Clin Path - Urinalysis
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
Which technique is the least appropriate for culture?
Free catch
Which technique is least likely to introduce epithelial cells?
Cystocentesis (urine picks up epithelial cells from the urethra)
Which technique is least likely to introduce blood?
Free catch
Which technique is least stressful?
Free catch
What is the meaning if the urine color is: light to medium yellow
Normal :)
What is the meaning if the urine color is: colorless/clear
very dilute urine
What is the meaning if the urine color is: very dark urine
Very concentrated
Bilirubinuria
What is the meaning if the urine color is: Red to Brownish-red
Hematuria
Hemoglobinuria
Myoglobinuria
What is the meaning if the urine color is: Reddish-brown to brown
Myoglobinuria
Hemoglobinuria
Methemoglobinemia
What is the meaning if the urine color is: Greenish tint
Bilirubinemia
What components on a dipstick are ignored in veterinary medicine?
Specific gravity, leukocytes, Nitrite, Urobilinogen
Should glucose normally be in the urine?
No - normally very low concentrations in urine
T or F: Glucose in the urine must be interpreted in context with blood glucose levels?
True
If a patient has elevated blood glucose exceeding the renal threshold & they have glucosuria, would this be considered appropriate or inappropriate?
Appropriate
What are ketones used for?
Alternate energy source
What are three ketones that we must consider in a urinalysis?
Acetone
Acetoacetate
Beta-hydroxybutyrate
What diseases are associated with altered carbohydrate metabolism?
Negative energy balance:
diabetes mellitus —> cannot utilize glucose, body shifts to ketones
bovine ketosis
pregnancy
Where do ketones accumulate first: urine, milk, or blood?
Urine and milk BEFORE blood
What is the normal pH of urine for carnivores and suckling herbivores?
5.5-7.5
What is the normal pH of urine for herbivores?
7 - 8.5
T or F: Blood pH adjusts based on urine pH.
F - urine pH adjusts based on blood pH
If your patient has acidemia (acidic blood), would you expect aciduria or alkaluria?
aciduria
What two conditions would you see bilirubin in the urine from?
Hepatobiliary dz and IMHA
Bilirubin in urine may be normal in _____.
Male dogs with concentrated urine
Which would you expect to clear with centrifugation?: hematuria, hemoglobinuria, or myoglobinuria
Hematuria
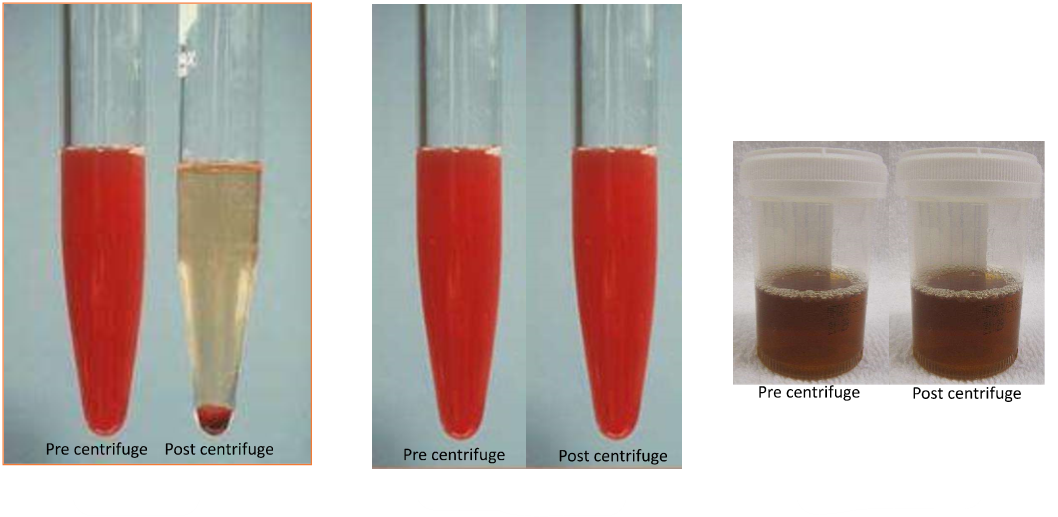
Label the image from left to right; options = myoglobinuria, hematuria, and hemoglobinuria
From left to right: Hematuria, hemoglobinuria, myoglobinuria
Name four reasons you may see hematuria
Cystitis
UTI
Mild pigmenturia
Blood contamination (cystocentesis)
What is concerning for proteinuria?
