Radiology positioning Study guide ♡
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Distal (Di)
situated away from the point of attachment or origin
Proximal (Pr)
situated closer to the point of attachment or origin
Plantar (Pl)
situated on the caudal aspect of the rear limb, distal to the tarsus
Palmar (Pa)
situated on the caudal aspect of the front limb, distal to the carpus
Rostral (R)
areas on the head situated toward the nose
Caudal (Cd)
structures or areas situated toward the tail
Rostral border lateral skull
tip of nose
Caudal border lateral skull
Occipital protuberance
Cranial (Cr)
structures or areas situated toward the head
Lateral (L)
body area situated away from the median plane or midline
Medial (M)
body area situated toward the median plan or midline
Ventral (V)
body area situated toward the underside of quadrupeds
Dorsal (D)
body area situated toward the back or topline of quadrupeds
The first letter designates where the x-ray beam will ___.
enter
Second letter designates where beam ___.
exits
Medial and lateral should go ____ when used on combination with other terms
second
Rostral, cranial, and caudal should go____when used in combination with other terms
first
Oblique (O)
added to the names of the projections where the central beam passes through obliquely to one of the 3 axis
Caliper
is used to measure the area of interest
Caliper measuring
Measure at the thickest area
Measure standing and positioned on table if possible
Take average if needed
Caliper reading
Read measurements in cm
Read measurements at the bottom of the arm
Thoracic rads should be taken at full ____.
inspiration
Abdominal rads should be taken at ____.
expiration
thorax collimator borders caudal
just caudal to last rib (1st lumbar vertebrae)
thorax collimator borders cranial
thoracic inlet
pelvis collimator border cranial
slightly cranial to the wing of the ilium (include at least 1
lumbar vertebrae)
pelivis collimator border caudal
caudal to the caudal ischium, include 1/3 of the femur
Abdomen
Cranial border landmark:
half way between caudal border of scapula and xiphoid
(full diaphragm and heart apex)
Abdomen
Caudal border landmark:
coxofemoral joints
how many cervical vertebrae are there?
7
how many thoracic vertebrae are there?
13
how many lumbar vertebrae are there?
7
how many sacral vertebrae are there?
3
how many coccygeal vertebrae are there?
20-23
general collimator borders for joints
include 1/3 of long bone on each side
general collimator borders for long bones
include both joints on each end
Atelectasis
A complete or partial collapse of a lung or lobe of a lung that develops when the alveoli within the lung become deflated
Atelectasis causes
Post surgical complication
Recumbency related
Cancer
Trauma
Improperly placed ET tube
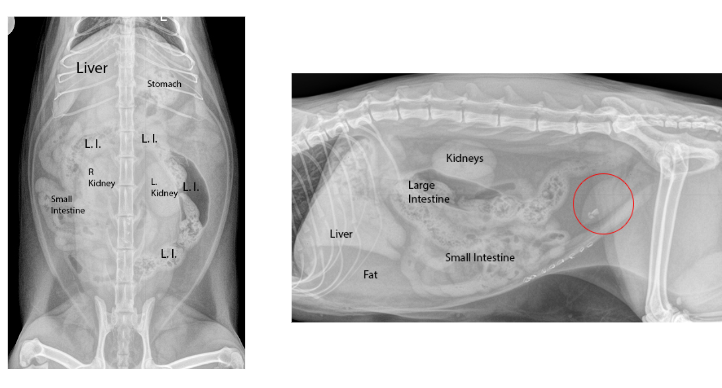
What organs can’t you see on an abdominal radiograph?
gallbladder, pancreas, adrenal glands
What organs can you see on an abdominal radiograph?
diaphragm, liver, stomach, spleen, kidneys, intestines, bladder, rectum
Forelimb Dorsal recumbency :
proximal portion (scapula, shoulder, humerus)
Forelimb Sternal recumbency :
distal portion (elbow, radius/ulna, carpus, metacarpus and digits)
Forelimb CdCr:
shoulder, scapula, humerus
Forelimb CrCd:
elbow, radius/ulna
Forelimb DPa
carpus, metacarpus and digits
Forelimb CrCd and CdCr views challenges:
Patient comfort, distortion
Small animal forelimb views
Lateral views and CdCr or CrCd (as opposed to VD or DV)
What makes an elbow rad diagnostic ?
Olecranon should be between the medial and lateral humeral epicondyles
Hip dysplasia
Abnormal development of the femoral joint
OFA stands for
Orthopedic Foundation for Animals
PennHip Distraction view= joint laxity
Measures to what degree the femoral head is displaced from the acetabulum.
