immuno- L4: antibodies and humoral immunoresponse
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
humoral immune response
cell-mediated immune response
what are the 2 adaptive immune mechanisms?
humoral
are B cells are antibodies involved in the humoral or cell-mediated immune response?
B cells (and antibodies)
what cells are involved in the humoral immune response?
cell-mediated
are T cells involved in the humoral or cell-mediated immune response?
T cells (cytotoxic T cells and T helper cells)
______cells are involved in the cell-mediated immune response
the ability of the immune system to respond more quickly and effectively to specific pathogens that have been encountered previously
what is immunological memory?
immunological memory, a function of the humoral immune system
in the first attack of measles, adaptive immunity is too slow to prevent the virus from growing and causing symptoms. however, in a second attack, and antibody response is made so rapidly that the virus is disposed of before symptoms appear. this is an example of ...
memory T cells
B cells
antibodies
what cells play a role in immune memory?
-memory cells respond more quickly and aggressively and have an increased number
-memory cells have a different gene expression profile (ex- memory CD8 T cells have more mRNA of perforin than naive T cells)
- memory cells are more mobile (because there is a different pattern of expression of surface proteins that allow this)
-memory cells are able to maintain their number by continual low level proliferation
what are the differences between memory cells and naive cells?
antibodies
B cell receptors
T cell receptors
MHC
what are the immune recognition molecules?
antigens select and stimulate lymphocytes carrying receptors that are specific for that antigen- the selected lymphocytes proliferate more so are more concentrated
what is Burnet's "clonal selection" theory?
Burnet's "clonal selection" theory-
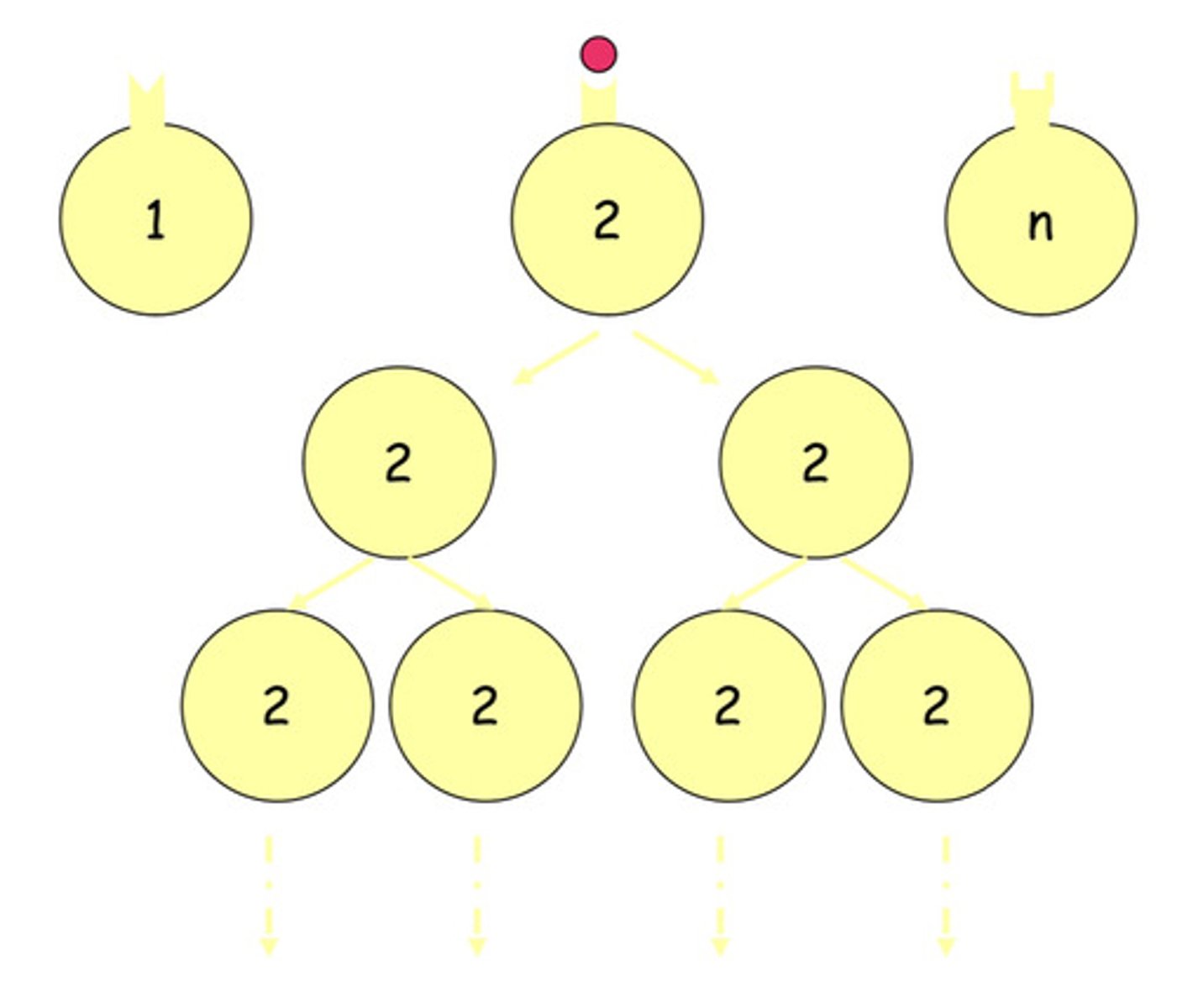
because lymphocyte 2 has the receptor for the antigen, it is selected and therefor proliferates
what theory represented here?
