CB2 - Cells and Control
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Asexual reproduction
Where an organism created genetically identical couples of itself, often by mitosis.
Sexual reproduction
Where an organism created genetically different versions of itself, involving two parents and fertilisation of gametes.
Structure of DNA
Double helix shape.
Each strand has a sugar-phosphate backbone.
Contains complimentary bases, joined by hydrogen.
Complimentary base pairs
A with T
C with G
Genome
All the genetic information in an organism
Gene
A section of DNA that codes for a specific protein - can be 1000s of based long.
How to extract DNA from plant cells?
Grind up cellular tissue
Add salt (to disrupt the membranes)
Add detergent (to dissolve the membranes)
Heat and filter, collect filtrate
Add ice cold ethanol to precipitate the DNA - white strings
Two stages of the cell cycle
Interphase and mitosis
What happens in interphase?
Normal cell processes, then new sub-cellular parts are made, chromosomes are copied for mitosis.
Stages of mitosis in order
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
Prophase
Nucleus breaks down, spindle fibres appear.
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up on equator of cell
Anaphase
Chromosomes copies are pulled apart to opposite poles by the spindle fibres.
Telophase
New nuclei form around split chromosomes.
Cytokinesis
Cell membrane separates into 2 cells.
Cells produced by mitosis
Two genetically identical, diploid daughter cells.
Why can’t sperm be produced using the cell cycle?
The cell cycle produces new body cells, not new gametes, and sperm is a gamete (also haploid).
Why is mitosis important?
Results in new cells for growth, repair or asexual reproduction.
How do body cells become cancer cells?
Mutations in the DNA cause cells to divide uncontrollably, forming a tumour.
What processes in animals result in growth and development?
Mitosis and differentiation
Chart to monitor growth in animals
Percentile chart
Percentile
Boundaries that show which percentage of a population will be within a certain growth range at different stages of their life.
Cell differentiation
Where cells that can become any cell (stem cells) become specialised and change to perform a specific function.
Neurones
Cells specialised for neurotransmission
Fat cells
Cells specialised with liposomes to store fat
Muscle cells
Specialised to have proteins that contract and shorten
Red blood cells
Specialised with haemoglobin to carry oxygen
Processes in plants that lead to growth and development
Mitosis, elongation and differentiation
Where does mitosis occur in plants?
Meristem - In the tip of the root and shoot
Cell elongation
After cells are made in the meristem, they elongate, to allow the plant to grow taller, or towards light and away from gravity.
How to measure plant growth?
Change in length of a feature or change in mass of the whole organism.
Where differentiation happen in plants?
After the zone of elongation and the meristem there is a zone of differentiation, where plant cells become specialised.
Why do meristematic cells have many ribosomes and mitochondria?
Ribosomes - to make proteins needed for new cells
Mitochondria - to release energy used in cell division
Embryonic stem cells
Found in embryos and can differentiate into any cell.
Adult stem cell
Found in adult tissues, are involved in growth and repair, but can only become a narrow range of cells (they’re part specialised).
Advantages of stem cell treatments
Stem cells can replace damaged cells not able to be repaired.
Very effective for some treatments e.g. bone marrow transplants.
Disadvantages of stem cells for growth treatments
May cause cancer so extensive testing is required before application.
May be rejected by the immune system.
How do impulses cross synapses?
The impulse reaches the axon terminus, which cause the release of a neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the gap and causes an impulse in the next neurone.
Neurotransmitter
A chemical released at a synapse to keep an impulse going.
Importance of synapses
They ensure one way neurotransmission and coordination
Synapses
A gap between neurones
Importance of reflex arcs
They allow more rapid response without the impulse having to reach the brain to make a decision, which could save your life.
