Teas exam Science
1/473
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
474 Terms
Hypothalamus
smart control coordinating center, keep your body in a stable state called homeostasis, helps manage your body temperature, hunger and thirst, mood, sex drive, blood pressure and sleeps
Cells
The basic unit of life ( organelles)
Mineralocorticoids
steriod hormones that play a role in salt and water balance
aldosterone = also stores sodium
Tissue
a group that is made up of cells with similar structures and functions (cardiac, Muscle)
Organs
made up of tissue that works together to function (heart,lungs,kidney)
Organ system
group of organs that work together to carry out a function (stomach, small and big intestines)
Organism
made up of one or more organ systems working together to ensure survival
Prokaryotes
Consisting of a single cell
Bacteria
Archaea
DNA (no nucleus)
Cytoplasm
Ribrosome
Cell Membrane
Pro=No
No membrane bound organelles
Eukaryotes
Fungi
Animals
Protist
Plant
DNA (in nucleus)
Cytoplasm
Ribrosome
Cell membrane
EU=DO
Has membrane-bound organelles
Cell membrane
Referred to as plasma membrane. Separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment and helps cells stable known as homeostasis
selective permeable
refers to the ability of a cell membrane to allow certain substances to pass through while preventing others, acting as a gatekeeper for the cell's internal environment. "Allows cells to maintain a stable internal environment, separate from the external environment. This process is also known at cytoplasm.
Cytoplasm
the gel-like fluid within a cell's membrane (excluding the nucleus), provides a medium for cellular processes, supports organelles, and facilitates transport and metabolic activities
Cytoplasm and Selective Permeability
The fluid within a cell, is maintained by the cell membrane's selective permeability, which regulates the passage of substances, allowing the cell to control its internal environment and maintain homeostasis.
Cytoskeleton
a network of protein filaments, provides cells with structural support, enables movement, and facilitates intracellular transport of organelles and vesicles.
Ribosomes
Intercellular structures made of both RNA and protein. Site of protein synthesis in the cell
Amino Acids
Small molecules that are the building blocks of proteins
Nucleus
Membrane enclosed organelle within a cell that contains the chromosomes (DNA)
Nucleolus
Area inside the nucleus of a cell that is made up of RNA and protein and is where ribosomes are made
Plant Cell
A plant cell is the basic unit of all plants and is eukaryotic. A small living part of a multicellular organism that makes its own food in chloroplast and reproduces sexually or asexually.
Plant cell features not found in animal cells
