Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
what are carboxylic acids
molecule withe carbonyl group
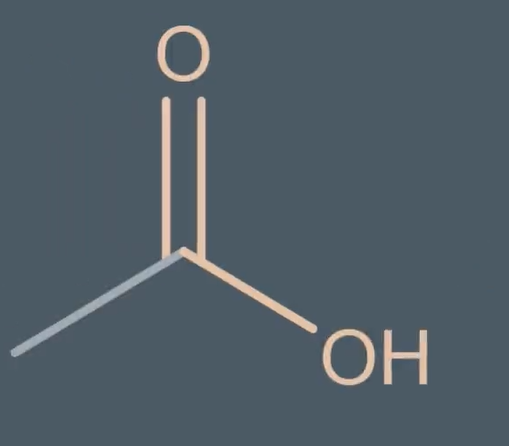
naming carboxylic acids
suffix -anoic acids
but with an alkene - enoic acids
why do carboxylic acids have high solubility in water
can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
what is a dimer and type of intramolecular force
2 carboxylic molecules , hydrogen bonds
carboxylic acid + metal →
salt + hydrogen
carboxylic acid + metal hydroxide
salt + water
carboxylic aid + metal carbonate →
salt + water + carbon dioxide
naming anion in salt
ethonic → ethanoate
why can carboxylic acids acras as acids
they can ionize , loosing a proton
what makes carboxylic acid more stable
extra electron is delocalized over the atom
ester funcional group
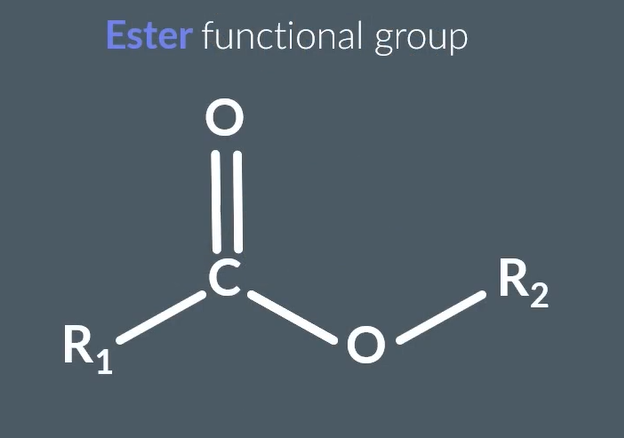
how to make esters
carboxylic acids + alcohols -( H2SO4 and heat ) → esters + water
naming esters
ethanal acid + methanol → methyl ethanoate
what is reverse of ester formation called
ester hydrolysis
what catalyst needed for ester hydrolysis
strong acid
products of hydrolyisis esters in alkaline conditions
alcohols and carboxylate salt
glycerol structure
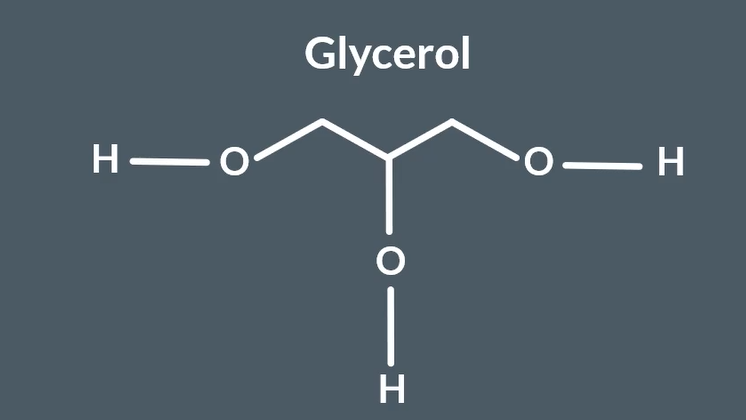
glycerols solubility in water
3 alcohol groups
forms loads of hydrogen bonds
