SNC2D - U3.10: Plant Organ Systems and Flowering Plants
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is a system?
In biology, a group of tissues and organs that performs specific functions

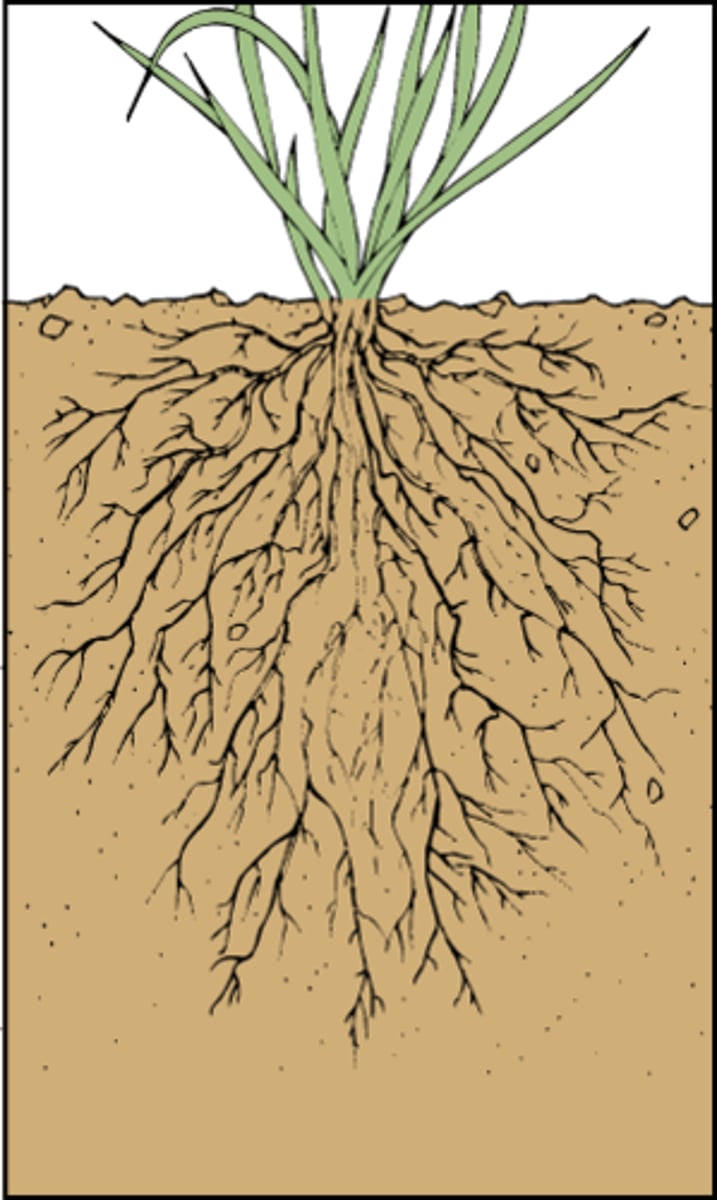
What is a root system?
An organ system in a plant which takes in water and minerals from the soil and transports them to the shoot system (super important for stability (ex. heavy wind/flooding)); all roots that lie below the surface of the ground - constantly growing to keep up with resource demand
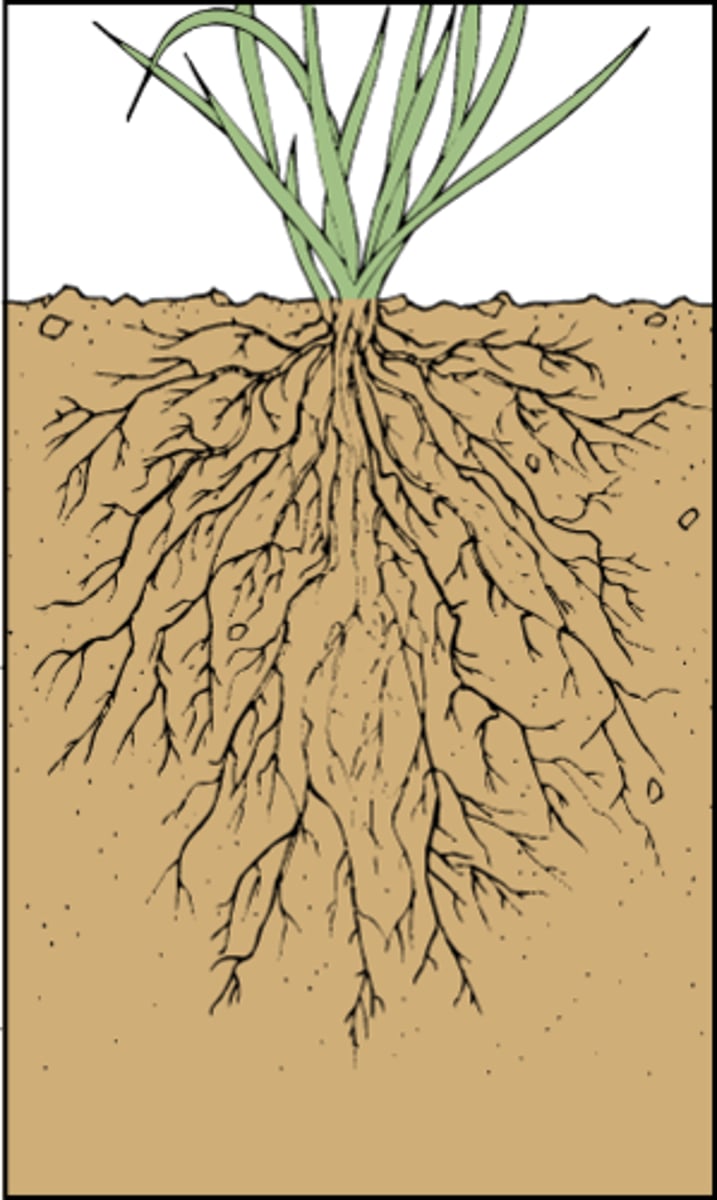
What is a shoot system?
