Earth and Space Science Chapter 9 (copy)
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
thunderstorms
localized storms involving lightning thunder strong winds heavy rain and sometimes hail or tornadoes

stable
under normal conditions currents of rising air are stopped by adiabatic cooling and thus do not rise to great altitudes
cumulus stage
the steady supply of warm humid air combined with the strong upward movement of the updraft forms a billowing rapidly growing cumulus cloud.
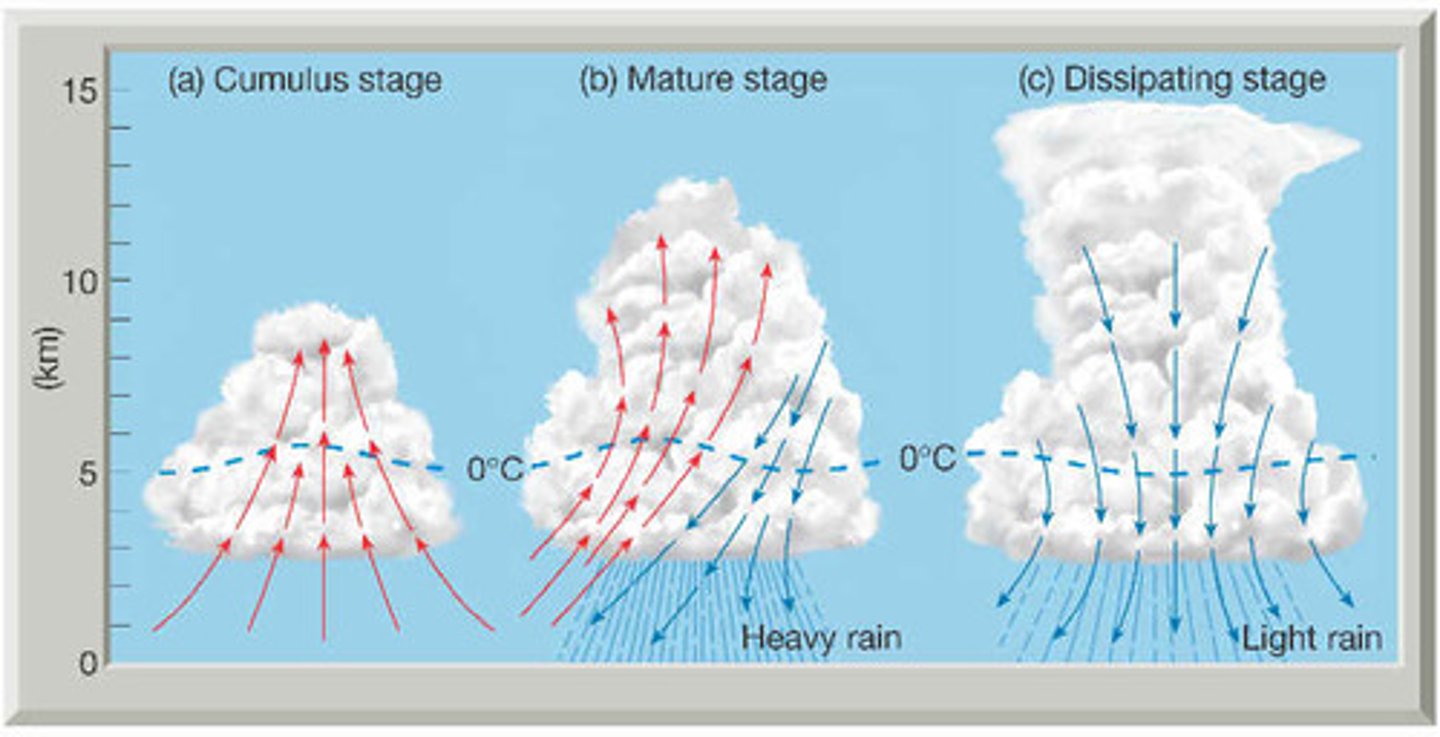
