Health Assessment Lecture 1
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
true or false: communication needs to be congruent (i.e. our words must match our words that we showing to the patient)
true
true or false: verbal communication is more reliable when it comes to the patient true feeling.
false; nonverbal does it as our body movements happen unconsciously and are therefore closer to the truth than the verbal
why is communication important in nursing?
- it builds trust and rapport between the nurse and patient
- it sets up for a better interview, showcasing we care and want the best care for them
- it helps in gathering the information we the nurses need (completely and accurate)
- it helps in passing information on to the next medical professionals and allows for collaboration
- it is important as the job of the nurse to teach the patient so that they can become involved in the decision making of their own health
what are the internal factors of communication?
- liking other
- empathy
- ability to listen
- respect
- self-awareness
how does the nurse exert the internal factor of liking others?
by being
- open to accepting others
- open to listening to a patient's story
- being interested in what they are saying
- willing to accept all types of people and backgrounds
how does the nurse exert the internal factor of empathy?
by being able to mentally place oneself in another's shoes and understand where they are coming from
how does the nurse exert the internal factor of the ability to listen?
- actively listening and engaging
- give full attention through good eye contact, not interrupting
- not just listening but hearing them out
how does the nurse exert the internal factor of respect?
by recognizes the dignity in everyone and honor their own wishes and cultures
how does the nurse exert the internal factor of self-awareness?
by understanding your own biases and putting those aside, and by being conscious of of your own body language (introspective assessment)
what are the external factors of communication?
- privacy
- physical environment
- refuse interruptions
- dress
- eye contact
- note-taking/computer
how does the nurse exert the external factor of privacy?
by:
- close blinders
- doors will not be opened by anyone but knock when needed
- if clothes off (can drape over body areas that are not presently be examined)
how does the nurse exert the external factor of the physical environment?
- ambient temperature
- quiet space
- remove distractions (be present in the movement even if it is quick)
- equal status seating
- use of space (don't standing over; sitting too close 4-5ft)
how does the nurse exert the external factor of dress?
dress professionally; confidence, whether you feel so or not (always introduce yourself)
how does the nurse exert the external factor of note-taking/computer?
write down any abnormalities and tic off normals to limit looking at them rather patient
what does the interview between patient and the nurse comprise of?
Overall, it is the collecting of subjective data from the patient, but the interview itself is a contract between the patient and the examiner that are comprised these things:
- time and place (on time ness)
- introduction and explanation
- purpose
- length
- expectations (achievements)
- presence of others
- confidentiality
- let the patient know what it is or to check with their insurance
should a patient ever leave not knowing whats happening?
no never
subjective data
things a person tells you about that you cannot observe through your senses; symptoms
confidentiality
the act of holding information in confidence, not to be released to unauthorized individuals
phases of the interview
1. pre-interaction phase
2. introduction
3. discussion
4. summary
pre-interaction phase of interview
collect and review data from chart (if available)
introduction phase of interview
- greeting/intro
- overview of process
- adapt physical setting PRN
discussion phase of interview
- no rushing, listen, use of space
- eye contact/non-verbal techniques
- open/closed questions
- patient story (allow them to tell)
summary phase of interview
- summarize, clarify
- begin formulating nsg problem list
- share POC
- teaching
- closing
techniques to enhance communication to encourage the patient
- active listening
- facilitation (help/make easier)
- silence
- reflection
- clarification
techniques to enhance communication to help the examiner
- confrontation
- interpretation
- explanation
- summary
what are the ten traps of interviewing
1. Providing false assurance or reassurance
2. Giving unwanted advice
3. Using authority
4. Using avoidance language
5. Engaging in distancing
6. Using professional/medical jargon
7. Using leading or biased questions
8. Talking too much
9. Interrupting
10. Using "why" questions
what are some challenges in the interviews
- overly talkative patient
- others in the room
- language barrier
- cultural difference
- sexually aggressive people
- confusing patient (unreliable source)
- poor historian
what are some things to be aware of in an interview
- cliches
- literal interpretations
- family member's input
- talking too much
- culture
- own biases
- jumping to conclusions
- avoidance language
how to overcome communication barriers in any interview?
- working with (and without) an interpreter
- who can be an interpreter
- use of nonverbal communication such as vocal cues (and silence), action cues (and silence), object cues, use of personal and territorial space, and touch
how do we choose an interpreter if we need one?
