Lymph Node Pathology and Lymphoma Overview
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Lymphadenopathy
Enlargement of lymph nodes due to various causes.
Benign Lymphadenopathy
Lymph node enlargement due to non-cancerous conditions.
Malignant Lymphadenopathy
Lymph node enlargement due to cancerous conditions.
Painful Lymphadenopathy
Lymph node enlargement due to acute inflammation.
Painless Lymphadenopathy
Lymph node enlargement due to chronic inflammation or malignancy.
Lymphoma
Cancer of lymphatic system; includes Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin.
Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL)
Characterized by Reed-Sternberg cells; localized spread.
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)
Diverse group; non-contiguous spread; can involve extranodal sites.
Reed-Sternberg Cells
Abnormal cells found in Hodgkin Lymphoma.
Cytogenetic Abnormalities
Genetic mutations associated with specific lymphomas.
Follicular Lymphoma
Associated with t(14;18) chromosomal translocation.
Burkitt Lymphoma
Associated with t(8;14) chromosomal translocation.
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
Associated with t(11;14) chromosomal translocation.
Hodgkin Lymphoma Cytogenetics
No characteristic cytogenetic abnormalities identified.
Bimodal Distribution
HL incidence peaks in young adults and >55 years.
Constitutional Symptoms
Symptoms like fever, night sweats, weight loss in HL.
Acute Inflammation
Body's immediate response to injury, causing pain.
Chronic Inflammation
Long-term inflammation, often painless lymphadenopathy.
Tumor Mass Composition
HL mass includes Reed-Sternberg cells and fibrosis.
Prognosis in HL
Stage is strongest predictor; often good outcomes.
Prognosis in NHL
Varies; can be good, bad, or ugly.
Leukemic Phase
Presence of leukemia-like symptoms in some NHL.
EBV Association
Epstein-Barr Virus linked to Hodgkin Lymphoma.
Hodgkin Lymphoma
No characteristic cytogenetic abnormalities present.
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
Characteristic t(9;22) chromosomal translocation.
Gastric MALToma
Type of lymphoma responsive to antibiotic therapy.
Burkitt Lymphoma
Aggressive B-cell lymphoma, often associated with EBV.
Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma
Indolent lymphoma, often presents with lymphadenopathy.
Nodular Sclerosis
Most common subtype of Hodgkin Lymphoma (65%-70%).
Lacunar Cells
Diagnostic neoplastic cells in Hodgkin Lymphoma.
Cervical Lymphadenopathy
Swelling of cervical lymph nodes, often indicative of lymphoma.
Mediastinal Involvement
Common in Nodular Sclerosis subtype of HL.
Fibrous Bands
Structure forming nodules in Nodular Sclerosis subtype.
Female Predominance
More common in females, especially in Hodgkin Lymphoma.
Myelofibrosis
Possible complication in Hodgkin Lymphoma patients.
Monomorphic Population
Uniform cell type observed in lymph node biopsy.
CD20
Surface marker commonly expressed in B-cell lymphomas.
CD19
B-cell marker used in lymphoma diagnosis.
CD10
Marker indicating germinal center B-cells.
TdT
Marker indicating immature lymphoid cells.
Surface Kappa Light Chain
Indicates B-cell clonality in lymphomas.
Anemia
Common finding in lymphoma patients, indicating systemic effects.
Waldeyer Ring
Lymphoid tissue in the oropharynx, often involved in lymphoma.
Enlarged Supraclavicular LN
Sign of possible malignancy, including lymphoma.
Lymphoblastic Lymphoma
Type of lymphoma associated with immature T-cells.