If renal - glomerular/tubular dz
T or F: Alkalinuria causes false positives of proteinuria, especially common in large animals.
T
Trace to 1+ protein in urine may be normal with (concentrated/dilute) urine
Concentrated
What does a sulfosalicylic acid (SSA) confirm?
Confirmatory test for dipstick positive for protein; graded based on turbidity
What is the protein: creatinine ratio used for?
To quantify proteinuria
T or F: complete urinalysis must be done concurrently to exclude hemorrhage or inflammation
True
How do you interpret urine protein: creatinine ratio?
If UPC > or = to 2: glomerular damage
If UPC < 2: tubular damage: tubular damage
What does Bence Jones Proteinuria tell you?
Free immunoglobin light chains; overload proteinuria from multiple myeloma
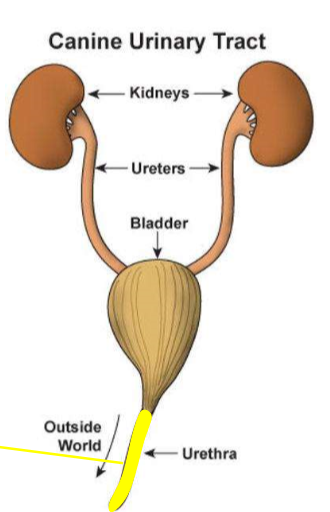
These cells line the full urinary tract, are relatively large, evaluated at 10x objective and low numbers of them may be normal.
Epithelial cells
Where do squamous cells come from?
Originate from distal urethra, vagina, or prepuce; yellow in picture
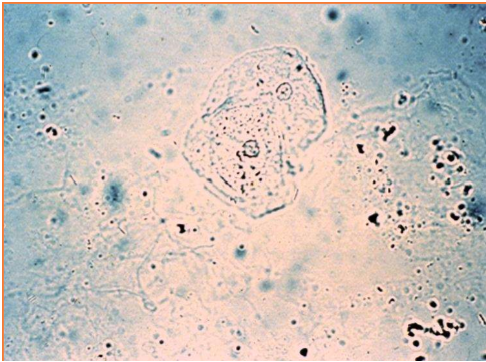
This type of epithelial cells are large, flat cells with angular sides and small nuclei.
Squamous epithelial cells
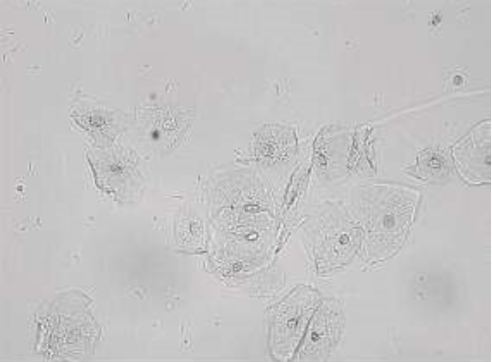
These cells are present on sediment evaluation. What are they?
Squamous epithelial cells
These cells are present on sediment evaluation. What are they?
Squamous epithelial cells
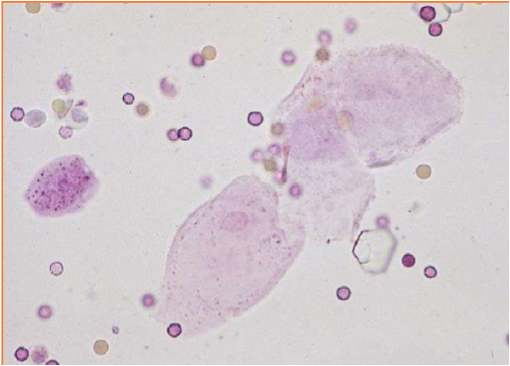
These cells are present on sediment evaluation. What are they?
