Levels of Organization and Homeostasis in Organisms
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Organism
A living thing
Homeostasis
Describes the maintenance of a constant internal environment.
Cell
The basic unit of life.
Atom
The smallest unit of matter held together by chemical bonds.
Molecule
Components of organisms, such as proteins and lipids.
Organelle
The main structures within a living cell (Example: A nucleus is an organelle).
Tissue
Groups of cells working together to carry out a specific function.
Organ
Structures composed of two or more tissues carrying out a specific function.
Organ system
Groups of organs that carry out a specific function in an organism.
Negative feedback
Organism senses a change in the internal environment and organ systems temporarily adjust their functions to return internal environment to the set point.
Positive feedback
Organism senses a change in the internal environment and response to change increases as time progresses.
Example of negative feedback
When human blood pressure is elevated, the brain senses the change and causes the heart to slow until pressure returns to a normal level.
Example of positive feedback
During childbirth, a woman's uterine contractions increase in intensity until her child is delivered.
Levels of organization
Different possible levels of organization that organisms participate in.
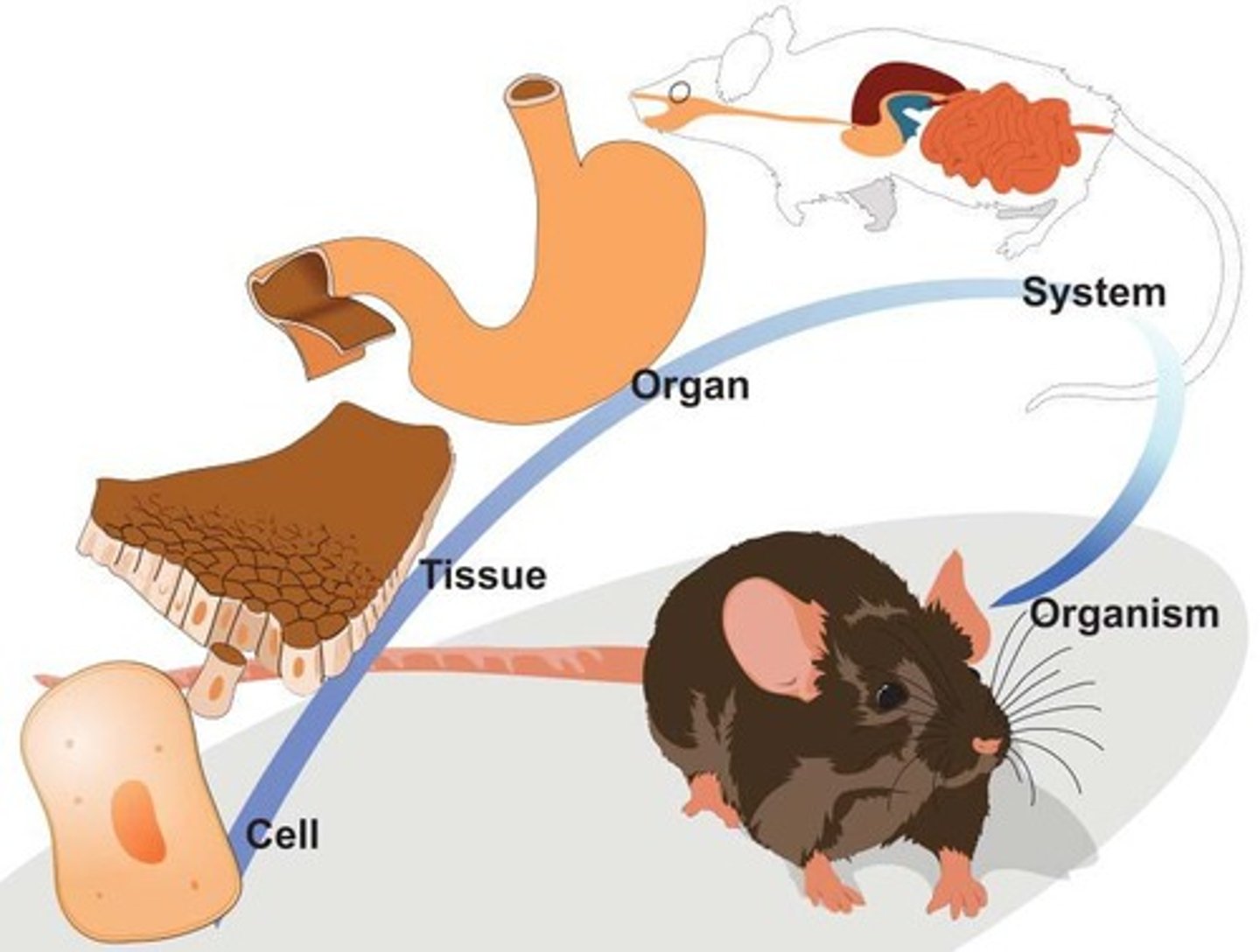
Multicellular organisms
Organisms composed of multiple cells that often involve complex homeostasis mechanisms.
Cytosol
The liquid found inside cells, where single cells regulate the amount of water.
Cytoplasm
The material within a cell, excluding the nucleus.
Set point
A certain level that the internal environment is restored to during homeostasis.
Complexity of an organism
Exhibited by the different levels of organization that exist.
Individual living things
Organisms.