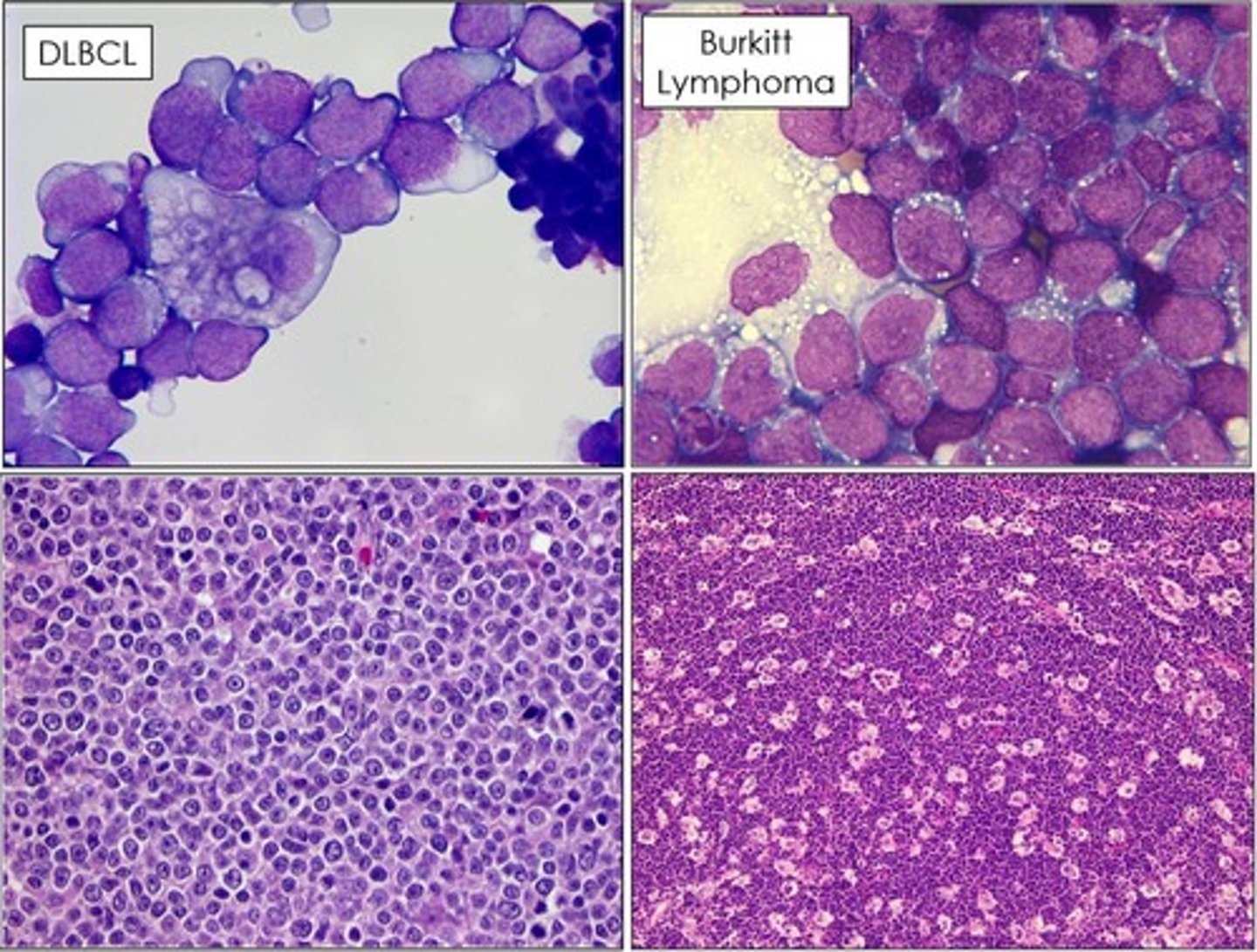
Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
Most common aggressive lymphoma in adults.
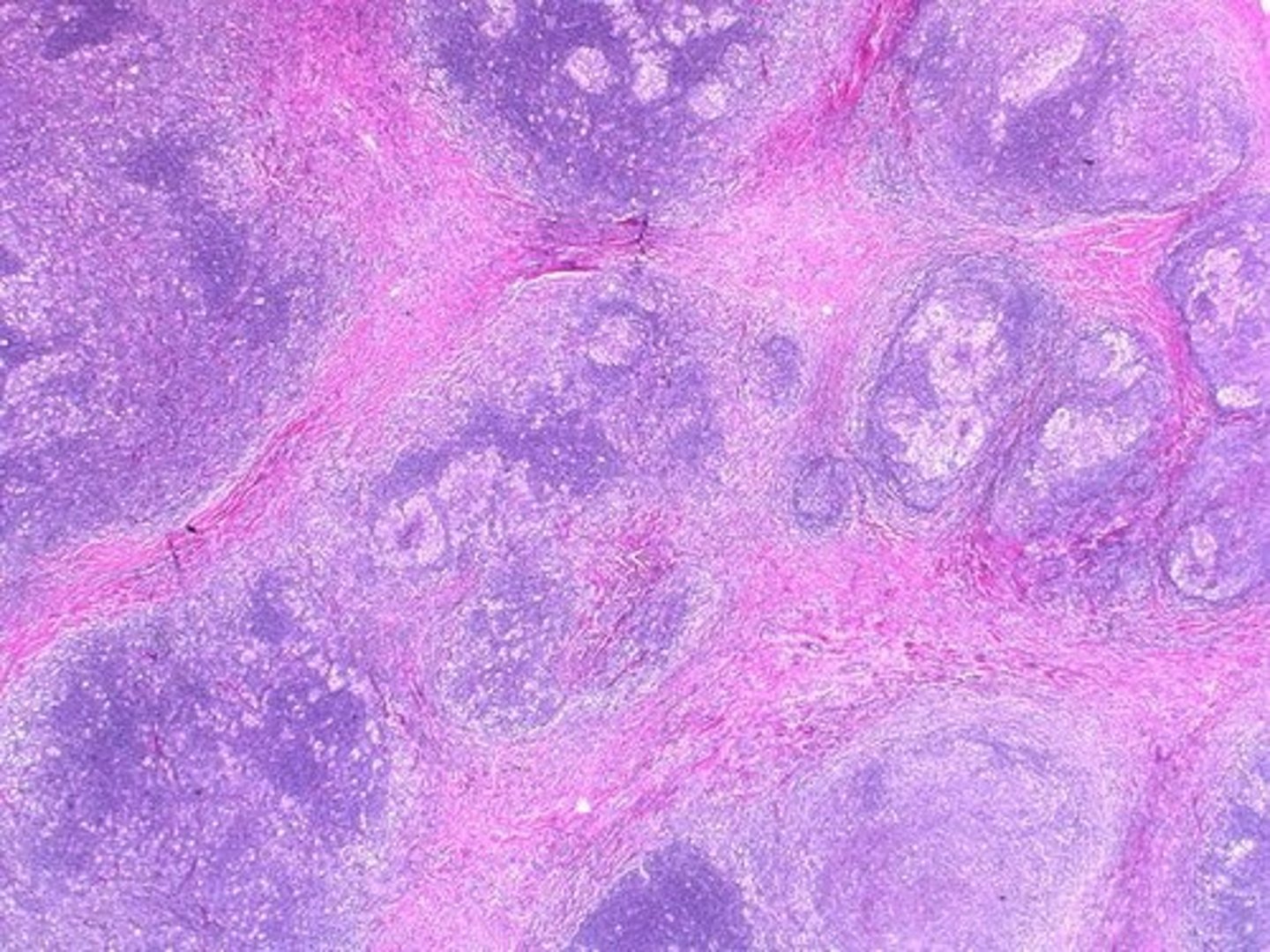
Follicular Lymphoma
B-cell neoplasm with follicular growth pattern.
Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL)
Lymphoma variant of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma
Aggressive B-cell lymphoma with diffuse growth.
Hodgkin Lymphoma
Characterized by Reed-Sternberg cells.
Reed-Sternberg Cell
Classic cell type in Hodgkin Lymphoma.
Germinal Center B-cell
B-cell in lymphoid follicles, PAX5 positive.
PAX5
Transcription factor expressed in B cells.
CD20
Surface marker typically absent in germinal center B-cells.
CD45
Common leukocyte antigen, negative in germinal center B-cells.
CD30
Surface marker associated with Reed-Sternberg cells.
CD15
Surface marker often expressed in Hodgkin Lymphoma.
WHO Classification
System for categorizing hematopoietic tumors.
Clonal Rearrangement
Genetic alteration indicating neoplastic proliferation.
t(9;22)
Chromosomal translocation linked to BCR-ABL in CML.
t(14;18)
Translocation associated with BCL2 overexpression in Follicular Lymphoma.
t(8;14)
Translocation leading to C-MYC overexpression in Burkitt Lymphoma.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