Squamous epithelial cells
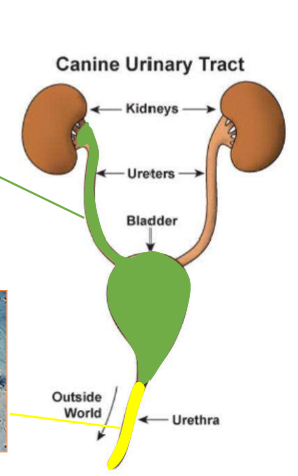
Where do transitional epithelial (urothelial) cells originate from?
the urinary bladder, ureter, and proximal urethra; green in diagram
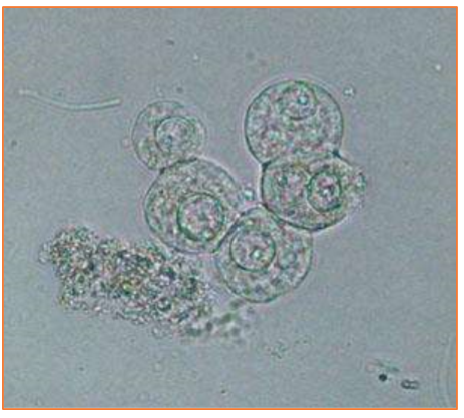
These epithelial cells are round in shape, variable size, have a low to moderate N:C ratio (higher than squamous), low numbers are normal
Transitional epithelial (Urothelial) Cells
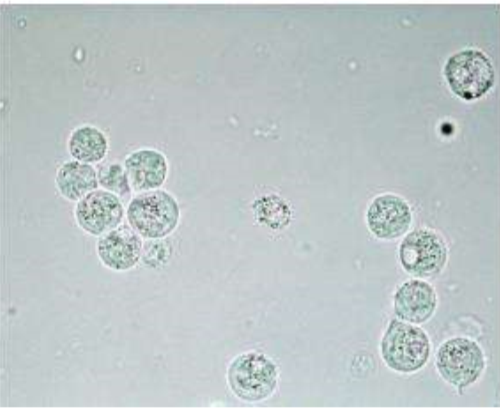
These cells are present on sediment evaluation. What are they?
Transitional epithelial (Urothelial) Cells
These cells are present on sediment evaluation. What are they?
Transitional epithelial (Urothelial) Cells
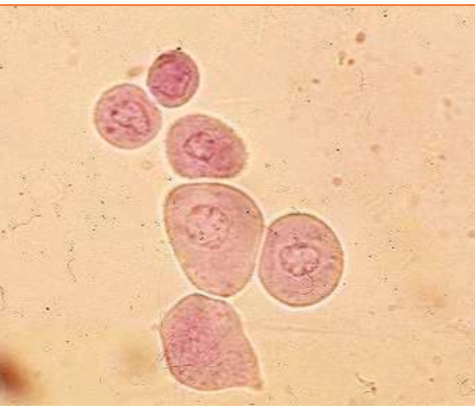
These cells are present on sediment evaluation. What are they?
Transitional epithelial (Urothelial) Cells
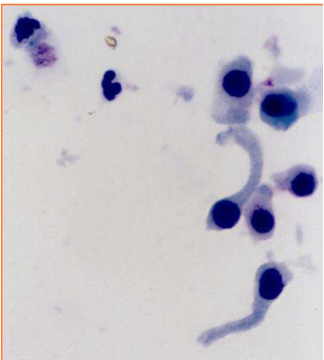
These cells are present on sediment evaluation. What are they?
Caudate epithelial cells
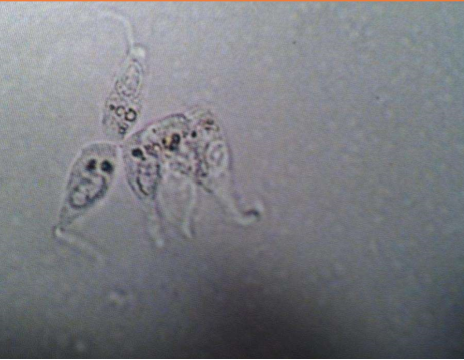
These cells are present on sediment evaluation. What are they?