An organ system in a plant which supports the plant, performs photosynthesis, and transports the sap (water and nutrients)
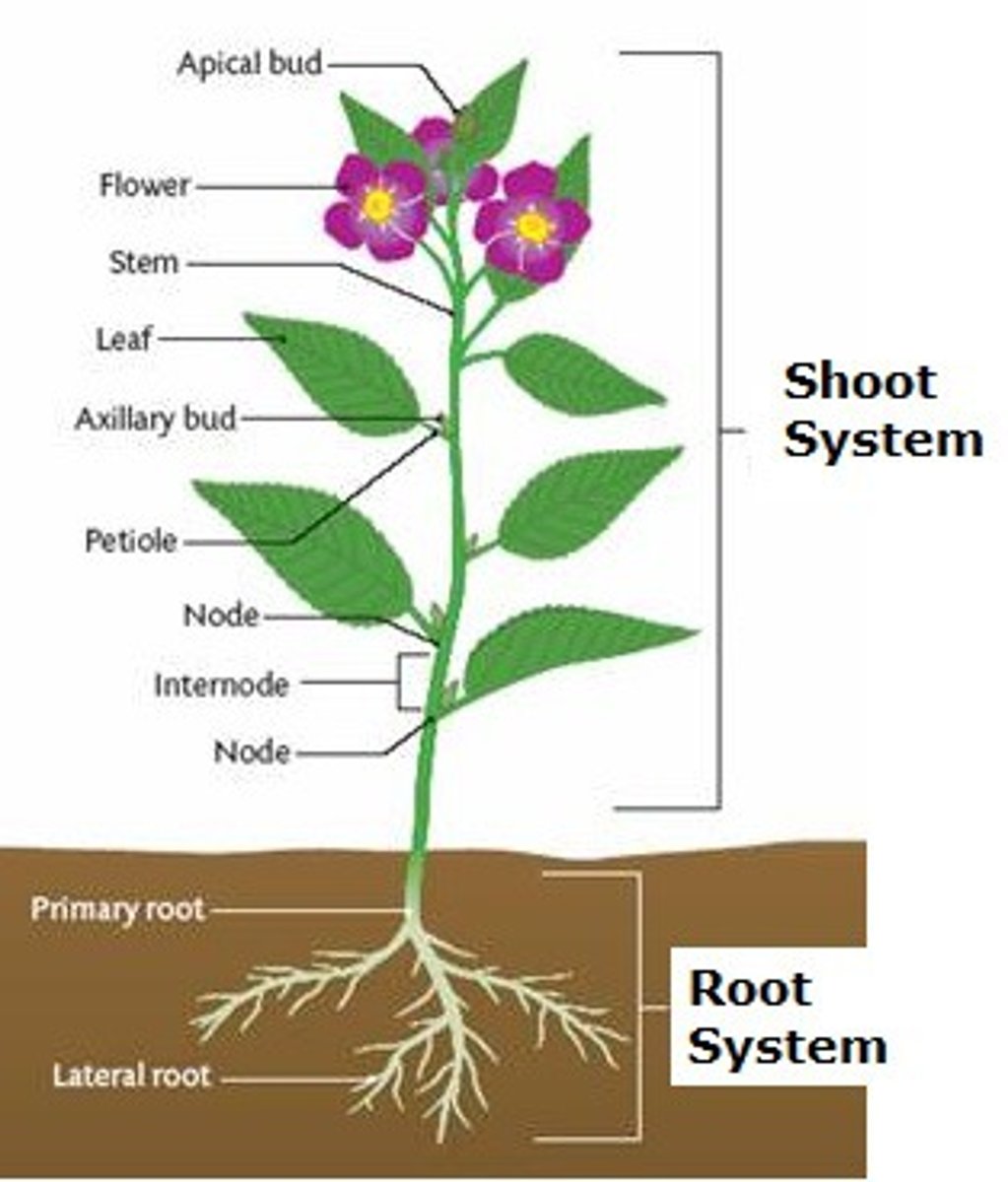
What systems are flowers and fruits considered a part of?
Either the shoot system or a separate system

What is angiosperm?
Flowering/fruiting plants whose seeds develop in the ovaries of plants

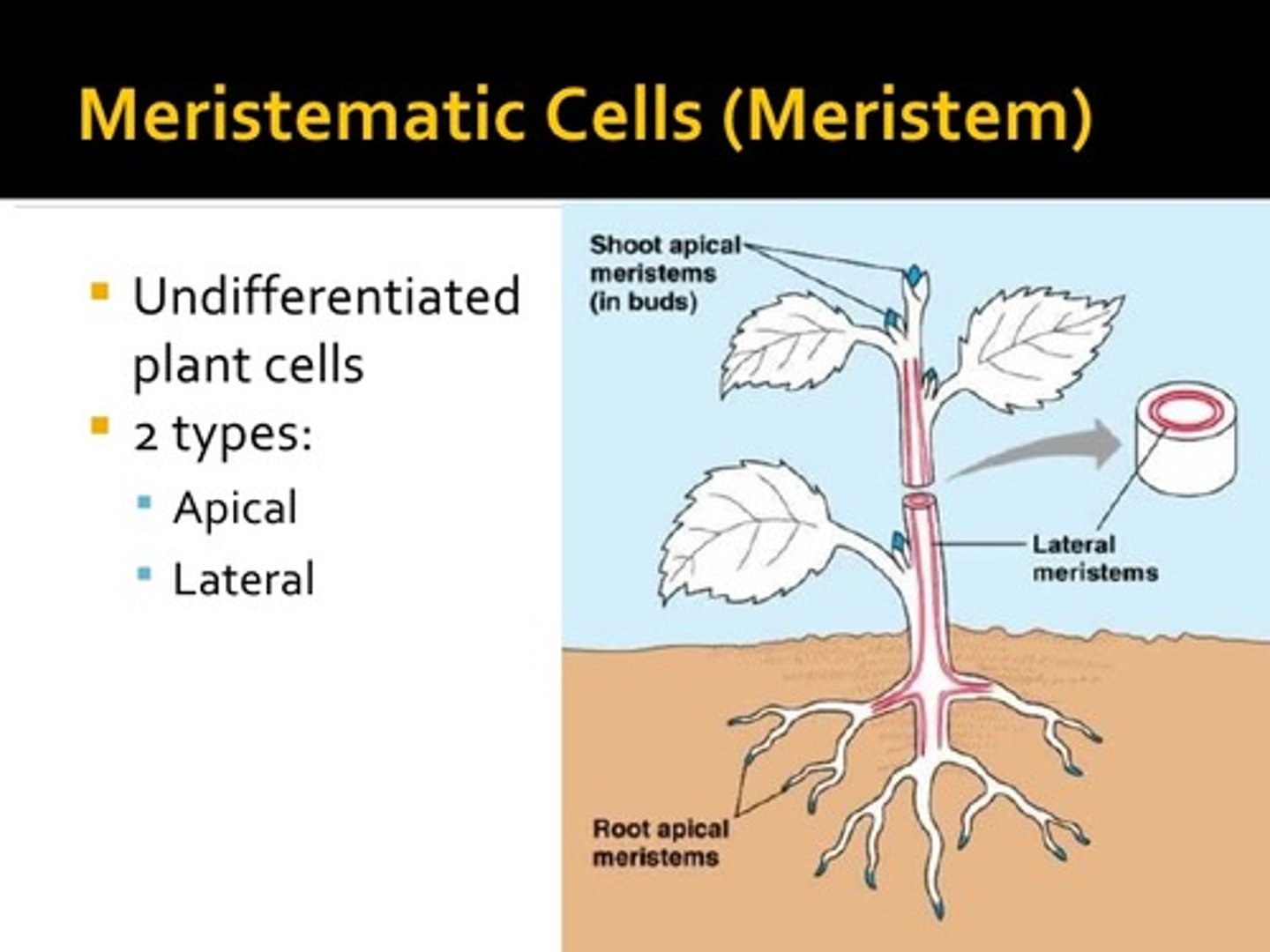
What is meristematic tissue?
