Genetics
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Allele
The different forms of a gene
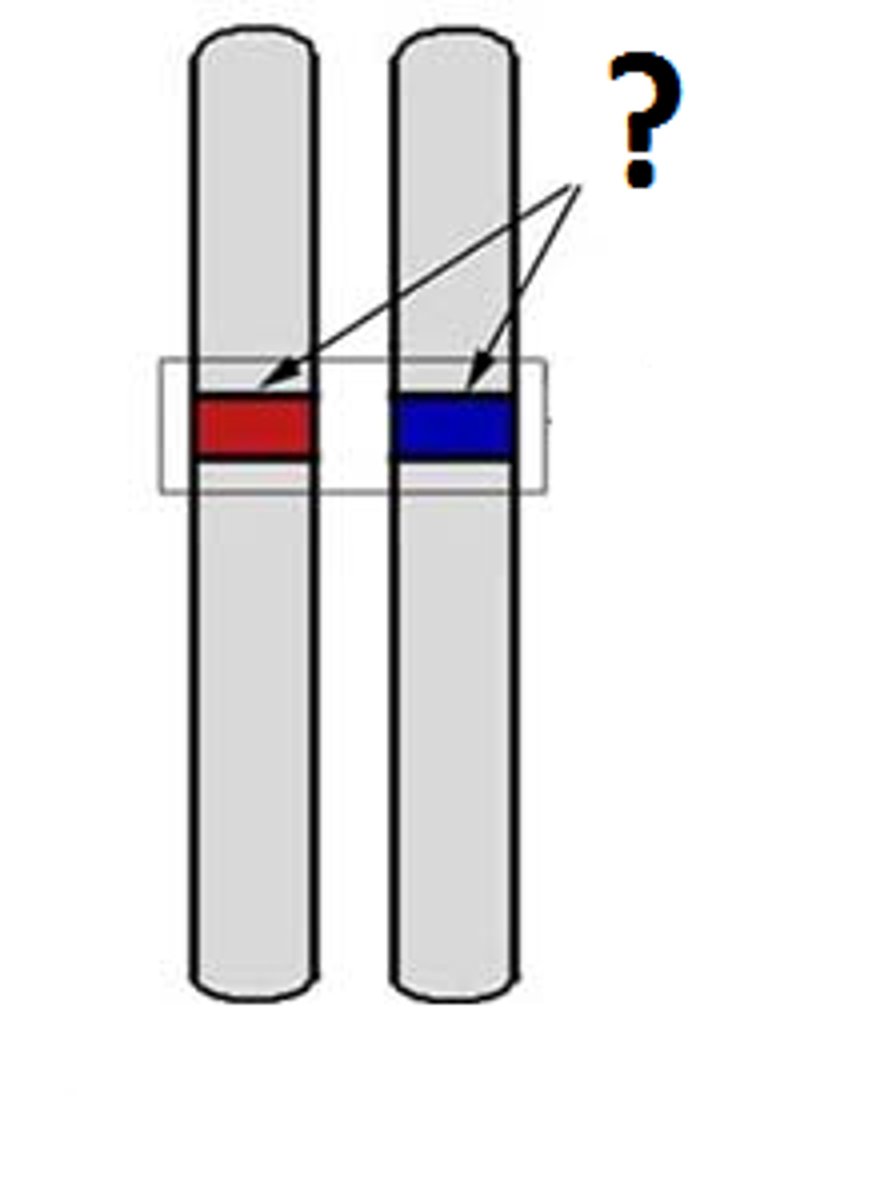
Dominant Allele
An allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present

Recessive Allele
An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present
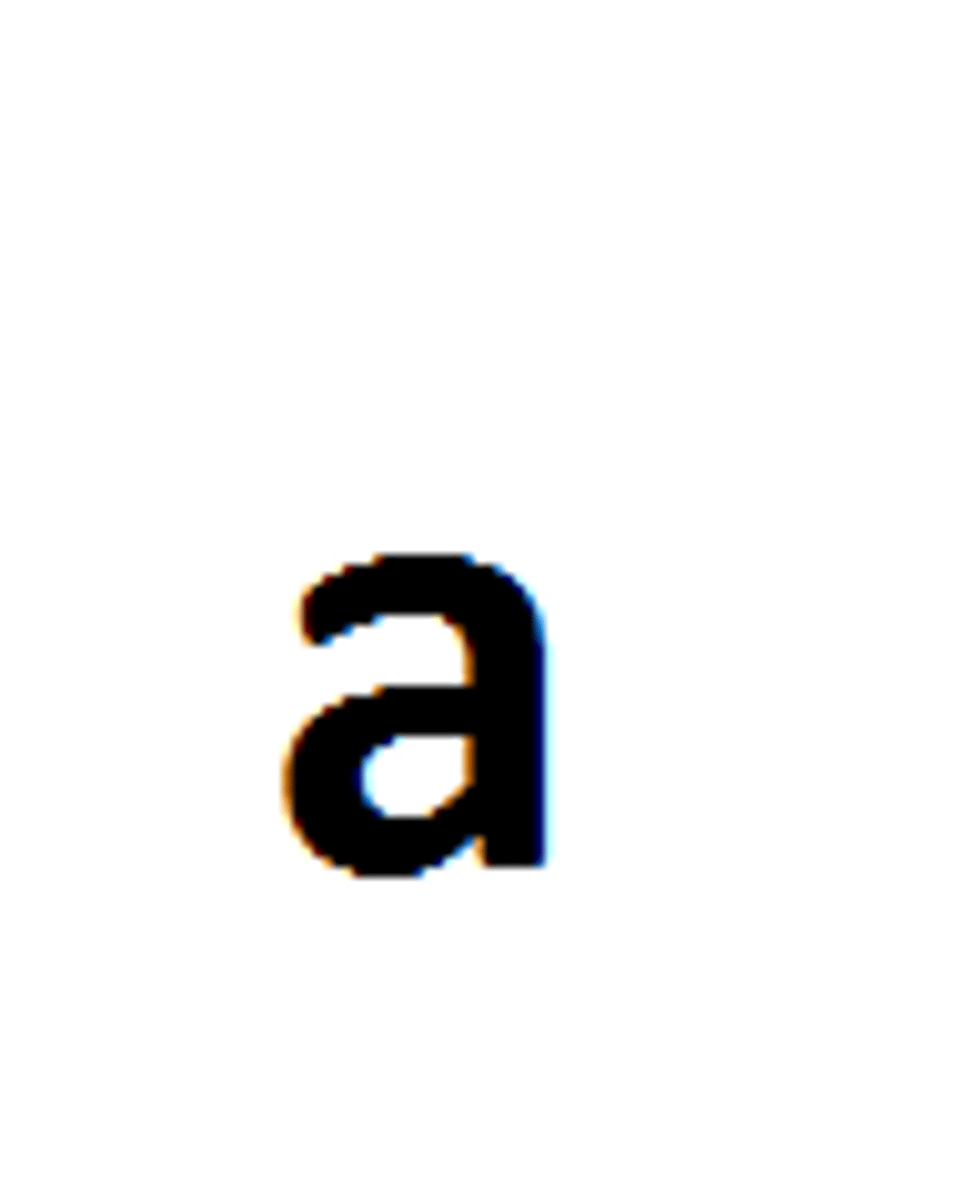
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a trait

Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a trait

Genotype
An organisms genetic makeup, or allele combinations
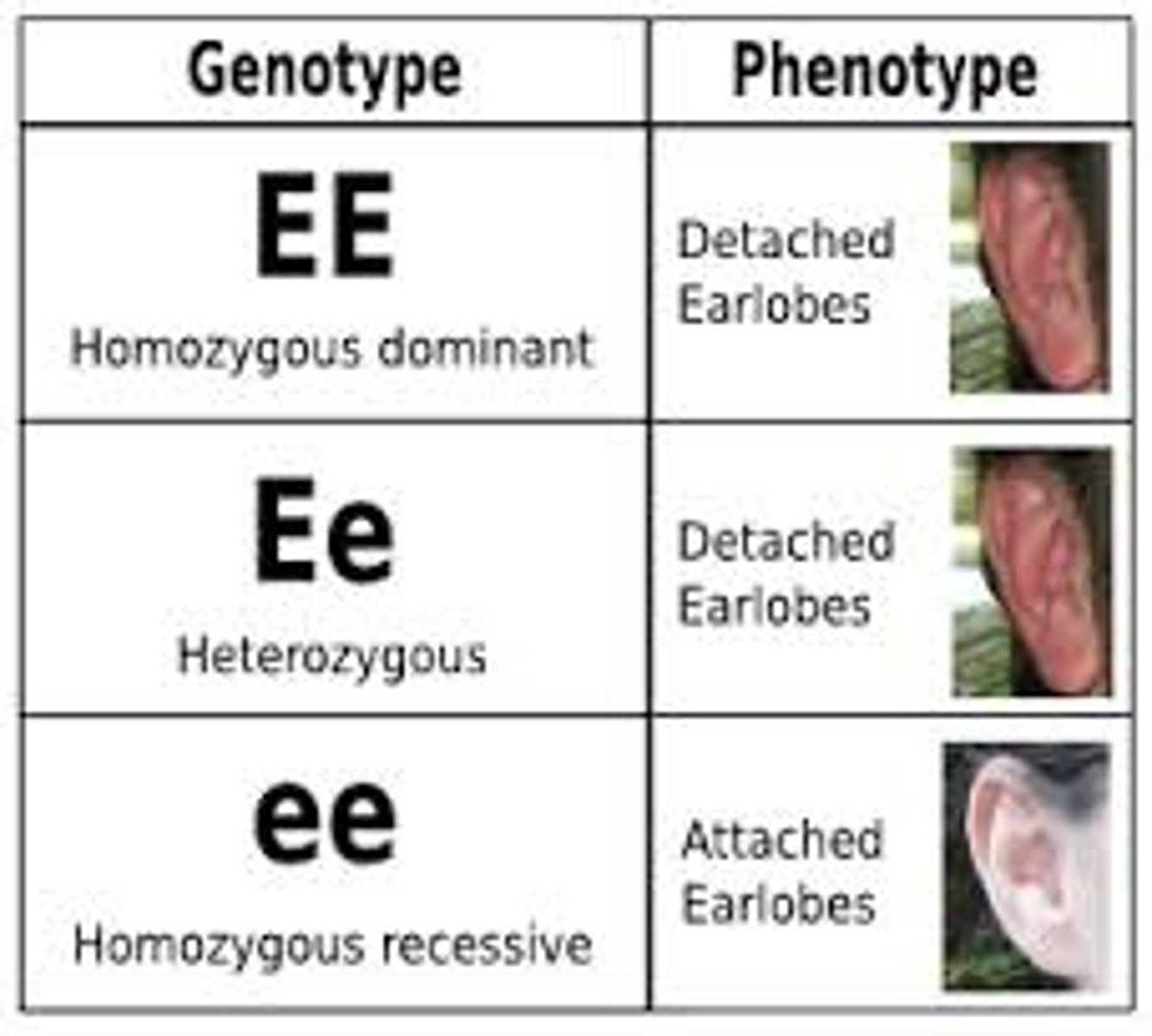
Phenotype
The physical traits that appear in an individual as a result of its genotype
Chromosome
A threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus. Each chromosome consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins. Most cells in your body have 46.