1. a B cell binds to the antigen for which it is specific
2. B cell proliferates and some become plasma cells or memory cells (usually with stimulation from a T helper cell)
3. the plasma cells proliferate and produce antibodies against the antigen
4. the memory cells can respond to any secondary encounter with the same atigen
describe the mechanism of the humoral immune response
1. a T cell binds to the MHC antigen complex on the surface of the infected cell, activating the T cell
2. activation of T cell releases cytokines which enhances to action of macrophages
3. CD8 T cells become cytotoxic T cells, which induce apoptosis of the target cell
describe the mechanism of the cell-mediated immune response
1. directly binding to the antigen (which does NOT induce antibody production)
2. binding to T helper cells
what are the 2 ways that a B cell can be activated?
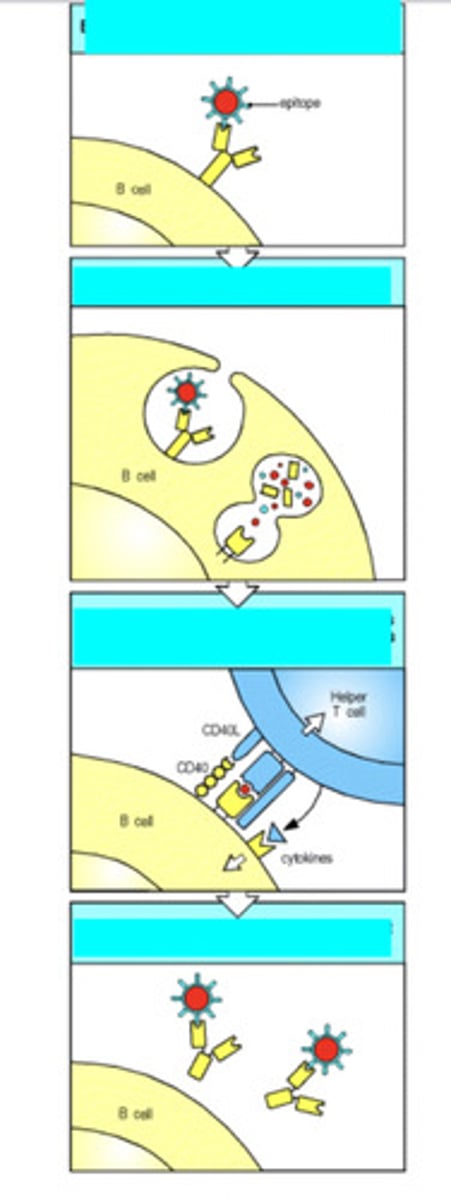
1. the B cell Ig recognizes the epitope on the viral cell
2. the B cell internalizes and degrades the virus
3. peptides from the ingested virus go to the B cell surface (bound to MHC II) and are presented to the T cell, which activates the B cell
4. now, the B cell produces antibodies against the protein
explain what is occurring here
the T helper cell that has previously encountered an antigen binds to the B cell. it expresses CD40, which is the B cell stimulatory molecule, and secretes IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, which cause proliferation and differentiation of the B cell
explain what is occurring here
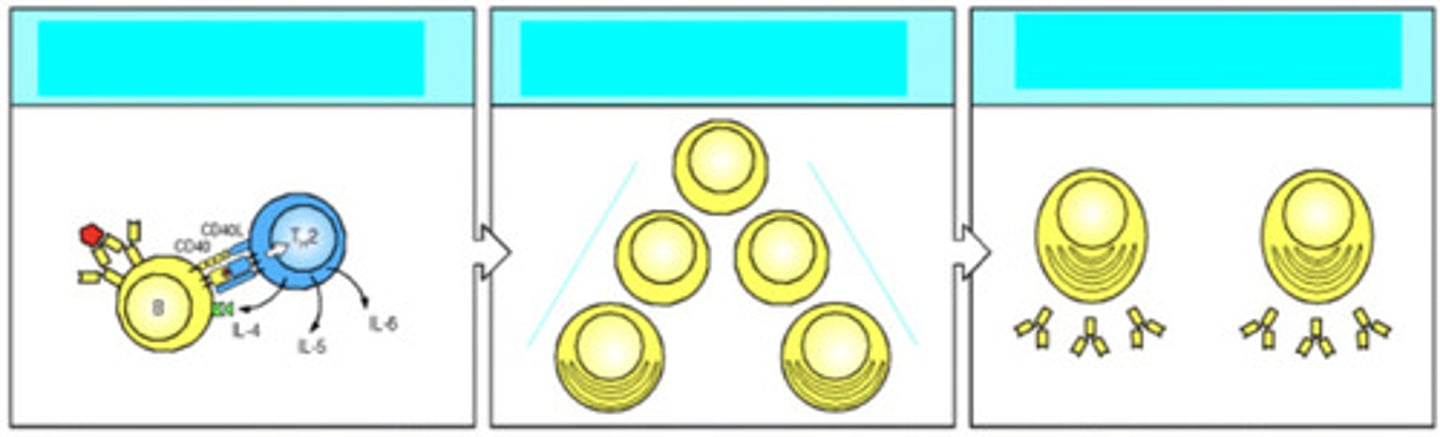
secreted by T helper cell in order to cause differentiation and growth of a B cell
what do IL-4 and IL-5 do, and who secretes them?