Stem cells for plants
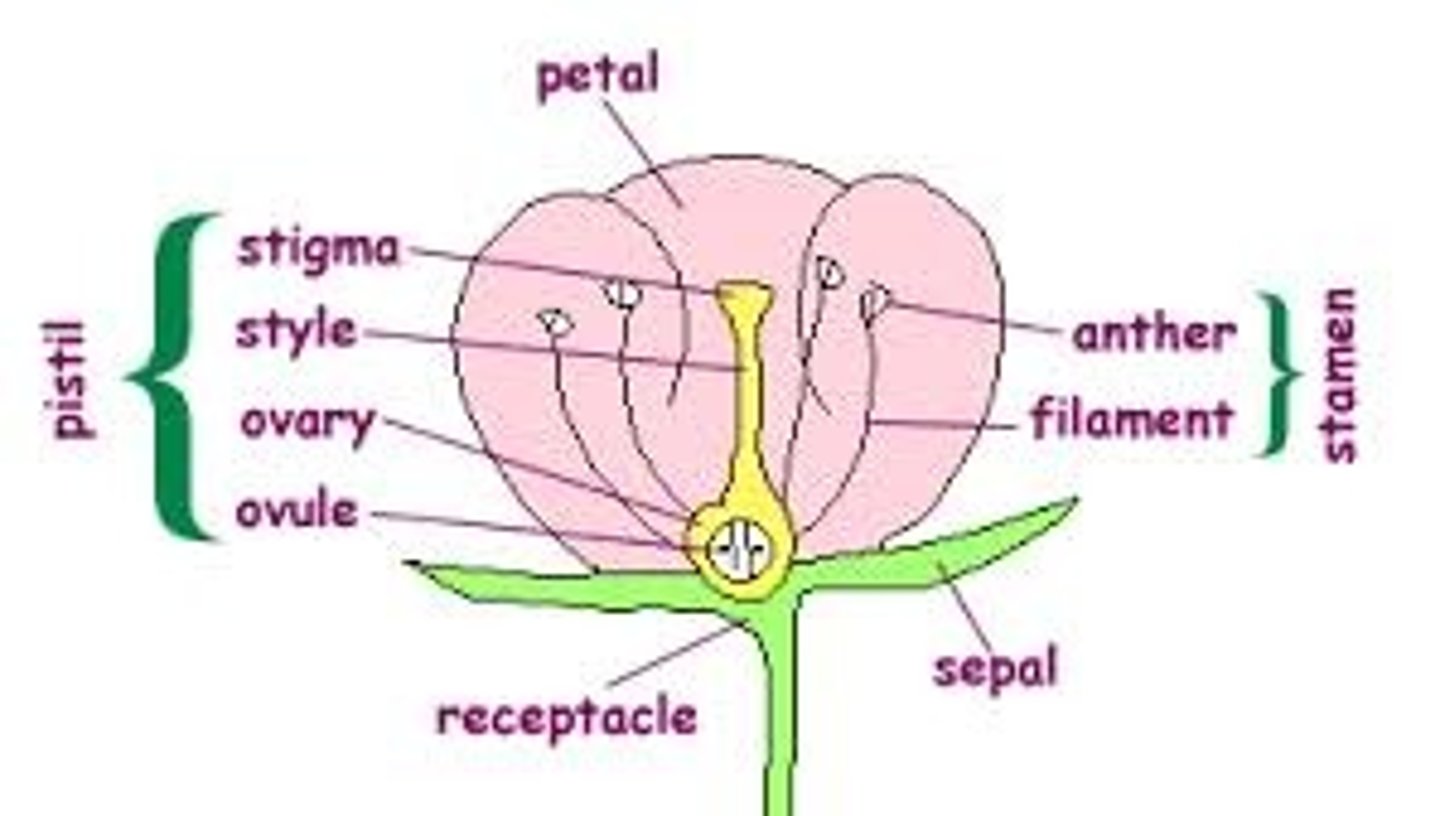
What is the stamen?