Trait
A describable feature of an organism.
e.g. ability to roll tongue
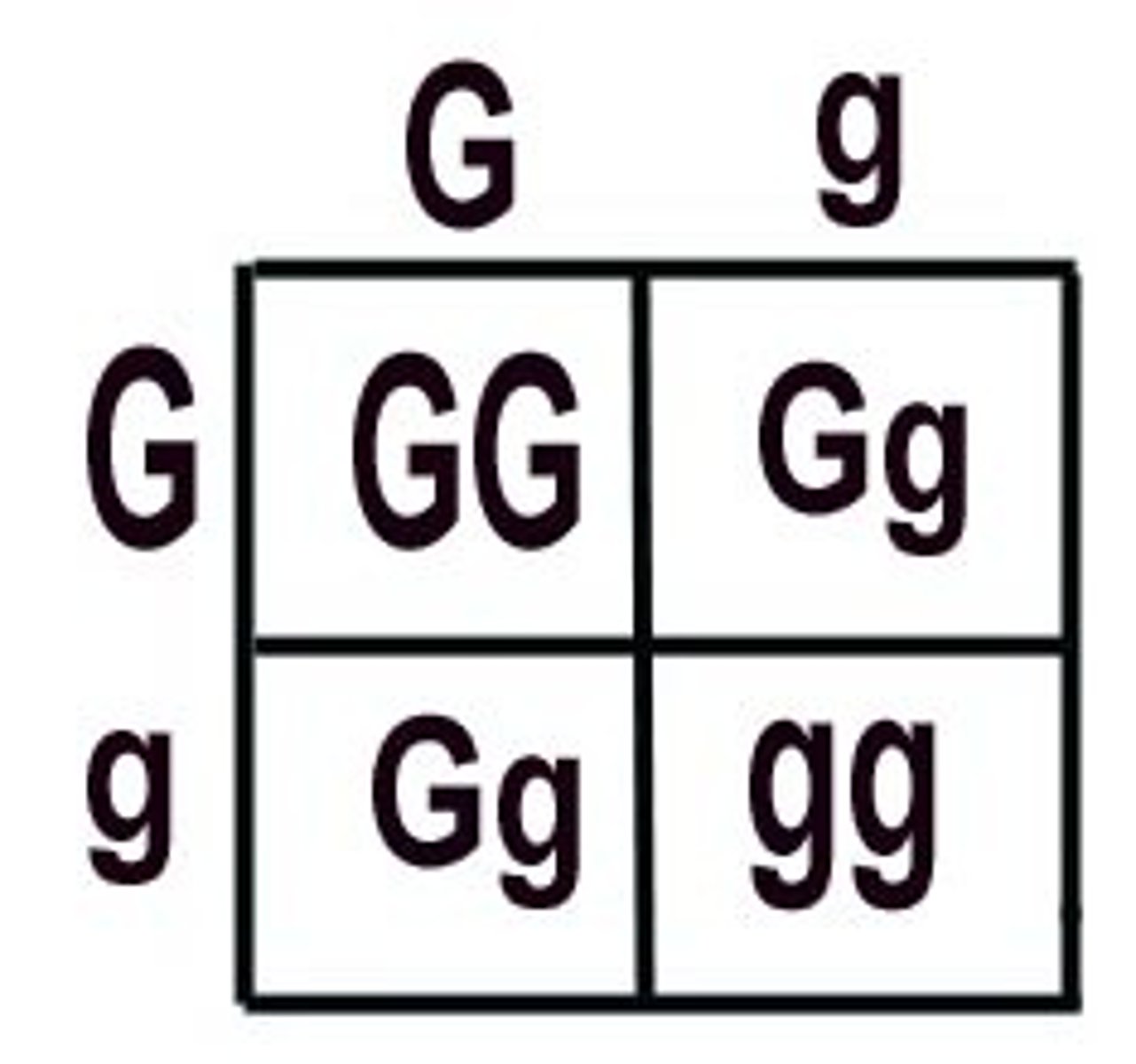
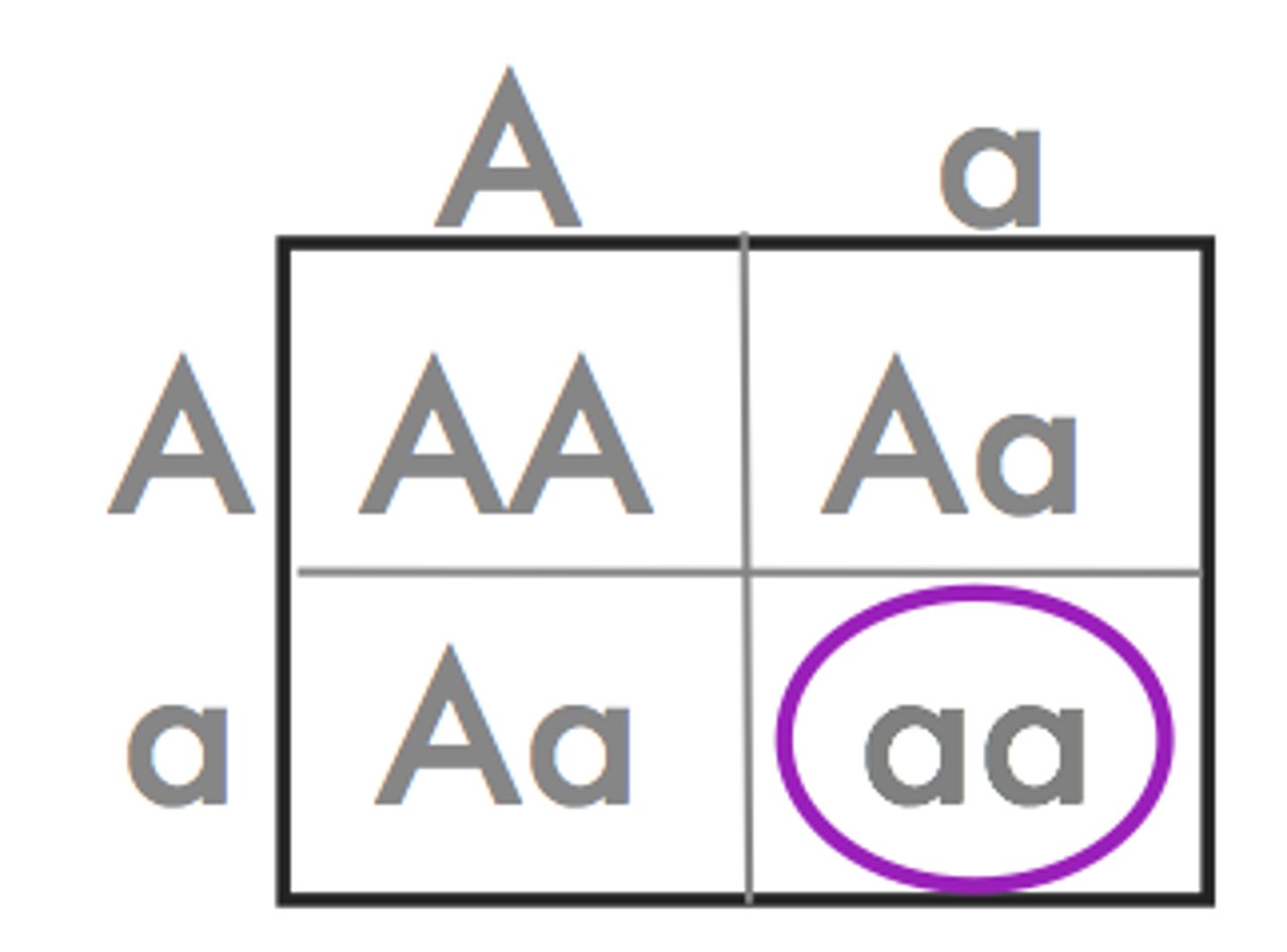
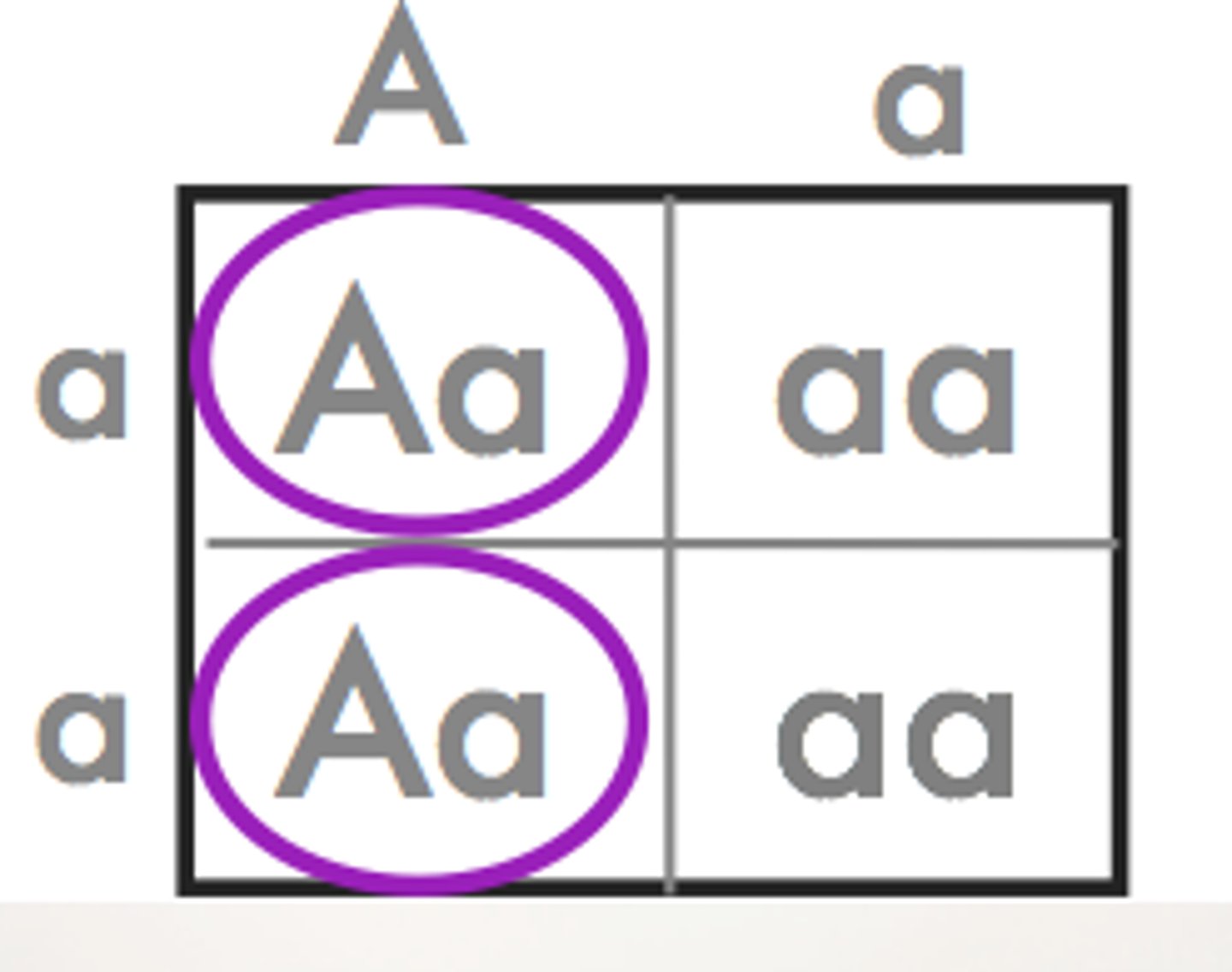
Punnett Square
diagram that can be used to predict the genotype and phenotype combinations of a genetic cross
Carrier
A person who has one recessive allele for a trait, but does not have the trait.

