Logical Fallacies
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ACT
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Hasty Generalization
> Over Generalization
> Assumption about a large population using a small, inadequate sample

Missing The Point
> Irrelevant conclusion
> Attempt to counter a point that they do not actually address
OR
> Premise of an argument supports a particular conclusion but not the one the arguer draws

Slippery Slope
> Claim of chain reaction ending in dire consequence without enough evidence for assumption

Weak Analogy
> The two things that are compared aren’t alike in relevant aspects
> Analogy is weak

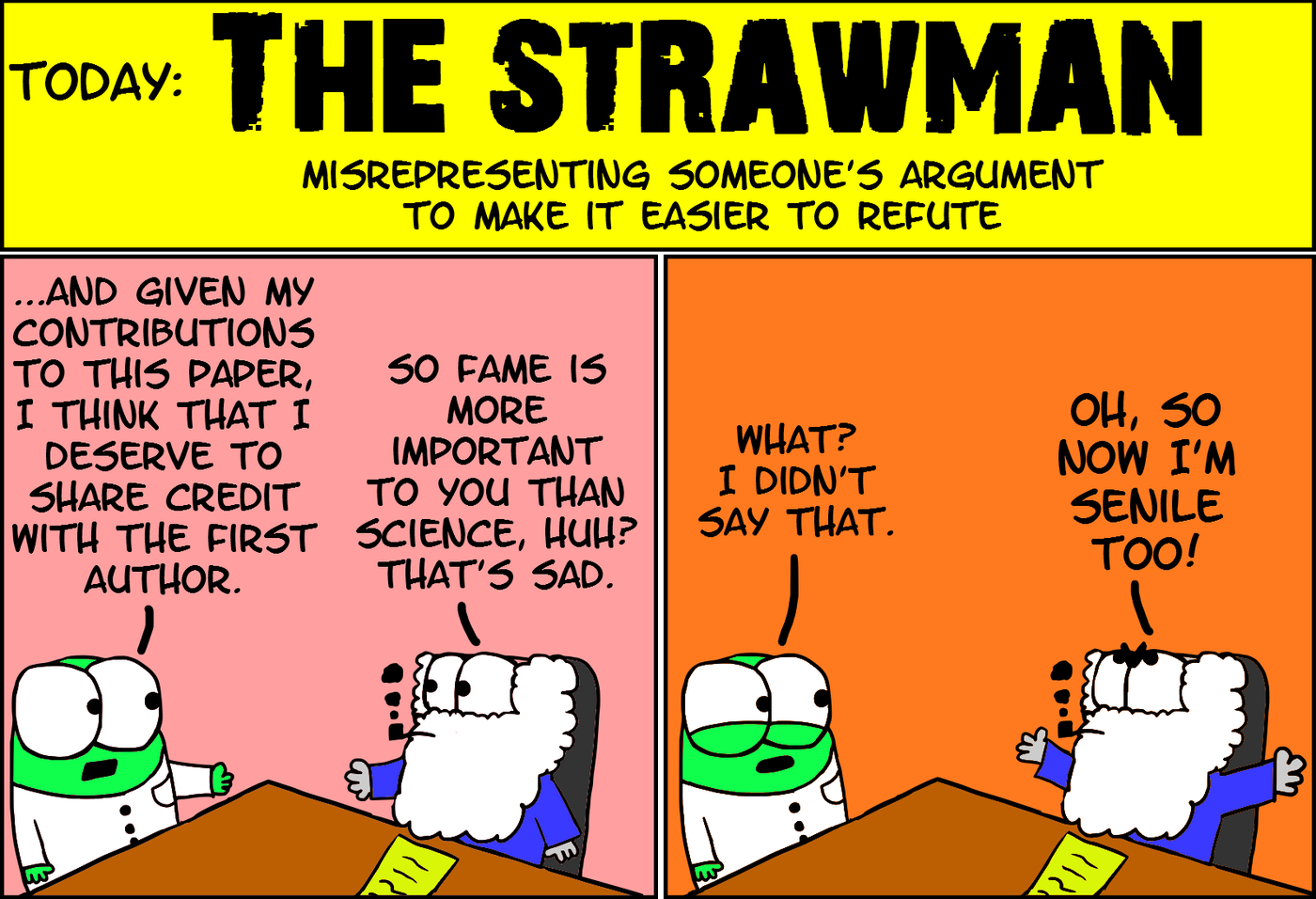
Straw Man
> the distortion or exaggeration of another person's argument or position, so it is easier to attack
> Arguer sets up weaker version of opponents position
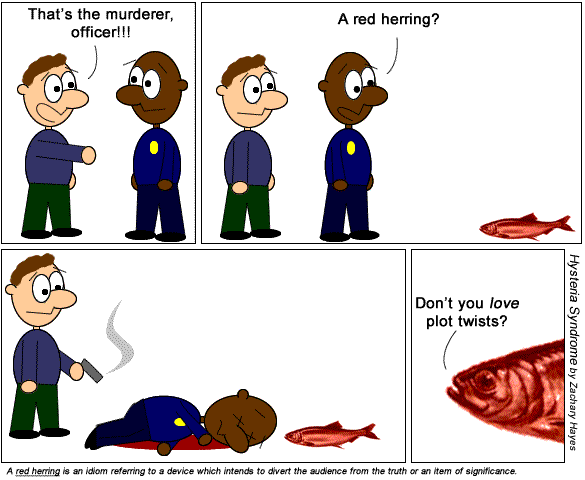
Red Herring
> A distraction
> Raising a side issue from whats being discussed
Begging The Question
> when an argument's premise assumes the truth of the conclusion, instead of supporting it

