SOCI 250
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/182
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:14 AM on 12/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
183 Terms
1
New cards
structural functionalism
crime has a purpose in society
* creates jobs
* teaches a moral compass (boundary/rule clarification)
* group unification
* aids in social adaptation/change
* **Emile Durkheim**
* ex. robbery frequency determines level people protect their possession
* creates jobs
* teaches a moral compass (boundary/rule clarification)
* group unification
* aids in social adaptation/change
* **Emile Durkheim**
* ex. robbery frequency determines level people protect their possession
2
New cards
latent functions of criminal behaviour
unintended/unrecognized consequences of social phenomenon
* ex. abortion laws causing an increase in illegal abortions
* ex. abortion laws causing an increase in illegal abortions
3
New cards
manifest functions of criminal behaviour
intended/recognized consequences of social phenomenon
* ex. abortion laws causing more babies born
* ex. abortion laws causing more babies born
4
New cards
anomie
state of normlessness in society - behaviour is unknown
* **Emile Durkheim**
* ex. being stranded on a deserted island
* **Emile Durkheim**
* ex. being stranded on a deserted island
5
New cards
strain theory
discrepancy between social goals/aspirations and legitimate capacity to achieve those goals
* **Robert Merton**
* crime results from unfulfilled human aspiration
* ex. wanting to go to college, but can’t afford tuition
* **Robert Merton**
* crime results from unfulfilled human aspiration
* ex. wanting to go to college, but can’t afford tuition
6
New cards
*Delinquency and Opportunity* by Richard Cloward and Lloyd Ohlin (1960)
there is a differential availability of illegitimate means
* focuses on low-income communities - who you know and what is available
* strain is caused by the position discontent of an individual
* 3 distinct gang subcultures:
* criminal gang: environments that foster criminal behaviour
* conflict gang: disorganized environment with neither legitimate or illegitimate instruction
* retreatist gang: progression of failures at innovating
* focuses on low-income communities - who you know and what is available
* strain is caused by the position discontent of an individual
* 3 distinct gang subcultures:
* criminal gang: environments that foster criminal behaviour
* conflict gang: disorganized environment with neither legitimate or illegitimate instruction
* retreatist gang: progression of failures at innovating
7
New cards
*Delinquent Boys: The culture of the gang* by Albert Cohen (1955)
* culture has a significant effect on deviant behaviour among young boys
* culture can determine behaviour, beliefs, interests, prejudices
* school culture caters to middle-class academic
* culture can determine behaviour, beliefs, interests, prejudices
* school culture caters to middle-class academic
8
New cards
Walter Reckless - containment theory (1961)
* inner and outer self control affects person’s likelihood to commit crime
* ex. personal sense of right and wrong
* inner containment - strong is:
* self-concept
* goal direction
* tolerance of frustration
* identification with lawful norms
* ex. personal sense of right and wrong
* inner containment - strong is:
* self-concept
* goal direction
* tolerance of frustration
* identification with lawful norms
9
New cards
Focal Concerns
socialization into cultural beliefs/values determines crime in delinquent boys
* Walter Miller (1958)
* 6 concerns:
1. trouble: excitement and toughness
2. toughness: prove themselves
3. smartness: street smarts
4. excitement: seek out thrills
5. fate: their future is already decided
6. autonomy: independent
* Walter Miller (1958)
* 6 concerns:
1. trouble: excitement and toughness
2. toughness: prove themselves
3. smartness: street smarts
4. excitement: seek out thrills
5. fate: their future is already decided
6. autonomy: independent
10
New cards
*Crime and the American Dream* by Steven Messner and Richard Rosenfeld (1993)
social institutions have consistently failed to make American Dream of economic success possible through legitimate means
* Strain Theory
* Strain Theory
11
New cards
Life-course Developmental Theory (Nagin, Farrington and Moffitt, 1995)
quality and quantity of social bonds fluctuate over our lives, and can have effect on crime committed