Describe a reflex arc
Receptor → sensory neurone → relay neurone → motor neurone → effector
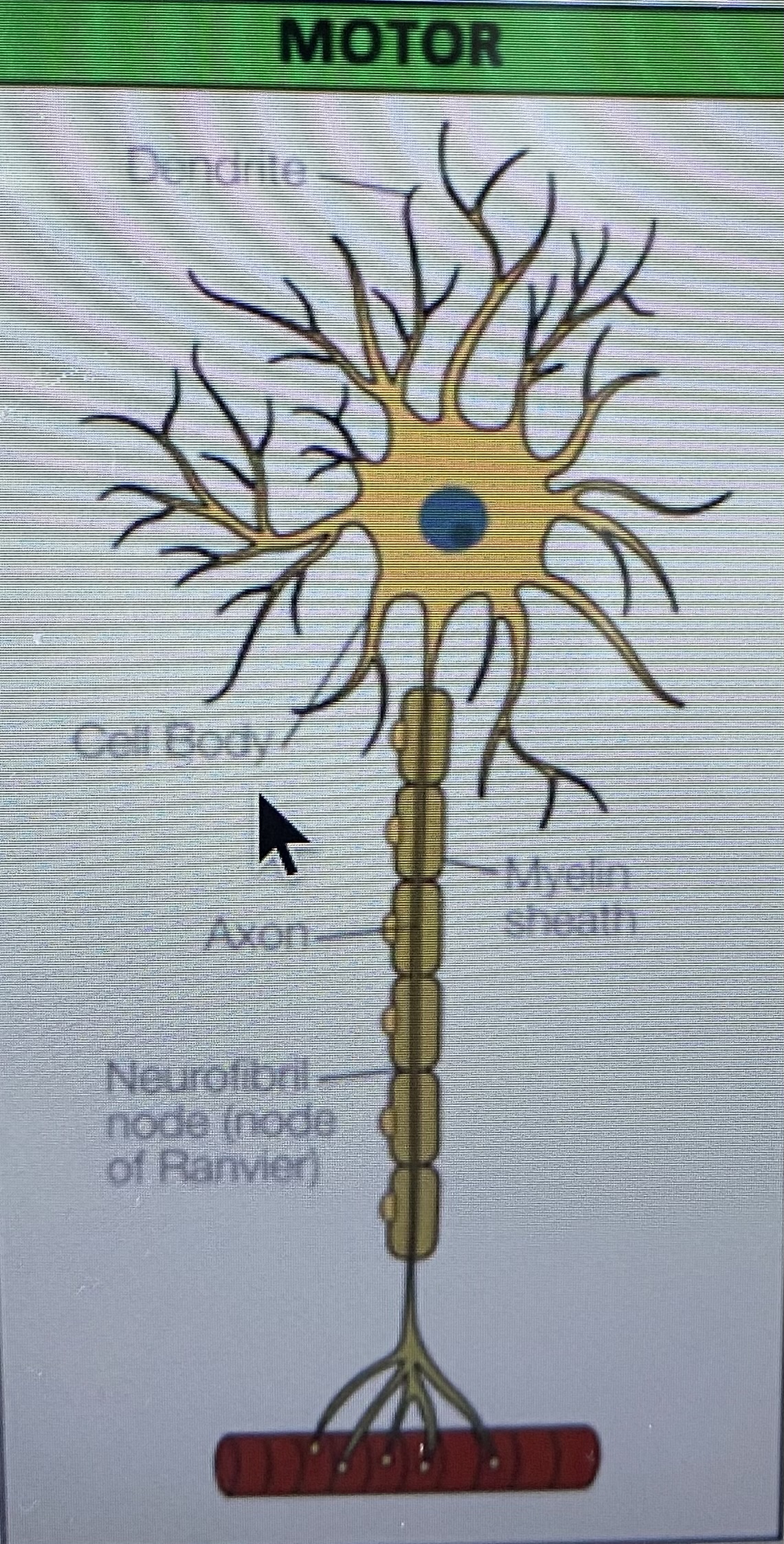
Function of motor neurones
Carry impulses to muscles for contraction
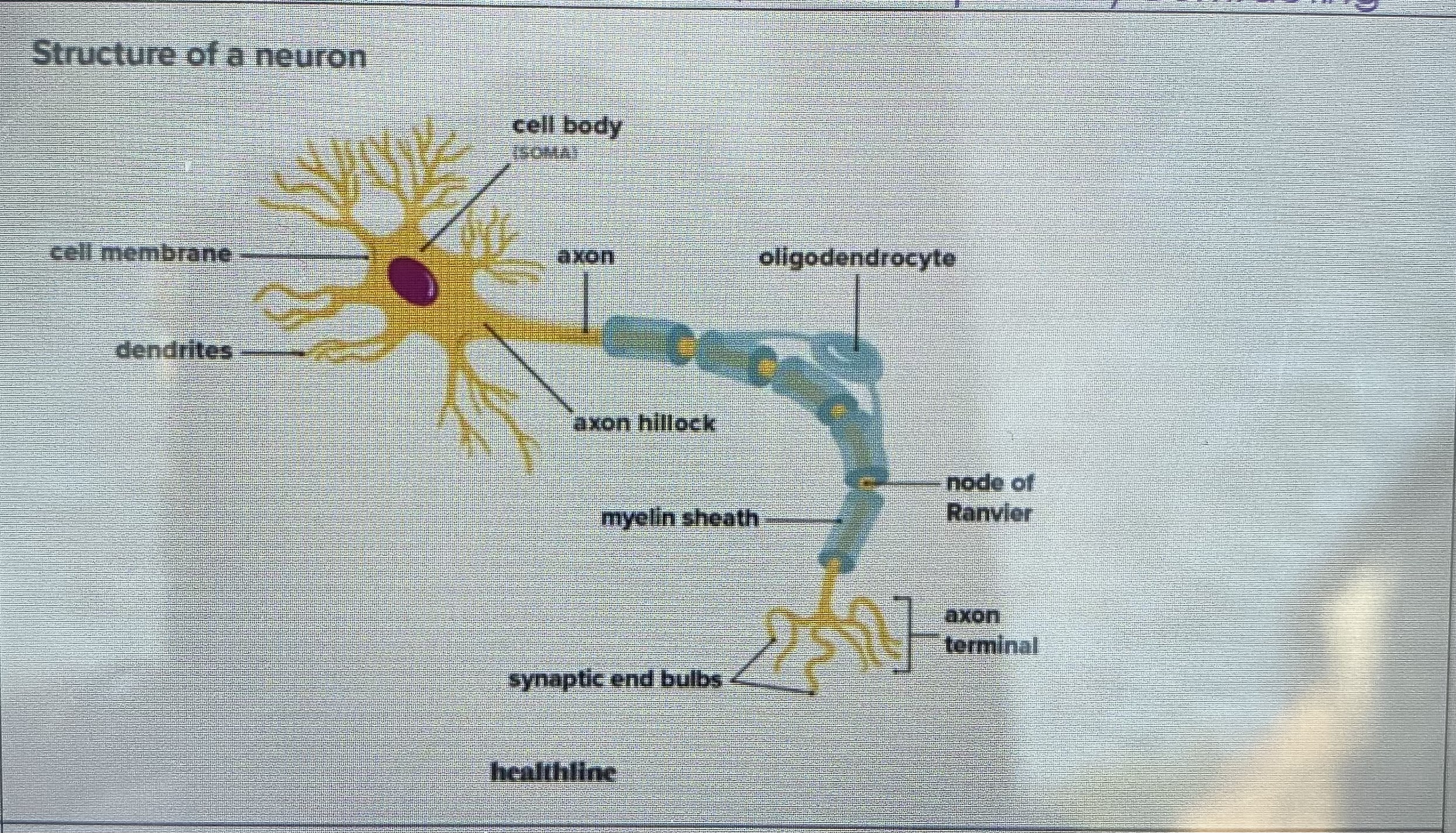
Relay neurones
Link sensory neurones and motor neurones in reflex arcs
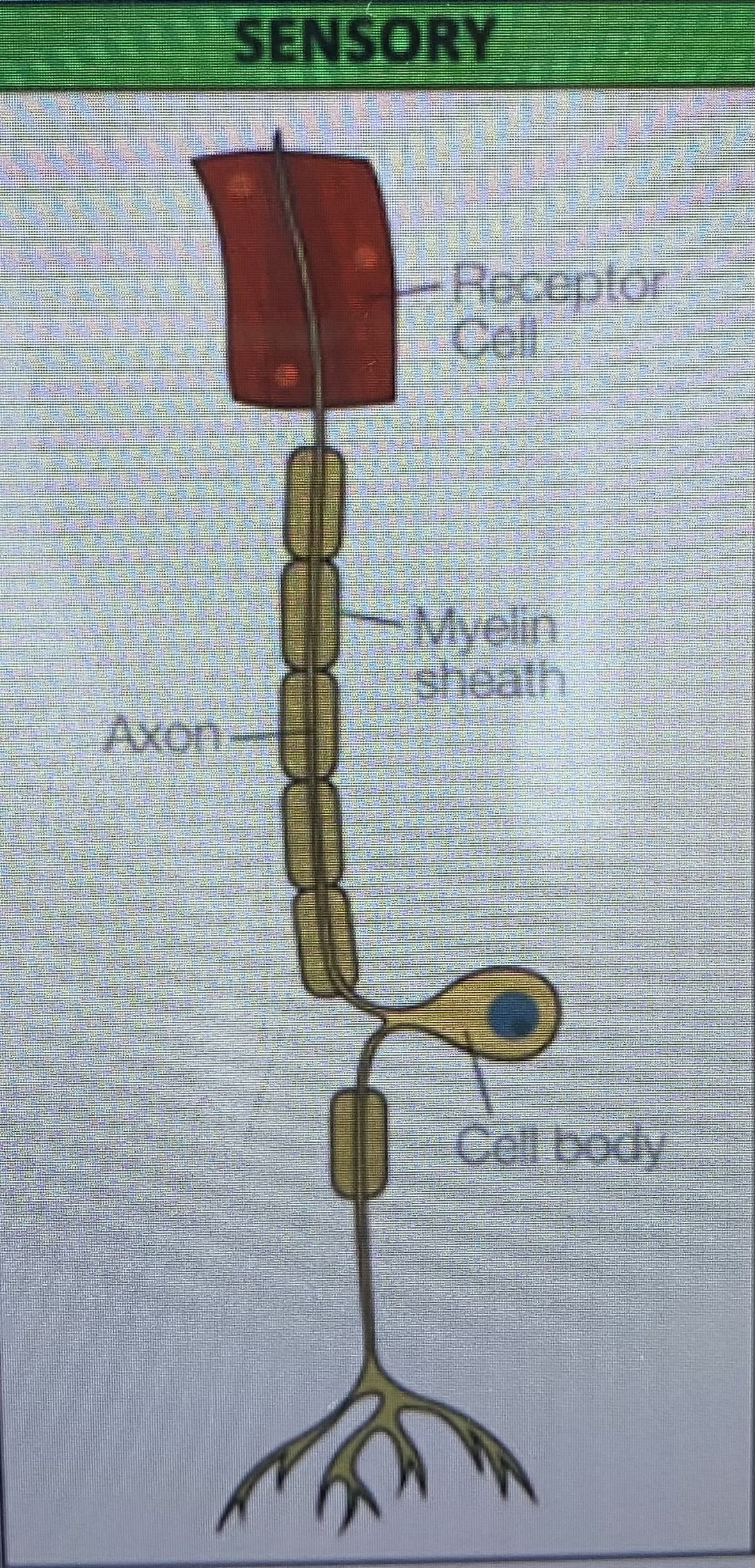
Sensory neurones
Carry impulses to the brain and spinal cord
Myelination
The myelin sheath is a fatty layer around the axons of neurones. It insulates the axon and speeds up neurotransmissions, ensuring they reach their desired location quickly.
Where are the different neurones found?
Sensory - in the body - linking receptors to the brain
Relay - in the brain and spinal cord
Motor - in the body - linking brain to muscles
Nervous system
The system, made of cells called neurones, that coordinate fast communication throughout the body.
Central nervous system
The brain and spinal cord. The rest is the peripheral nervous system.
Consequences of reduced myelination
No insulation mean impulses travel more slowly/less frequently so muscle contraction doesn’t happen in a controlled way.
Describe the structure of a sensory neurone
Describe a relay neurone
Describe a motor neurone
What is a nerve impulse (neurotransmission)?
An electrical signal that is carried by the neurone
Stimulus
A change in the environment around you
Receptor
A cell that detects stimuli
Response
Something that an organism does once it detects the stimulus
Effector
Something that does the response - a muscle or gland.