Equivocation
> When a word or expression given in an argument is used in an ambiguous way
> Calling two different things by the same name

False Dichotomy
> Conclusion that oversimplifies argument by reducing it to 2 sides or choices
> Even though more than 2 choices are possible

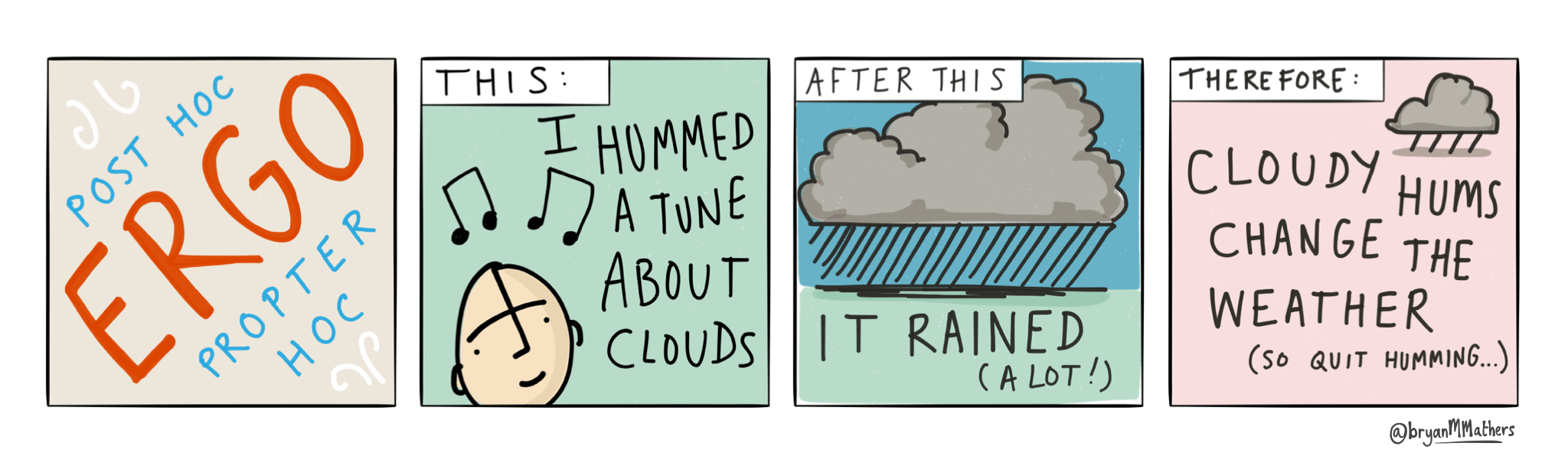
Post Hoc
> Full name: Post Hoc Ergo Propter Hoc
> Assumptioin that if Y happened after X then X must have caused Y
OR
> Assumption that because one event preceded another event, they must be causally related
Ad Hominem
> Counter argument by attacking the opponent rather than addressing the argument

Appeal To Popular Belief
> conclusion based on the fact that most believe in it
