science test (december 2024)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Collision Theory
Particles must collide with the right orientation and energy for a reaction to occur
3 things for collision theory
Correct orientation, particles must collide, and sufficient energy
Increase of temperature in a reaction
Increases the rate of reaction by increasing the frequency and energy of collisions
How is pressure and concentration the same conceptually?
Both relate to the number of particles in a given space
Definition of Activation Energy
The minimum amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to occur
Factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions
Temperature, concentration/pressure, surface area, catalyst (presence or absence)
Solid particle diagram
Tightly packed
Liquid particle diagram
Close together, but not tight
Gas particle diagram
Far away and not packed
Affect of pressure on a reaction
Increases or decreases collison
Affect of temperature on a reaction
Provides activation energy
Affect of volume on a reaction
Increases or decreases collision
Affect of the number of particles on a reaction
Increases or decreases collision
Conversion from C to Kelvin
C + 273
Characteristics of an Ideal Gas
Molecules are moving fast and random, have no volume, do not attract or repeal each other, elastic collisions, temperature of the gas is proportional to the average kinetic energy
Definition of elastic collisions
No kinetic energy is lost when gas molecules collide with each other
Characteristics of a Real Gas
Under a low temperature and high pressure, they move in straight lines between collisions, take up volume, and are attracted to each other under conditions.
Difference between real gases and ideal gases
Real gases do not follow gas laws for all values of temperature and pressure
Ideal Gas Law meaning
Under the same temperature, pressure, and volume all gases contain the same number molecules but not the same.
Charles Law
V1/T1=V2/T2
Charles Law meaning
Describes how gases tend to expand when heated
Lab for Charles Law
Balloon lab
What changes the rate of reaction
Changes with a catalyst, temperature, pressure, and surface area.
A higher temperature equals
A higher rate of reaction
Lab for temperature rate of reaction
Disappearing X
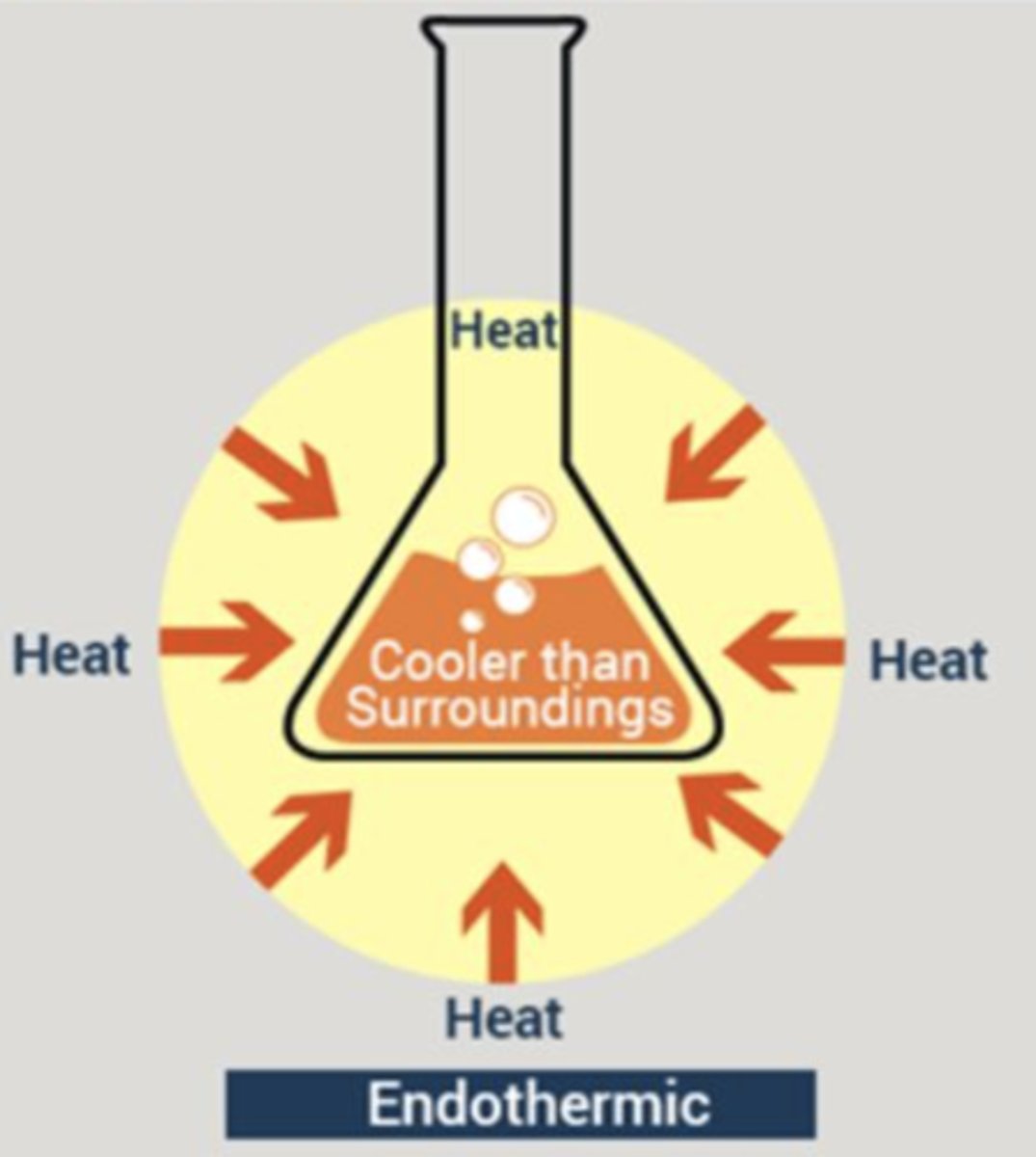
Endothermic
Absorbs heat
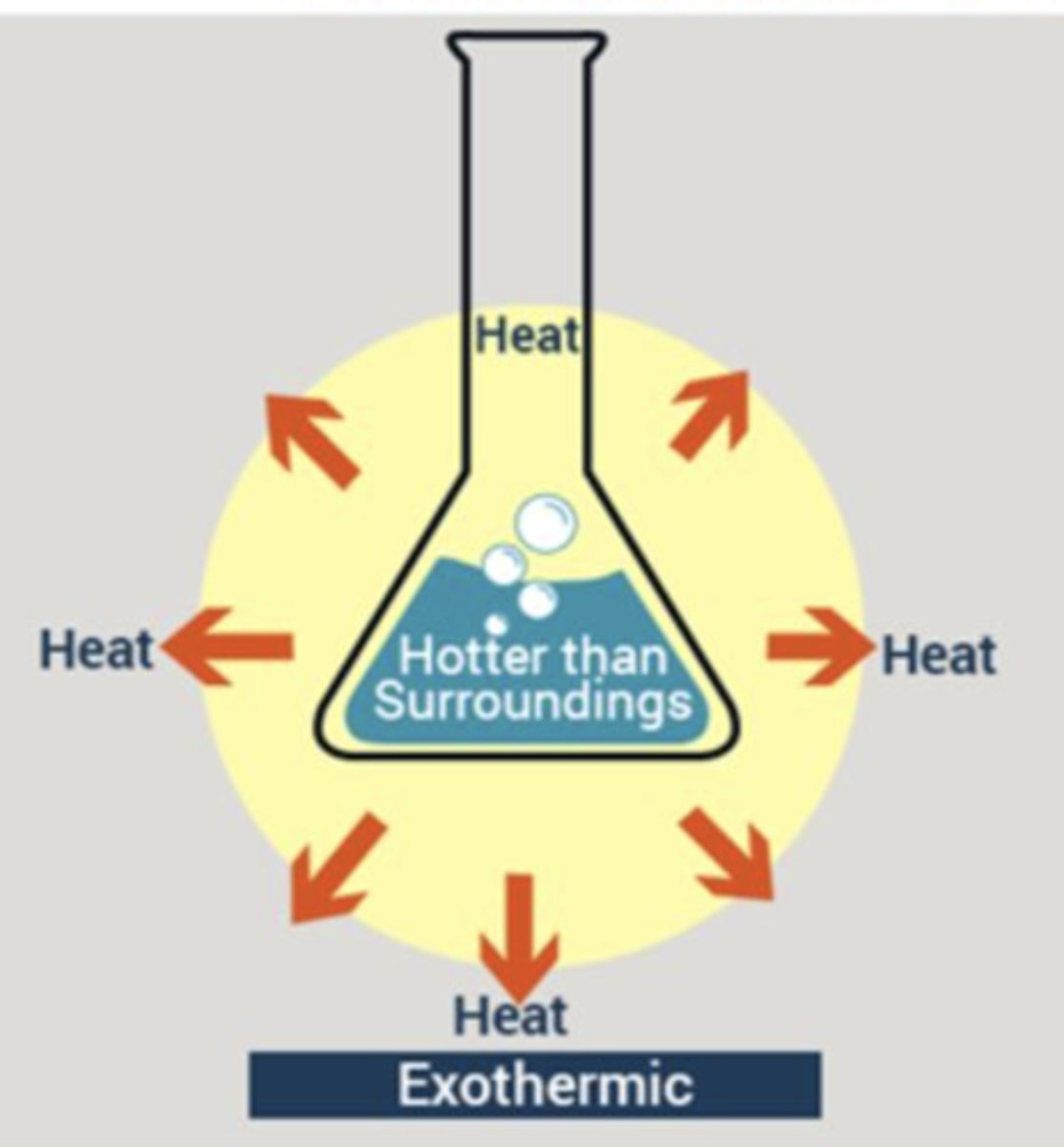
Exothermic
Releases heat
Examples of Endothermic reactions
Melting of ice, photosynthesis, water evaporation, reaction between vinegar and baking soda, gas burning, ice pack
Examples of Exothermic reactions
Combustion reactions, formation of snow, neutralization reactions (bases and acids), rusting, hot pack
Characteristics of Endothermic reactions
Is cooler than the surroundings
Characteristics of Exothermic reactions
Is hotter than the surroundings
What degrades an enzyme?
Temperature or pH (Acidic environment)
Rate of reaction equation
Reactant lost/Time or Product/Time