Pollen producing reproductive organ in the flower consisting of an anther and filament
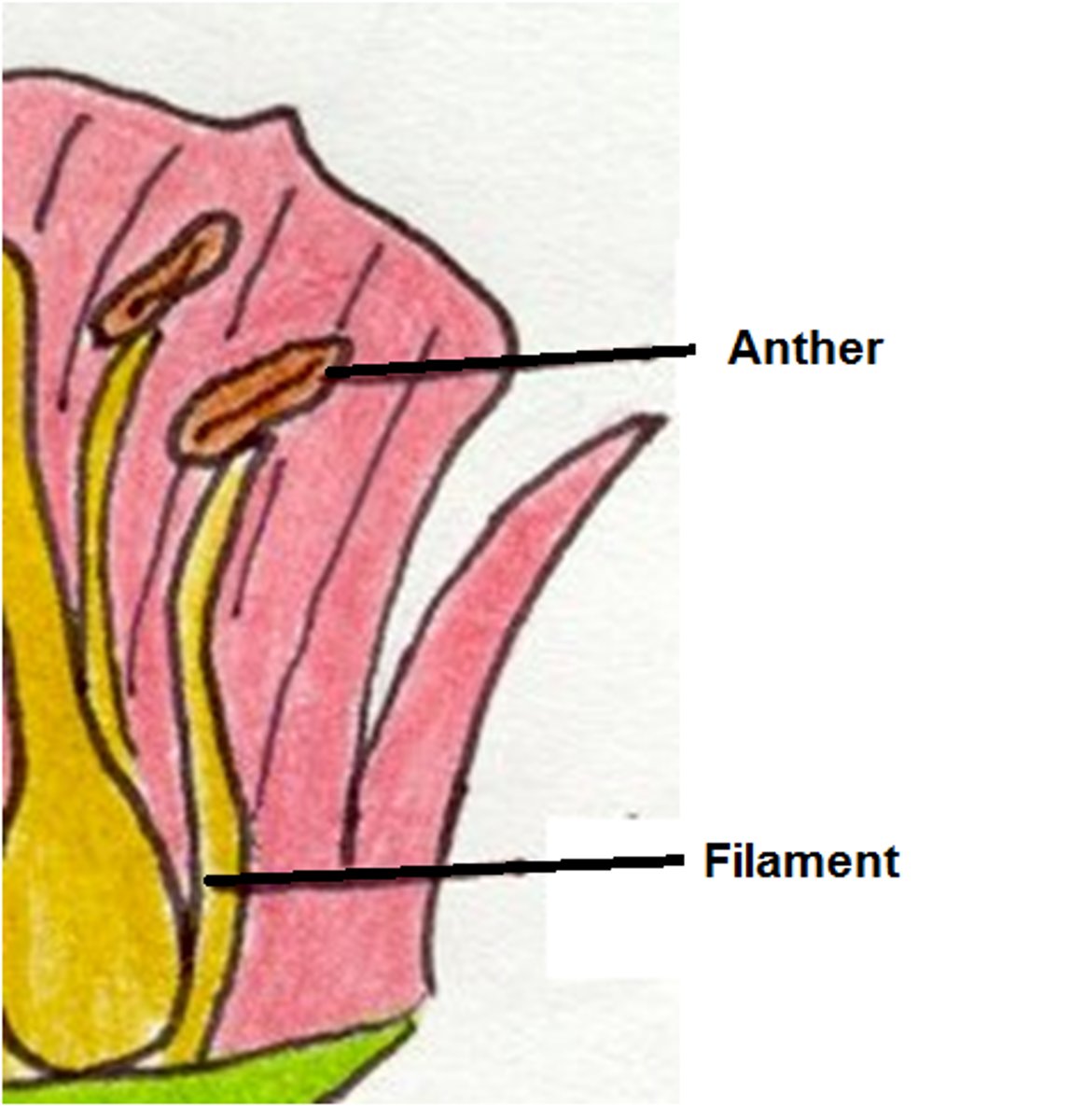
What is an anther?
Pollen-filled sac
