lab 7 digestion
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
organs of digestion
gastrointestinal tract & accessory organs
reactants consist of
substrate and enzyme
substrate
substance that enzyme is acting on, undergo the chemical change
enzyme
protein catalyst in rxn
reagents
chemical indicators
negative control
set up where nothing is expected to happen
emulsifier (do not chemically digest) example
bile salts
bile salts role in digestion
physically break up lipids (mechanical digestion) into small droplets which provides more surface area for lipase to break down lipids
pancreatic lipase
produced b acinar cells in pancreas, enzyme that chemically digests triglycerides into fatty acids, glycerol, and monoglycerides in the small intestines
triglycerides
1 glycerol & 3 fatty acids, when broken down by lipase the 3 fatty chains are released.
bromothymol blue
chemical pH indicator that detects lipid catabolism, because released fatty acids lower pH of solution
bromothymol blue pH >7
blue, left

bromothymol blue pH <7
yellow, right

pepsin
enzyme produced by chief cells of stomach, greatest in acidic environment, breaks down into chain peptides in stomach
biuret reagent
used to detect partly digested peptides
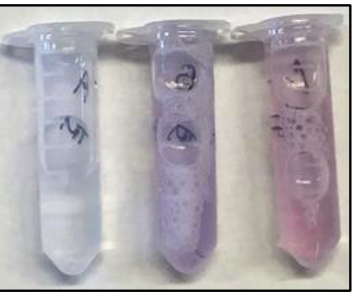
biuret test negative
left, clear or pale blue
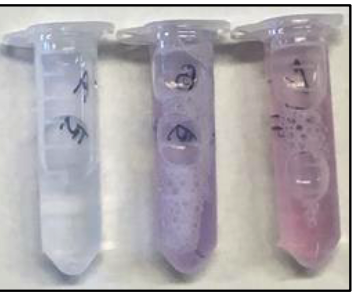
biuret test positive
middle, purple
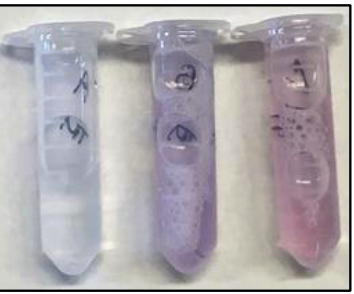
biuret test positive for shorter peptides
right, pink
amylase
enzyme produced by salivary glands and pancreas, breaks down dietary starches (polysaccharides) into simple sugars (disaccharides and monosaccharides)
lugol’s solution
detects the change in starch level overtime
lugol’s test
purple/black is positive and progressively lighter as less is present