B-cell neoplasm with small, mature lymphocytes.
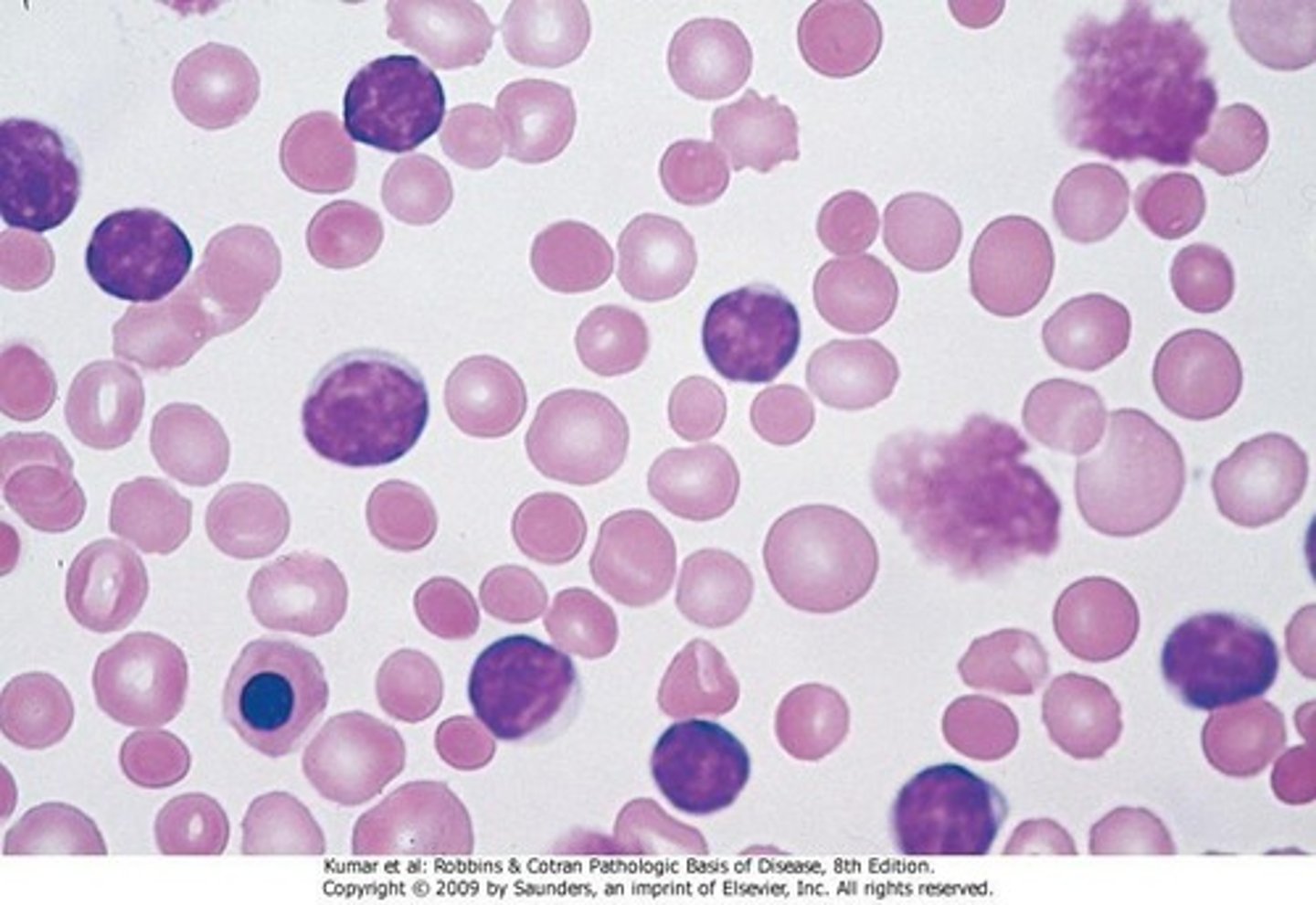
Smudge Cells
Disrupted tumor cells seen in CLL smears.
Lymphocytosis
Increased lymphocyte count in peripheral blood.
Anemia
Low hemoglobin level, indicated by Hb: 9.5 g/dL.
Thrombocytopenia
Low platelet count, indicated by Plt=120,000/mm3.
Leukocytosis
Increased white blood cell count, indicated by WBC=42,000.
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
Condition causing spherocytes in CLL.
Nucleated Erythroid Cells
Cells indicating marrow infiltration or anemia.
Lymph Node Biopsy
Diagnostic procedure to assess lymph node pathology.
Malignant lymphoma
Cancer of lymphatic tissues with abnormal cell growth.
Monoclonality
Derived from a single transformed cell.
Kappa light chains
Type of immunoglobulin light chain in B cells.
Lambda light chains
Another type of immunoglobulin light chain in B cells.
Light chain restriction
Presence of only one type of light chain.
Polyclonal
Mixture of multiple B cell types.
T cell receptor gene rearrangements
Indicates clonal expansion in T cell neoplasms.
Burkitt lymphoma
High-grade lymphoma associated with MYC translocation.
t(8;14)
Translocation involving MYC gene in Burkitt lymphoma.
Extranodal
