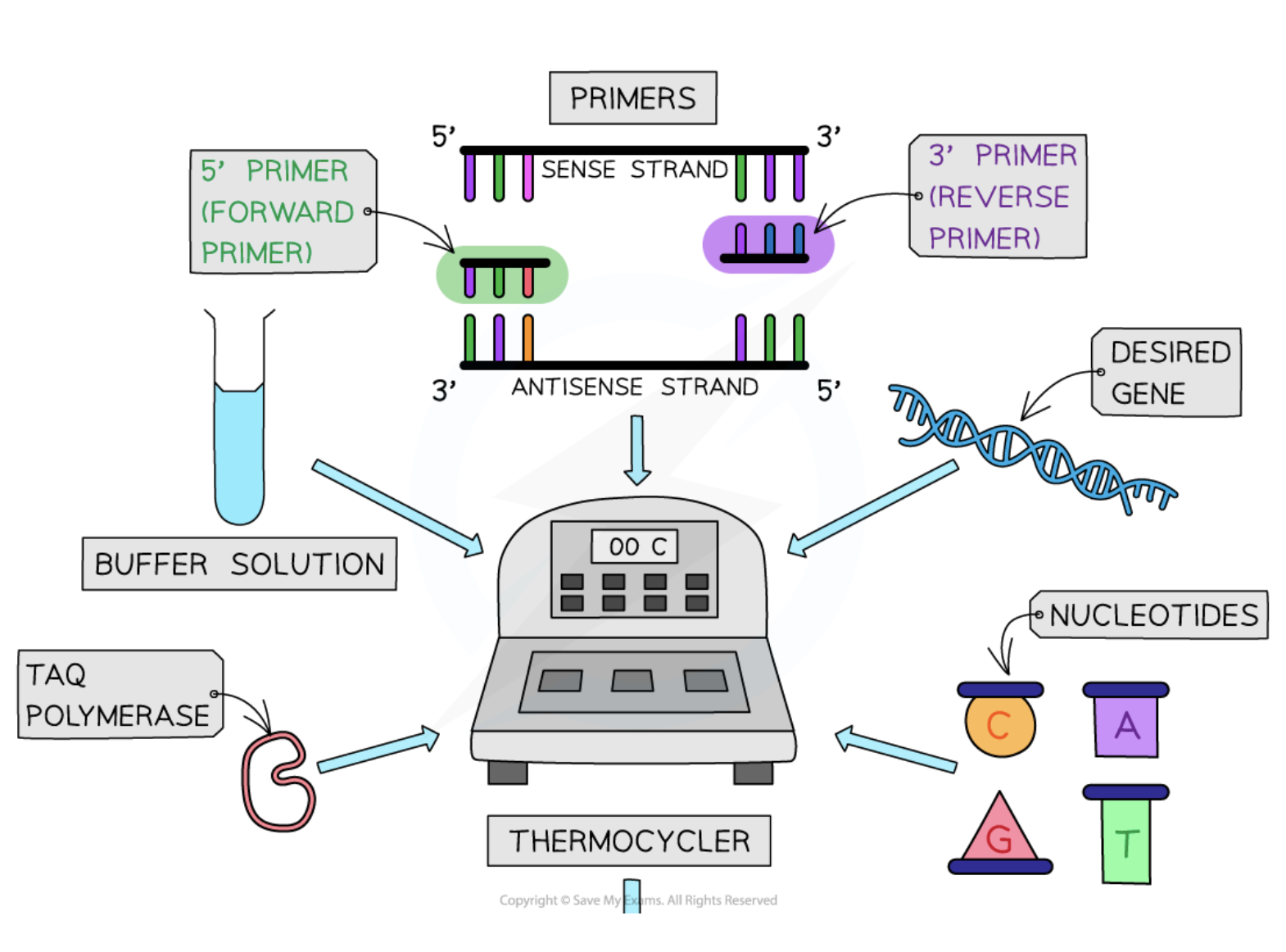
(CIE A2 Biology) The polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
A molecular biology technique used to amplify DNA or RNA, producing billions of identical copies from a small sample.
DNA profiling
Application of PCR for identifying individuals, such as in criminal identification and paternity determination.