* weak ties are important (jobs, opportunities)
* troubled family and friend life as a youth can have lifelong effects
* affected by turning points in life
* weak ties are important (jobs, opportunities)
* troubled family and friend life as a youth can have lifelong effects
* affected by turning points in life
12
New cards
social ecology
social disorganization theory, differential social organization
13
New cards
social disorganization theory
ecological differences in levels of crime in different neighbourhoods are based on structural/cultural factors shaping social order
* ex. self regulations in rural communities
* ex. self regulations in rural communities
14
New cards
differential social organization
crime rate of group is determined by extent to which group is organized in favour or against crime
* ex. growing up in a gang family
* ex. growing up in a gang family
15
New cards
*The Polish Peasant in Europe and America* by Florian Znaniecki and William Thomas (1920)
discussed why crime rates increased dramatically when Poles immigrated to US
* strain theory - racism, language barrier, skills
* environment changed, they didn’t bring crime with them
* factors contributing to neighbourhood character
1. degree of cultural heterogeneity
2. high degree of mobility
3. no development of community base
* strain theory - racism, language barrier, skills
* environment changed, they didn’t bring crime with them
* factors contributing to neighbourhood character
1. degree of cultural heterogeneity
2. high degree of mobility
3. no development of community base
16
New cards
4 steps to community stability (Robert Park and Ernest Burgess)
1. Invasion
2. Conflict - poor communities don’t get past here
3. Accommodation
4. Assimilation
17
New cards
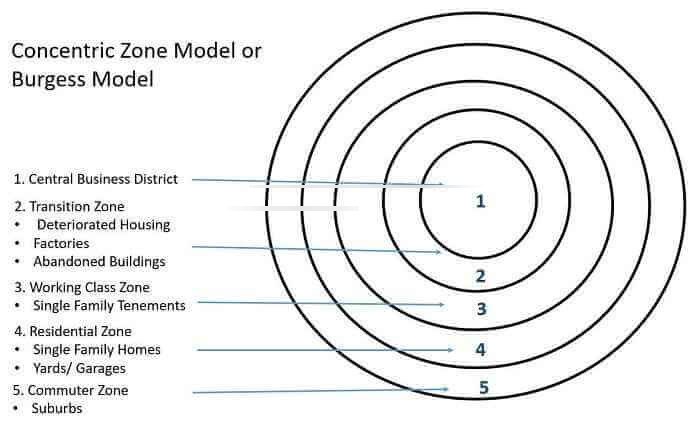
concentric-circle theory
cities develop from inner city to suburbs in concentric rings
* each has set of environmental/social characteristics
* Ernest Burgess (1925)
* each has set of environmental/social characteristics
* Ernest Burgess (1925)
18
New cards
Oscar Newman - Defensible Space
good spaces = safe environment
* crime prevention through environmental design
* spaces should not attract crime or generate fear
* crime prevention through environmental design
* spaces should not attract crime or generate fear
19
New cards
conventional crime
crime classified in criminal code/agreed upon as bad
20
New cards
larceny
unlawful taking/carrying away of property belonging to another individual
* shoplifting
* shoplifting
21
New cards
breaking and entering
unlawful entry of a structure to commit a felony/theft
* nothing has to be stolen to lay charge
* breaking in and stealing something = charged with two crimes
* no direct confrontation
* three categories: residential, business, non-residential private structures
* more b&es happen in summer
* rational choice theory
* nothing has to be stolen to lay charge
* breaking in and stealing something = charged with two crimes
* no direct confrontation
* three categories: residential, business, non-residential private structures
* more b&es happen in summer
* rational choice theory
22
New cards
criminal distance theory
observed relationship between distance of target from offender’s home and likelihood the offender will attack
23
New cards
crime clearance rates
proportion of reported crimes solved by police
24
New cards
crime displacement effect
crime is not actually prevented, criminal moves to another target
* ex. home security
* ex. home security
25
New cards
robbery
theft of another’s property with threat of physical violence against victim
* includes commercial, highway, street, armed, strong-armed, drug-related robbery, and home invasion
* includes commercial, highway, street, armed, strong-armed, drug-related robbery, and home invasion
26
New cards
robbery trends
* most robbers only commit robbery as a crime
* 90% committed by young men
* money most commonly stolen
* 90% committed by young men
* money most commonly stolen
27
New cards
explaining robbery
* high unemployment among young men
* learning theory: opportunistic vs professional robbers, often start young
* learning theory: opportunistic vs professional robbers, often start young
28
New cards
assault
unlawful physical harm committed against victim
29
New cards
level 1 assault
no serious bodily harm intended/inflicted
* 85% of assault charges laid
* 85% of assault charges laid
30
New cards
level 2 assault
use of weapon, infliction of bodily harm