-regulates construction of antigen receptor
-ensures each cell only has one specificity
-checks and disposes of self reactive B cells
-exports useful cells
-provides a site of antibody production
what are the roles of the bone marrow in B cell development?
when it makes contact with developing B cell
what makes stromal cells of the bone marrow secrete cytokines that aid in B cell development?
this contact triggers the stromal cell to secrete cytokines that further aid in the development/maturation of the B cell
when the stromal cells of the bone marrow make contact with a developing B cell, what happens?
stimulated B cells
plasma cells develop from ________
lymph node cortex and paracortex, and marginal zones of the spleen
where are plasmablasts located in the body?
secrete Ig (antibody) molecules (up to 10,000 per second)
what do plasma cells do?
no
do plasma cells divide?
no, they die within a few days
are plasma cells long lived?
neutrilization of bacteria
opsonization
complement activation
what are the 3 roles of the antibodies released by plasma cells?
plasma cells
antibodies are secreted by....
adaptive
are antibodies a product of innate or adaptive immunity?
a unique antigenic epitope
antibodies are made specifically to bind to ....
yes, so that different antibodies can bind
can a virus have different antigenic determinant sites?
the number of binding sites it has
what is the valence of an antibody?
usually 2
how many binding sites does an antibody have?
monomer
Y shaped
4 protein chains- 2 light and 2 heavy
sections at the end of Y arms have antigen binding sites
the stem of the Y and lower arms are the constant region
the Fc region at the stem of the Y is where the Ab can bind to complement or cells
what is the structure of an antibody?
the end of the arms of the Y
which part of the antibody has antigen binding sites?
the stem of the Y
which part of the antibody is able to bind to cells/complement?
lower arms and stem of Y
which part of the antibody is the constant region?
blue
which part (color) is the constant region?
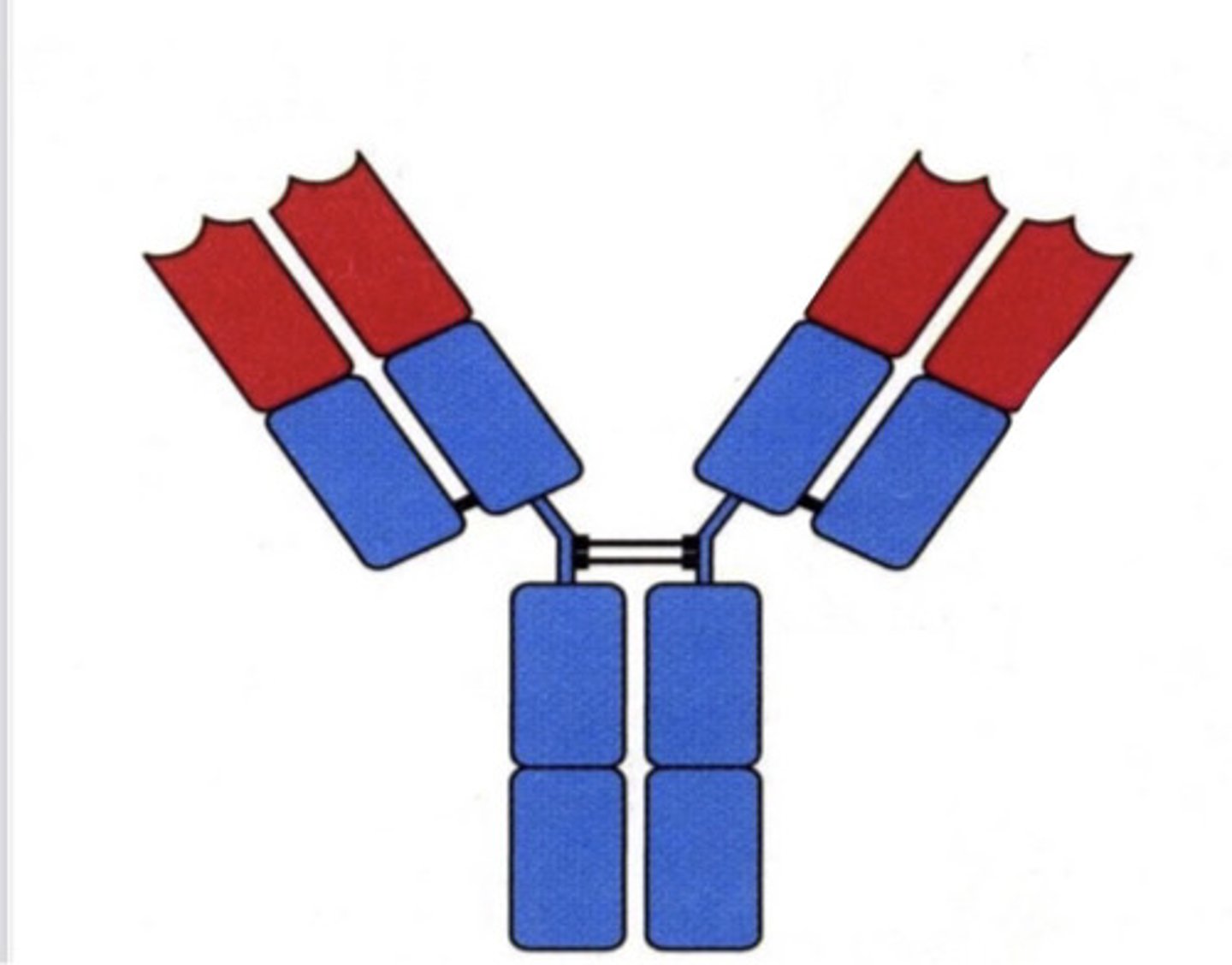
red
which part (color) is the antigen binding site?
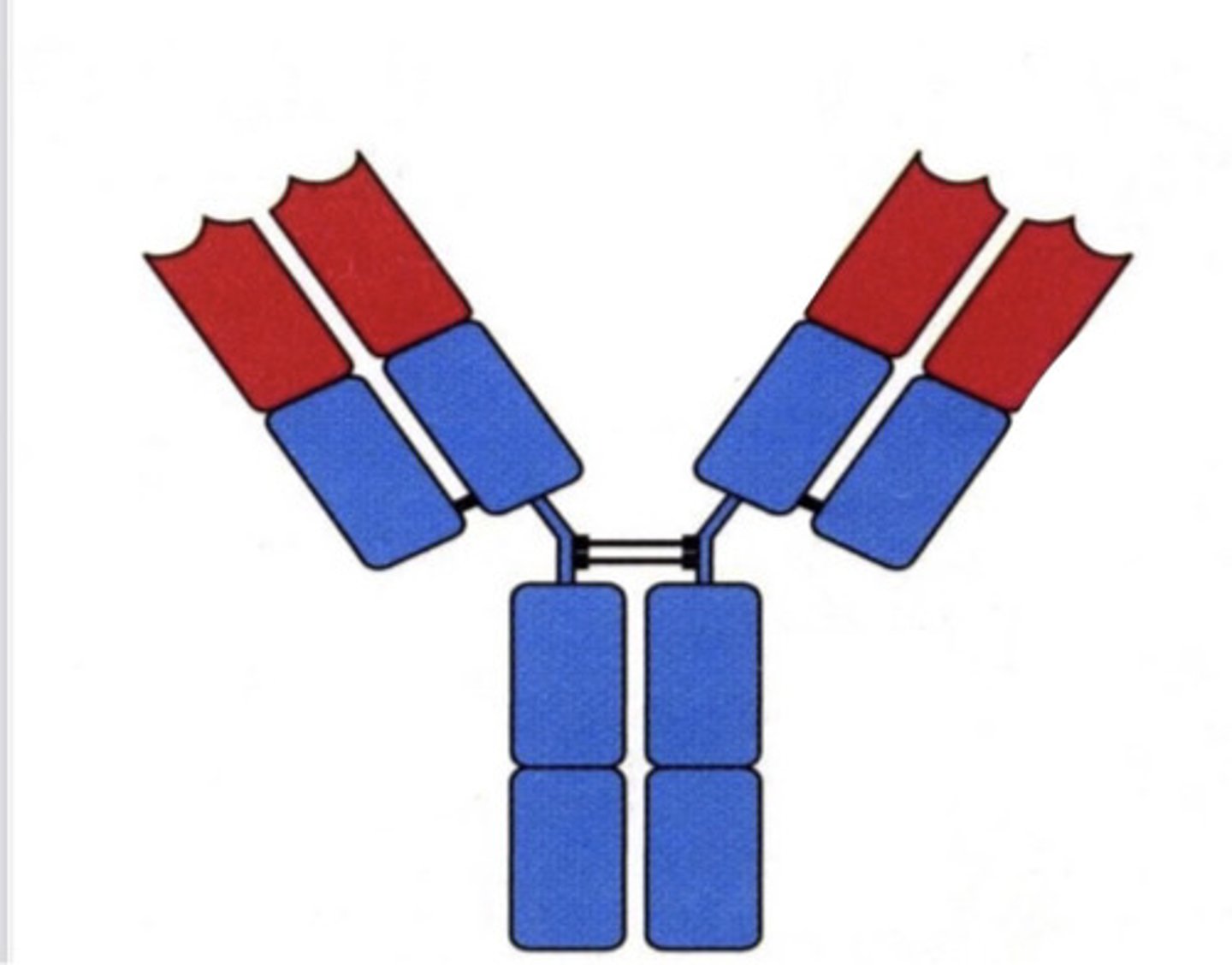
an antibody
what is this?