Caudate epithelial cells
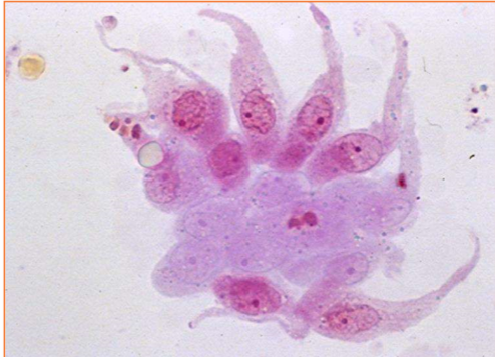
These cells are present on sediment evaluation. What are they?
Caudate epithelial cells
This epithelial cell is spindle or tadpole-shaped and is not normally seen in sediment
Caudate epithelial cells
Where do caudate epithelial cells orginate from?
Renal pelvis; blue in image
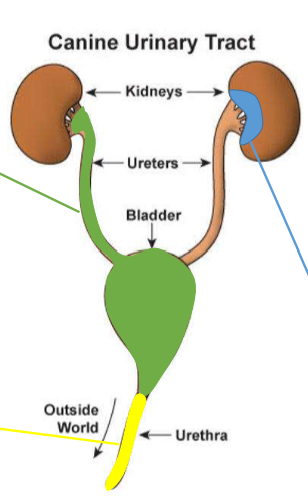
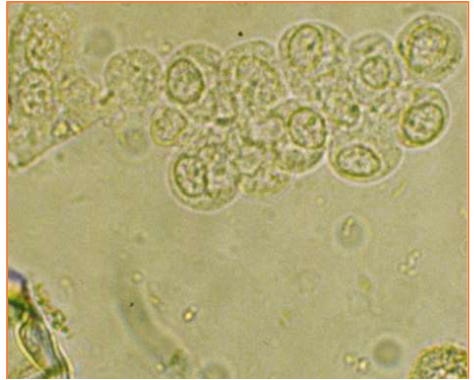
These cells are present on sediment evaluation. What are they?
Renal tubular epithelial cells
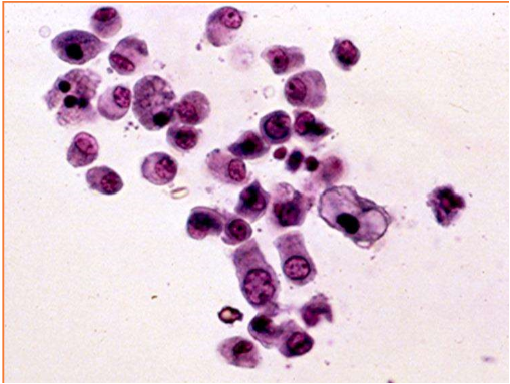
These cells are present on sediment evaluation. What are they?
Renal tubular epithelial cells
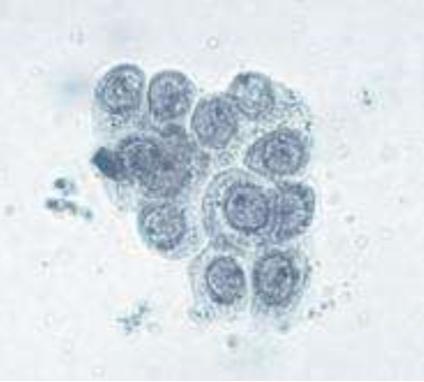
These cells are present on sediment evaluation. What are they?
Renal tubular epithelial cells
Where do renal tubular epithelial cells originate from?
renal parenchyma; orange in image
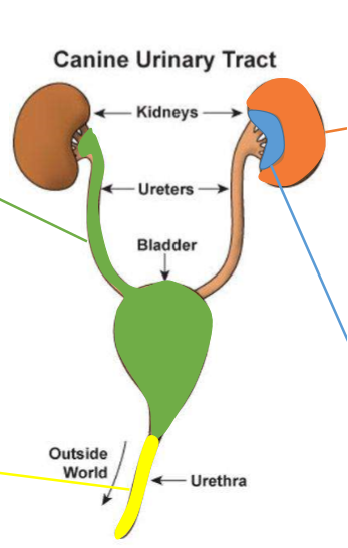
This type of epithelial cell is small, round/rectangular (cuboidal/columnar) and may contain vacuoles if from a cat.