mature stage
the arrival of precipitation marks the beginning of this stage during which the thunderstorm reaches the peak of its strength
downbursts
very strong localized downdrafts can create sudden concentrated blasts of cool wind that can blow downward at 130 mph or more
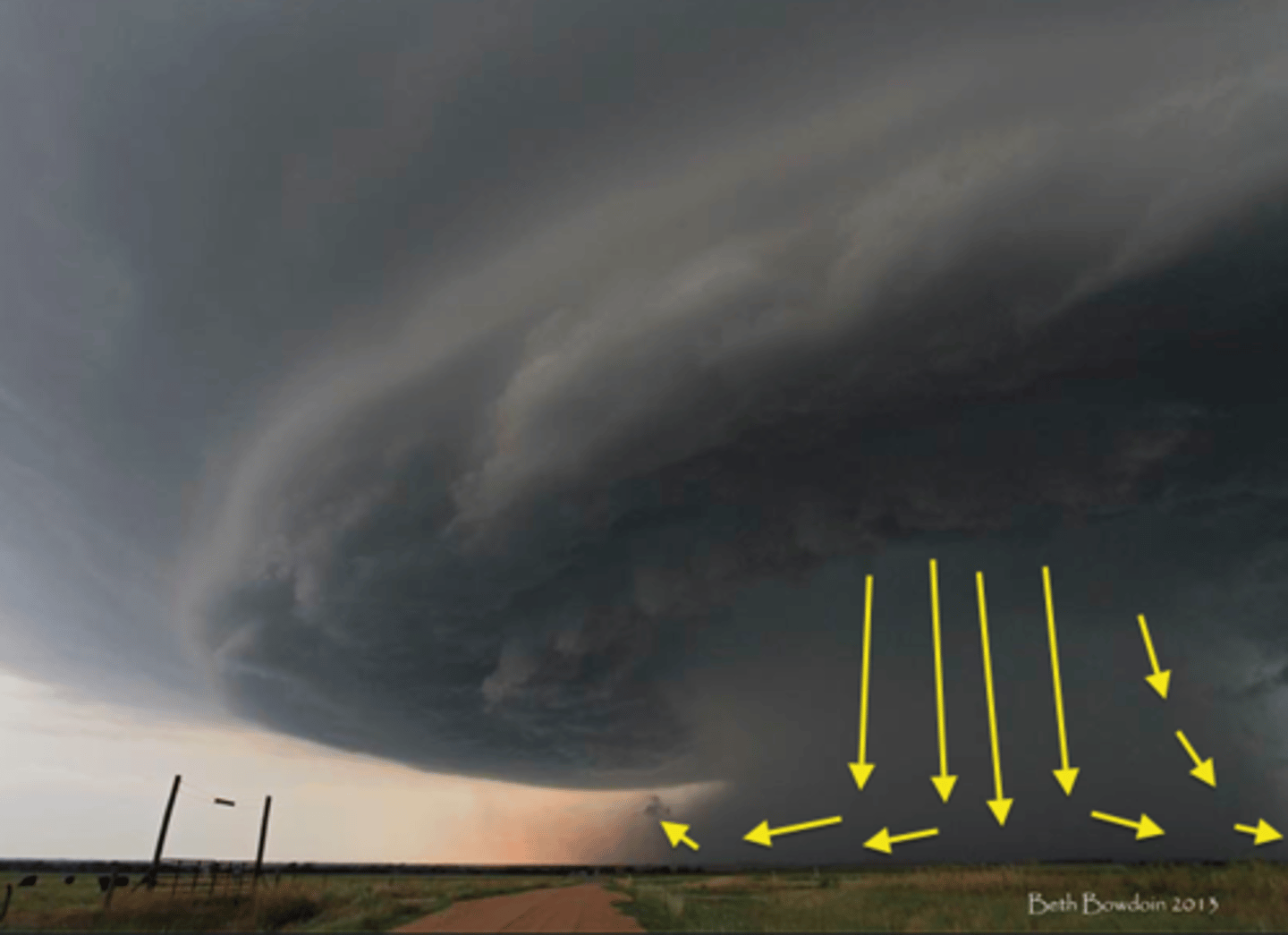

microbursts
smallest and most intense downbursts that may produce winds approaching at 170 mph

dissipating stage
the stage where the cumulonimbus cloud will dissipate. The air returns to a stable state.