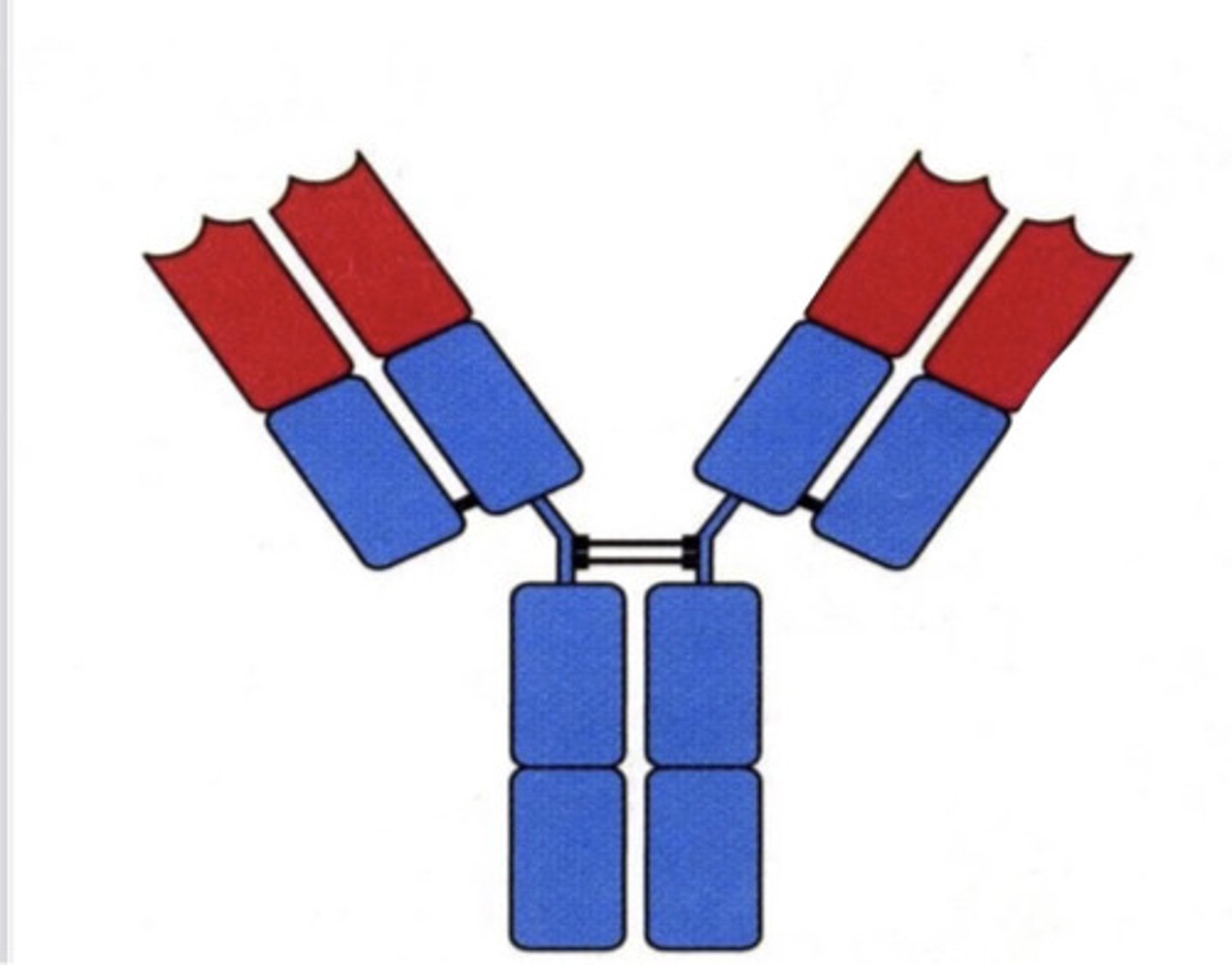
the lower blue part (stem)
which part can bind to cells/complement?