Renal tubular epithelial cells
What do renal tubular epithelial cells indicate on a urine sediment?
indicate renal damage or inflammation (tubular nephritis)
What two conditions can caudate epithelial cells indicte?
Pyelonephritis (inflammation of renal pelvis)
Calculi in renal pelvis
What is a typical early indicator of renal tubular disease?
Casts
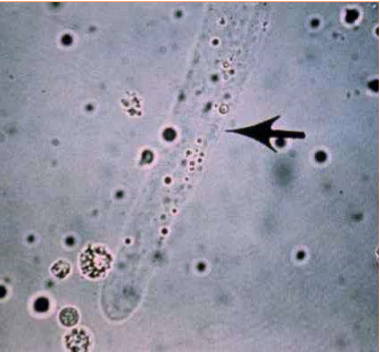
What type of cast is this?
Hyaline
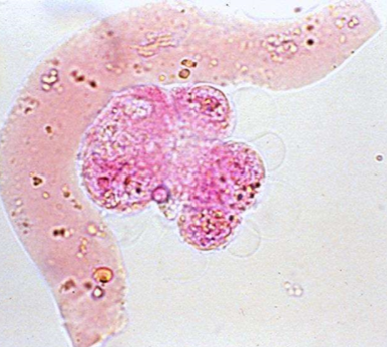
What type of cast is this?
Hyaline cast
What are hyaline casts?
Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein precipitates secreted by renal tubular epithelial cells
Are hyaline casts a significant finding on sediment evaulation?
Low numbers are insignificant —> exercise and hyperthermia
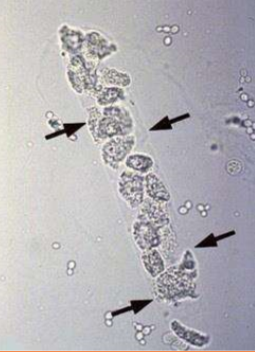
What type of cast is this?
Cellular cast (renal tubular epithelial casts)
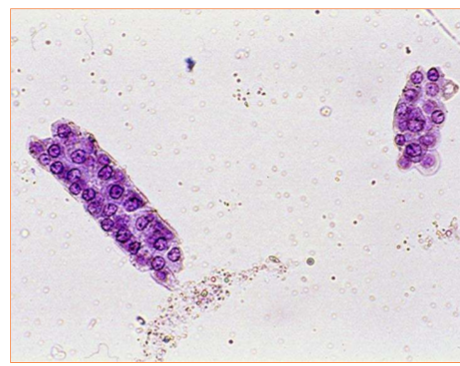
What type of cast are these?
Cellular cast (renal tubular epithelial casts)
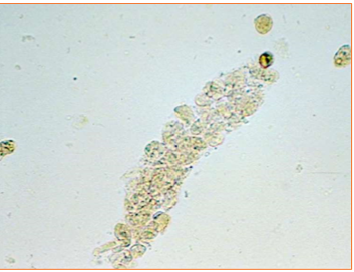
What type of cast are these?
Cellular Casts (renal tubular epithelial casts)
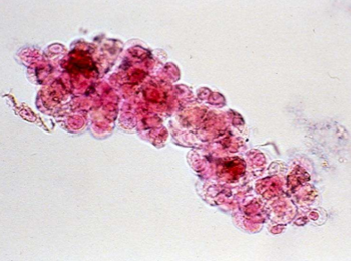
What type of cast are these?
Cellular Casts (renal tubular epithelial casts)
This type of cast consists of round to polygonal epithelial cells in tubular arrangement
Cellular casts (renal tubular epithelial casts)
What do renal tubular casts (cellular casts) indicate?
Renal tubular damage; may be seen with nephritis/pyelonephritis (you would also expect specific gravity to be dilute
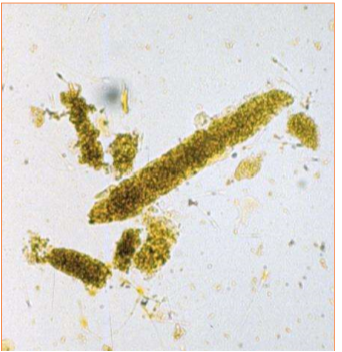
What type of cast is pictured?
