CHEMISTRY ATOMIC STRUCTURE
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemistry- y12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What was Dalton’s model?
An indivisible solid sphere, surrounded by an atmosphere of heat.
What was Thompson’s model?
Rings of electrons randomly embedded in a ball of positive charge. He discovered electrons.
What did the gold foil experiment determine? (Rutherford-Nucelar model)
That an atom is made up of mostly empty space. He believed the mass of the atom was concentrated in the small positively charged nucleus, that had electrons surrounding it.
What did Niels Bohr discover? (Plentary model)
Electrons orbit the nucleus in distinct energy levels at specific distances to the nucleus.
What is the atomic structure now?
A central, dense, positive nucleus containing protons and neutrons surrounded by orbiting electrons in energy levels. Most of an atom's mass is concentrated in the nucleus.
What is the mass number (A)
The number of protons + neutrons in the nucleus.
What is the atomic number? (Z)
The number of protons in the nucleus. It is unique to each element.
What is an isotope?
Atoms which have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
What is an atom?
The smallest particle of an element that still has properties of that element
What is an ion?
A charged particle.
What are the 2 properties of isotopes?
They have similar chemical properties as the have the same number of valence electrons and protons + Slightly different physical properties due to different masses.
How do you calculate the mass of one particle?
Mass of one particle = Mass of 1 mole (relative mass)/ number of particles in 1 mole (6.022×1023 )
What is the function of the TOF Mass Spectrometry
Find the abundance and mass of all isotopes present in an element to determine its Ar.
Find the relative molecular mass made of substances made of molecules.
Time of flight (ToF) mass spectrometry basic overview
Particles of the same substance are ionised to form 1+ ions which are accelerated so they all have the same kinetic energy. The time taken to travel a fixed distances is then used to find the mass of each ion in the sample
Why is TOF Mass Spectrometry kept under a high vacuum?
To prevent the ions that are produced from colliding with molecules present in the air.
Why does a sample need to be ionised in a ToF mass spectrometer?
1. Ions, not atoms, will interact with and be accelerated by an electric field
2. Only ions will create a current when hitting the detector
How does Electrospray Ionisation work?
The sample is dissolved in a volatile and polar solvent.
Injected at high pressure through a fine hollow needle connected to the positive terminal of a high voltage supply.
The particles are ionised by gaining a proton (H+ ) from the solvent, forming XH+ ions.
X (g)+ H+ —> XH+(g)
The solvent evaporates into the vacuum while the XH+ ions do not.
Why is Electrospray ionisation used with large organic molecules?
Because fragmentation does not occur.
How does Electron Impact work?
The sample being analysed is vaporised and injected at low pressure.
An electron gun fires high energy electrons at the sample.
This causes an electron to be knocked out from each particle, forming a 1+ ion
X(g) —> X+(g) + e-
When is Electron Impact Ionisation used?
Elements and substances with low formula mass.
What happens in the acceleration stage?
The positive ions are accelerated to the same kinetic energy by an electric field towards a negatively charged plate.
Why do some ions travel faster than others?
They all have the same kinetic energy, however, ligher ions travel faster since their velocity depends on their mass.
What happens in the Flight tube?
The positive ions travel through a hole in the negatively charged plate into a tube. The time of flight of each particle depends on its velocity. The ions set off at the same time and the lighter ions reach the detector first. (velocity dependent on mass)
What happens at the stage of detection?
The positive ions hit the negatively charged detection plate. This causes the ions to gain an electron which generates a movement of electrons and hence an electric current that is measured. The size of this current is proportional to the abundance of the species.
The ToF equation shows that...
ToF is directly proportional to the square root of the mass of the ions. Therefore lighter ions travel faster and reach the detector faster than the heavier particles that move slower and take longer to reach the detector
The mass spectrum
A computer uses the data to produce a mass spectrum. This shows the mass to charge (m/z) ratio on the x-axis and the abundance of each ion that reaches the detector on the y-axis. Given that most ions produced during ionisation have a 1+ charge, the m/z is effectively the mass of each ion
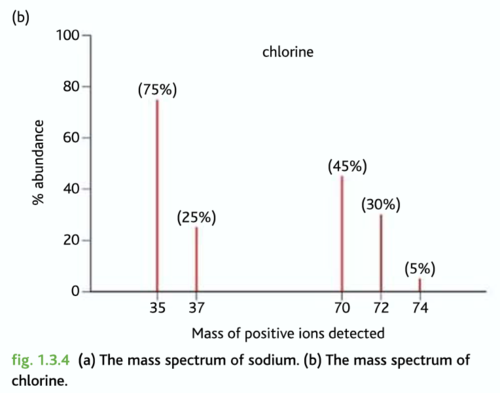
Relative atomic mass formula
Ar = Combined mass of all isotopes / Combined abundance of all isotopes
Or
Ar = m/z x abundance / Total abundance
During electron impact ions may be formed of charge...