A rigid cell wall is made of cellulose, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and large vacuoles for storage and maintaining turgor pressure (force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall.)
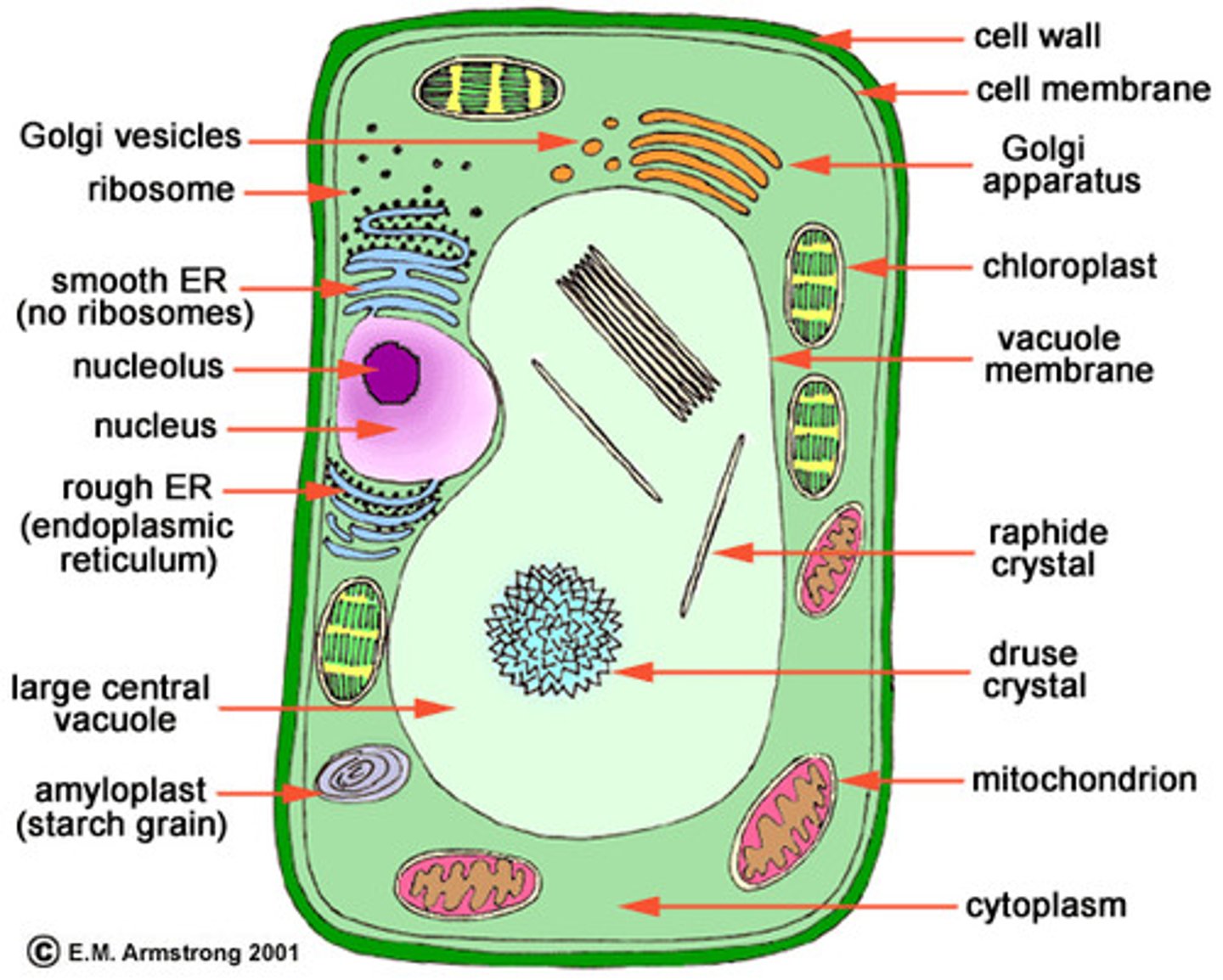
What is the function of the nucleus in a plant cell?
The control center of the cell, containing the plant's genetic material (DNA).
What is the role of the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) in a plant cell?
A network of membranes involved in protein and lipid synthesis and transport.
What does the Golgi Apparatus do in a plant cell?
Processes and packages proteins and lipids, often forming vesicles for transport.
What is the function of mitochondria in a plant cell?
The 'powerhouses' of the cell, responsible for energy production through cellular respiration.
What is unique about chloroplasts in plant cells?
They contain chlorophyll and are the sites of photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy.
What is the function of the vacuole in a plant cell?
A large, membrane-bound sac that stores water, nutrients, and waste products, and helps maintain cell turgor.
What is the purpose of the cell wall in a plant cell?
A rigid outer layer that provides support and protection to the plant cell, made of cellulose.
What role do peroxisomes play in a plant cell?
Involved in various metabolic processes, including breaking down fatty acids and detoxifying harmful substances.
What are plasmodesmata in plant cells?
Channels that connect the cytoplasm of adjacent plant cells, allowing for the passage of molecules.
Animal Cell
An animal cell is a type of eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall and has a true, membrane-bound nucleus along with other cellular organelles. A small living part of a multicellular organism that eats to gain energy and reproduces sexually.

A plant cell does not have
lysosomes and centrioles
Name the cell organelle that contains the genetic material of the animal cell.
Nucleus
Which cell organelle is responsible for the generation of energy for cellular activities in animal cell?
Mitochondria
Name the double-layered membrane responsible for enveloping the nucleus in animal cell
Nuclear envelope
State the various types of animal cells
Skin Cells
Muscle Cells
Blood Cells
Nerve cells
Fat Cells
What is the role of lysosomes in animal
Lysosomes help in digestion, excretion and cell renewal process
Explain how an animal cell varies from a plant cell
An animal cell is usually irregular and round in shape. This is primarily due to the absence of the cell wall, which is a characteristic feature of plant cells. Furthermore, animal cells do not have plastids as animals are not autotrophs.