very high solubility in water
uses of glycerol
solvent, plasterer , moisturizing agent
glycerol reactw with carboxylic acid to form
triester
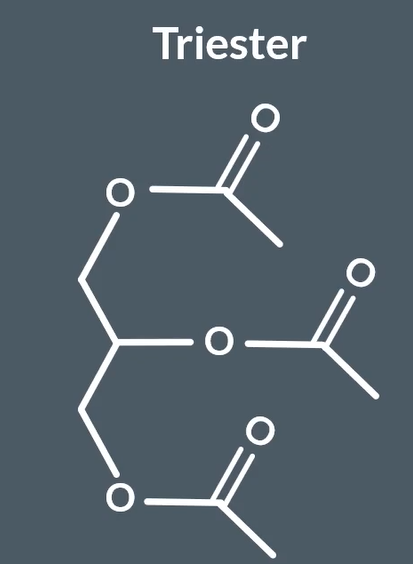
glycerol reacts with long chain carboxylic acid to form
vegetable oil
what is a fat
tryester chin is so long that sold at room temp
how to hydolize oils and fats
like other esters
when hydrolyze oil/fat in alkane conditions
salt produced = soap
oil also reacts with metate , with what catalyst
OH- catalyst
oil also reacts with metate , products
methyl esters formed that have a long chain can be used as a biodisel
what are carboxylic acid derivatives
molecules from a reaction including
what is an an acyl chloride
a derirative when acyl group reats with chlorin
reaction to form an acyl chlroide
RCOOH + SOCl2 → RCOCL + SO2 + HCl
naming acyl chloride
root no of carbon in max chain
suffix -anoyl chloride
how are acid anhydrides formed
2 molecules of ethanoic acid → remove 2H and O to form water
general formula for acid anhydrides
RCOOCOR
R(CO2)O
how to name acid anydride
removing the - acid and replacing with anhydride
why is it impossible to measure solubility of acid anhydrides and acyl chloride
when reacted with water they both form carboxylic acid
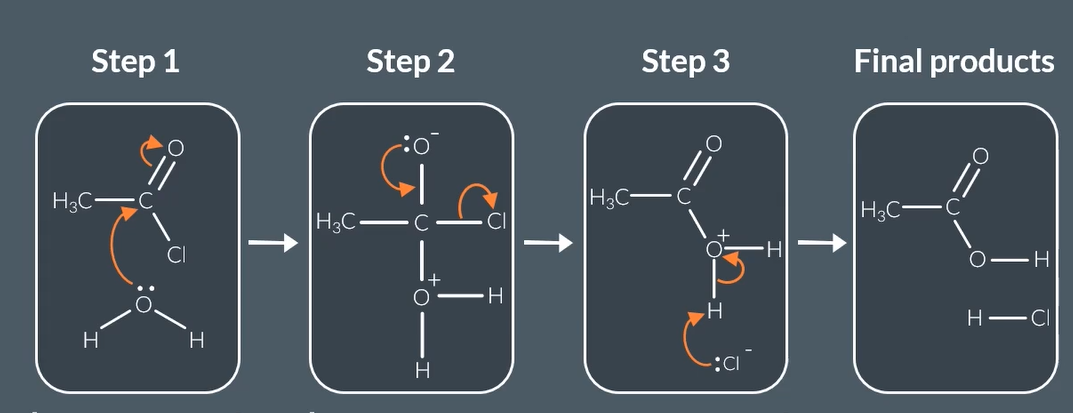
how does acyl chloride react with water