- choose one wisely
- orient to agenda - what will be talked about
- physical environment
- eye contact/non-verbal cues
- seating
- short and sweet
- talk to patient
- verifying/validate
- patience
- closed end questions/easy to answer
health literacy
a person's capacity to learn about and understand basic health information and services, and to use these resources to promote one's health and wellness
open-ended questions
Questions for which the patient must provide detail to give an answer.
closed ended questions
questions a person must answer by choosing from a limited, predetermined set of responses
ex: which is the best open-ended question for the nurse to begin the interview?
a. what brought you in today?
b. where does it hurt?
c. why are you seeing the doctor?
d. when was the last time you were seen by the doctor?
a
what is the layout for the complete health history of a patient?
1. biographical data
2. source of history (source and reliability)
3. reason for seeking care
4. present health or history of present illness
5. past health
6. family history
7. review of systems
8. functional assessment or ADLS
biographical snapshot includes
person's age, marital status, gender, occupation or prior occupation, race and ethnic origin, religious identity, general health, appearance
source of history
Record who furnishes the information, judge how reliable the informant seems and how willing, note any special circumstances
reason for seeking care
chief complaint or presenting problem from a symptoms (subjective sensation) or sign (objective abnormality which is detectable on physical exam or in lab reports)
what are the two guides/mnemonic devices for collecting history of present illness
OLDCARTS (used more often) or PQRSTU
OLDCARTS mnemonic
Onset
Location
Duration
Characteristics
Aggravating/Alleviating factors
Related Symptoms
Timing of pain and patients thoughts
Severity
Past Medical History (PMH)
information gathered regarding the patient's health problems in the past like:
- childhood illnesses
- accidents or injuries
- serious or chronic illness
- hospitalizations
- operations
-obstetrical history
- immunizations
- last exam dats
- allergies and reaction
- current mediations
true allergy
rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing if patient comes in contact or ingest
what should the nurse do in consideration about the past medical history of an older adult patient?
their mediation profile
things to consider when collecting a mediation profile of the older adult
- Polypharmacy, different prescribers (lots of meds)
- Patient may not know drug name or purpose (ask person to bring in drug to be identified)
- When person is unable to afford drug, he or she may decrease dosage or not refill immediately
- Travel to pharmacy may present a problem
- May use over-the-counter medications for self-treatment
- Some share medications with neighbors or friends
- Ask about herbal medications
family history
any significant illnesses that run in the patient's family
what should one include in the family history?
- age and health or cause of death for blood relatives
- health of close family members
- family history of various chronic conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, stroke, diabetes, blood disorders, cancer, obesity, mental illness, and others
the family history should be displayed using what?
genogram
Review of Systems (ROS)
physical examination of all body systems in a systematic manner as part of the nursing assessment through a series of questions targeted at every body system starting with a general overall health state
what kind of info is recorded in the ROS?
subjective
functional assessment
An assessment of the contingencies responsible for problem behaviors (i.e. daily activities and lifestyle)
what are some points the nurse would record in the functional assessment?
- self-esteem/concept
- activity/exercise
- sleep/rest
- nutrition/elimination
- relationships
- personal habits
- alcohol and drugs
- partner violence
- stress and coping
- environment/hazards
- work
perception of health
How do you define health?
How do you view your situation now?
What are your concerns/goals?
What do you think will happen in the future?
What do you expect from your health care providers?
is the definition of health objective or subjective?
subjective
when collecting a past health history on a child, what should the nurse record?
- developmental history (birth to present) including growth, milestones, current development for children 1 month through preschool age, and school-age child
- nutritional history
- family history
what is the mnemonic we use for adolescents?
HEEADSSS
HEEADSSS
Home
Education and employment
Eating
Activities
Drugs
Sexuality
Suicide and depression
Safety
psychosocial interview
A detailed interview that gathers background information and information about the client's current psychological and social situation. (maximize communication)
what are the assessment techniques during a physical assessment and what is their order?
in the order of first to last:
1. inspection
2. palpation
3. percussion
4. auscultation
*except in the abdomen (auscultation)
inspection
the act of examining or reviewing (what do you see? smell?)
with inspection, one should
- not rush
- compare patient's right side with left side
- use good lighting
- obtain adequate exposure (of the patient)
- will include instruments in many body systems: otoscope/ophthalmoscope, specula (vaginal, nasal), penlight
paplation
the hands on part of exam
-bones, ligaments, muscles/tendons
when should one use their fingertips to palpate?
best used for fine tactile discrimination of skin texture, swelling, pulsation, determining presence of lumps
when should one use their fingers and thumb to palpate?
detection of position, shape, and consistency of an organ or mass
when should one use their dorsa of hands and finger to palpate?
best used for determining temperature because skin here is thinner than on palms
when should one use their base of fingers or ulnar surface of and to palpate?
best used for vibration
characteristics to describe what is felt during palpation?