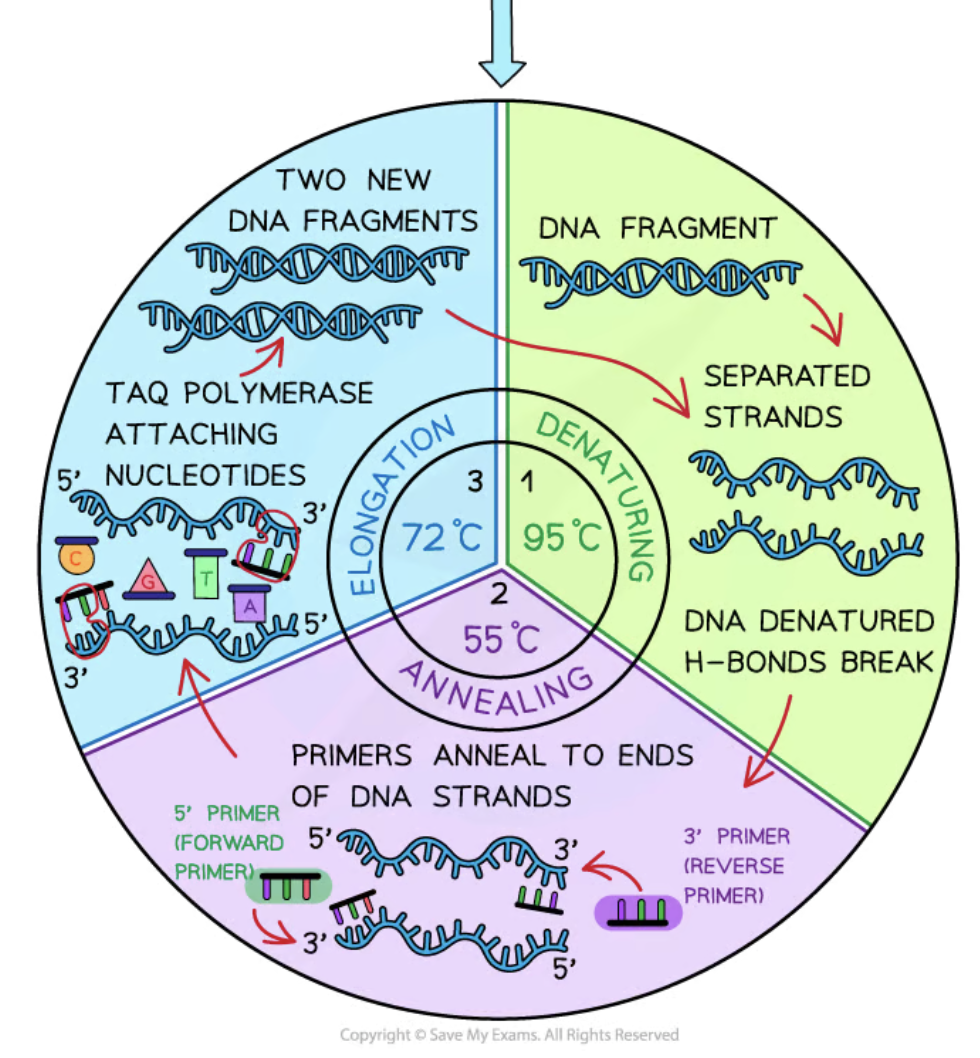
Denaturation
The first stage of PCR where DNA is heated to 95°C to break hydrogen bonds, separating the double strands.