2+. These ions will be affected more by the electric field during ionisation so will have double the kinetic energy of the other ions. It's m/z ratio is halved and this can be seen on the spectra as a trace at half the expected m/z value
For molecules ionised by electron impact, the signal with the...
Greatest m/z value is from the molecular ion and its m/z value gives the Mr. There may be smaller peaks present around the molecular ion peak due to molecular ions containing different isotopes (e.g. hydrogen-2 or carbon-13) . There may also be peaks at smaller m/z values due to fragments caused by the break up of molecular ions
For molecules ionised by electrospray ionisation, the relative molecular mass =
The first peak's m/z - 1
Ionisation energy
The enthalpy (energy) change when one mole of electrons are removed from one mole of gaseous atoms forming ions of a single positive charge. Measured in kJmol^-1
First ionisation energy
The enthalpy (energy) change when an electron is removed from a gaseous atom
Factors affecting first ionisation energy
1. Nuclear charge - Nuclear charge increasing increases first ionisation energy
2. Atomic radius - Atomic radius increasing decreases first ionisation energy
3. Shielding - Shielding decreasing increases first ionisation energy
Trend in first ionisation energy down a group
First ionisation energy decreases down a group as atomic radius and shielding increase down a group, meaning the outer shell electron is further away from and less attracted to the nucleus, so less energy is required to remove it
Trend in first ionisation energy across a period
First ionisation energy increases across a period as nuclear charge increases, atomic radius decreases and shielding stays the same across a group, meaning the outer shell electron is closer to and more attracted to the nucleus, so more energy is required to remove it
Successive ionisation energies
Occur when further electrons are removed. Requires more energy, as, the more electrons removed, the greater the electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the outer electron. More energy is needed to overcome this attraction so ionisation energy increases
When successive ionisation energies are plotted on a graph, a sudden large increase in energy indicates a...
Change in energy level, as the electron is being removed from an orbital closer to the nucleus, so more energy is required to do so. This large energy increase provides evidence for the atomic orbital theory
How many electrons can an energy level of number n hold?
2n^2
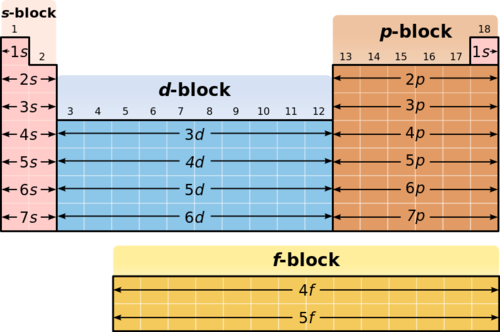
Electrons are held in...
Clouds of negative charge within energy levels called sub-levels / orbitals
These orbitals correspond with...
Blocks on the periodic table. Each element in the block has its outer electron in that orbital
How many s-orbitals are there and how many electrons can they hold in total?
1 orbital, 2 electrons
How many p-orbitals are there and how many electrons can they hold in total?
3 orbitals, 6 electrons
How many d-orbitals are there and how many electrons can they hold in total?
5 orbitals, 10 electrons
Sodium electron configuration
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
Within an orbital, electrons pair up with...
Opposite spin so the atom is as stable as possible. Electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spin. Spin is represented with arrows
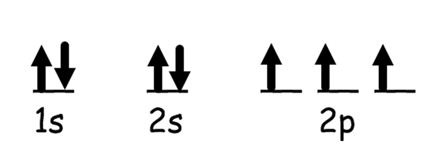
Rules for writing out electron configurations
1. The lowest energy orbital is filled out first
2. Electrons with the same spin fill up an orbital first before pairing begins
3. No single orbital holds more than two electrons
Why is boron's first IE lower than beryllium's?
Boron's outer shell electron is in the 2p orbital while beryllium's outer shell electron is in the 2s orbital. Boron's outer shell electron is further from the nucleus and experiences shielding from the 2s electrons. This weakens the attraction between boron's nucleus and its outer shell electron, lowering boron's first IE
Why is oxygen's first IE lower than nitrogen's?
Oxygen's outer shell electron has to pair up in a 2p orbital. The paired electrons experience mutual repulsion. This weakens the attraction between oxygen's nucleus and its outer electron, lowering oxygen's first IE
When scandium is reached, the 3d orbitals are lower in energy than...
The 4s orbital
Scandium electron configuration
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1
Chromium electron configuration
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5
Copper electron configuration
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10
When writing the electron configuration of a transition metal, remove electrons from the...
4s orbital first