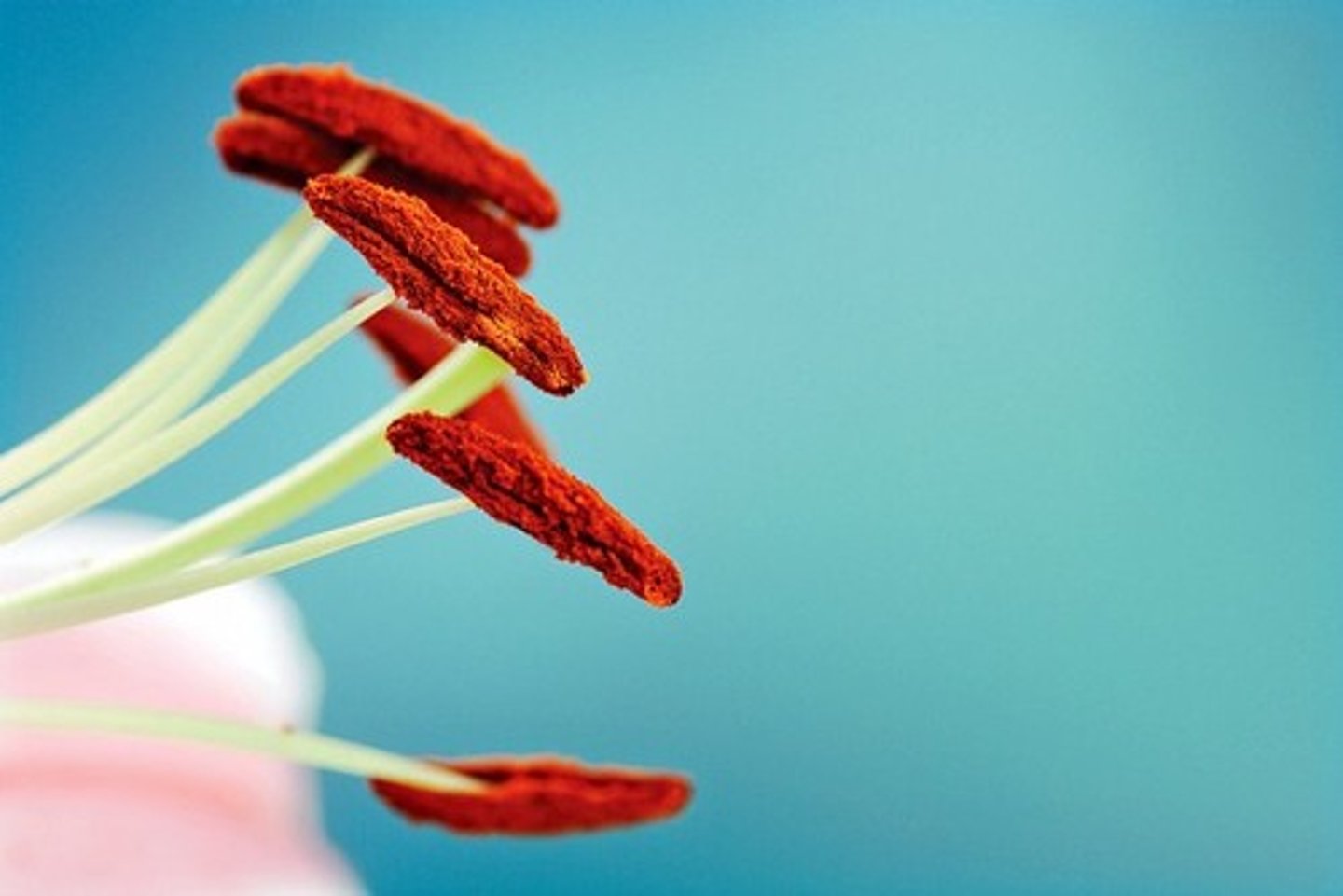

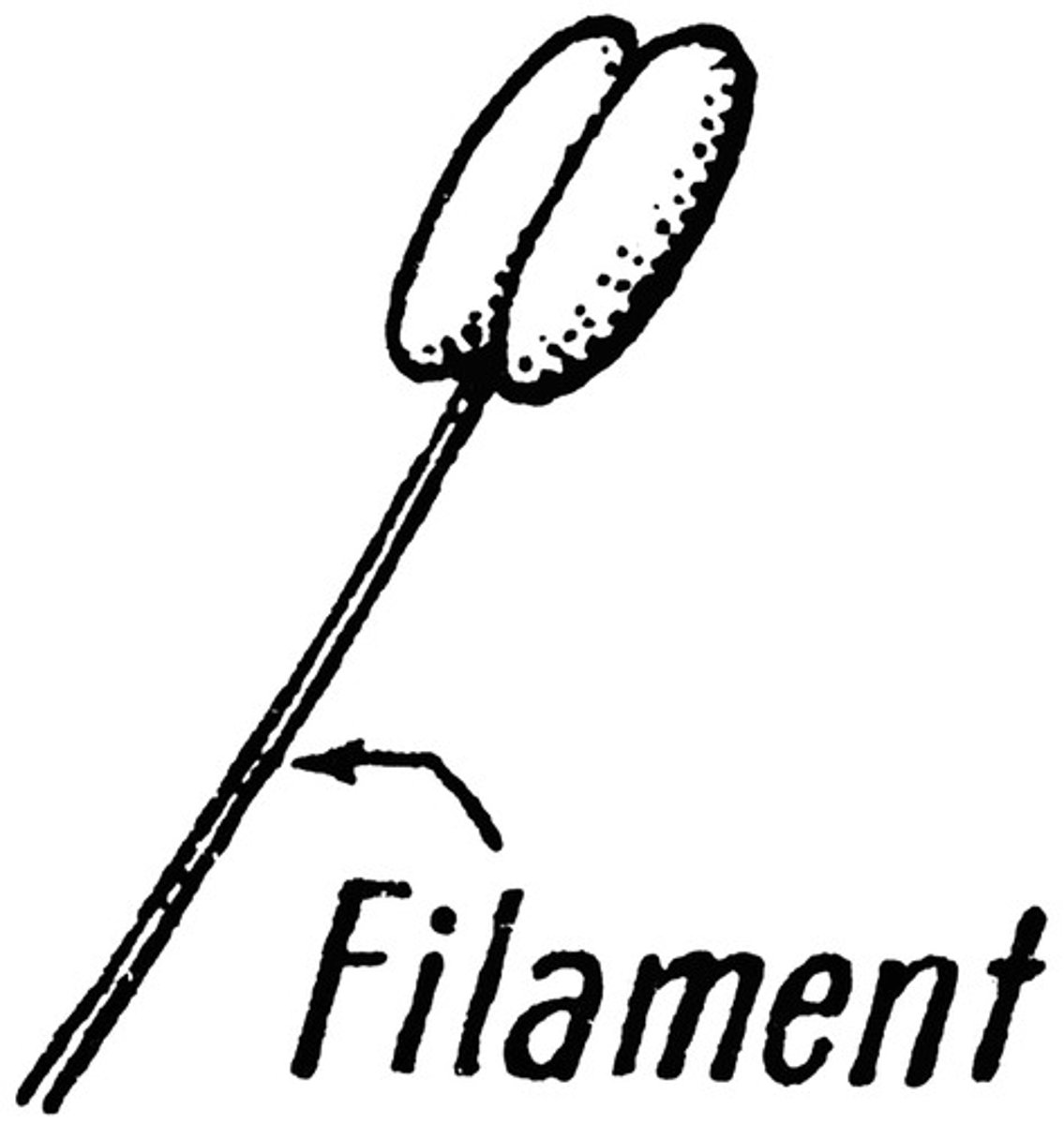
What is a filament?
Holds the anther in position making it available to plants
What are sepals?