* 10% of all assault charges laid
* 10% of all assault charges laid
31
New cards
level 3 assault
intention to commit serious bodily harm (aggravated assault)
* 5% of assault charges
* 5% of assault charges
32
New cards
low crime
get caught quickly, sporadic
33
New cards
middle crime
some knowledge/planning beforehand
34
New cards
high crime
don’t get caught quickly
35
New cards
Cybercrime
illegal activity using computer equipment/technology
* ransomware, revenge porn, identity theft, fraud (most), bullying, criminal harassment, intimidation
* ransomware, revenge porn, identity theft, fraud (most), bullying, criminal harassment, intimidation
36
New cards
cybercrime trends
* costs Canada $5 billion/yr
* rapidly accelerating and increasing
* younger generations are more conscious of online presence
* rapidly accelerating and increasing
* younger generations are more conscious of online presence
37
New cards
fraud
unlawful use of cheating or deception to obtain something of value
* mostly committed out of economic need
* done by individuals or
* mostly committed out of economic need
* done by individuals or
38
New cards
7 deadly sins hackers exploit
1. apathy
2. curiosity
3. gullibility
4. courtesy
5. diffidence
6. greed
7. thoughtlessness
39
New cards
lifestyle exposure theory
probability of victimization varies by time, space, social setting
* amount of time spent in public spaces, type of neighbourhood, time of day, amount of time spent with non-family members
* Hindelang, 1978
* amount of time spent in public spaces, type of neighbourhood, time of day, amount of time spent with non-family members
* Hindelang, 1978
40
New cards
equivalent groups hypothesis
offender and victim share similar characteristics
41
New cards
proximity hypothesis
some people put themselves at risk by choosing a high-risk lifestyle - bad choices
42
New cards
deviant place hypothesis
some areas are more conductive to criminal activity
43
New cards
routine activity approach (Lawrence Cohen and Marcus Felson)
crime is a rational choice - occurs when 3 elements converge:
1. motivated offender
2. suitable target
3. absence of capable guardian
1. motivated offender
2. suitable target
3. absence of capable guardian
44
New cards
corporate crime
committed by high profile groups/businesses to max profits illegally - high class individuals with legitimate corporate fronts
* crimes against economy, crimes against the environment, crimes against consumers, crimes against employees
* ex. child labour, offshore accounts, opioid crisis, tax evasion, illegal dumping, poaching, market manipulation
* no standard legal definitions
* crimes against economy, crimes against the environment, crimes against consumers, crimes against employees
* ex. child labour, offshore accounts, opioid crisis, tax evasion, illegal dumping, poaching, market manipulation
* no standard legal definitions
45
New cards
white-collar crime
illegal activities conducted by employees and officers for personal gain or benefit of the company
46
New cards
victimless crime
no identifiable victim - activity is consensual or directed against a corporate entity
47
New cards
G10
group of 10 - participate in general arrangements to borrow
* Canada is part of it
* Canada is part of it
48
New cards
regulating corporate crime
* poorly enforced, ineffective deterrents
* dealt with as fraud or embezzlement
* typical punishment rationale is retribution and just deserts
* dealt with as fraud or embezzlement
* typical punishment rationale is retribution and just deserts
49
New cards
50
New cards
ponzi scheme
promise high return rate by giving away other ponzi scheme people’s money
51
New cards
corporate criminal
person of respectability and high social status in course of their occupation (Edwin Sutherland, 1949)
* high status allows access to materials, power to fire, invisibility, afford legal team
* high status allows access to materials, power to fire, invisibility, afford legal team
52
New cards
tax evasion
1. bank country residency
2. non-domestic status
3. corporate accounts
4. bank account in other country
5. smuggle cash
53
New cards
The Paradise Papers
leaked info about offshore accounts for many major businessmen and figures
54
New cards
Competition Act (1889) - Canada
An Act to provide for the general regulation of trade and commerce in respect of conspiracies, trade practices and mergers affecting competition
55
New cards
crimes against the economy