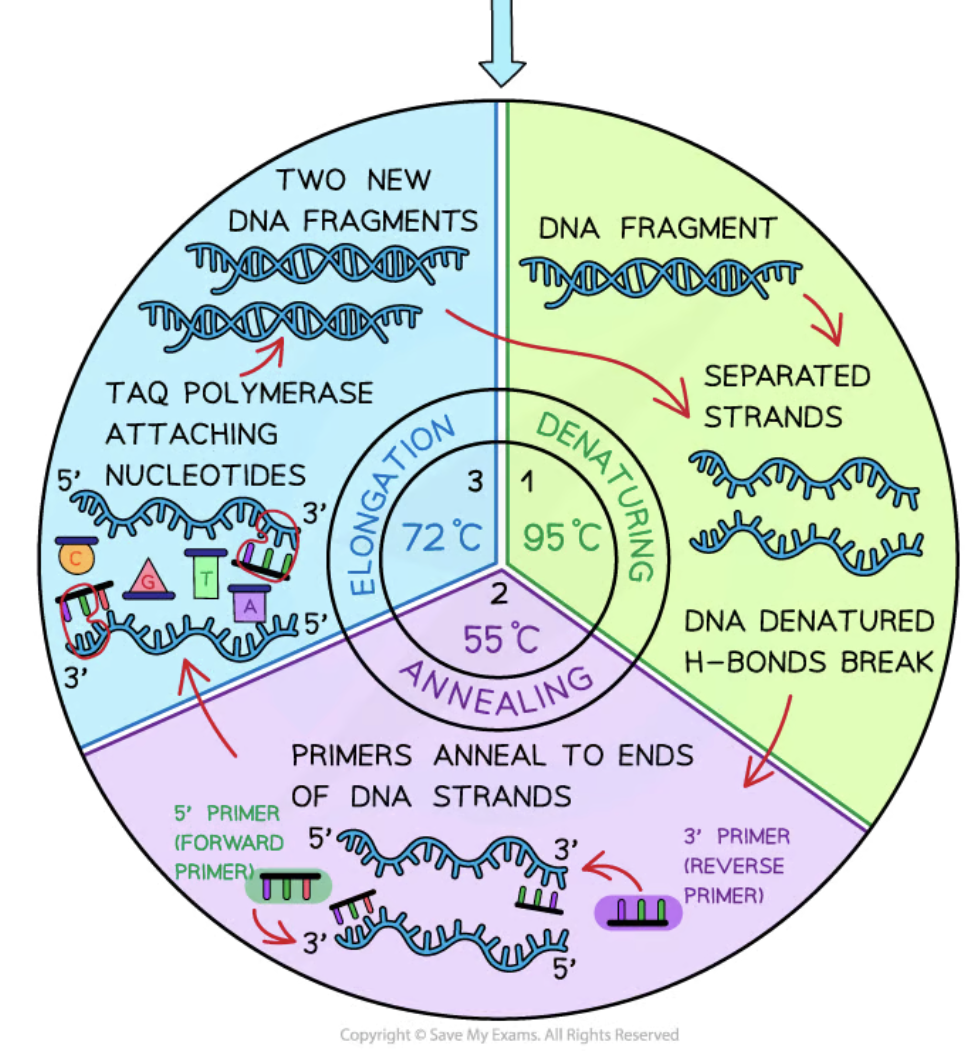
Annealing
The second stage of PCR where the temperature is lowered to 50-60°C allowing primers to attach to the single DNA strands.
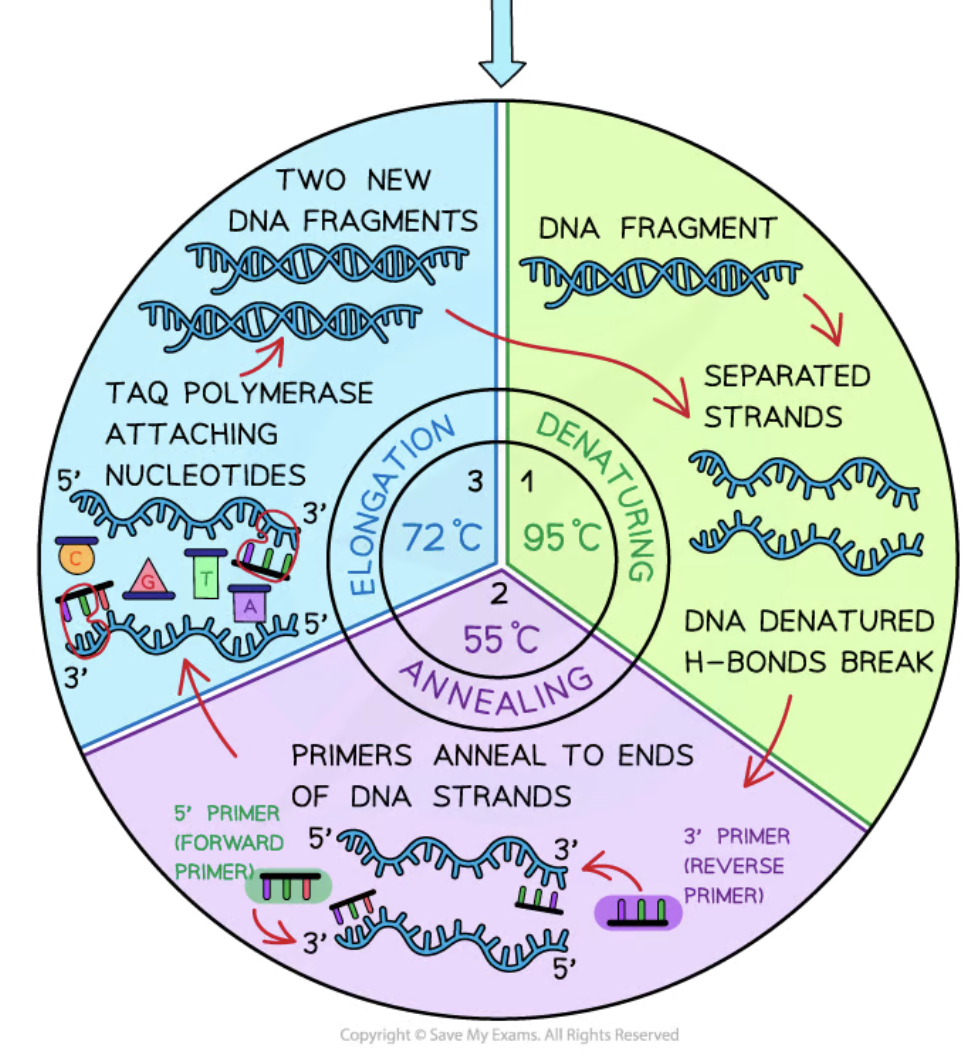
Elongation/Extension