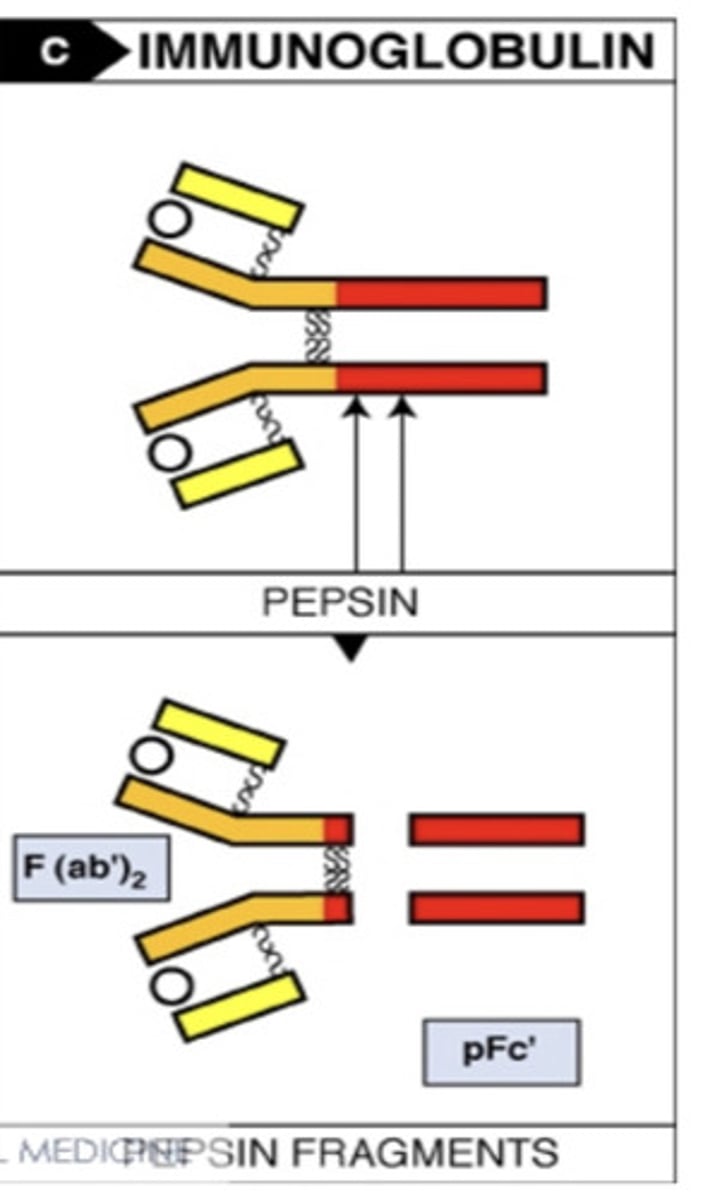
2 antigen binding fragments
when the papain cleavage breaks to the disulfide bonds at the hinge region, it results in..
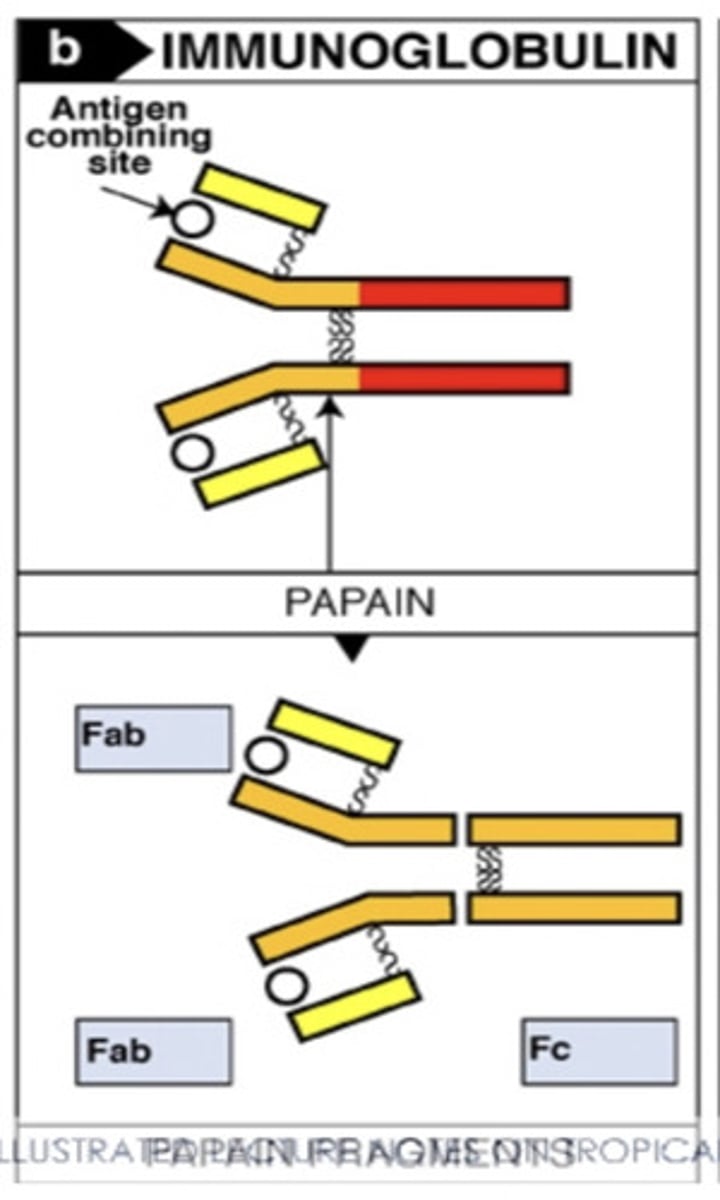
F (ab')2 molecules connected, and the rest fragments
when the pepsin cleavage breaks the antibody below the disulfide bond, it results in ...