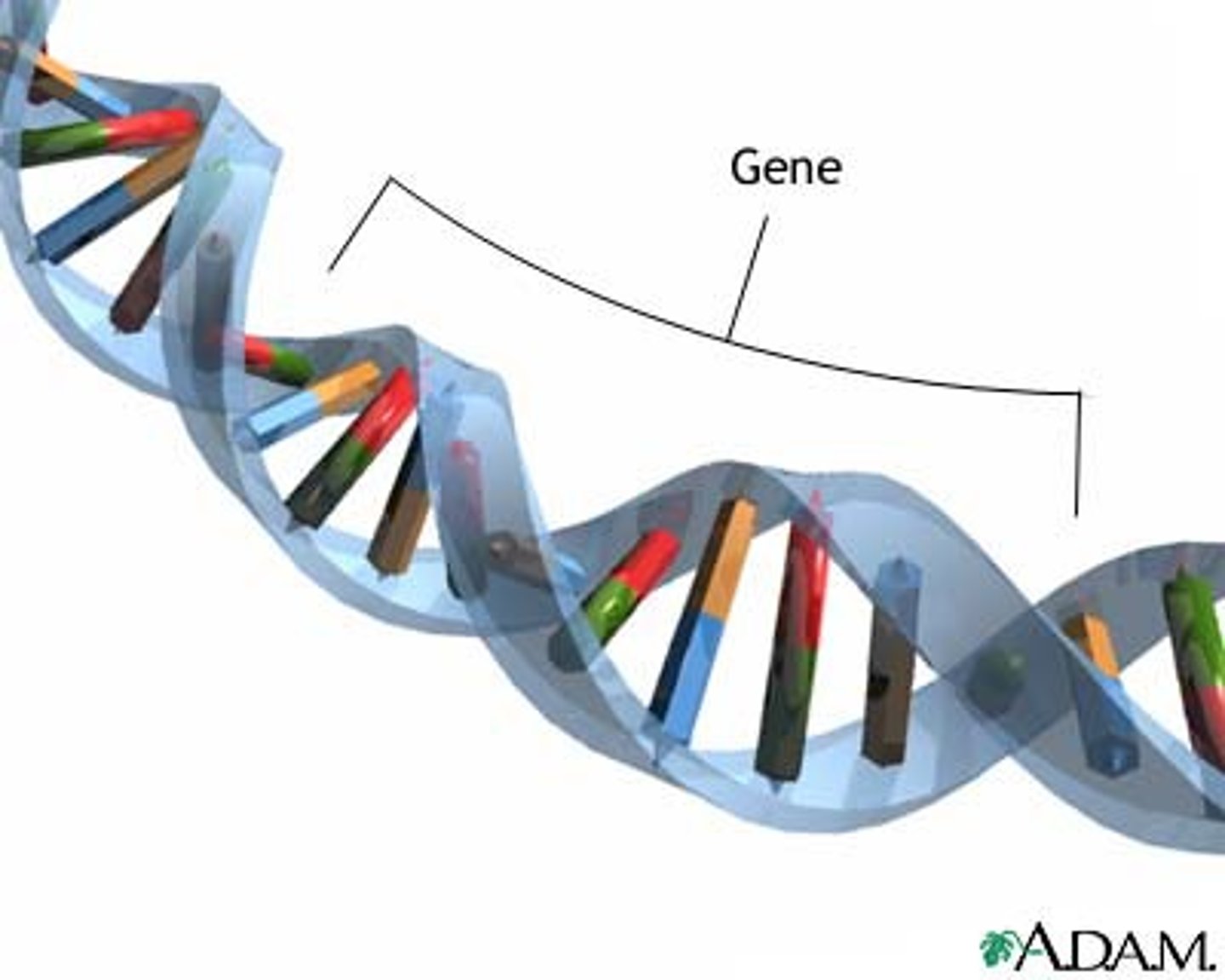
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
maternal
of or like a mother

paternal
of or like a father

Hybrid
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait
Purebred
An organism in which both alleles for a trait are the same

Heredity
Passing of traits from parents to offspring
mutation
a random error in gene replication that leads to a change

Mendelian Genetics
The pattern of inheriting characteristics that follows the laws formulated by Gregor Mendel

Gregor Mendel
Father of genetics

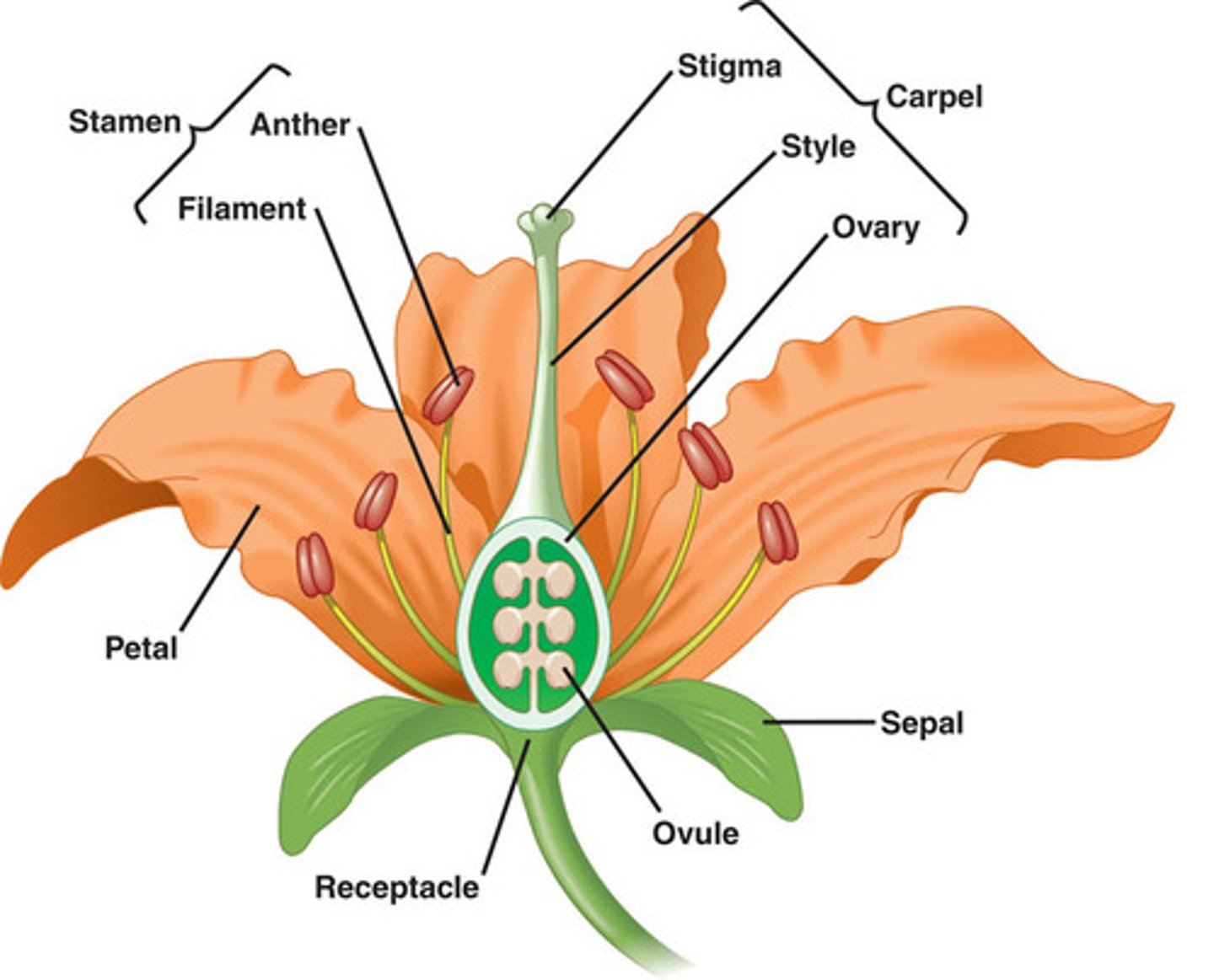
Angiosperms
flowering plants that bear fruits and flowers
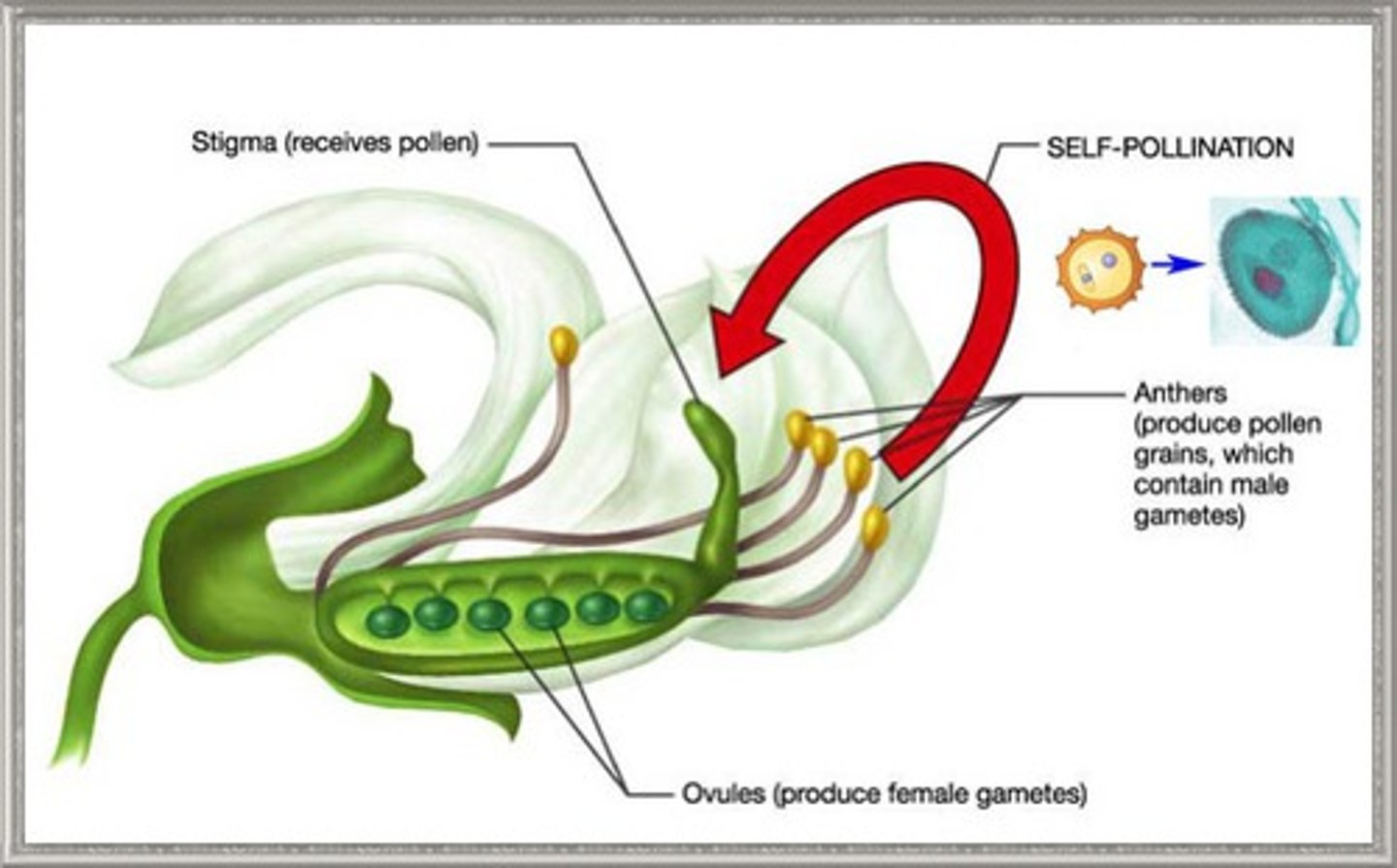
self-fertilization
When pollen from an anther fertilizes the eggs on the same flower.
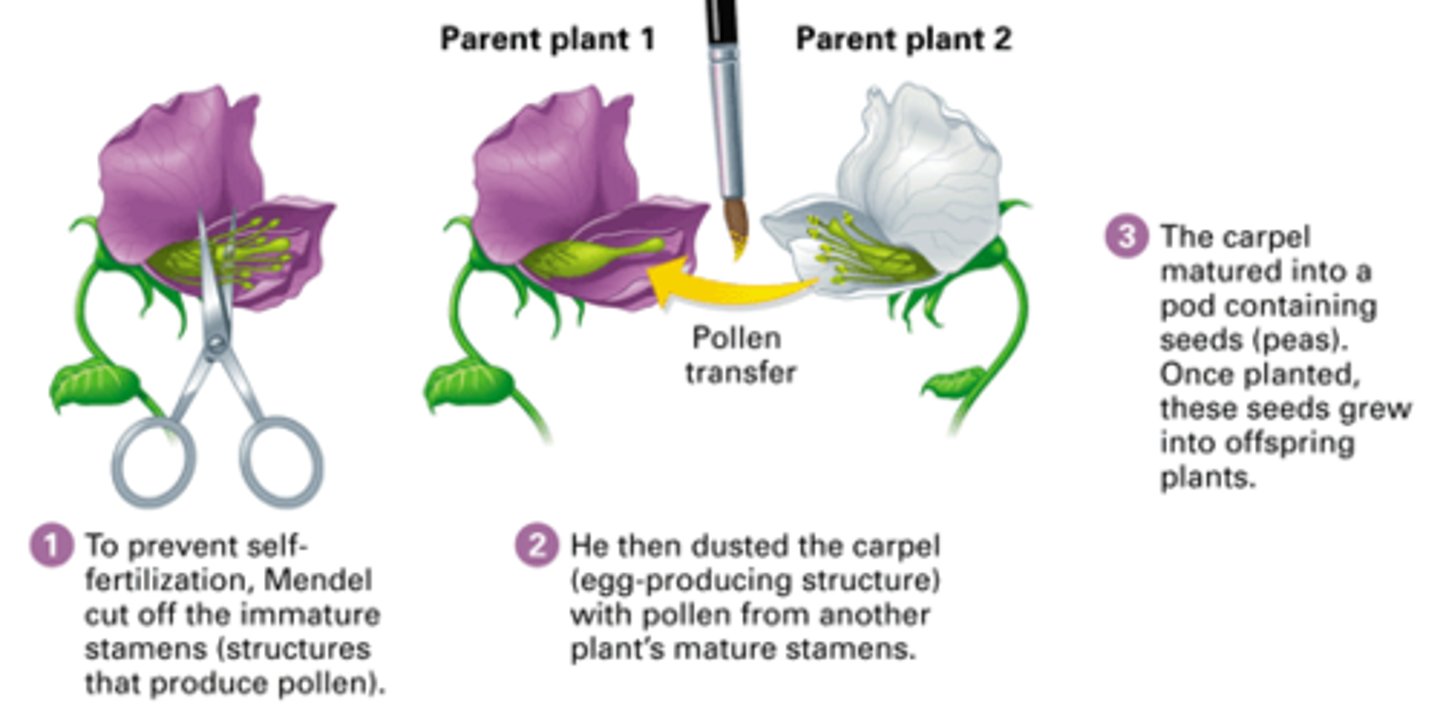
cross-fertilization
When the pollen is transferred to the stigma of an entirely different plant
genetics
The scientific study of heredity
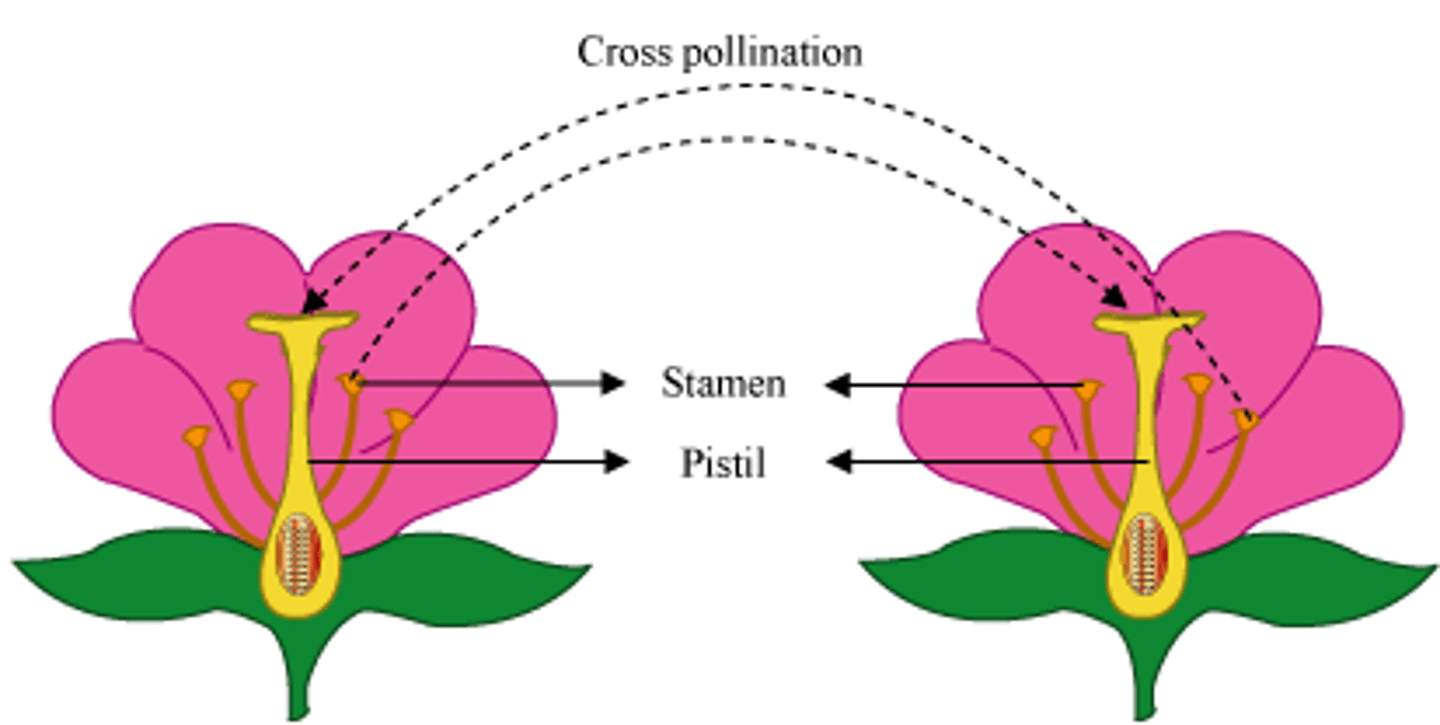
pollination
The transfer of pollen from male reproductive structures to female reproductive structures in plants
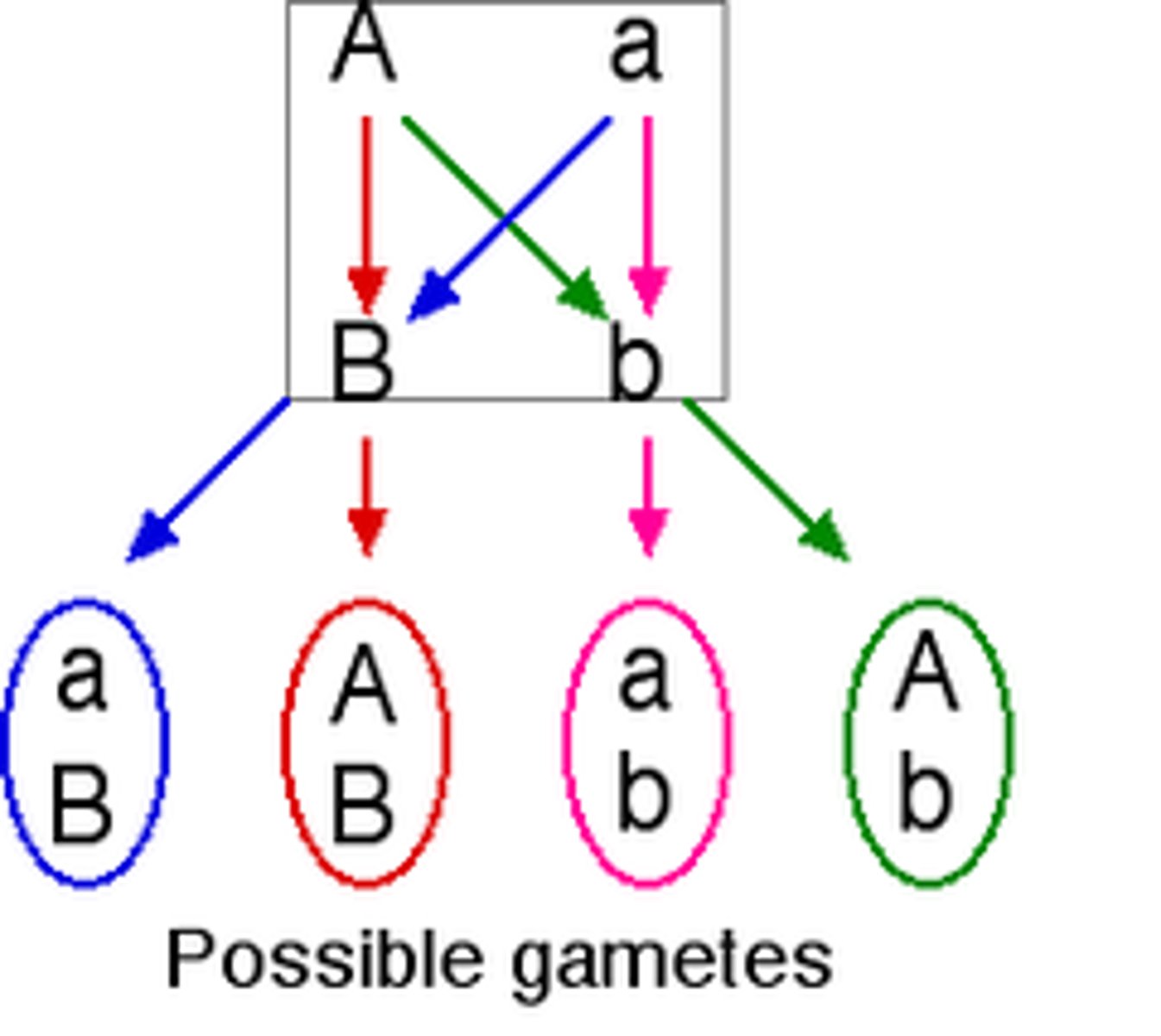
Law of independent assortment
Mendel's second law, stating that allele pairs separate from one another during gamete formation
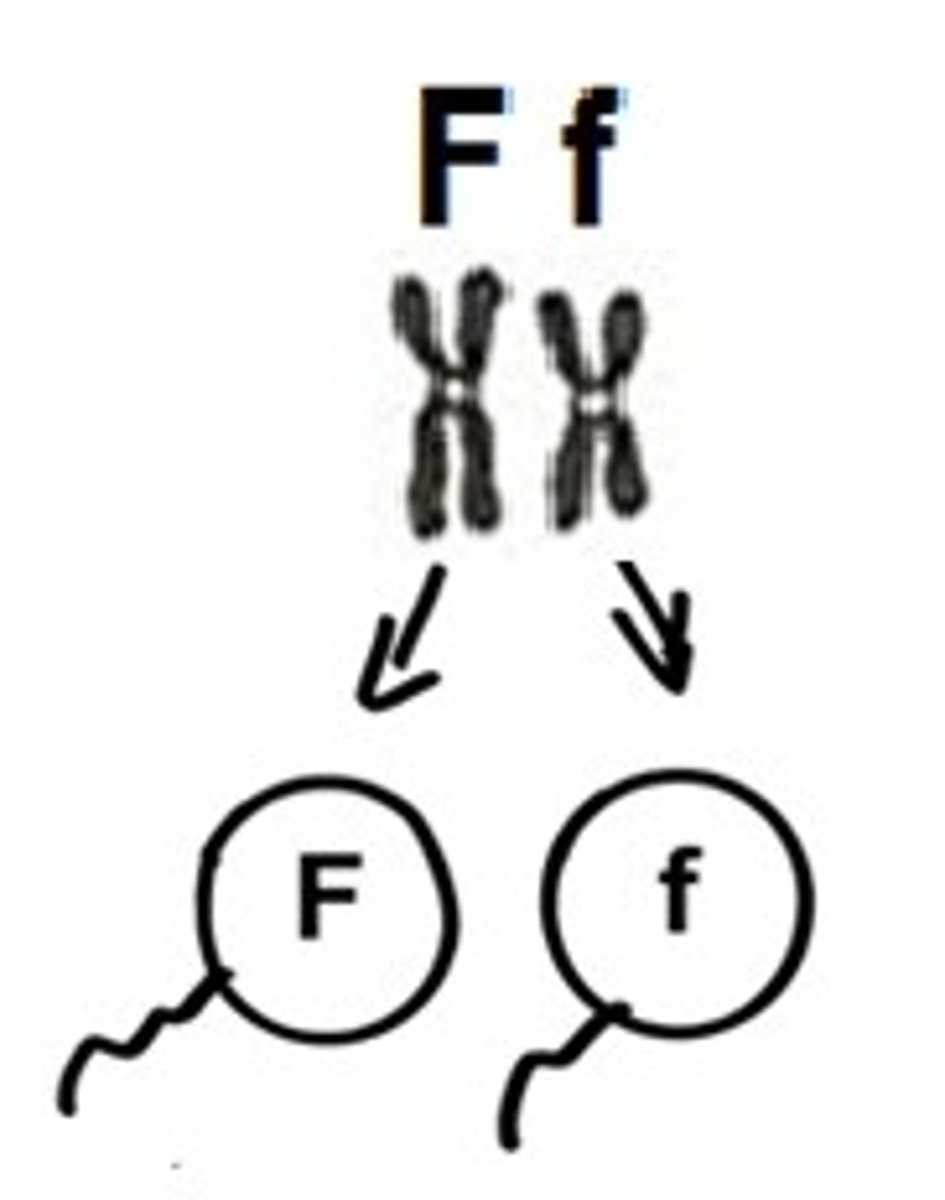
Law of Segregation
Mendel's law that states that the pairs of homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis so that only one chromosome from each pair is present in each gamete
incomplete dominance
Situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele
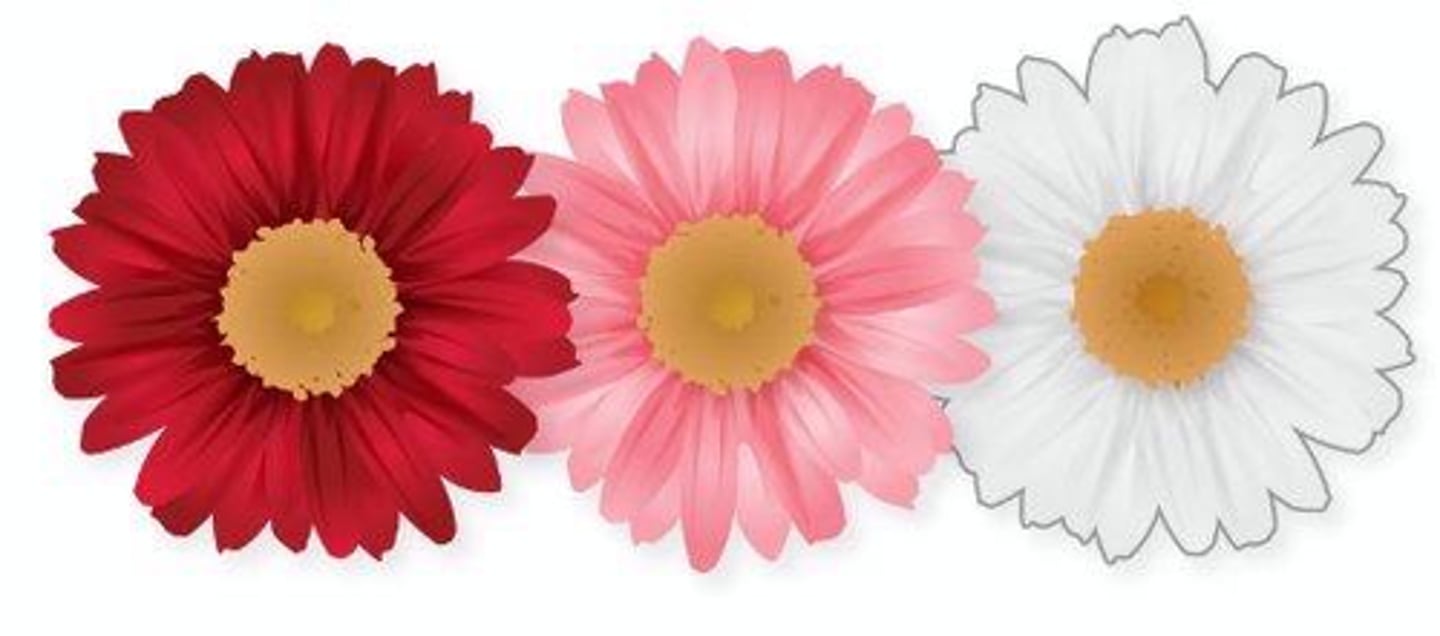

Codominance
A condition in which neither of two alleles of a gene is dominant or recessive.

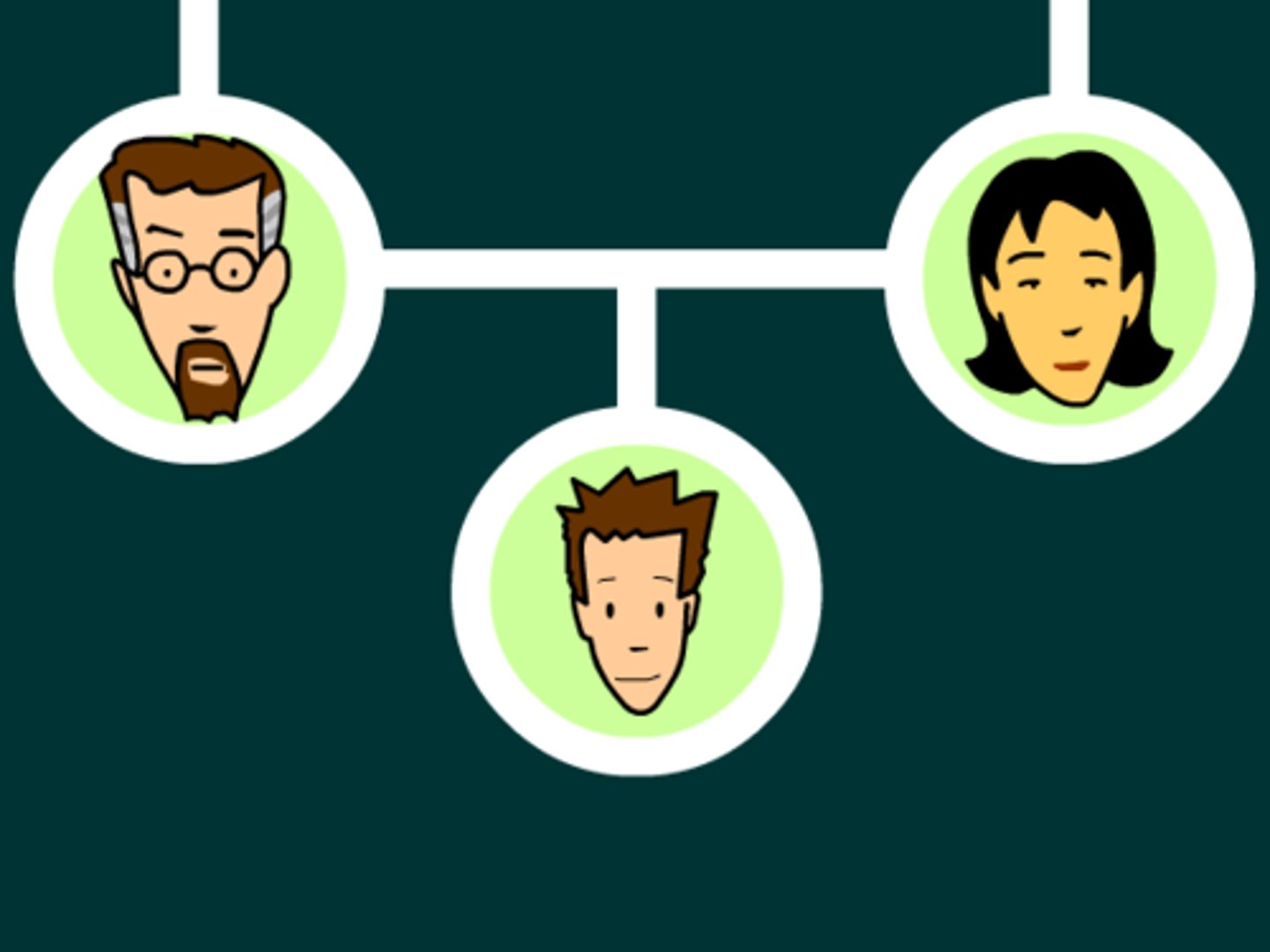
Pedigree
A diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family.
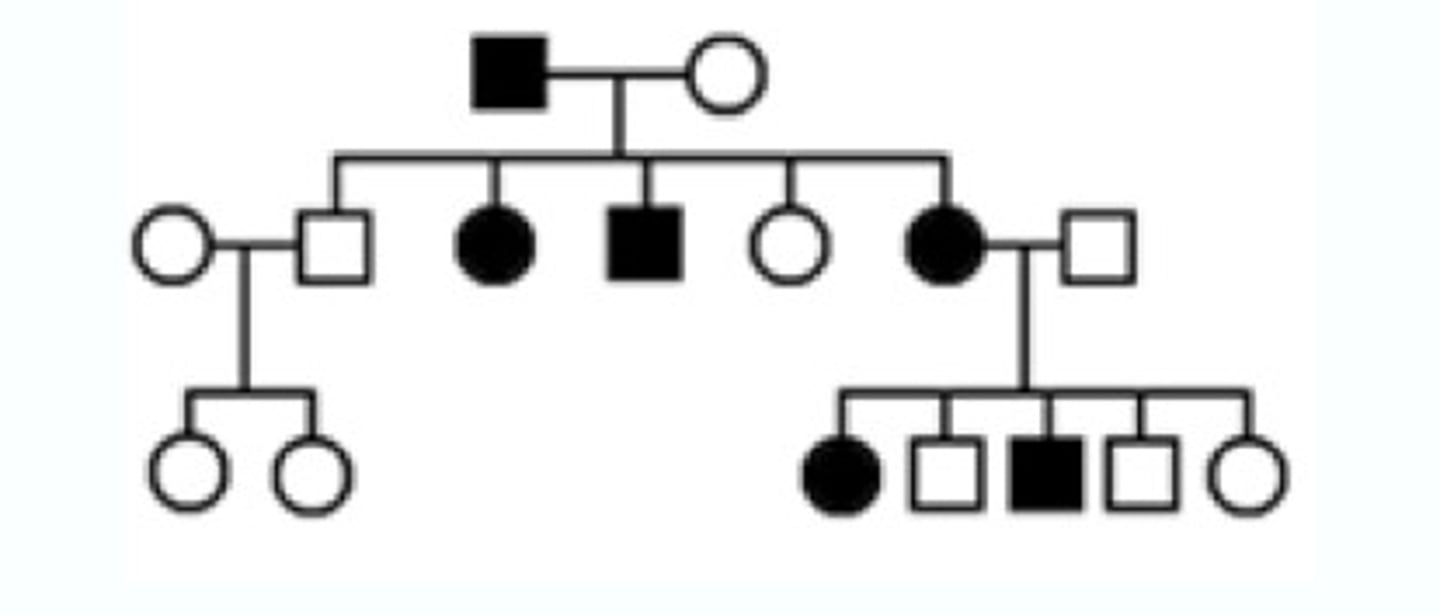
autosomal recessive
two copies of an abnormal gene must be present in order for the disease or trait to develop
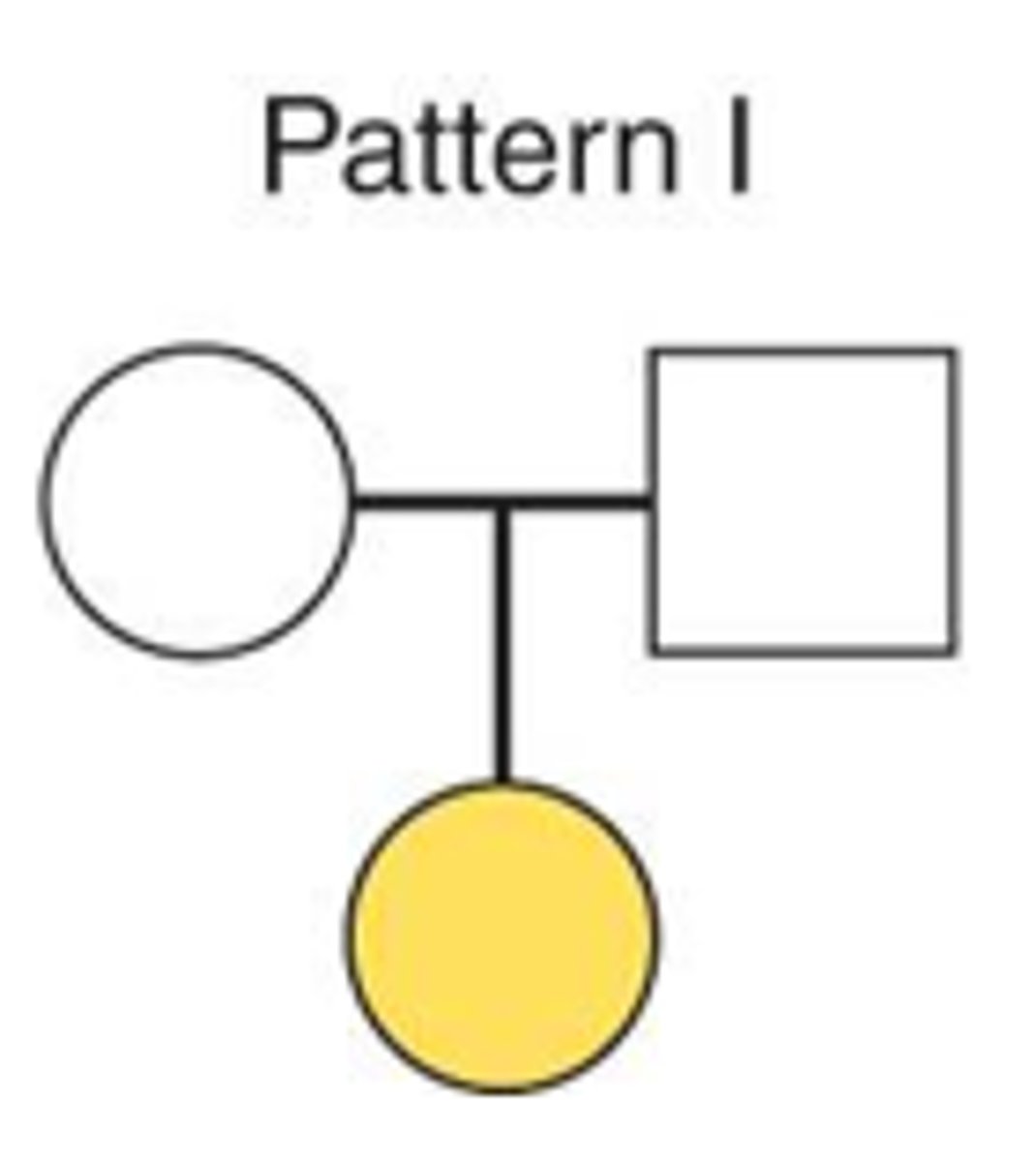
autosomal dominant
Name the pattern of genetic transmission characterized thus: both M and F are affected; M may transmit to M; each generation has at least one affected parent; and one mutant allele may produce the disease.
sex-linked traits
Traits controlled by genes located on sex chromosomes.
In a pedigree, a horizontal line represents?
marriage

In a pedigree a vertical line represents?
offspring
In a pedigree - diagonal line through symbol
deceased
In a pedigree, a shaded circle represents?
affected female
In a pedigree, a shaded square represents?
affected male
Genome
the complete instructions for making an organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that organism's chromosomes
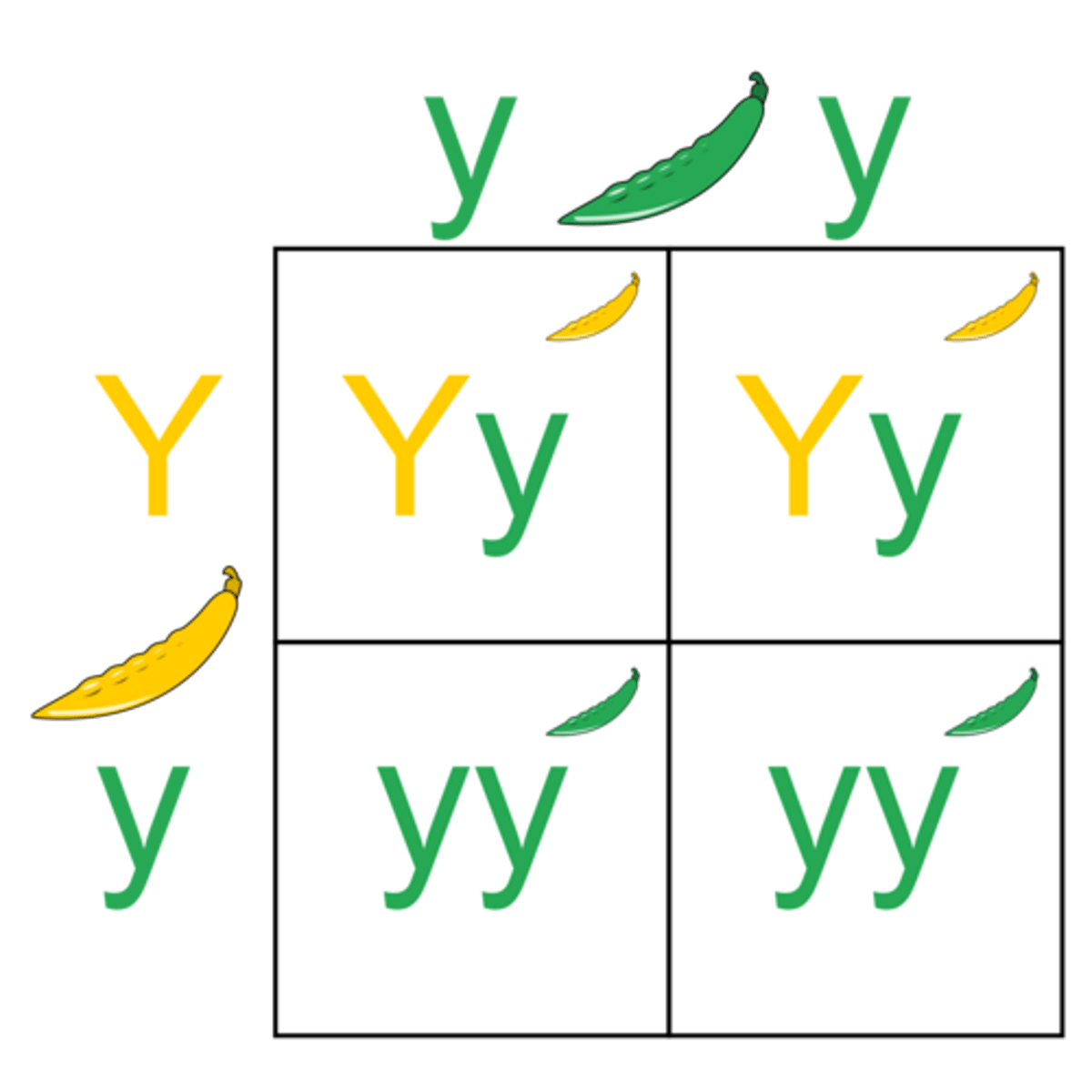
monohybrid cross
A cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits
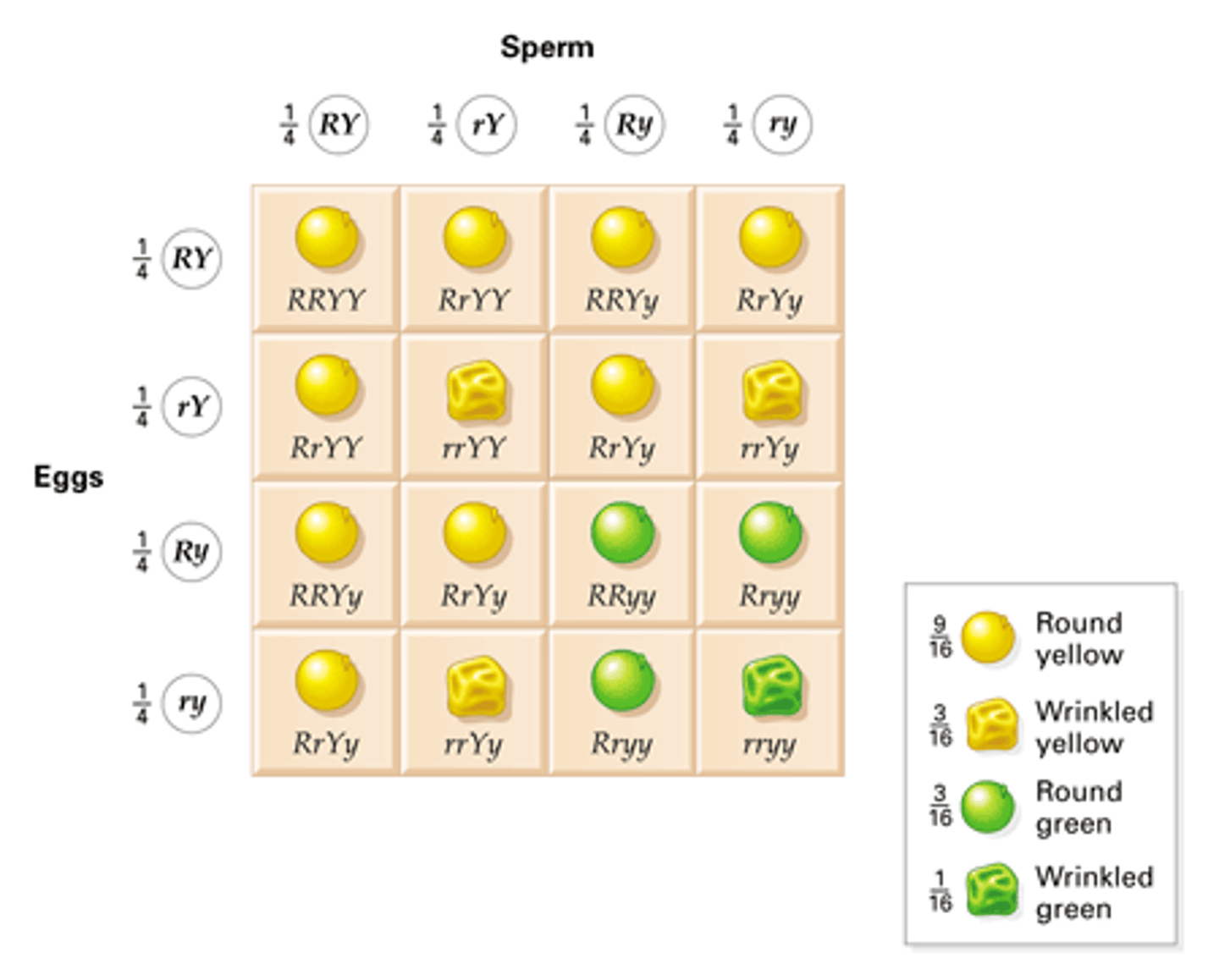
dihybrid cross
A cross between individuals that have different alleles for the same gene
P generation
Parental generation, the first two individuals that mate in a genetic cross
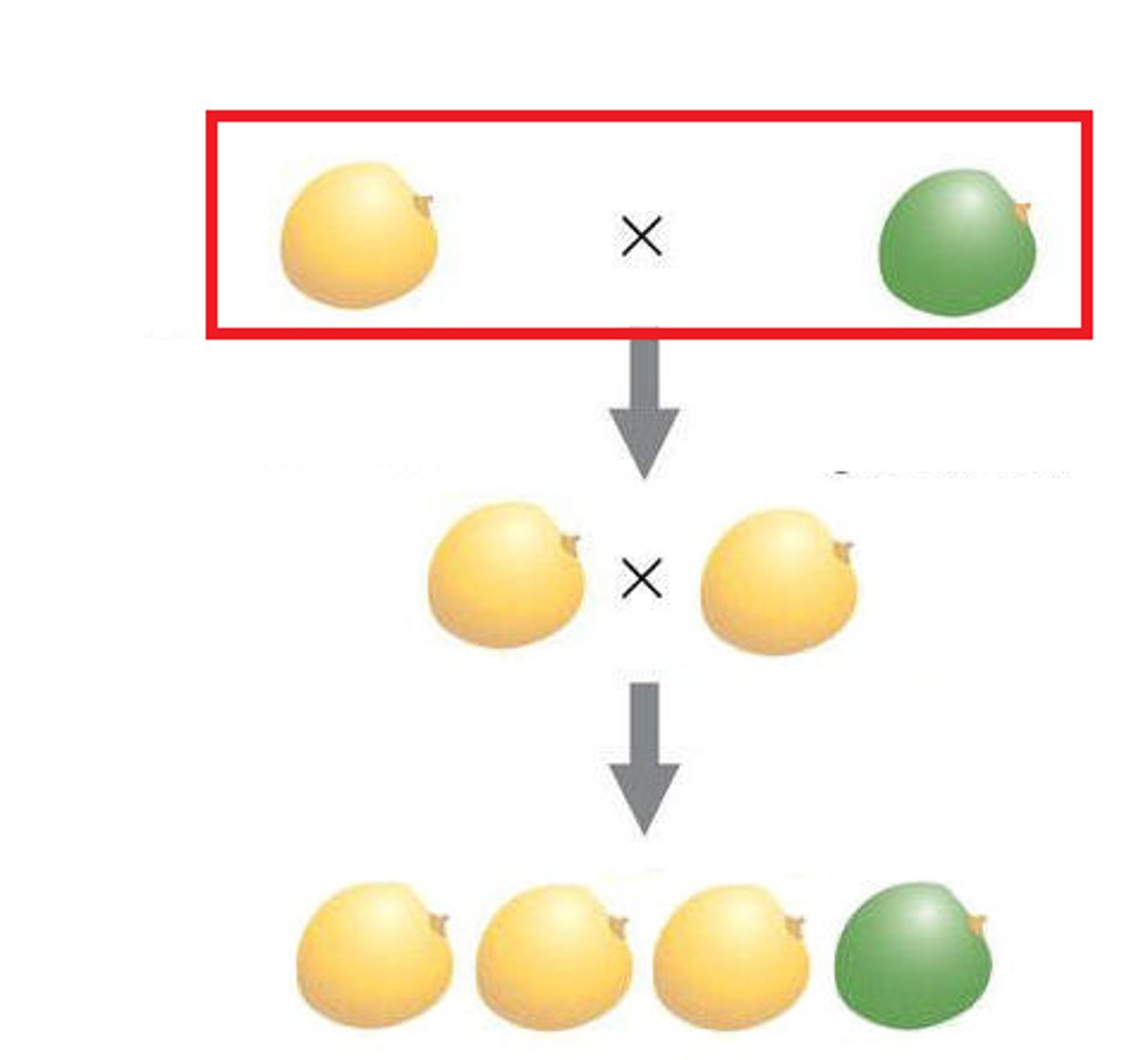
F1 generation
the first generation of offspring obtained from an experimental cross of two organisms
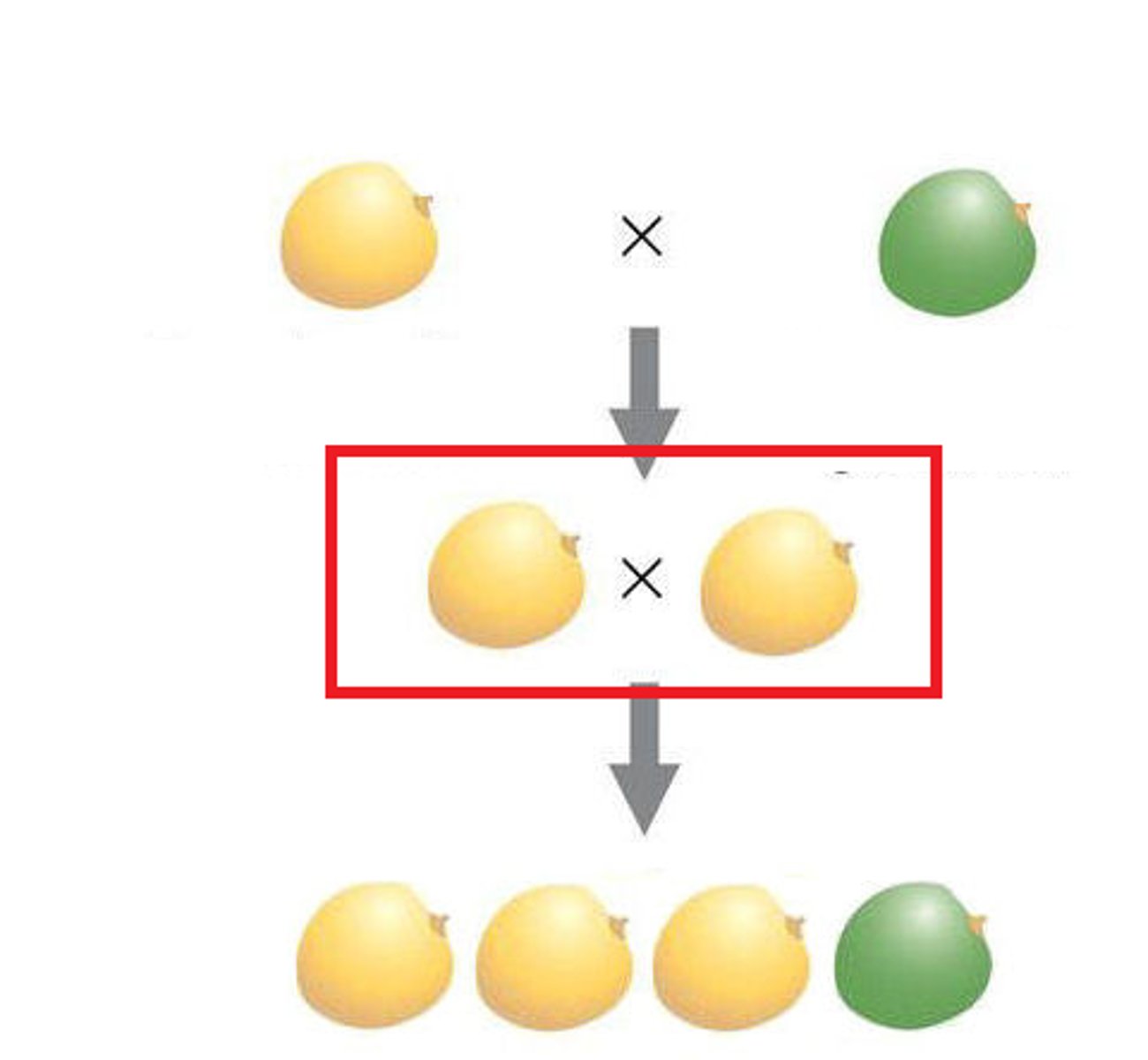
F2 generation
offspring of the F1 generation
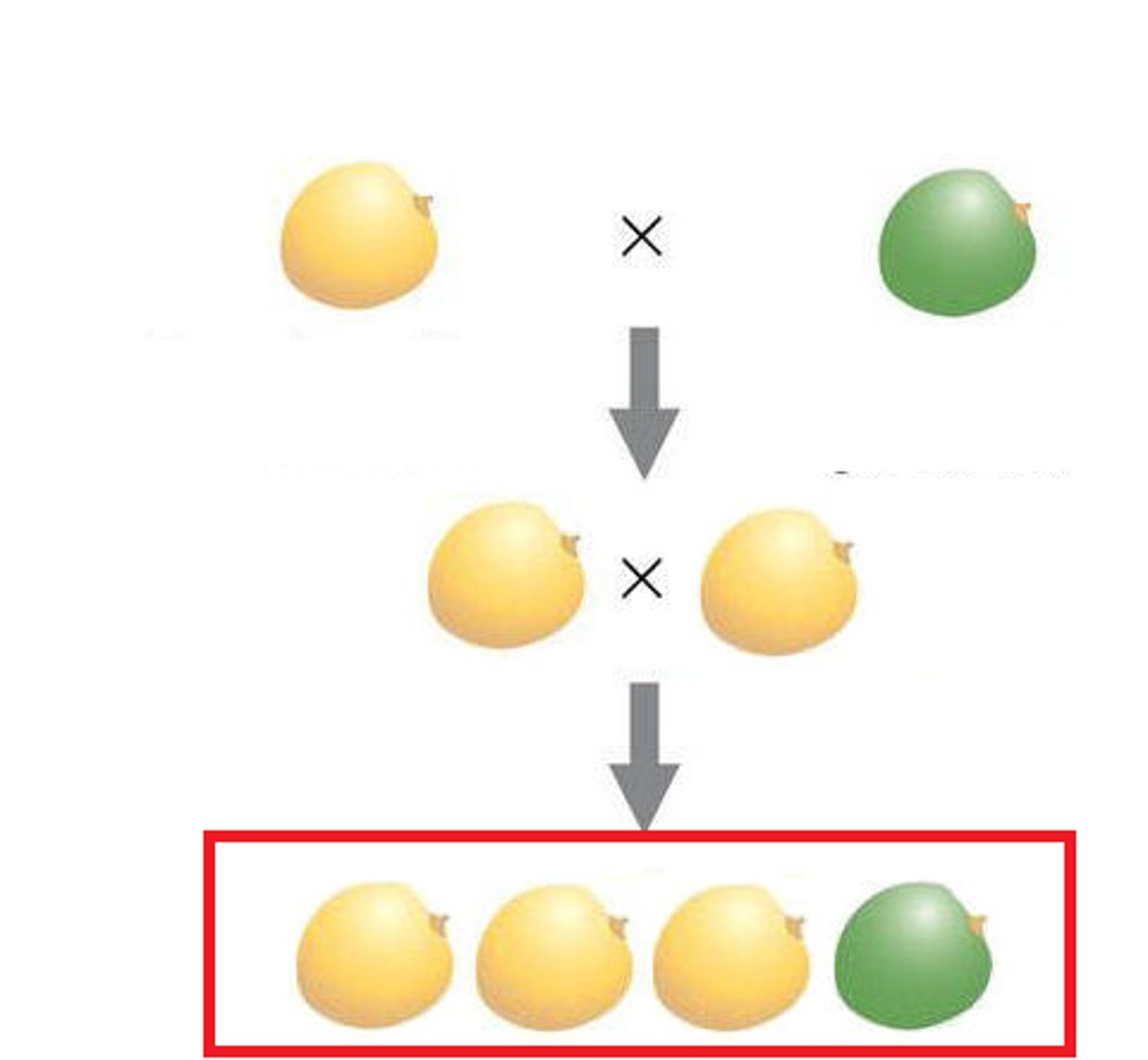
polygenetic characteristics
personal traits or physical properties that are influenced by many genes working in combination

Number of years Mr. McNeeley has been teaching
40