violations that contravene federal/provincial statutes
* goal is to make the most money
* tax evasion, stealing patents, buying up small businesses, violations of regulations governing stock market
* goal is to make the most money
* tax evasion, stealing patents, buying up small businesses, violations of regulations governing stock market
56
New cards
crimes against environment
corporate practices resulting in pollution, depletion, degradation of environment
* oil spills, improper disposal of hazardous environment, illegal denuding of land, improper safety mechanisms
* oil spills, improper disposal of hazardous environment, illegal denuding of land, improper safety mechanisms
57
New cards
crimes against consumers
activities aimed at gaining extra profit at expense of consumers'
* price fixing, deceptive advertising, marketing/selling defective products
* price fixing, deceptive advertising, marketing/selling defective products
58
New cards
crimes against employees
physical harm, inhumane employment conditions, arbitrary dismissal
59
New cards
crimes against humanity
legal activities but violate accepted human values
* labour practices in 3rd world countries
* establishment of free trade zones
* labour practices in 3rd world countries
* establishment of free trade zones
60
New cards
external causes of corporate crime
* environmental uncertainty
* market structure
* strain
* culture of competition
* market structure
* strain
* culture of competition
61
New cards
internal causes of corporate crime
* internal organization control (upper class are willing to take more risks, more likely to be punished)
* individual control
* techniques of neutralization
* individual control
* techniques of neutralization
62
New cards
what creates internal opportunity for corporate crime?
* high turnover of mid-level managers (don’t know what to look for in workplace culture)
* too much financial authority resting with only a few senior managers
* inadequate channels for reporting crime
* unhappy workers - want to damage the company
* too much financial authority resting with only a few senior managers
* inadequate channels for reporting crime
* unhappy workers - want to damage the company
63
New cards
Barriers to combatting corporate crime
* dismissing it as a victimless crime
* corporate crimes are laundered through (pro-business ideology, don’t want to cut revenue/funding)
* definitions are varied
* absence of reliable data
* corporate crimes are laundered through (pro-business ideology, don’t want to cut revenue/funding)
* definitions are varied
* absence of reliable data
64
New cards
explaining corporate crime
1. differential association
2. conflict theory
3. neutralization: temporary neutralization of values preventing someone from committing crime
4. culture of denial: extent of corporate crime is unknown
5. stress/strain
65
New cards
**learning perspective**
deviance is learned from other people - primarily psychology based
* deviance is highly relative, deliberate, and intentional (actively sough out and learnt)
* deviance is highly relative, deliberate, and intentional (actively sough out and learnt)
66
New cards
types of learning deviance
1. contextualized: associative subcultural theory
2. indirect-imitative learning
3. informal learning
4. formal instruction
67
New cards
**Imitation theory of crime** (Gabriel Tarde, 1890)
3 laws of imitation
1. law of close contact
2. law of imitation of superiors by inferiors
3. law of insertion
1. law of close contact
2. law of imitation of superiors by inferiors
3. law of insertion
68
New cards
**differential association** (Edwin Sutherland, 1947)
association with different groups leads to crime
* deviance occurs when individuals feel a situation is appropriate for stepping beyond normative boundaries - innovation
* deviance socially learned through frequent negative influences
* psychology + symbolic interactionism
* deviance occurs when individuals feel a situation is appropriate for stepping beyond normative boundaries - innovation
* deviance socially learned through frequent negative influences
* psychology + symbolic interactionism
69
New cards
differential reinforcement theory
crime is learned behaviour reinforced through consequence
* Differential Association variation
* Differential Association variation
70
New cards
differential association-reinforcement
learn social skills through operant conditioning controlled by stimuli following behaviour