IgG
what Ig is the major antibody of the secondary immune response?
IgG
which Ig is the only Ig that can pass through the placenta and protect the fetus/newborn?
enhance phagocytosis
neutralize toxins and viruses
protect fetus and newborn
what are the functions of IgG?
IgM
what Ig is the first antibody produced during an infection?
IgM
which is the "early antibody"?
IgM- composed of 5 Y structures
which Ig is this?
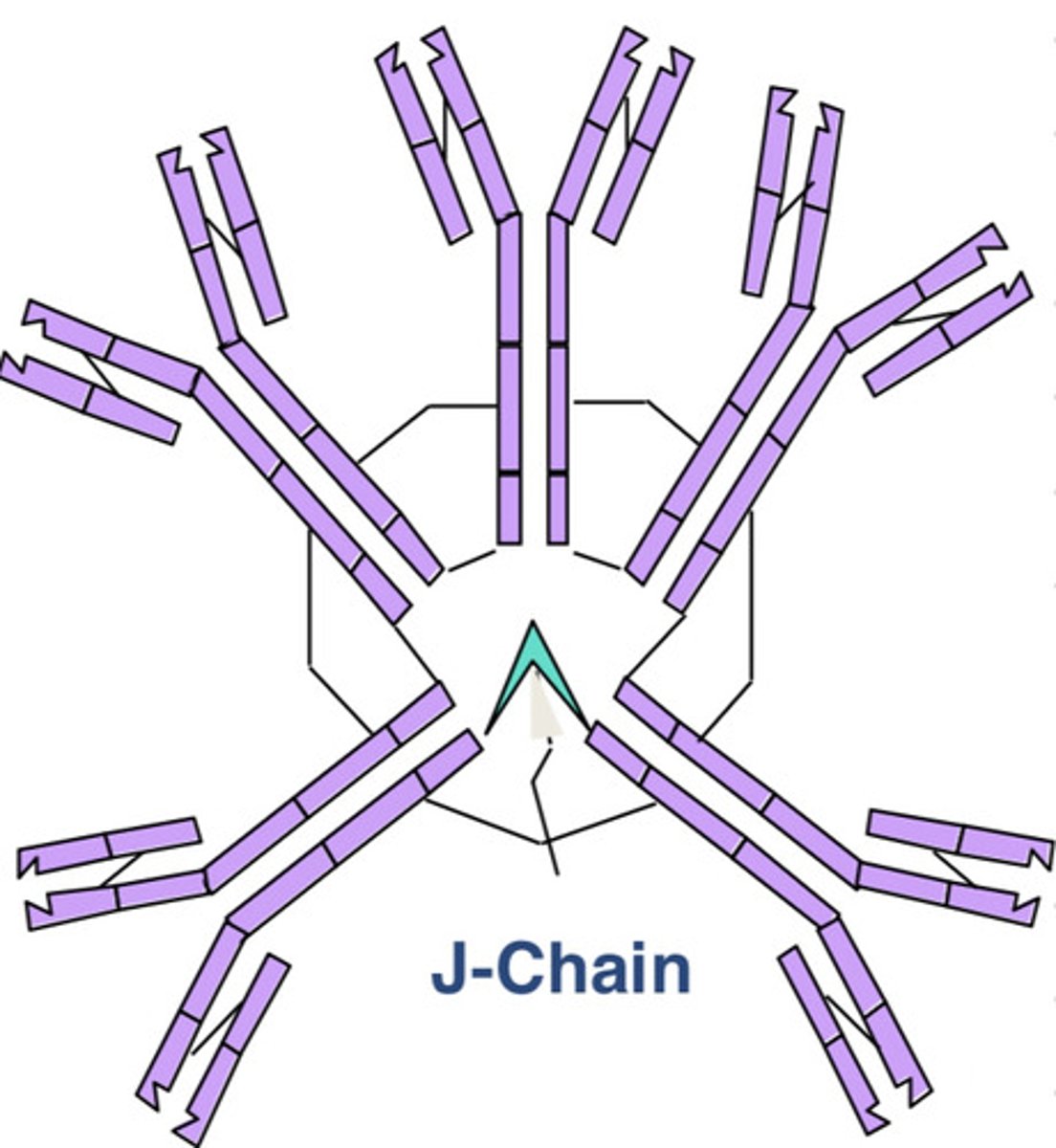
when the pathogen invades
when are IgM produced?
protects mucosa surfaces
provides immunity to the GI tract
what is the role of IgA?
