Applied econometrics lectures 7-8 - Cointegration
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Non-stationarity vs cointegration

Cointegration defenition
two or more separate variables that by themselves they are non-stationary, but they tend to co-move
The concept of cointegration points to the existence of a long-run equilibrium to which an economic system converges over time
Which 2 conditions must be met for cointegration
Yt & Xt both nonstationary and integrated of order 1 I(1)
There exists a linear combination of the two variables (Yt - θXt ) that is stationary
What is the Engle - Granger cointegration test looking for
cointegration → εt should be stationary
Cointegration implies that a linear combination of two integrated variables is stationary
EG test for cointegration steps
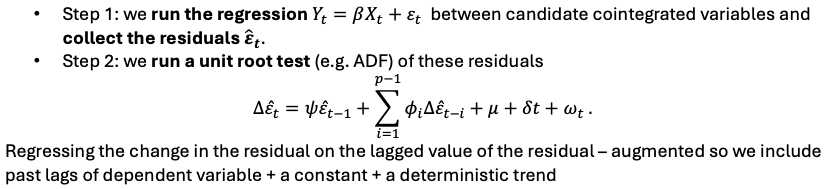

Error / Equilibrium correction model
a rearranged ARDL model, but with the long-run multiplier/effect already contained inside the model
In the LR we correct (move towards) the equilbrium
How to form a Error correction model steps
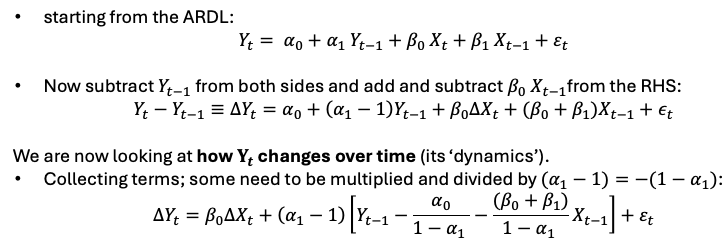
Error correction model split
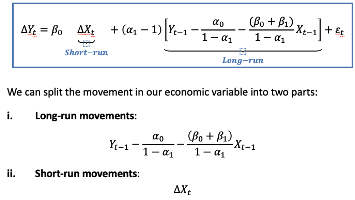
Error correction model LR
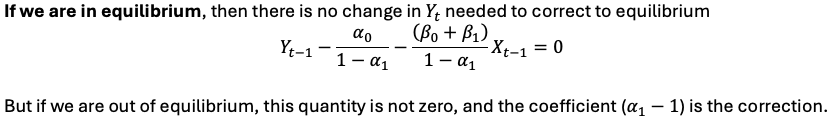
Error correction model SR
movements that bear no relation to the long-run equilibrium
e.g. some external shock
Engle-Granger Two-Step Procedure
Step 1a: estimate the long-run (equilibrium) equation using OLS and collect the residuals ̂εt Yt = βXt + εt
Step 1b: Use the residuals to do a test of cointegration (unit root test)
Step 2: Estimate the Error Correction Model by OLS

+ The adjustment coefficient ν must be negative
superconsistent estimator
the OLS estimator converges to the true β much faster than in the stationary world
implication: there is no need to include I(0) variables in the cointegrating equation
Summary
Two nonstationary series may lead to a spurious regression…
• … but they can have a meaningful long-run relationship if they are (a) of the same order of integration, and (b) cointegrated
We can test for cointegration and/or study the dynamic properties (long-run, short-run) of a bivariate relationship ( Yt and Xt )
There are different ways of representing long-run relationships, e.g. inside an error correction mechanism/model (ECM).