The third stage of PCR where the temperature is increased to 72°C for Taq polymerase to synthesize new DNA strands.
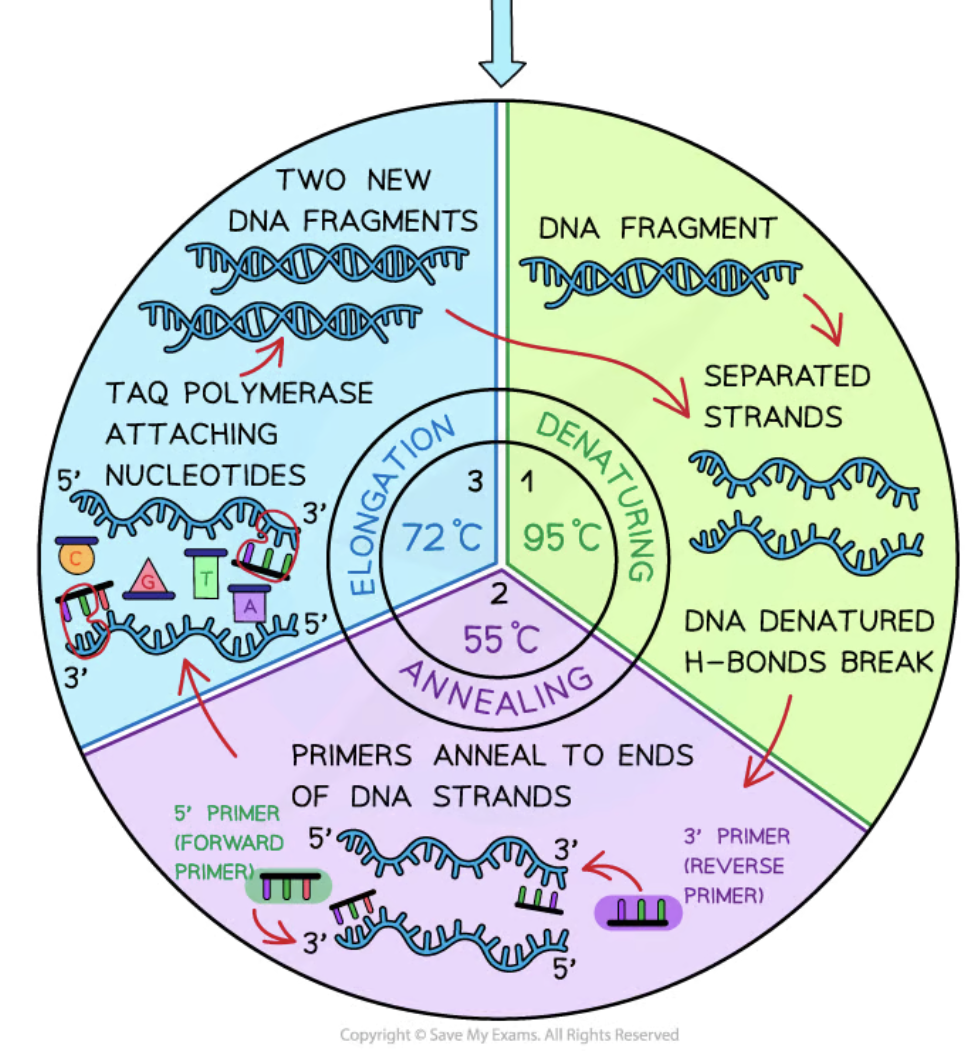
Taq polymerase
An enzyme used in PCR that remains stable at high temperatures and allows for efficient DNA strand synthesis.
