week 9 pt.2 and week 10 (confidence intervals)
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
interpretation and significance
reject the null or fail to reject (not accepting the null hypothesis)
statistical significanceL there was enough statistical evidence to reject the null
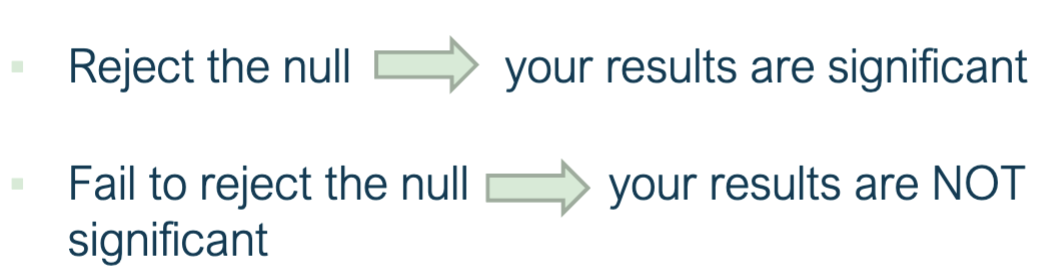
interpretation example

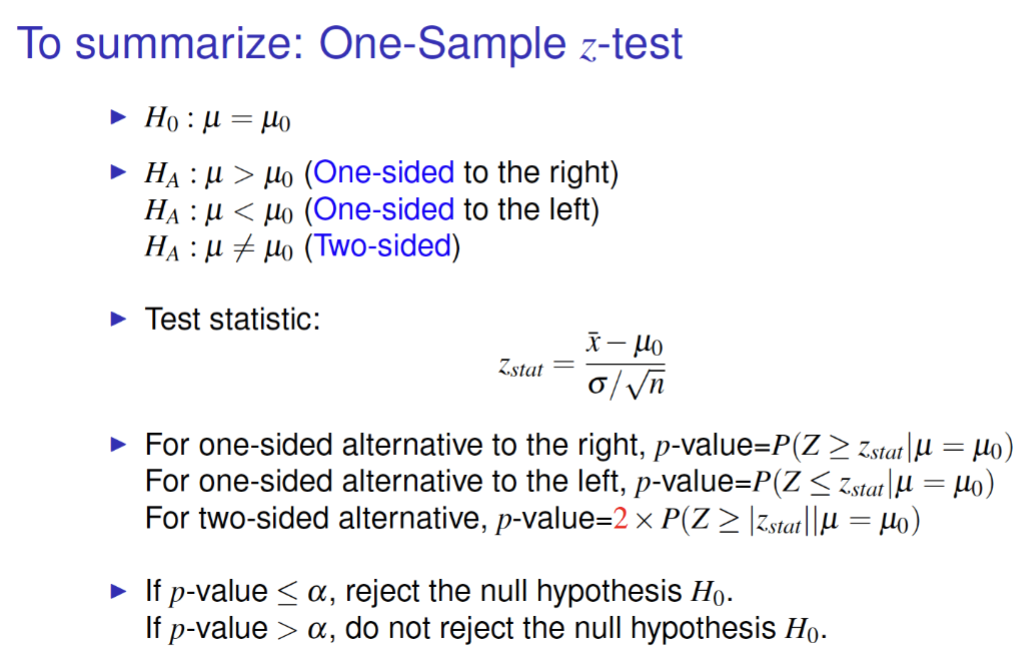
summary: one sample z-test
intervel estimation
not the same as hypothesis testing (inferences of sample to a population
interval estimation: involves generating point and interval estimates
point estimates are the calculation of a SINGLE statistic
confidence intervals
confidence represents your studies ability to correctly retain (fail to reject) the null when the null is true
success rate of the method
CI of the mean is used to make an interval estimation of the population mean from the sample data
confidence = 1- alpha =
we want high confidence
MEANINGS:
95% CI: We believe would contain the true population mean and 5 would not
to calculate CI: margin of error
margin of error: the distance from the center (point estimate) of the interval
A. for e 2 sided test: z value equal to one (z1-a/2)
for a 2 sided test at a=0.05 → ±1.96 for 95% CI
CONFIDENCE INTERVAL LENGTH of 2 sided interval: L = 2m
2 times the margin of error
for a 2 sided test: (larger sample size is better)
larger SD → larger margin/length (larger CI since larger cl results in larger critical value of the statistic)
larger sample size →
confidence interval and interpretation
interval: (lower limit, upper limit)
CL: xbar sample mean -
interpretation: