Uncertainties and equations of motion
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
scale reading uncertainty
an indication of how precisely and instrument scale can be read
random uncertainty
when measurements are repeated and slight variations occur
systematic uncertainty
when reading taken are either all too small or all too large
scalar quantities
distance
time
mass
energy
speed
vector quantities
displacement
acceleration
weight
force
velocity
acceleration
change in velocity in a unit of time
gravitational field strength
the force on a unit mass placed in the field
horizontal assumptions
no forces
constant velocity
acceleration = 0
vertical assumptions
only the force of gravity
velocity is changing at a constant rate
acceleration = (-)9.8ms-1
universal constant of acceleration (G)
6.67 × 10-11 m3kg-1s-2
Newton’s Law of gravitation
the gravitational attraction between two objects is directly proportional to to the mass of each object and is inversely proportional to the square of their distance apart
bouncing ball graphs
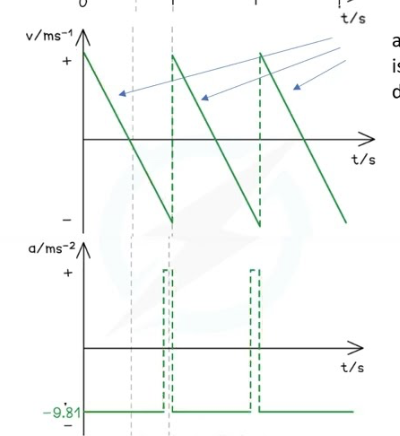
horizontal component of velocity
cosθ*hyp
vertical component of velocity
sinθ*hyp