Name the selectively permeable structure that envelopes the entire animal cell.
Cell membrane
Which cell organelle is responsible for packing in animal cell
Golgi apparatus
Mitosis
Cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes
Meiosis
Cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cells
Mitosis
PMAT
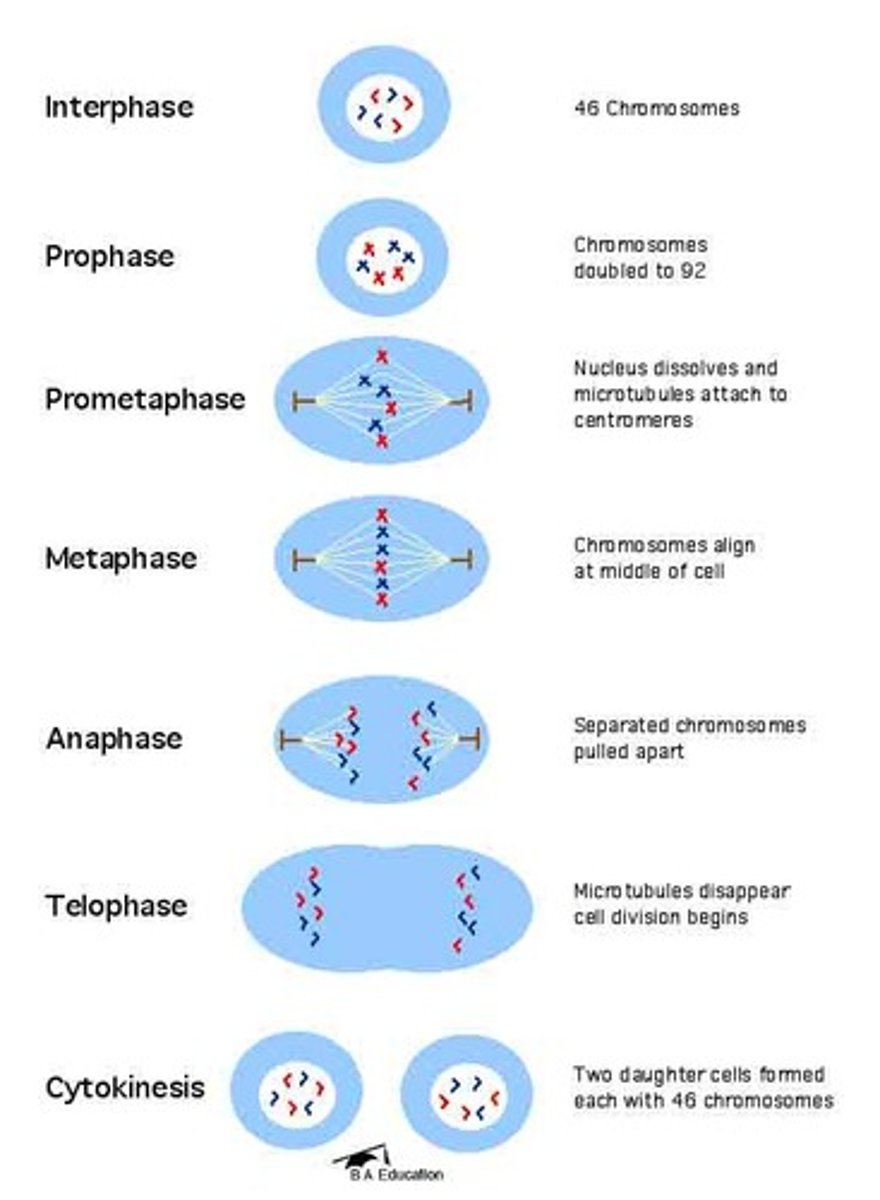
Mitosis (Prophase)
Pro:Before
Chromosomes becomes visible as they condense and thicken
Mitosis (Metaphase)
Me: Middle
Chromosomes align in the middle of the cell's center forming a single row
Mitosis: Anaphase
Chromatids are separated and drawn to the opposite ends of the cell by spindle fibers
Mitosis: Telophase