supercell
the most powerful type of thunderstorm, a fierce single-updraft giant, which usually occur during the spring and early summer when temperature differences are most dramatic
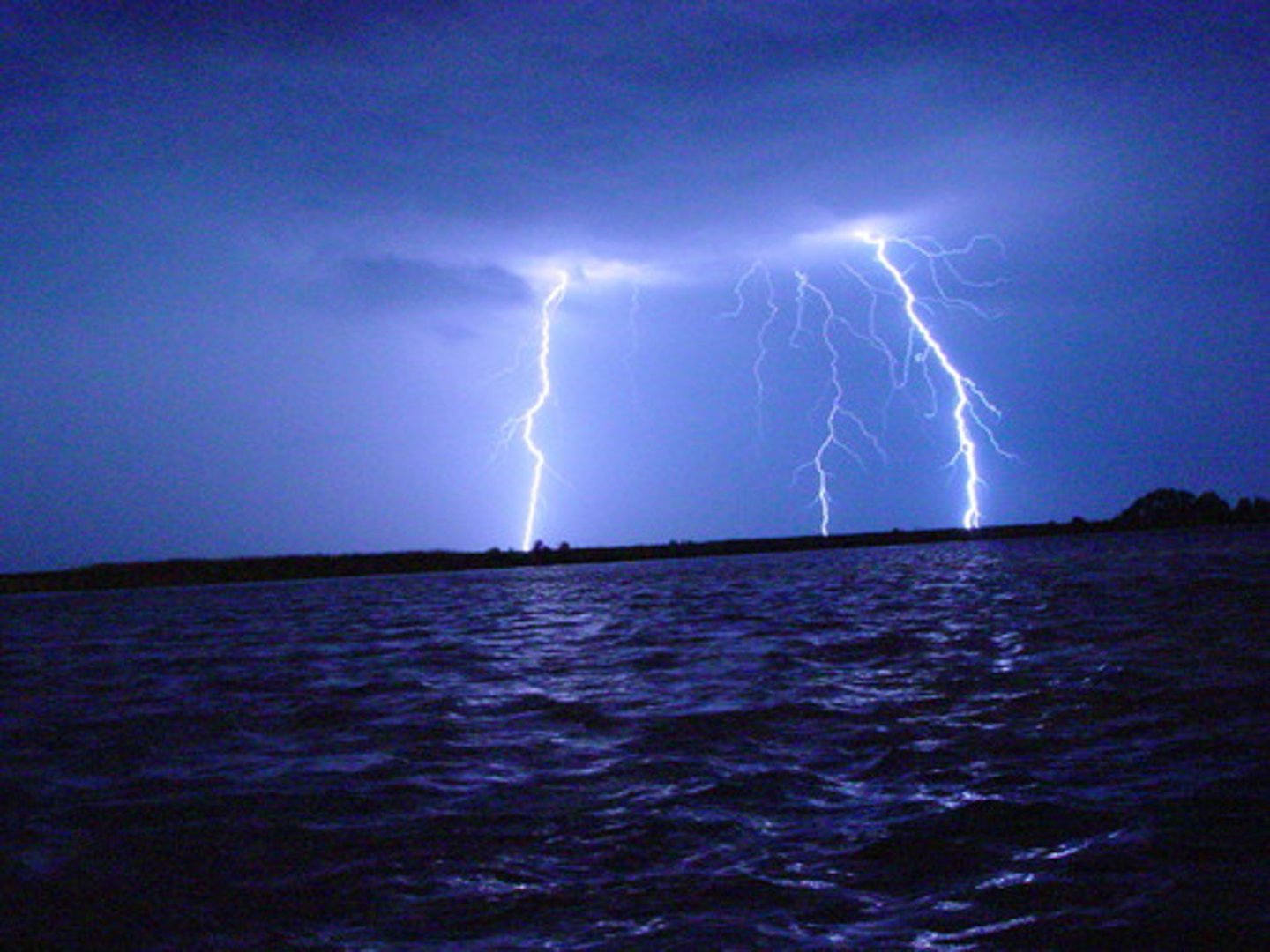
lightning
an abrupt discharge of electricity through the air that produces a quick flash of bright light
stepped leader
from the cloud a stream of electrons begins to move jerkily toward the ground
positive streamer
the positive charge on the ground attracted by the approaching stepped leader launches upward in this that rises to meet the stepped leader
return stroke
upward flow of positive charge which forms the brilliant flash of light that can be seen
thunder
the heat from the return stroke causes the air near the lightning bolt to expand explosively forming a shock wave of sound known as this
tornado
a narrow funnel of powerful rapidly whirling wind that stretches from a cloud to the ground
cyclones
a term that refers to any low pressure system in which winds rotate in the direction that would be caused by the coriolis effect
mesocyclone
the most powerful tornadoes are believed to form from the rotating updrafts found in many supercell thunderstorms this is such a rotating updraft
wall cloud
a large rotating cylindrical extension from the base of the supercell
Enhanced Fujita Scale
the scale that classifies tornadoes
waterspout
a tornado that forms over water, usually not associated with supercell thunderstorms unlike tornadoes
dust devil
a phenomenon similar but not a tornado, but it lacks a cloud
tropical cyclones
hurricanes and other rotating tropical low-pressure systems are also called this
hurricane
the tropical storm becomes this if it reaches 74 mph
Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale
hurricanes are ranked using this scale
eye
the center of a hurricane which rotates counter clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere. Has calm weather
eye wall
the cylinder of thick whirling clouds and rain that sorrounds the eye
rain bands
long narrow lines of thunderstorms which carry rain in a hurricane
wind, storm surge, inland flooding
the 3 most destructive forces of a hurricane