Small, green, leaf-like structures that protect that flower bud
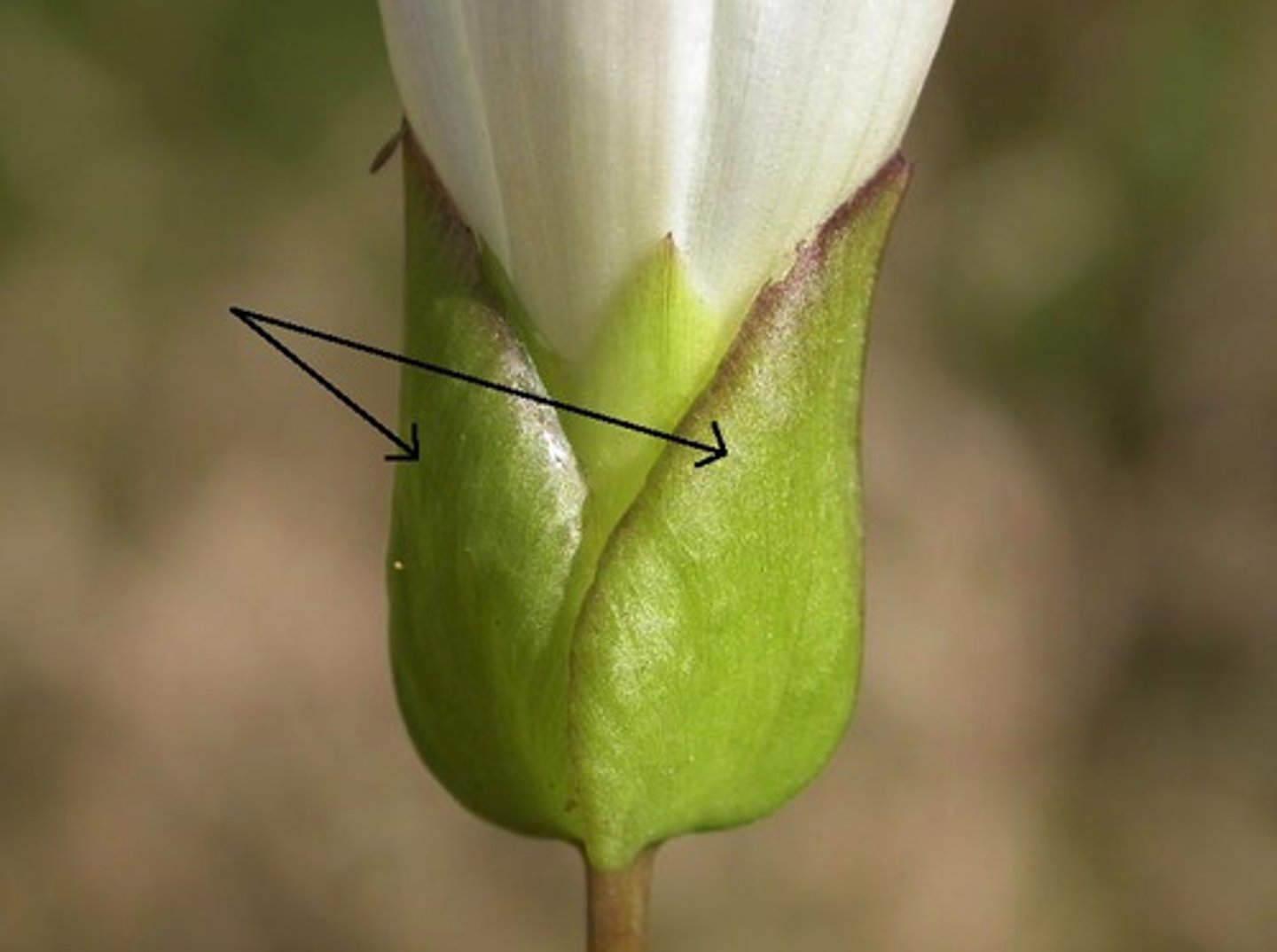

What are calyx?
Collective term for the sepals
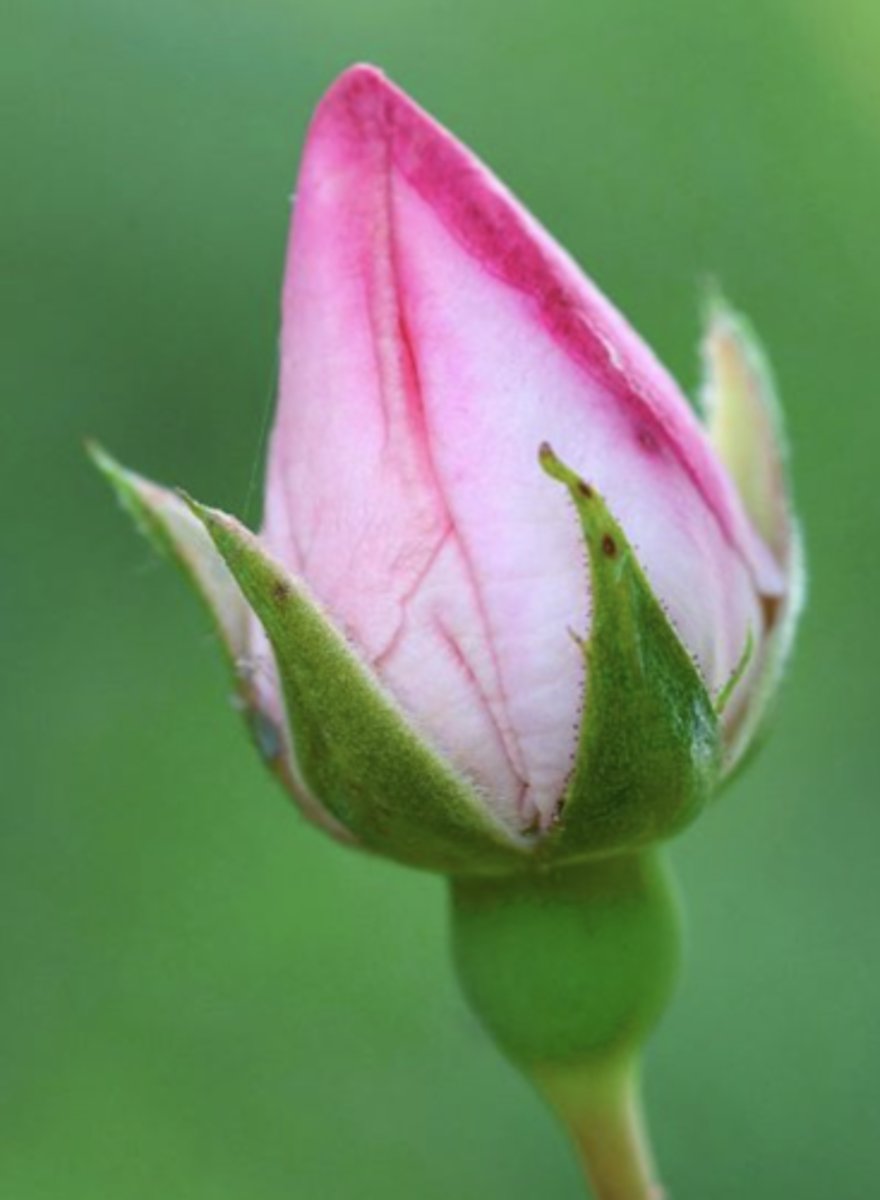

What is the pistil?