Chromosomes reach the opposite sides of the cell. Forming new nuclear envelopes around the chromosomes
Mitosis: Cytokinesis
splits the cytoplasm of the cell into two identical diploid cells
Meiosis
P1, M1, A1, T1, P2, M2, A2, T2
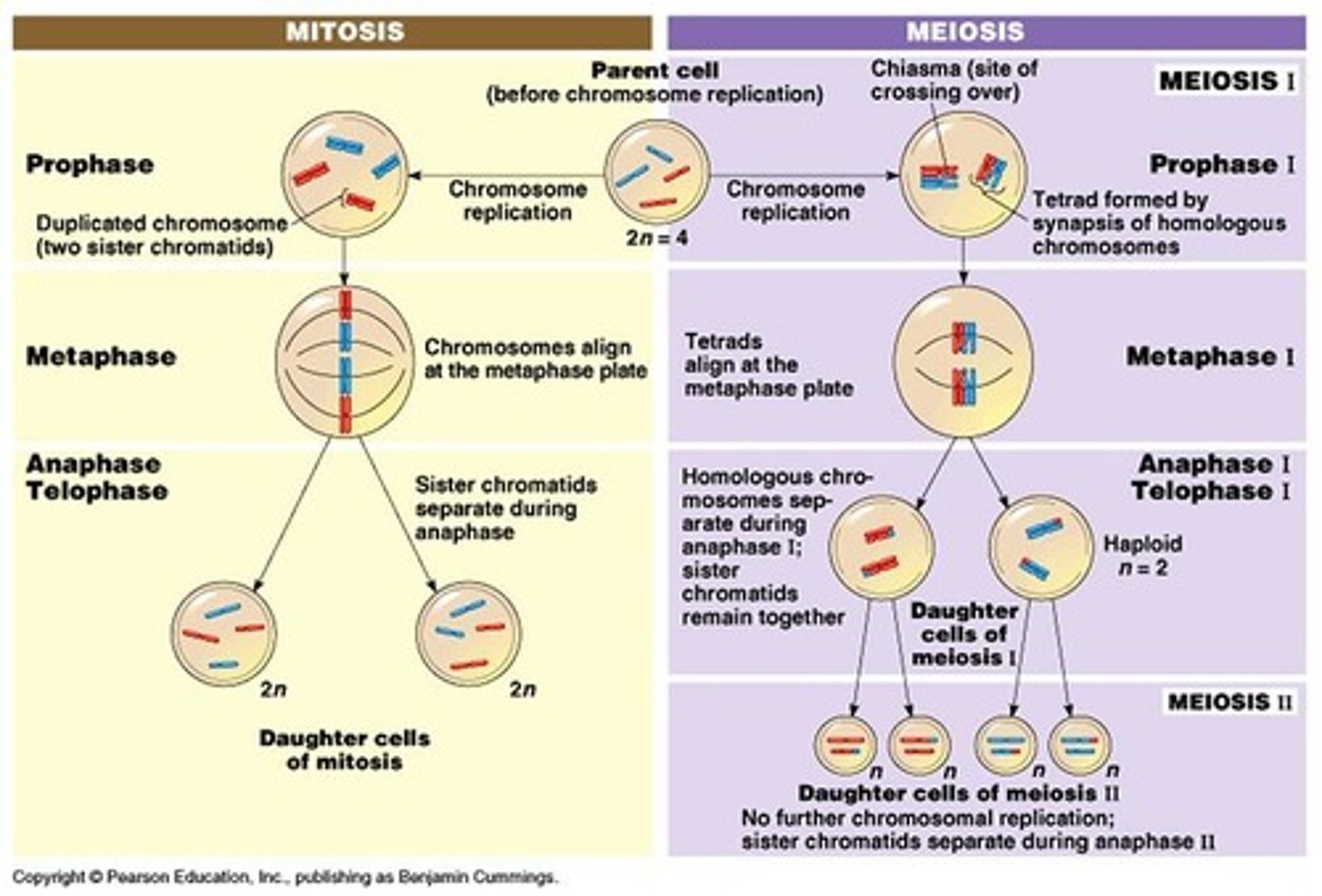
Meiosis Prophase 1
Chromosomes condensation and pairing of homologous chromosomes
Meiosis Metaphase 1
Chromosomes align in the middle of the cells center. Maintaining their homologous pairs
Meiosis Anaphase 1
Chromosomes are separated and drawn to the opposite ends of the cell by spindle fibers
Meiosis Telophase 1
Chromosomes reach the opposite sides of the cell forming new nuclear envelopes around the chromosomes.