Primers
Short single-stranded DNA sequences that are complementary to target DNA, guiding where DNA polymerase begins replication.
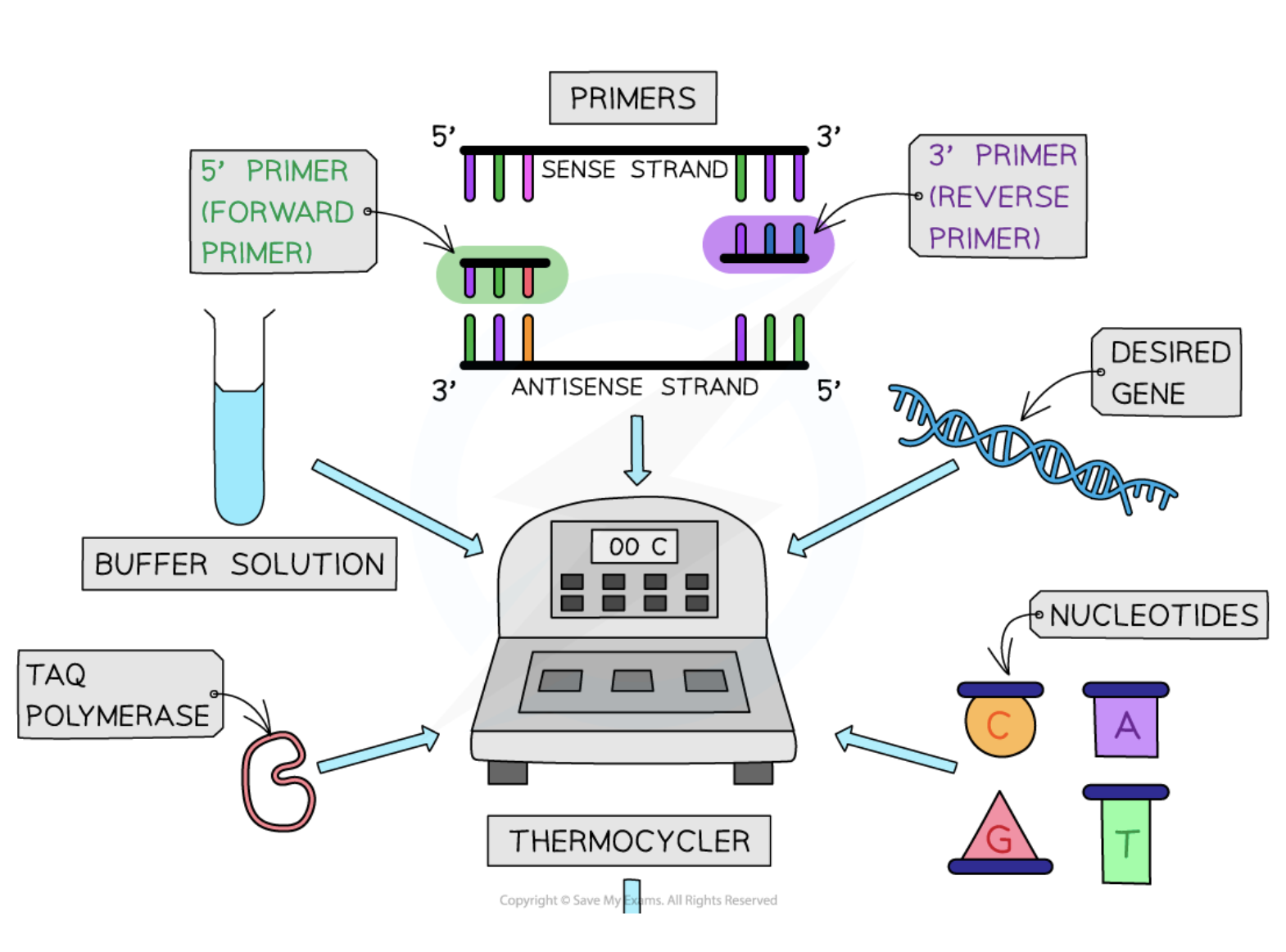
Buffer solution
A solution that maintains the optimal pH for the PCR reactions to occur efficiently.