Female reproductive parts of the flower consisting of the stigma, the style, and the ovary; shaped like a bowling pin and located in the centre of the flower, it develops into a seed if an egg is fertilized
What are monoecious plants?
Plants with both male and female reproductive organs on the SAME plant (ex. squash)

What are diecious plants?
Separate plants for male and female reproductive organs (ex. holly)

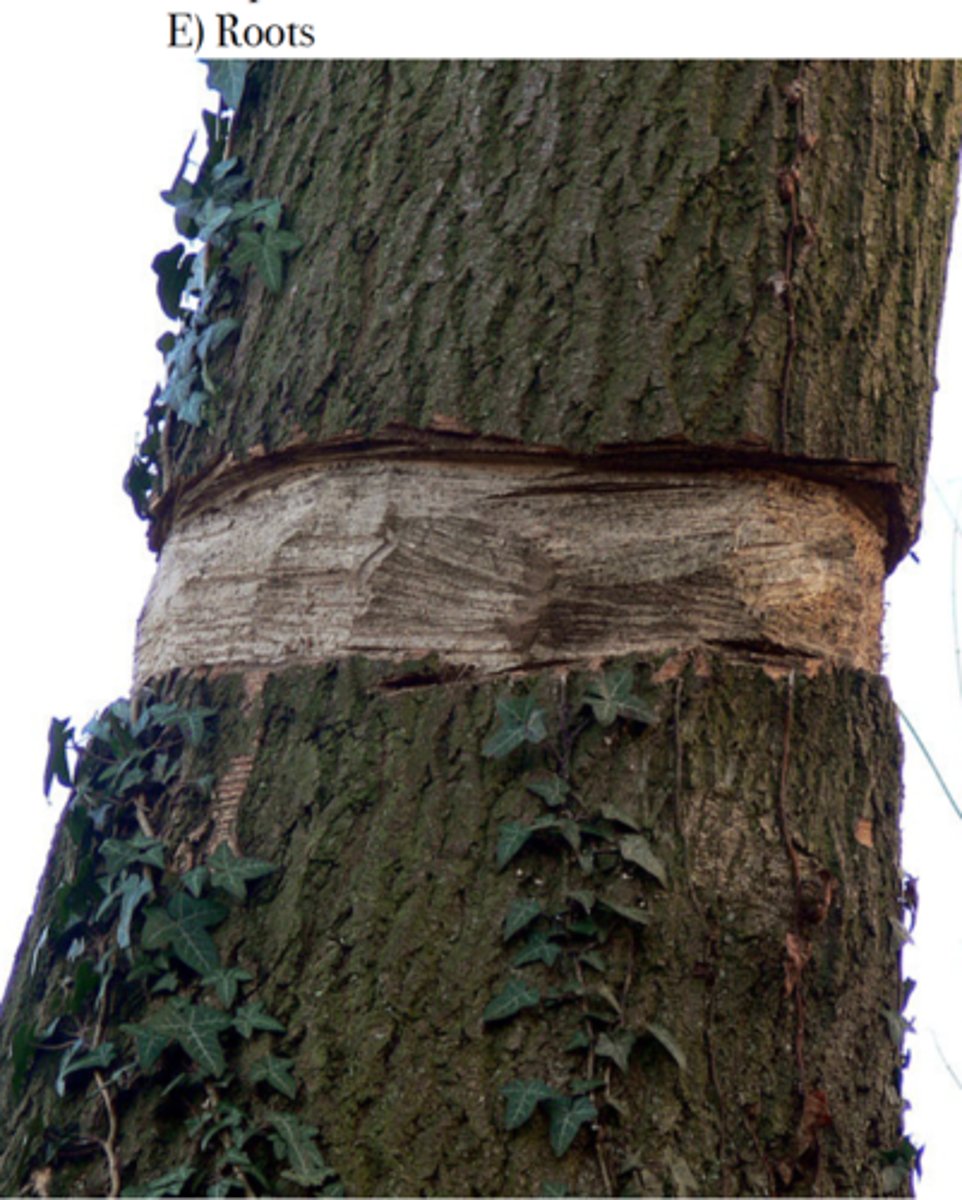
What was the Malpighi experiment?
Malpighi peeled a ring of bark and phloem from a tree. Shortly after, a swelling appeared immediately above the ring, and the tree died a few weeks later. Swelling shows that the sugar molecules are trapped in the upper part of the tree - so tree girdling makes fruit have extra sugar.