Meiosis: Cytokinesis
Splits the cytoplasm of the cell
Meiosis: Prophase 2
Chromosomes condensation in both cells
Meiosis: Metaphase 2
Chromsomes align in the middle of the cell's center, forming a single row
Meiosis: Anaphase 2
sister chromatids are separated and drawn to the opposite ends of the cell by spindle fibers.
Meiosis: Telophase 2
Chromosomes reach the opposite side of the cell, forming new nuclear envelopes around the chromosomes
Meiosis: Cytokinesis
Splits the cytoplasm of the cells four nonidentical cells (Gemetes)
Heredity
the passing on of physical or mental characteristics genetically from one generation to another. Ex Height, eye color, hair color
DNA
main constituent of chromosomes phosphate, deoxyribose, nitrogenous
Chromosomes
long, continuous thread of DNA that consists of numerous genes and regulatory information and wraps around protein called histones
Histones
protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin
Chromosomes also are
structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells. Carring genetic information in the form of a gen
Genes
are the units of heredity and are made up of segments of DNA
Regulation Genes
produce proteins or RNA that control the expression of other genes
RNA
a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling the synthesis of proteins
mRNA
Carries genetic information to the main proteins. The RNA molecule synthesized during transcription, which carries the genetic code for protein synthesis.
rRNA
Serves as a location for protein synthesis
tRNA
An RNA molecule that functions as an interpreter between nucleic acid and protein language by picking up specific amino acids and recognizing the appropriate codons in the mRNA
Transcription
Process of making an RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence. RNA polymerase uses a DNA template to create a complementary RNA molecule, which is then processed to form mRNA, a single-stranded molecule that carries genetic information for protein synthesis
Translation
translates the sequence of a mRNA to amino acids during protein synthesis
Which component is essential for initiating the transcription of a gene into mRNA in eukaryotic cells
RNA polymerase
In eukaryotic cells, RNA polymerase is the crucial enzyme responsible for transcription, reading DNA sequences to synthesize complementary mRNA strands, while DNA ligase is involved in DNA replication and joining DNA fragments.
RNA Polymerase
This enzyme is essential for transcription, as it binds to the DNA at a region called the promoter, unwinds the DNA, and then uses one strand as a template to synthesize a complementary RNA molecule.
DNA Ligase
This enzyme is involved in DNA replication, where it joins Okazaki fragments (short DNA sequences) and seals breaks in the DNA backbone
What is the role of mRNA in protein synthesis?
It serves as a template for assembling amino acids into proteins
Mendel & Non Mendelian Inheritance
Refers to the inheritance of traits controlled by a single gene with two alleles, one of which may be dominant to the other. EX: earlobe, dimples
Inheritance patterns that deviate from the simple dominant/recessive patterns described by Mendel's laws.