Granular cast
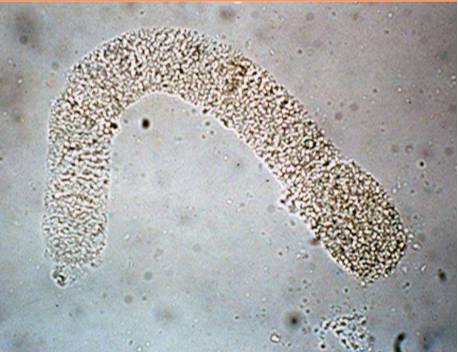
What type of cast is pictured?
Granular cast
What do granular casts indicate?
Degenerated tubular epithelial cells; slow progression through tubule
Evidence of tubular damage
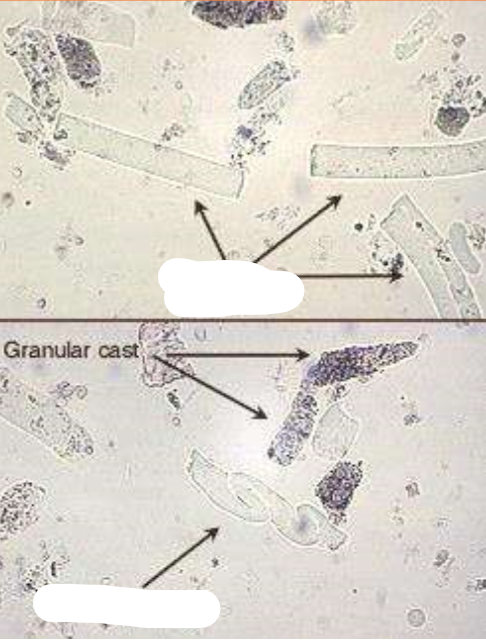
What type of cast are the arrows pointing to?
Waxy casts
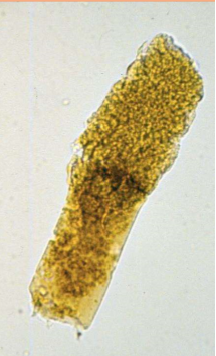
What type of cast is pictured?
Waxy casts
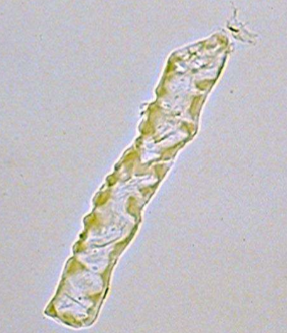
What type of cast is pictured?
Waxy casts
What do waxy casts indicate?
complete breakdown of epithelial cells; very slow progression through tubule; rare
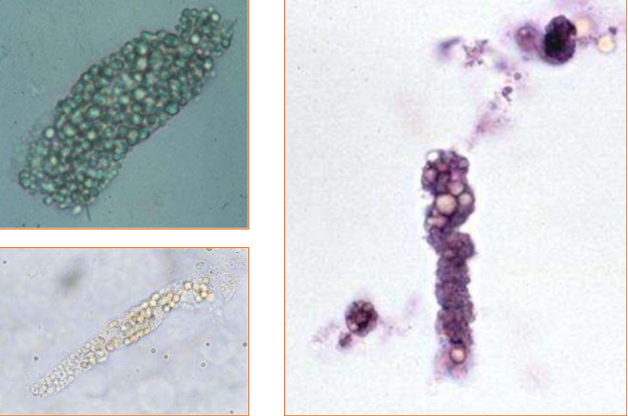
What type of casts are pictured? Are they common or uncommon? What species are they usually seen in?
Fatty casts
Uncommon
Usually seen in cats
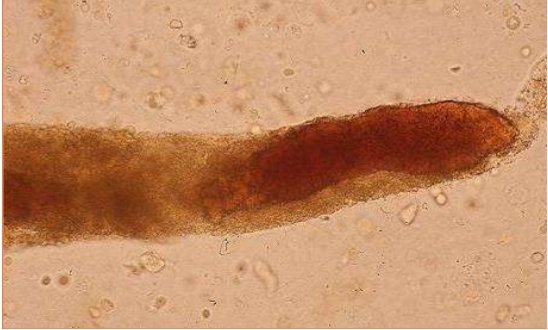
What type of cast is pictrued?