- texture
- temperature
- moisture
- organ location and size
- swelling
- vibration or pulsation
- rigidity or spasticity
- crepitation
- presence of lumps or masses
- presence of tenderness or pain
auscultation
listening to sounds within the body with a stethoscope
Diaphragm of stethoscope
flat endpiece of the stethoscope used for hearing relatively high-pitched heart sounds

Bell of stethoscope
cup-shaped endpiece used for soft, low-pitched heart sounds

when auscultating, one should eliminate what?
confusing artifacts
percussion
tapping on a surface to determine the difference in the density of the underlying structure; evaluates size, location, borders, consistency of organs, density, and fluid
direct percussion
involves striking a finger or hand directly against the patient's body

indirect percussion
strike finger or hand placed over body surface
if one were to percuss in the area of the lungs, what would be the tone and quality of the sound?
the tone would be resonant and the quality would be clear and hollow
if one were to percuss in the area any bone/muscle/tumor, what would be the tone and quality of the sound?
the tone would be flat and the quality would be extremely dull
if one were to percuss in the area of the liver (viscera), what would be the tone and quality of the sound?
the tone would be dull and the quality would be thud-like
if one were to percuss in the area of the stomach/gas, what would be the tone and quality of the sound?
the tone would be tympanic and the quality would be drum-like
if one were to percuss in the area of potential trapped air in a chronic lung, what would be the tone and quality of the sound?
the tone would be hyper-resonant and the quality would be booming
infection control principles
-Hand washing*** (universal)
-Isolate patients/barrier precautions
-Decontamination of environment
-Decontamination of items and equipment
-Prudent use of antibiotics
general survey
physical appearance, body structure, mobility, behavior
physical appearance
posture, body movements, dress, grooming and hygiene
behavior
level of consciousness, facial expression, speech (quantity, rate, rhythm, volume/amplitude), mood and affect (is it appropriate for setting?)
abnormal findings of mood and affect
Flat affect (blunted affect)
Depression
Depersonalization (lack of ego boundaries)
Elation
Euphoria
Anxiety
Fear
Irritation
Rage
Ambivalence
Lability
Inappropriate affect
objective measurements
weight, height, BMI, waist circumference
how to measure for height?
- use a wall-mounted device or measuring pole on scale
- person should be shoeless, standing straight, looking straight ahead, with feet and shoulders on hard surface
BMI (body mass index)
a measure of body weight relative to height (practical marker of optimal weight for height)
BMI
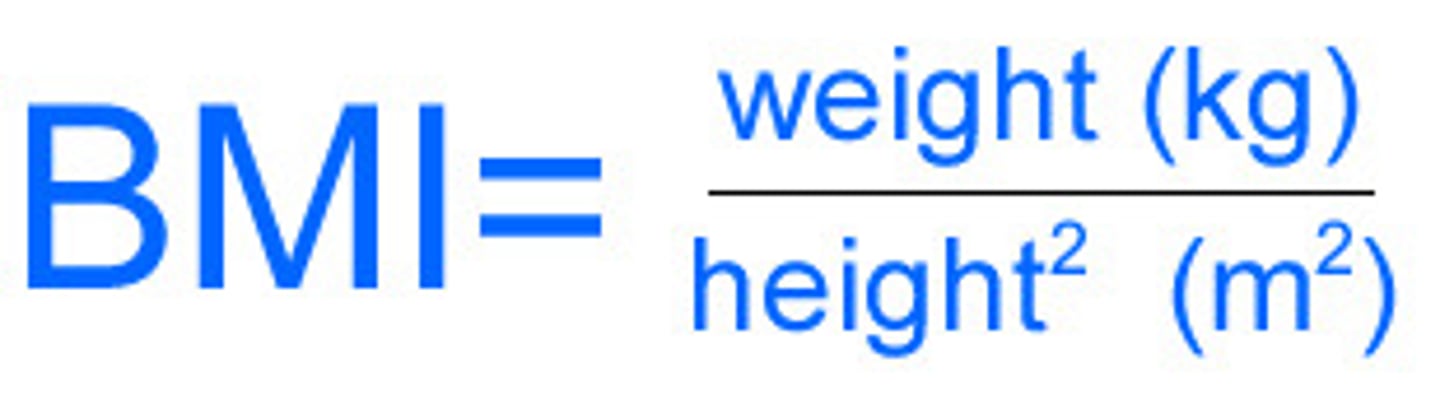
what is a normal BMI?
18.5-24.9
how to measure for weight circumference?
- assesses body fat disstribution as indicator of health risk
-waist circumference measured in inches at smallest circumference below rib cage and above iliac crest
- hip circumference is measured in inches at largest circumference of buttocks
- note the measurement at end of normal expiration
WC greates than 35 inches in females or 40 in males indicates
increased risk of heart disease, type 2 DM, metabolic syndrome