71
New cards
micro-level interactions
social-process theories - learning interactions
* differential association, social learning, labelling
* differential association, social learning, labelling
72
New cards
**containment theories**
outer and inner containments are required for a person to develop restrained law-abiding behaviour
73
New cards
personal containment
self-control mechanisms created through socialization
74
New cards
social containment
imposed controls of family, school, popular culture, religion
75
New cards
Ivan Nye - Containment Theory
4 types of control:
1. internal
2. indirect: outer controls - not formal punishments
3. direct: outer controls - formal punishments
4. legitimate needs satisfaction: need to belong has to be fulfilled
1. internal
2. indirect: outer controls - not formal punishments
3. direct: outer controls - formal punishments
4. legitimate needs satisfaction: need to belong has to be fulfilled
76
New cards
containment theory - multi-systemic therapy
focus on parenting skills to treat high risk juvenile offenders to prevent serious crime in the future
77
New cards
containment theory - techniques of neutralization
trying to deny committing a crime to avoid feelings of guilt
1. denial of responsibility
2. denial of injury
3. denial of victim
4. condemnation of condemners
5. appeal to higher loyalties (teaching a lesson)
1. denial of responsibility
2. denial of injury
3. denial of victim
4. condemnation of condemners
5. appeal to higher loyalties (teaching a lesson)
78
New cards
containment theory - drift
deviants can drift in and out of commitment to deviant or dominant values, resulting in episodic deviance
79
New cards
subterranean values
values that exist in society and aren’t talked about
* violence
* violence
80
New cards
**labelling theory**
negative labelling can predispose people to feel like outcasts
* deviance is made worse by labelling and punishment by authorities
* crime is relative
* discrimination and racism hold major significance
* criminalization has to be seen as legitimate by the public
* moral entrepreneurs create laws and norms
* deviance is made worse by labelling and punishment by authorities
* crime is relative
* discrimination and racism hold major significance
* criminalization has to be seen as legitimate by the public
* moral entrepreneurs create laws and norms
81
New cards
moral entrepreneurs
use their power/influence to shape legal system to their advantage - what they believe is a social problem
82
New cards
primary deviance
behaviour running counter to societal norms but not socially recognized or labelled as deviant
* ex. stealing a candy bar from a store
* ex. stealing a candy bar from a store
83
New cards
secondary deviance
deviant behaviour resulting from labelling
84
New cards
gambling
* predominately done by men
* compulsive gamblers often struggle with other addictions/disorders
* compulsive gamblers often struggle with other addictions/disorders
85
New cards
substance abuse
abuse of alcohol/drugs affect sense of public order because of altered behaviour
* alcohol is not regulated like other drugs
* strong link between substance abuse and criminal activity
* alcohol is not regulated like other drugs
* strong link between substance abuse and criminal activity
86
New cards
Safe Streets Act (Bill M 202)
to criminalize vagrant kids
* fine $85-150 for solicitation and have reason to arrest when they didn’t pay fees
* not dealing with root problem - when you have many people in a criminalized group, it's not individual
* fine $85-150 for solicitation and have reason to arrest when they didn’t pay fees
* not dealing with root problem - when you have many people in a criminalized group, it's not individual
87
New cards
containment theory - neoconservative view on crime
* human nature is selfish, weak, hedonistic
* root causes of crime are unimportant
* criminal behaviour largely product of family dysfunction or liberal social values
* soft penalties, rehabilitation, diversion programs don’t help
* street crime is worse than white collar (more fear)
* stiff/long penalties
* root causes of crime are unimportant
* criminal behaviour largely product of family dysfunction or liberal social values
* soft penalties, rehabilitation, diversion programs don’t help
* street crime is worse than white collar (more fear)
* stiff/long penalties
88
New cards
*Thinking About Crime* by James Q. Wilson