EX: Hemophilia, blood type, skin color
Law of Segregation
During the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells), the two alleles for a trait separate, so each gamete carries only one allele
Law of Independent Assortment
During gamete formation, different genes are inherited independently of each other
Allele
One of the two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome
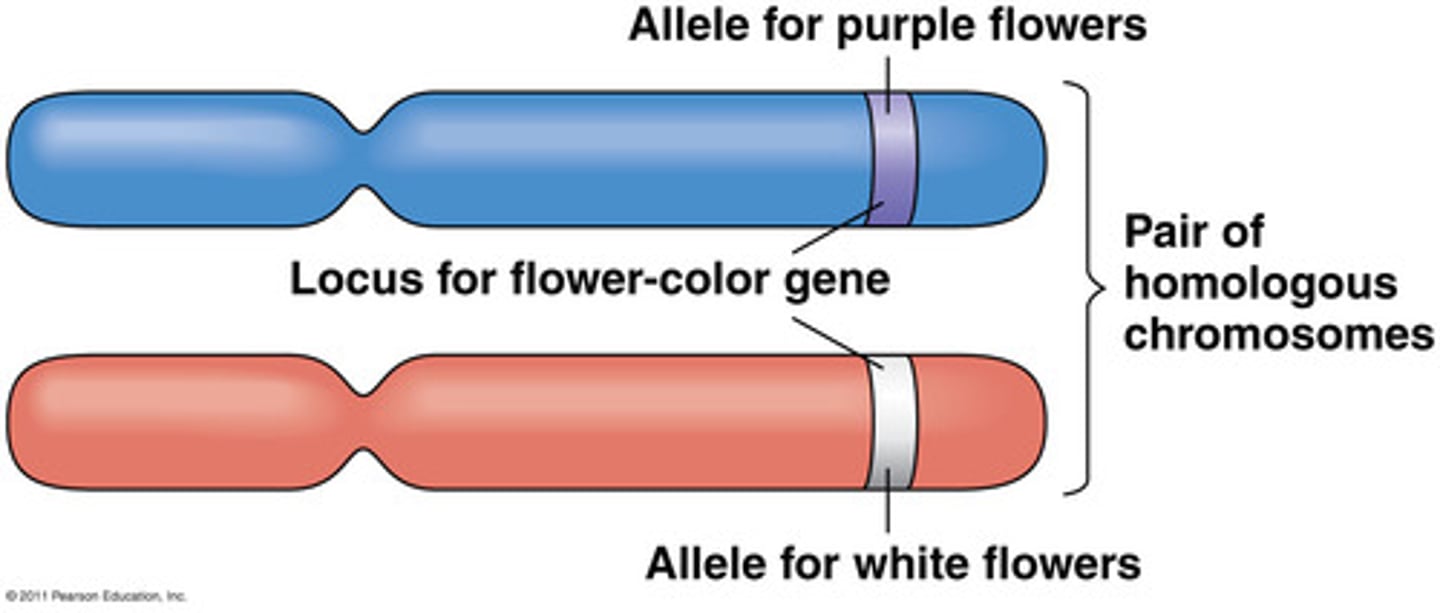
Genotype
refers to the two alleles present at a specific locus in the genome and encompasses the entire genetic makeup of an individual
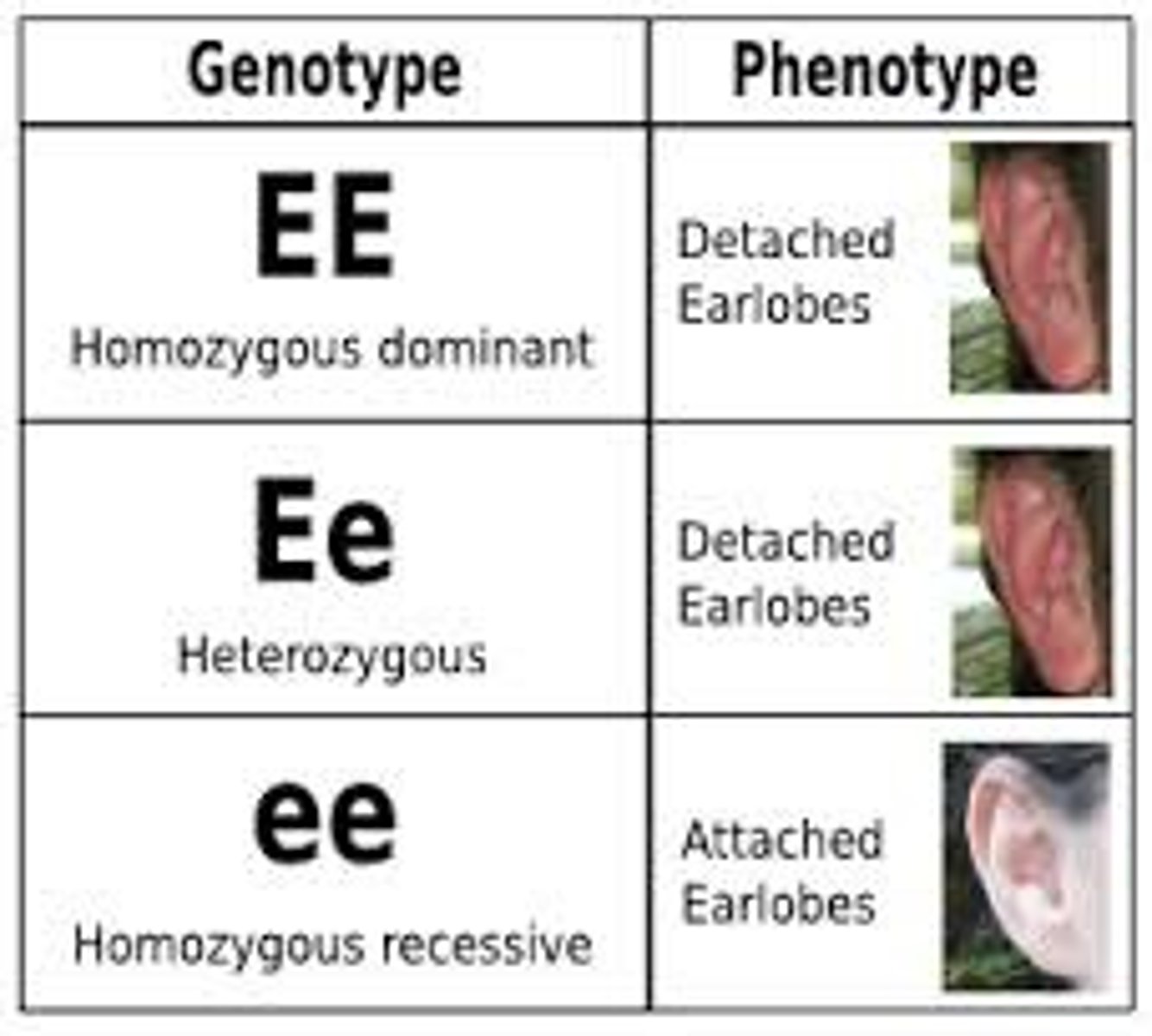
Homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait
Homo= Same Ex: FF ff
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait
Heter= different Ex: Ff
Punnett Square
diagram showing the gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross
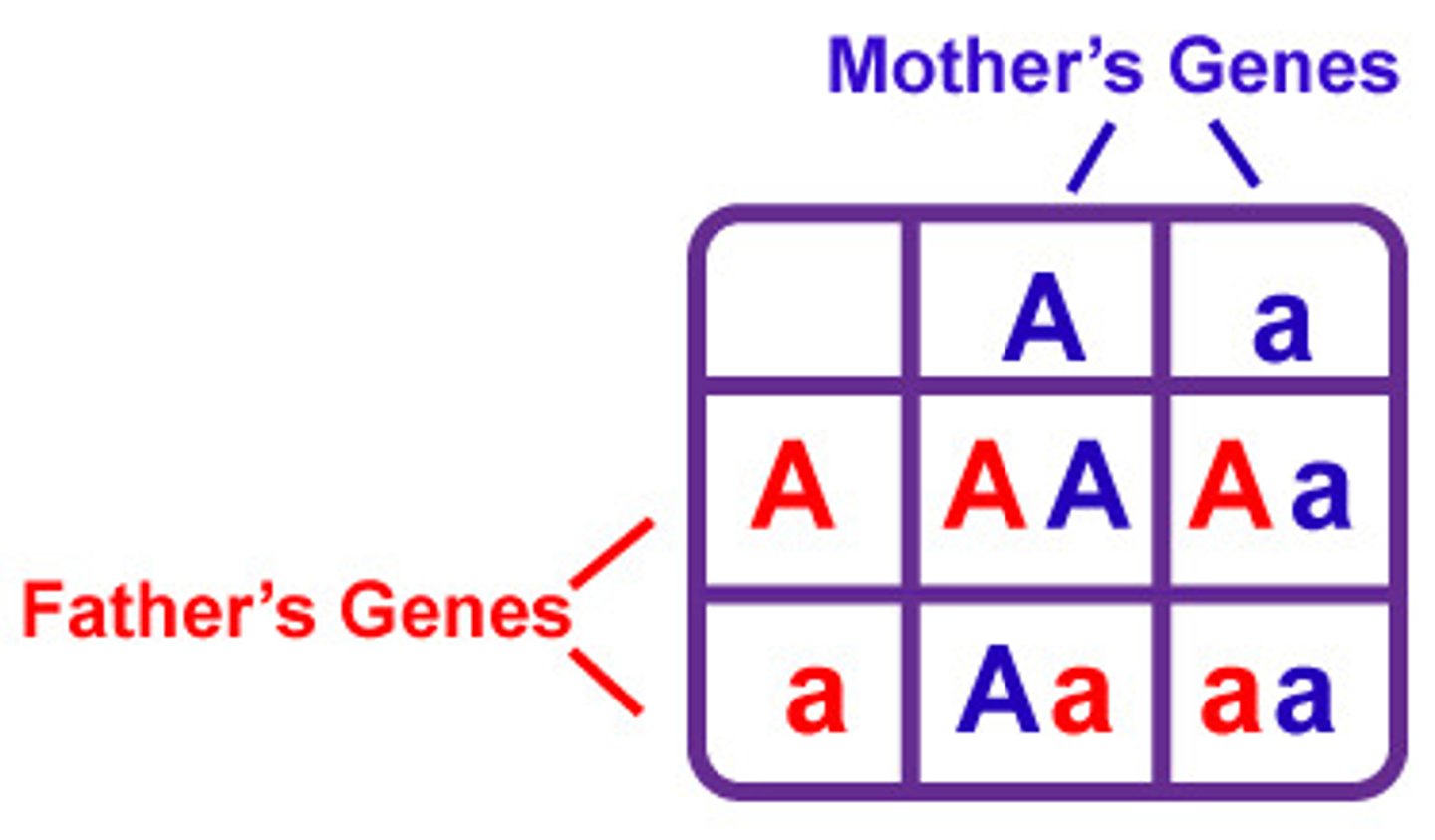
If an individual who has the genotype DdGg is crossed with an individual who has the genotype ddGg what percent of the offspring will be homozygous recessive for both trait. What would the probability of this occuring twice in a row be?