IgA
which Ig provides immunity to the GI tract?
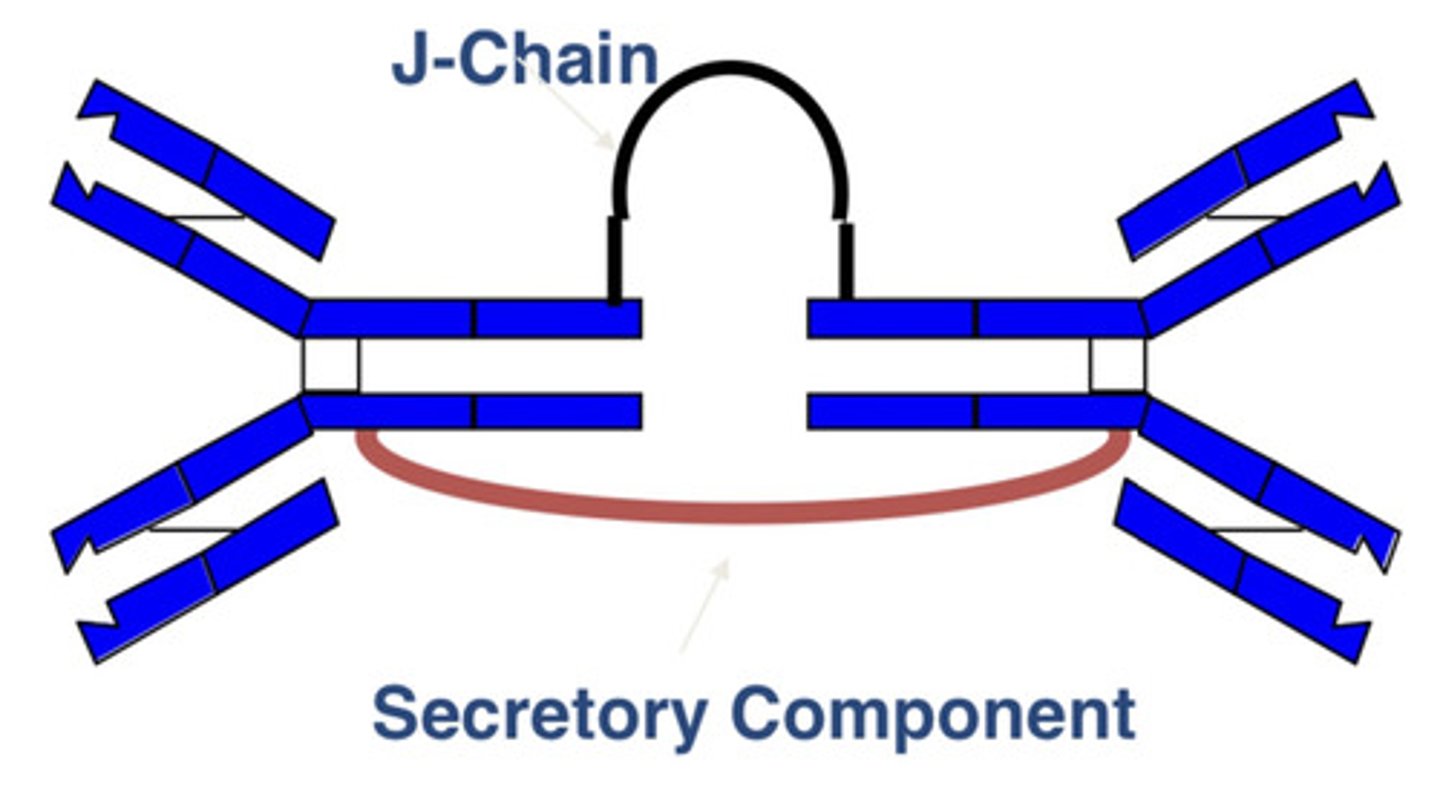
sIgA (secretory IgA)
what is the major Ig of secretions?
sIgA (secretory IgA)
what is this?
IgD
which Ig induces antibody production?
induce antibody production- initiate immune response by B cells
what is the main role of IgD?
IgE
which Ig is the main in allergic response?
IgE
which Ig is important in the lysis of worms/parasites?
lysis of parasites/worms
allergic reactions
what are the roles of IgE?
IgG
which is the most concentrated Ig?
IgE
which is the least concentrated Ig?