Use of distractor rods placed between the hindlimbs at the femoral heads
PennHip Compression view=joint congruity
Determine how good the fit is of the femoral head into the acetabulum
PennHip Hip-extended view =evals the integrity of the hip joint
May mask true hip joint laxity
The joint capsule is tightened when hips are extended
Most common view for dx of hip dysplasia is
VD hip extended
True or False: Certification required to take correct PennHIP radiographs
true
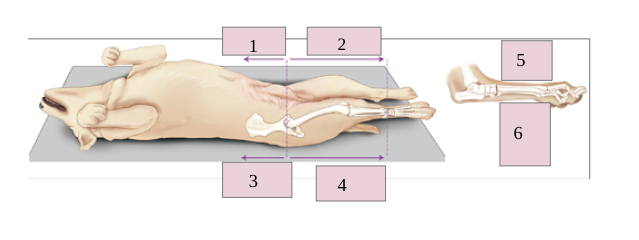
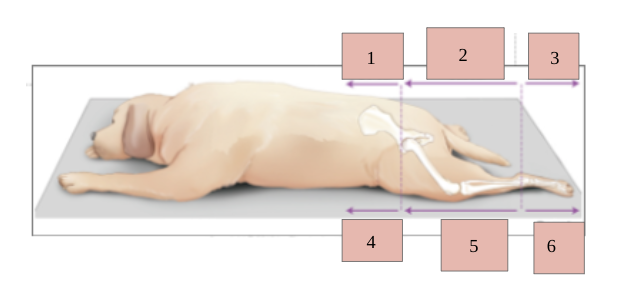
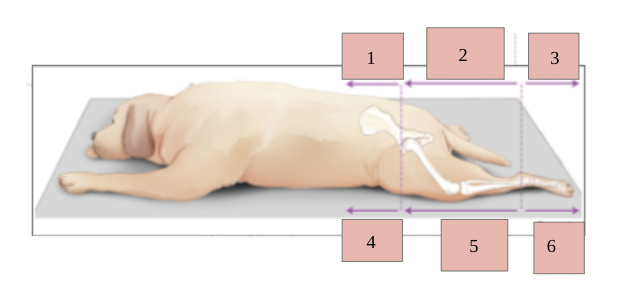
1
venteral
2
cranial
3
dorsal
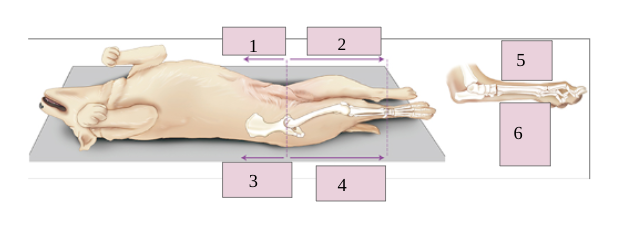