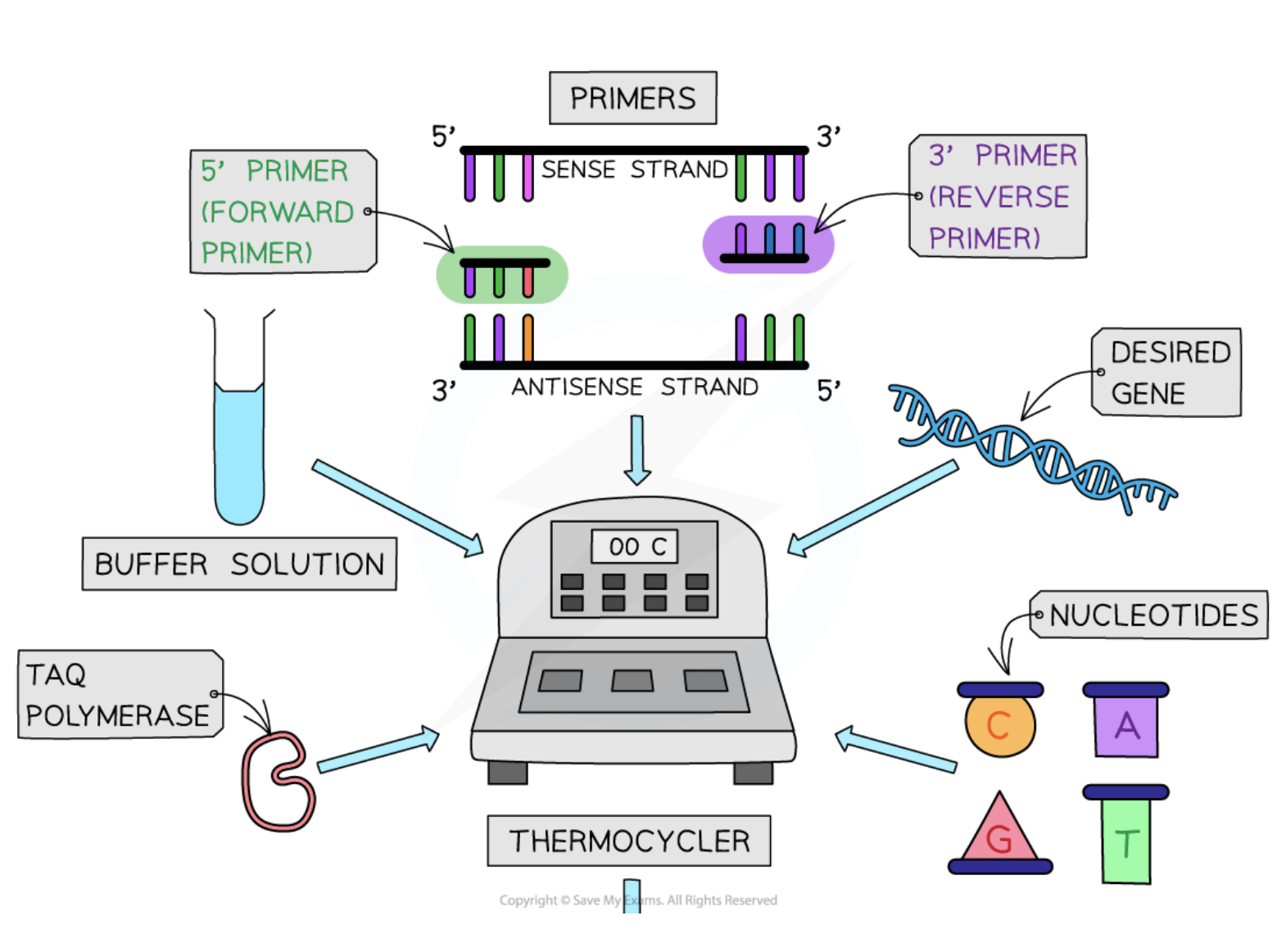
Free nucleotides
Nucleotides that are required for constructing new DNA or RNA strands during PCR.