Hemoglobin casts
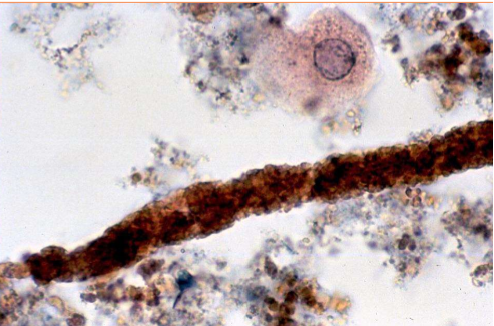
What type of cast is present?
Hemoglobin cast
What does hemoglobin casts indicate?
Intravascular hemolysis (Hemoglobinemia)
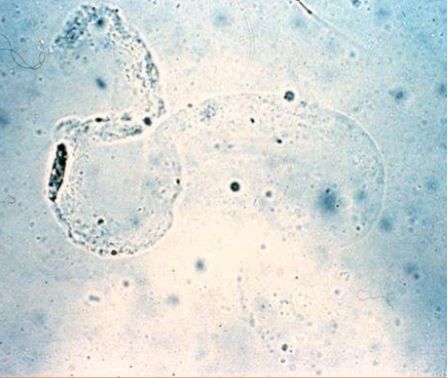
What type of cast is pictured?
Pseudo-casts
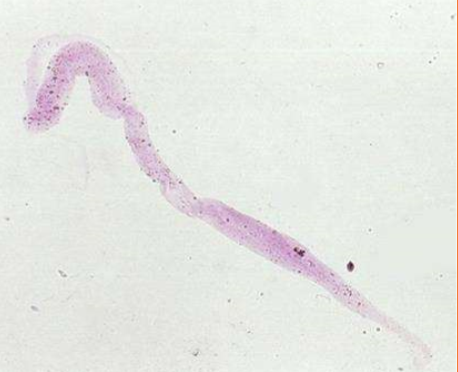
What type of cast is pictured?
Pseudo-casts
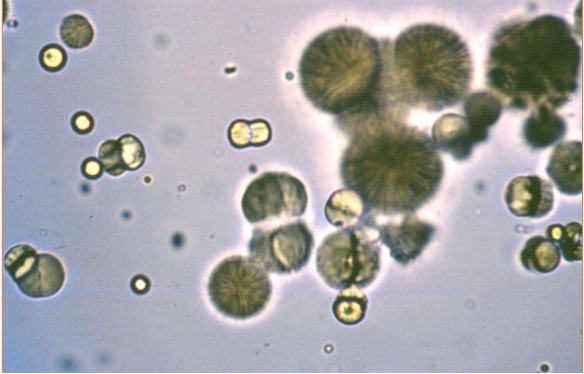
Name the crystal
Calcium carbonate
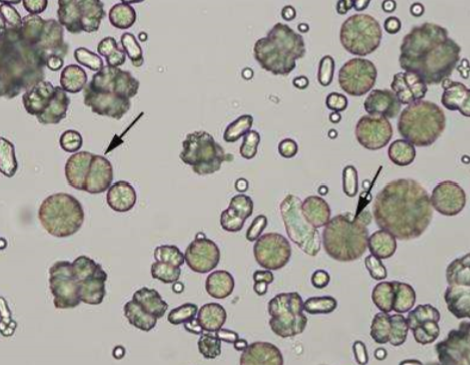
Name the crystal
Calcium Carbonate
What species are calcium carbonate crystals common in?
Normal in species that excrete calcium in urine: Horse, rabbit, guinea pig, elephant
Are calcium carbonate crystals found in acidic or alkaline urine?