4
caudal
5
dorsal
6
plantar
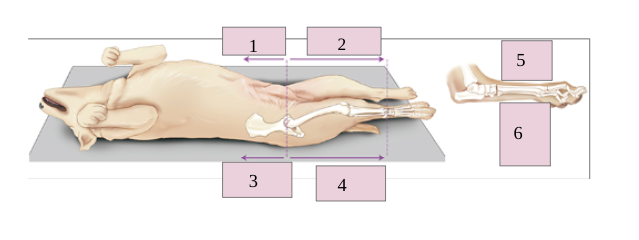
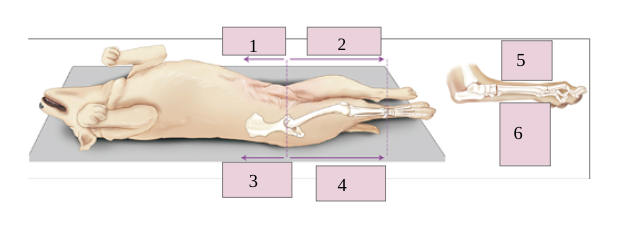
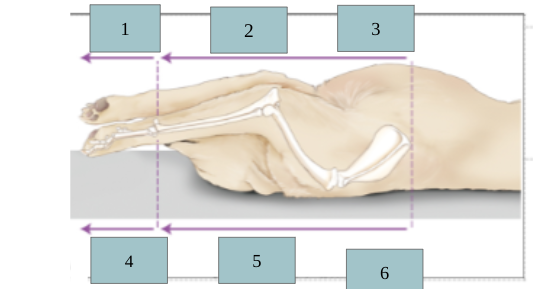
1
dorsal
2
caudal
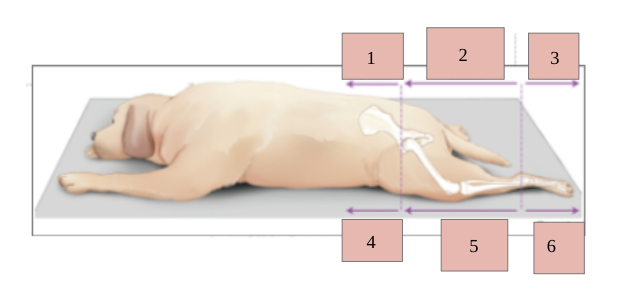
3
plantar
4
ventral
5
cranial
6
dorsal
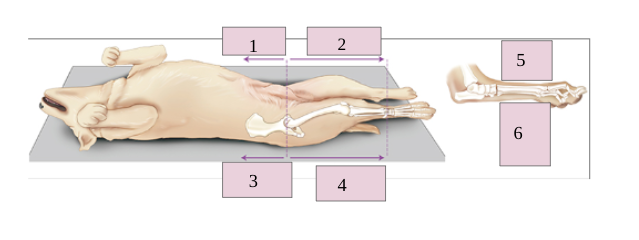
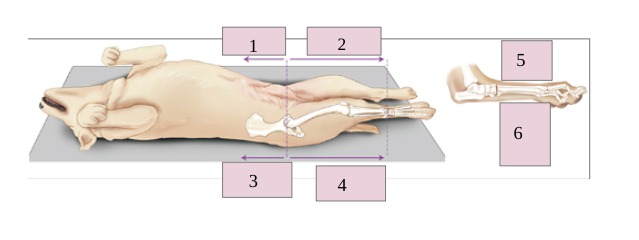
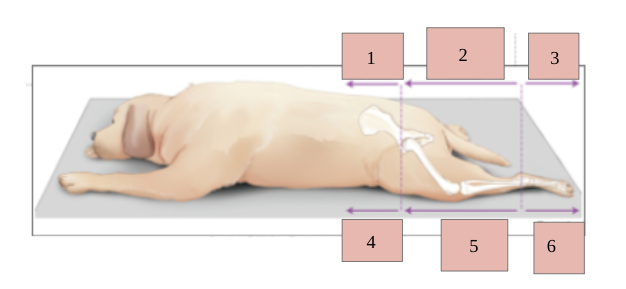
1
palmar
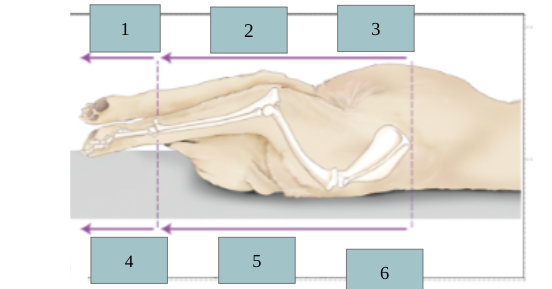
2
caudal
3
ventral
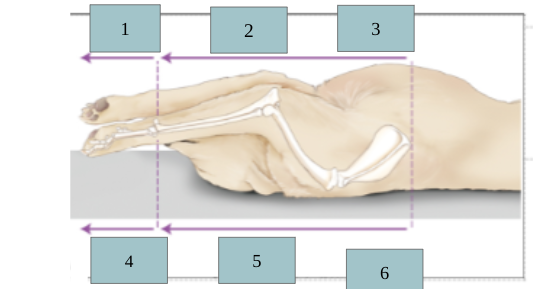
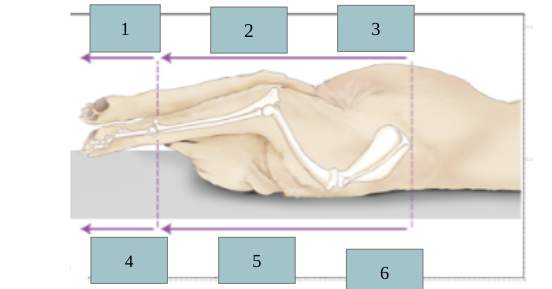
4
dorsal
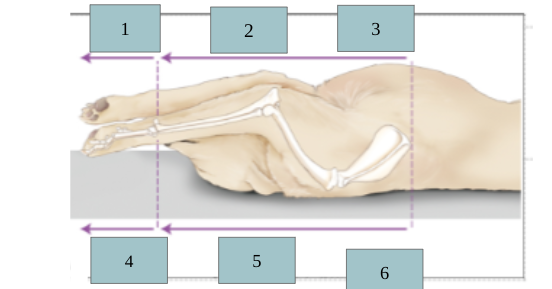
5
cranial
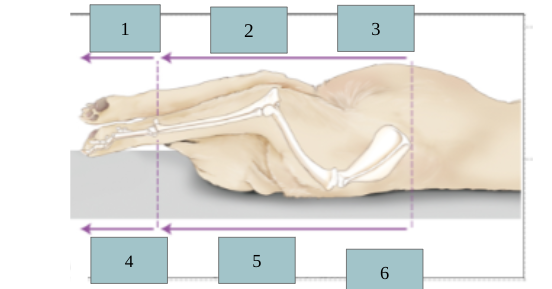
6
dorsal