first to discuss neoconservatism - police should have power to “rough up” young people
89
New cards
Broken Windows by Wilson and George Kelling
reasonable policing policies include
* maintain community/social order
* increase foot patrols
* increase private security
* quicker trails and more severe penalties
* maintain community/social order
* increase foot patrols
* increase private security
* quicker trails and more severe penalties
90
New cards
victimology
relationship between criminals and victims
* importance of victim first recognized by Benjamin Mendelsohn
* neoconservative origin
* importance of victim first recognized by Benjamin Mendelsohn
* neoconservative origin
91
New cards
Victims Bill of Rights Act
* right to information, protection, participation, restitution
* victim services
* victim impact statement
* victim services
* victim impact statement
92
New cards
victimization surveys
ask respondents if they have been the victim of a crime - those who have are asked about their experiences and impressions of the justice system
* insight into dark figure of crime, prevalence of certain crimes, impact, risk of victimization
* General Social Survey (GSS) - Statistics Canada, Violence Against Women Survey (1993), surveys on family violence (est. 2001), International Crime Victims Survey (1989-2005)
* insight into dark figure of crime, prevalence of certain crimes, impact, risk of victimization
* General Social Survey (GSS) - Statistics Canada, Violence Against Women Survey (1993), surveys on family violence (est. 2001), International Crime Victims Survey (1989-2005)
93
New cards
victim characteristics
* most likely **young** people (15-24), least likely old 65+)
* **women** more likely to be (85 vs 67 per 1000)
* women more likely to be victims of sexual assault and theft
* men more likely to be victims of of robbery and assault
* **higher income homes** more likely to be robbed
* **single people** higher rate of violent victimization
* **Indigenous** over-represented in victimization
* **women** more likely to be (85 vs 67 per 1000)
* women more likely to be victims of sexual assault and theft
* men more likely to be victims of of robbery and assault
* **higher income homes** more likely to be robbed
* **single people** higher rate of violent victimization
* **Indigenous** over-represented in victimization
94
New cards
victim financial compensation
* property loss recovery: find stuff, offender-paid restitution, insurance
* victims of violence: most apply promptly, civil litigation, litigation against government
* victims of violence: most apply promptly, civil litigation, litigation against government
95
New cards
victim assistant programs
* court services: assistance with attending court and dealing with justice system
* public education: information about the law and crime prevention
* crisis intervention: support to those who have experienced a negative impact from crime
* victim-offender reconciliation programs: restorative justice
* public education: information about the law and crime prevention
* crisis intervention: support to those who have experienced a negative impact from crime
* victim-offender reconciliation programs: restorative justice
96
New cards
victim precipitation theory
some people make themselves targets for victimization through actions or inaction
* victim blaming
* victim blaming
97
New cards
secondary victimization
insensitive, victim-blaming, trauma-compounding behaviour towards victims of violence
* leads to reluctance to seek help
* leads to reluctance to seek help
98
New cards
victim impact statements
statement presented by victim during sentencing to describe personal impact of crime
99
New cards
critical criminology
intersectionality of politics and crime
* criminal categories created/defined in Western society to maintain social order and power of privileged
* social difference politicized
* current laws are ineffective
* media representation of crime is biased and sensationalized
* police presence had no effect on crime rates
* criminal categories created/defined in Western society to maintain social order and power of privileged
* social difference politicized
* current laws are ineffective
* media representation of crime is biased and sensationalized
* police presence had no effect on crime rates
100
New cards
social development approach
community-based public education used to inform people of risks to their safety to take steps in avoiding becoming victims of crime