Alkaline urine

Name the crystal
Magnesium ammonium phosphate (MAP, Struvite)
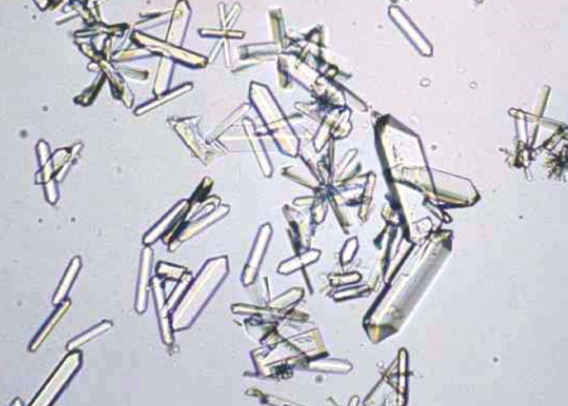

Name the crystal
Magnesium ammonium phosphate (MAP, Struvite)
Are magnesium ammonium phosphate crystals more common in acidic or alkaline urine?
Alkaline urine
What do magnesium ammonium phosphate crystals indicate in dogs? What about cats?
Dogs: secondary to UTI
Cats: sterile cystitis; seen in cats b/c they excrete NH3 via renal tubules

Name the crystal
Calcium oxalate dihydrate

Name the crystal
Calcium oxalate dihydrate
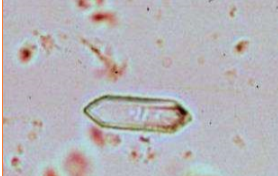
Name the crystal
Calcium oxalate monohydrate
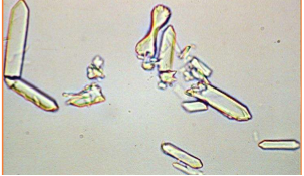
Name the crystal
Calcium oxalate monohydrate
What do calcium oxalate dihydrate crystals indicate?
can be normal
ingestion of oxalate containing plants
Calciuresis from hyperadrenocorticism
Increase number d/t storage at room temp and refrigeration
What do calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals indicate?
seen in acute ethylene glycol poisoning, 3-18 hrs after ingestion
Increase number d/t storage at room temp and refrigeration
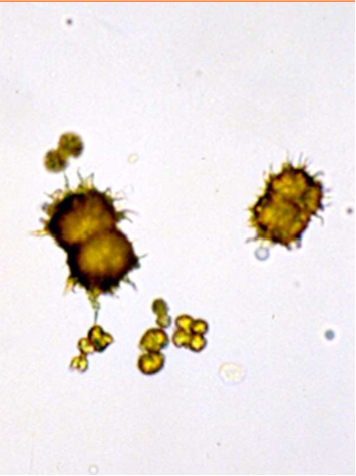
Name the crystal
Ammonium biurate
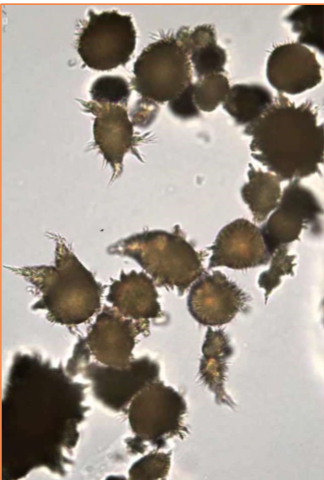
Name the crystal
Ammonium biurate
What does ammonium biurate indicate?
Liver dz (ammonia not converted to urea)
portosystemic shunt (vascular malfunction)
sago palm toxicity
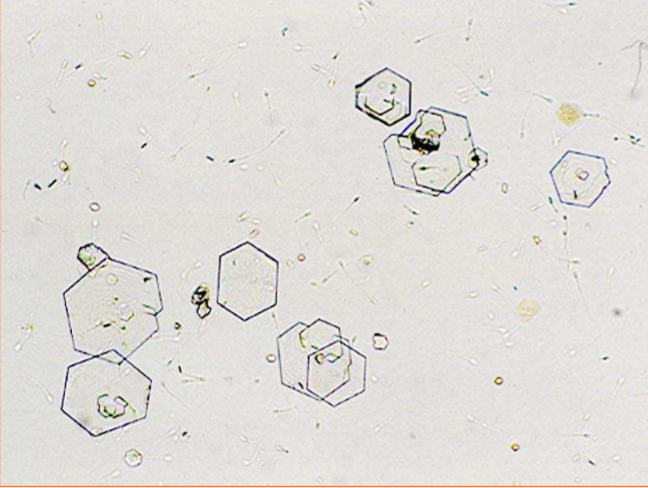

Name the crystal
Cystine crystal