1/4 x 1/2 =1/8 =12.5%
1/8 x 1/8= 1/64= 1.6%
Codominance
a genetic pattern where two different versions of a gene are expressed equally, resulting in multiple traits in an organism. This is different from dominant-recessive inheritance, where one allele is dominant and masks the other.
Ex: In the ABO blood type system, people with type AB blood have one A allele and one B allele
Mono
Di
Poly
one
two
many
Carbohydrates
biomolecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, often in a 1:2:1 ratio, and include sugars, starches, and structural materials like cellulose.
What carbohydrates end in ose
Fruit sugar is also known as fructose and the sugar in milk is called lactose. You can recognize other sugars on labels because their chemical names also end in "-ose." For example glucose (also called dextrose), fructose (also called levulose), lactose and maltose.
Lipids
are fatty, waxy, or oily compounds that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in polar solvents such as water. Lipids include: Fats and oils (triglycerides) Phospholipids. Waxes Monoglycerides and diglycerides
Hydrophobic ( don't like water)
Plays a key role in forming cellular membranes
soluble
able to be dissolved, especially in water
solvent
a usually liquid substance capable of dissolving or dispersing one or more other substances.
insoluble
incapable of being dissolved
Protein
large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid
Nucleic acids
Large and complex organic molecules that store and transfer important information in the cell
Ex sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base
Mononer
the molecule that serve as a building blocks that can react together with other monomers to form a large polymer chain
Plant cells
have cell walls composed of a carbohydrates called cellulose
Fungi
has cell walls made of a carbohydrate known as chitin
Glucose
a simple sugar, is a primary source of energy for living organisms, broken down through cellular respiration to produce ATP, the cell's energy currency
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work also makes carbohydrates
Lipids break down into what?
glycerol and fatty acids