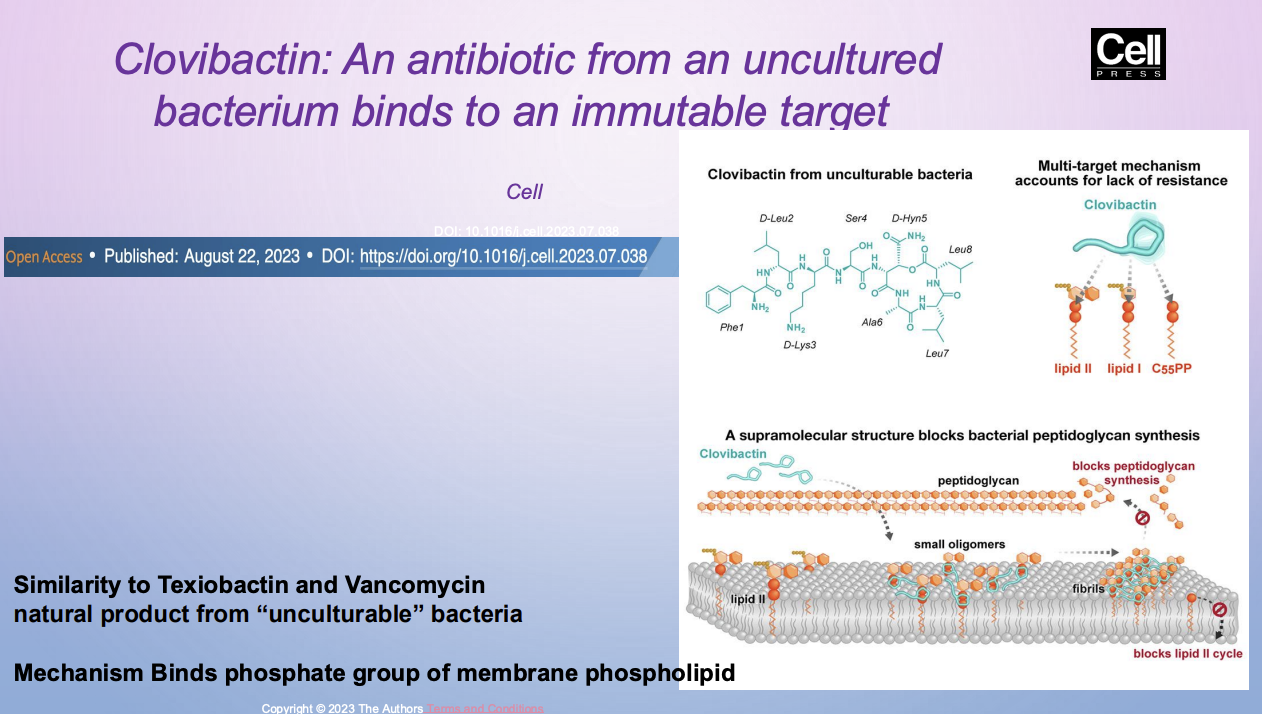
clovibactin
antibiotic from uncultured bacterium binds to an immutable target
like teixobactin and vancomycin
mech binds phosphate group of membrane plipid —> prevents bacterial peptidoglycan synth
cornea
has T cells that protect eyes from viral infections. Previously thought to be free of immune cells

Variolation
early method of inoculation used to protect people from smallpox by intentionally infecting them with a small amount of smallpox material
China: blow dried smallpox scabs into nose
Thimerosal/Wakefield
thimerosal = mercury preservative found in vaccines
Wakefield = guy who said autism is caused by thimerosal in vaccines
Onesimus
An enslaved African, Onesimus helped to save hundreds of Bostonians from smallpox in 1721. Left out of the history books, he taught others about the practice of inoculation, which was common in Africa and Asia long before vaccines were established

BCG
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine, which is used to treat tuberculosis and bladder cancer, may be associated with a lower risk of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias (ADRD)
Coley’s toxins
a mixture containing toxins filtered from killed bacteria of species Streptococcus pyogenes and Serratia marcescens. 1800s treatment for cancer
precursor to modern cancer immunotherapy, although at that time their mechanism of action was not completely understood
no evidence that effective against cancer. Lots of risks
Malaria
life-threatening disease caused by a parasite that is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito
Why no HIV vaccine
virus itself integrates into host DNA, it limits the vaccine platforms we can use.
medications directed against reverse txnase - like proteins that would stick to viral rep machinery and not our own —> no host toxicity.
Flu Mist
live attenuated virus
Dogs Lyme’s Vaccine
dog vacc against lyme, but humans are not. Bc lyme’s vaccine for humans caused side effect claims (?), and companies aren’t interested in making products that might get them sued
Gardasil Lawsuits
Patients filed lawsuits, Charlotte's U.S. District Court alleging medical issues triggered after receiving Merck's HPV vaccination Gardasil.
VAERS
Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System
“have you had a reaction following a vaccination?”
Covid vax prevents?
prevents severe disease and death, but not really infection (modest and often short-lived)
adverse effects/placebo arm of COVID vaccine
Significantly more AEs were reported in the vaccine groups, but AEs in placebo arms (“nocebo responses”) accounted for 76% of systemic AEs after the first COVID-19 vaccine dose and 52% after the second dose
polyclonal sera
antibodies that are secreted by different B cell lineages within the body (whereas monoclonal antibodies come from a single cell lineage). They are a collection of immunoglobulin molecules that react against a specific antigen, each identifying a different epitope.
variants
a subtype of a microorganism that is genetically distinct from a main strain, but not sufficiently different to be termed a distinct strain