violently
acyl chloride reacts with water to form
carboxylic acid + HCL
mechanism for acyl chloride with water
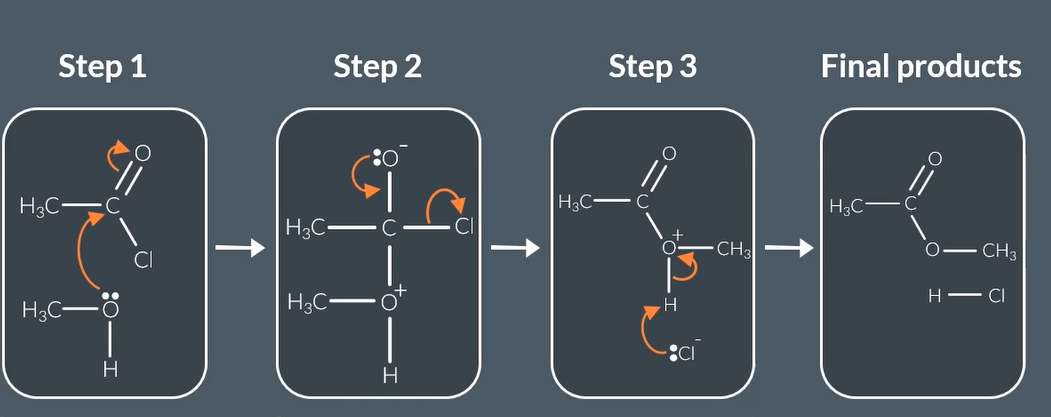
acyl chloride + alcahol forms
esters +HCL
reaction mechanism for acyl chloride + alcahol forms
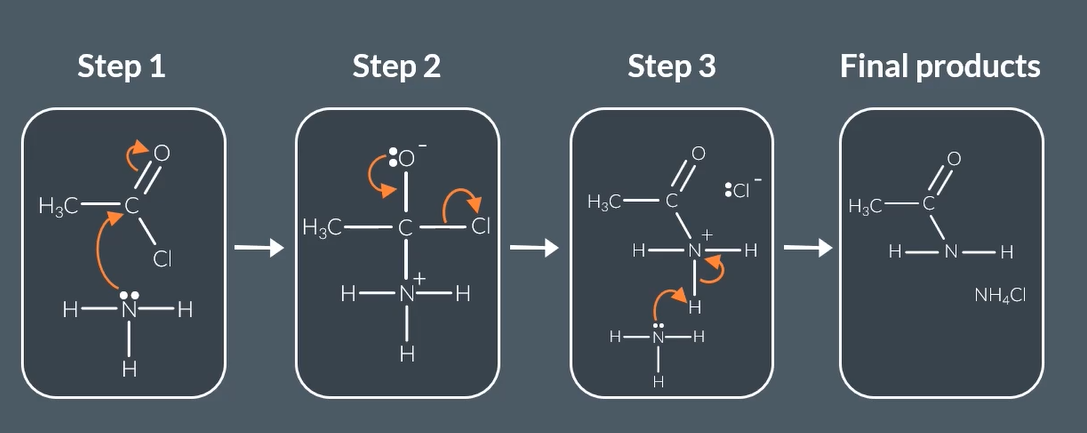
acyl chloride reacts with excess amine to form
amide + ammonium chloride
reaction mechanism when acyl chloride reacts with excess amine
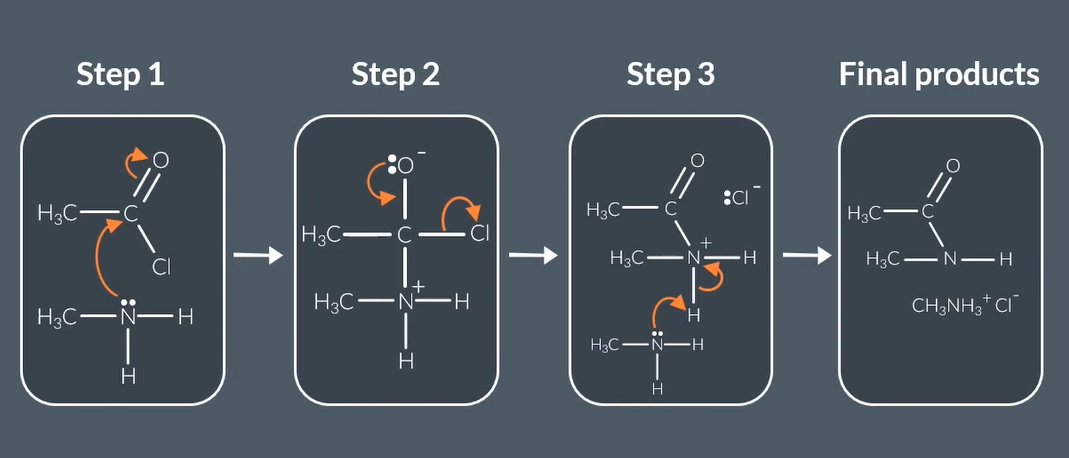
acyl chloride + primary amines form
secondary amines + Salt
reaction mechanism for acyl chloride + primary amines form
acyl anhydride + water
2 carboxylic acids
acyl anhydride +alcahol
ester + carboxylic acids
acyl anhydride + ammonia
primary amide + carboxylic salt
acyl anhydride + excess amonia
primary ammide + ammoniacarboxlic salt
acyl anhydride + excess primary ammine _> secondary amide + carboxylic salt
order of reactivity for acyl anhydrides, acyl chloride and carboxylic acids
acyl chloride > acyl anhydride > carboxylic acids
why do chemist prefer to use acyl anhydradride
acyl chloride so reactive
asprin products
saligic acid + ethonic anyhdride
why use ethanoic anyhydride ininstead of acyl chloride
less exothermic , easier to control
acyl chloride produces HCL dangerous gas
ethanoic anhydride , cheaper and easier to recylce