forecast
to predict the weather
thermometer
air temperature is measured with this
thermograph
records temperature changes over time
barometer
measures atmospheric pressure
mercury barometer
the oldest type of barometer which uses mercury
aneroid barometer
a more compact and rugged type of barometer which uses a flexible air-tight metal box to measure changes in pressure
hygrometer
measures relative humidity
weather vane
a simple device that points into the wind, points into the wind
anemometer
measures wind speeds near the earth's surface
rain gauge
measures the amount of rainfall or other precipitation
Stevenson screen
a type of shelter which contains meteorological instruments and keeps them from getting damaged by weather
automatic weather stations
allow atmospheric conditions to be monitered without a meteorologist at the site (a type of weather station)
transmissometer
a device which measures visibility
weather ballons
meteorologists often measure high altitude weather conditions by attaching instruments to these unmanned helium or hydrogen ballons
radiosondes
instruments that simulataneously measure and transmit meteorological data from ballons to weather stations below
celiometer
to measure the distance from the ground to the base of clouds meteorologists use this
radar
(radio detection and ranging) an important tool of the meteorologist which uses radio waves to detect objects and measure their distance
Doppler radar
a specialized type of radar that can detect precipitation as well as the movement of small particles, which can be used to measure wind speed and direction
weather satellite
devices that circle the earth and take pictures of the weather providing meteorologists with valuable information
hurricane
intense low-pressure systems that develop in the tropics
tropical disturbances
Tropical region of low pressure without rotating winds.
Warm ocean and region where the Coriolis effect is very pronounced
two ingredients for a hurricane to form
Tropical depression
tropical cyclone with sustained winds less than 39 mph
Tropical storm
tropical cyclone with sustained winds of at least 39 mph but less than 74 mph