Lymphoma occurring outside lymph nodes.
Growth fraction
Percentage of cells in the cell cycle.
S-phase
Phase of the cell cycle for DNA synthesis.
Cervical lymphadenopathy
Swelling of cervical lymph nodes.
Intermediate-sized lymphoid cells
Lymphoma cells with moderate size and features.
Coarse chromatin
Nuclear feature indicating active cell division.
Numerous mitoses
High cell division rate in tumor pathology.
Firm, nontender lymph nodes
Physical exam finding in lymphoma cases.
CD30 antigen
Marker used to identify certain lymphomas.
Germinal centers
Sites of B cell maturation in lymph nodes.
Flow cytometry (FCM)
Technique to analyze cell populations by surface markers.
Endemic Burkitt lymphoma
Form associated with EBV, common in Africa.
Sporadic Burkitt lymphoma
Form not associated with EBV, seen globally.
Chemotherapy response
Effectiveness of treatment based on tumor growth rate.
Lymph node biopsy
Procedure to diagnose lymphoma through tissue sampling.
Burkitt Lymphoma
Endemic form presents with jaw/orbital lesions.
c-MYC gene
Translocated on chromosome 8 in Burkitt lymphoma.
Translocation t(8;14)
c-MYC gene partners with IgH locus.
Starry sky pattern
Result of numerous tingible-body macrophages.
Follicular Lymphoma
Indolent lymphoma with generalized lymphadenopathy.