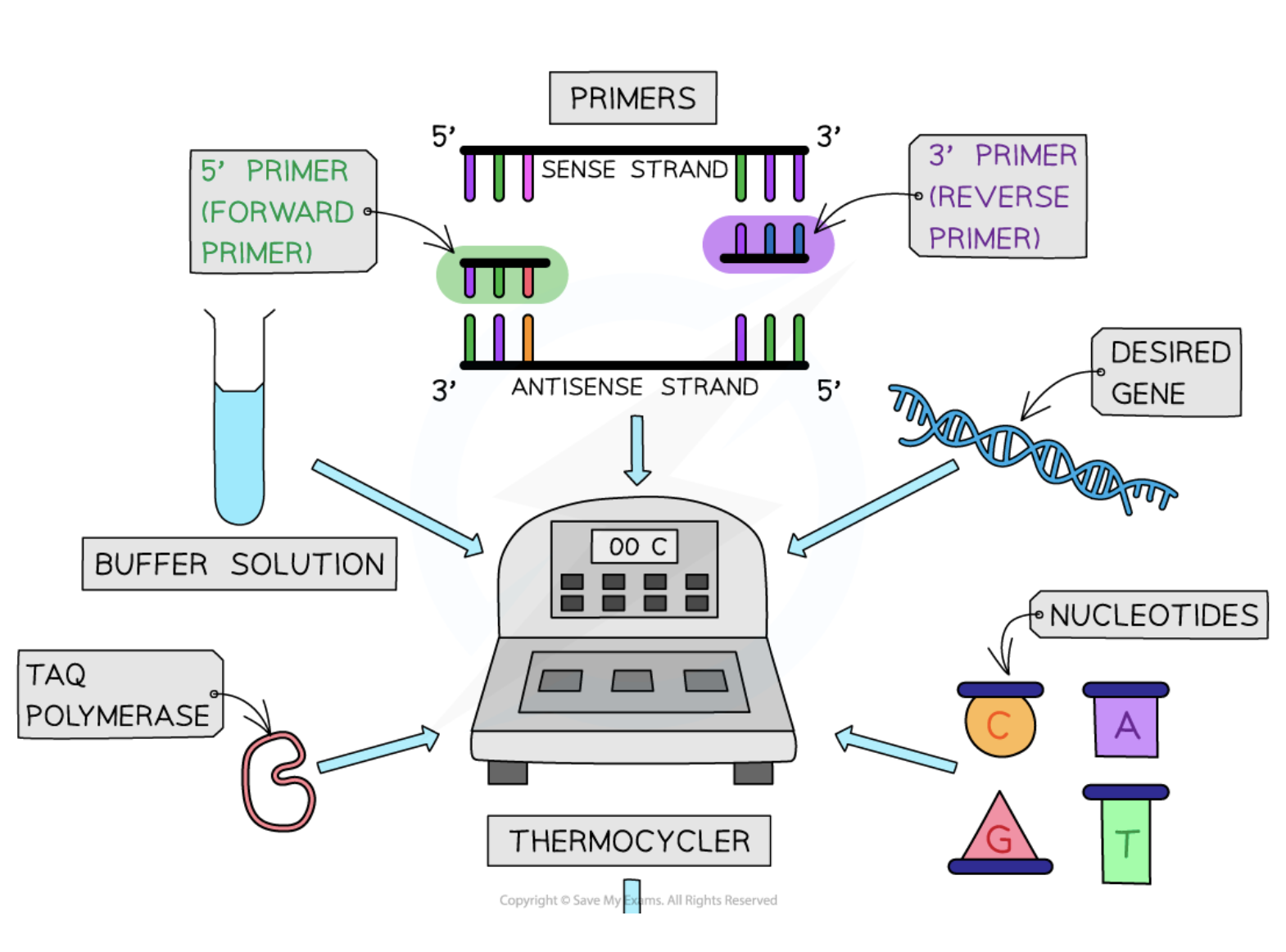
Thermal cycler
A PCR instrument that automatically controls the temperatures and timing needed for each stage of the PCR process.