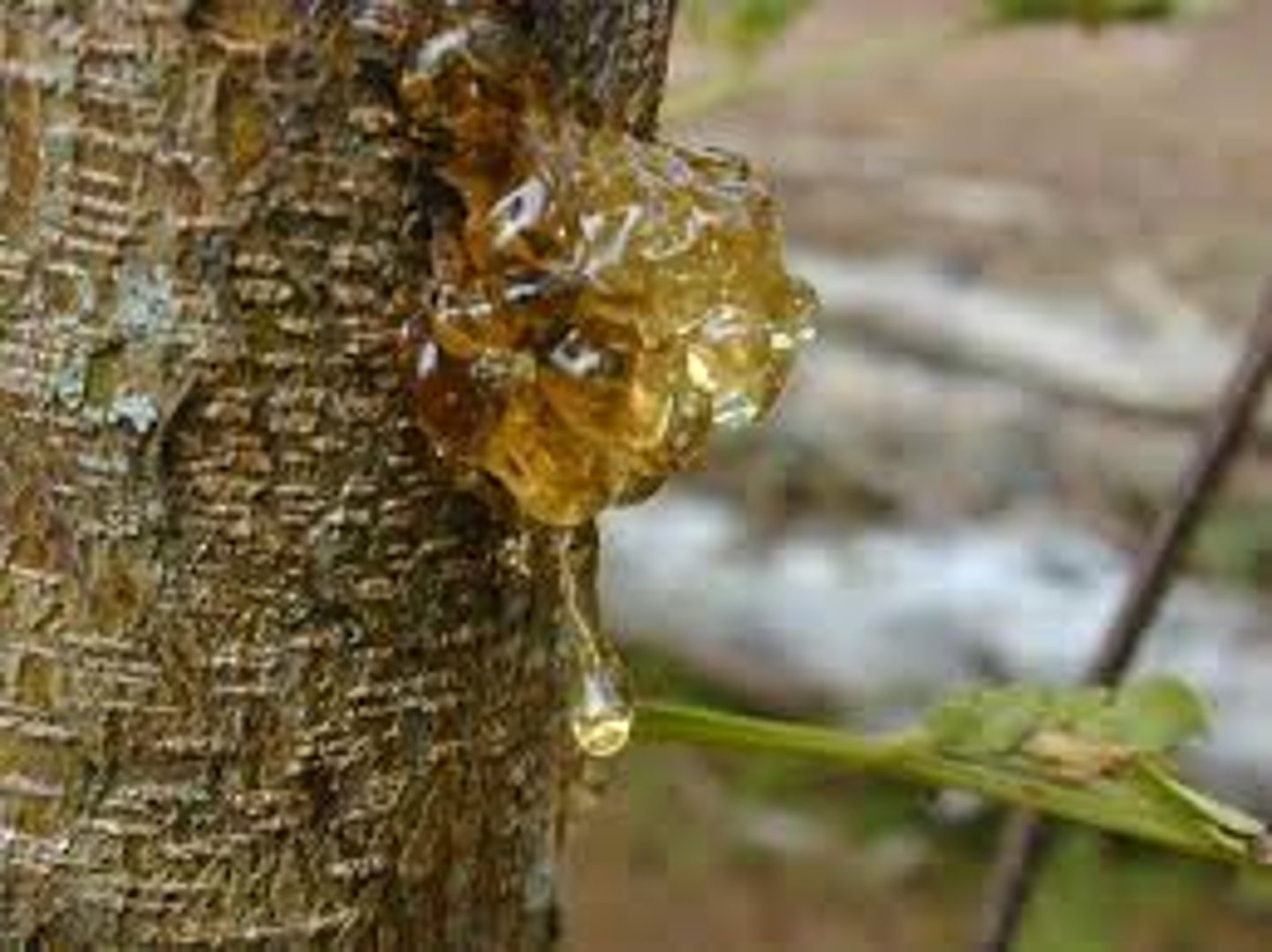
When does sap move?
During the spring

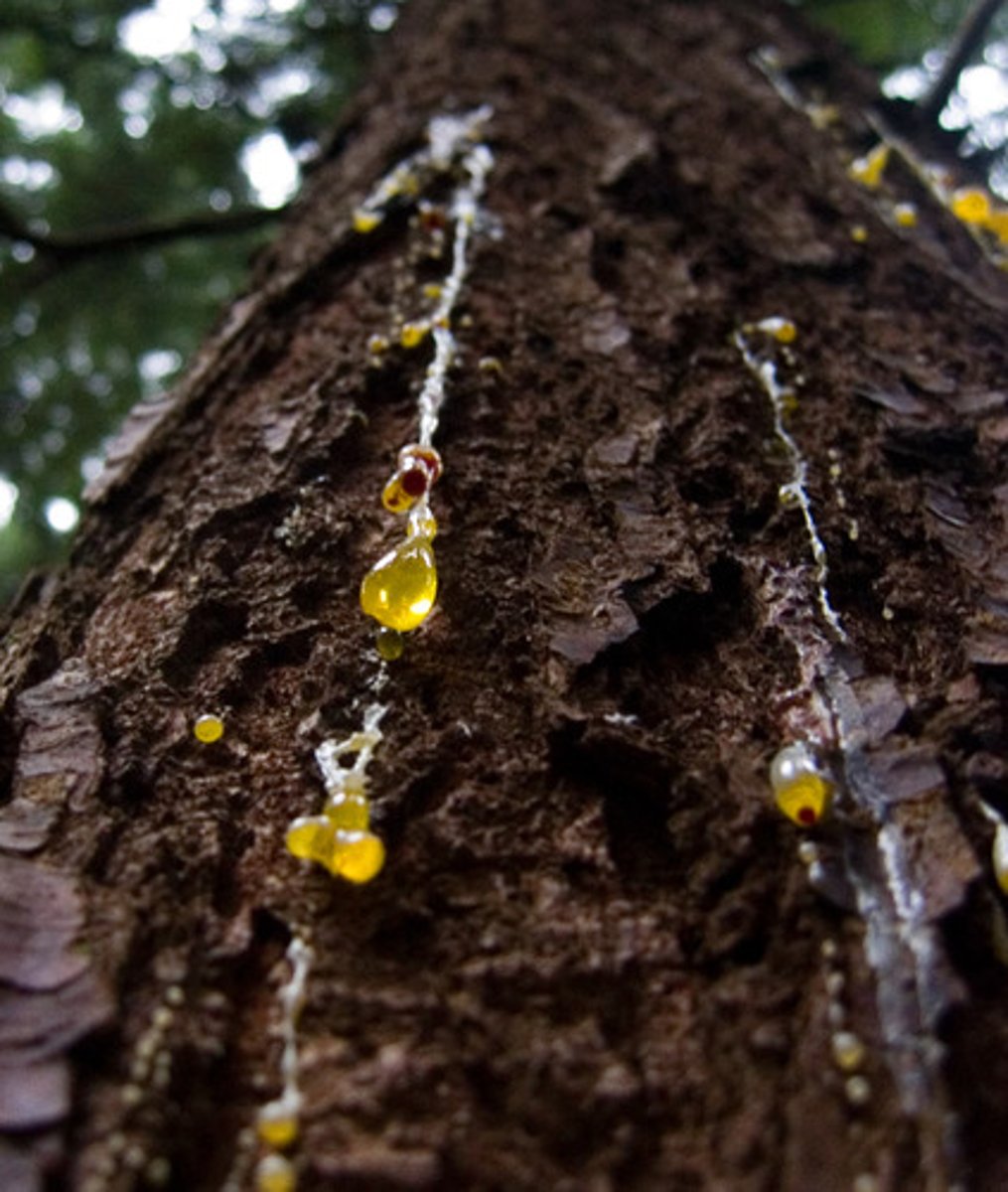
Why is sap needed?
For new buds to grow and produce leaves, they need nutrients. Once leaves have grown, they can carry out photosynthesis and obtain their own glucose.

What happens to plants in the summer and fall (nutrients)?
The extra glucose is transported to other tissues or stored in the roots as starch